Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Osong Public Health Res Perspect > Volume 6(6 Suppl); 2015 > Article
-
Brief Report
Summing up the Global Health Security Agenda 2015 High Level Meeting in Seoul - GHSA Preparation Task Force Team
-
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives 2015;6(6 Suppl):S6-S24.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.12.005
Published online: December 21, 2015
Ministry of Health and Welfare, Sejong, Korea
- ∗Corresponding author. ghsa2015seoul@gmail.com
Copyright © 2015 Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Published by Elsevier Korea LLC.
This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
- 2,861 Views
- 19 Download
- 3 Crossref
Abstract
- The Second Global Health Security Agenda (GHSA) 2015 High Level Meeting was successfully held in September 7 to 9 in Seoul, the Republic of Korea (ROK). Delegations from 46 countries including 26 ministerial level officials and 9 international organizations participated in the meeting. ROK, one of the 10 steering group countries of GHSA, shared the importance of multi-sectoral response through the experiences of Able Response Exercise, and MERS outbreak countermeasure with international communities. ROK promised to input 10 billion USD to strengthen the capacities to respond infectious diseases in developing countries. Seoul Declaration, the first collaborative efforts on heal security, was announced at the end of the meeting. Seoul Declaration holds GHSA vision promising international collaboration and commitment.
- The Global Health Security Agenda (GHSA) is an effort between nations, international organizations, and civil society to accelerate progress toward a world safe and secure from infectious disease threats whether naturally occurring, deliberate, or accidental, and to promote global health security as a national and international priority.
- On February 13, 2014, 29 nations, the World Health Organization (WHO), the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), and the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE) committed to the collective goals of the GHSA, thereby successfully launching the effort. The G7 endorsed the GHSA in June 2014, and Finland and Indonesia hosted commitment development meetings in May and August 2014, respectively.
- On September 26, 2014, the United States' President Obama hosted the First GHSA High Level Meeting at the White House in Washington, DC. By January 2015, 44 nations and eight international organizations have decided to share the vision of health security under the name of GHSA as shown below:
- Australia, Azerbaijan, Canada, Chile, China, Denmark, Ethiopia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Guinea, India, Indonesia, Israel, Italy, Japan, Jordan, Kenya, Liberia, Malaysia, Mexico, Netherlands, Norway, Pakistan, Peru, Portugal, Republic of Korea, Saudi Arabia, Sierra Leone, Singapore, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Thailand, Turkey, Uganda, Ukraine, United Arab Emirates, United Kingdom, United States, Vietnam, Yemen
- World Health Organization, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, World Organization for Animal Health, INTERPOL, African Union, European Union, ECOWAS, World Bank Group
Introduction
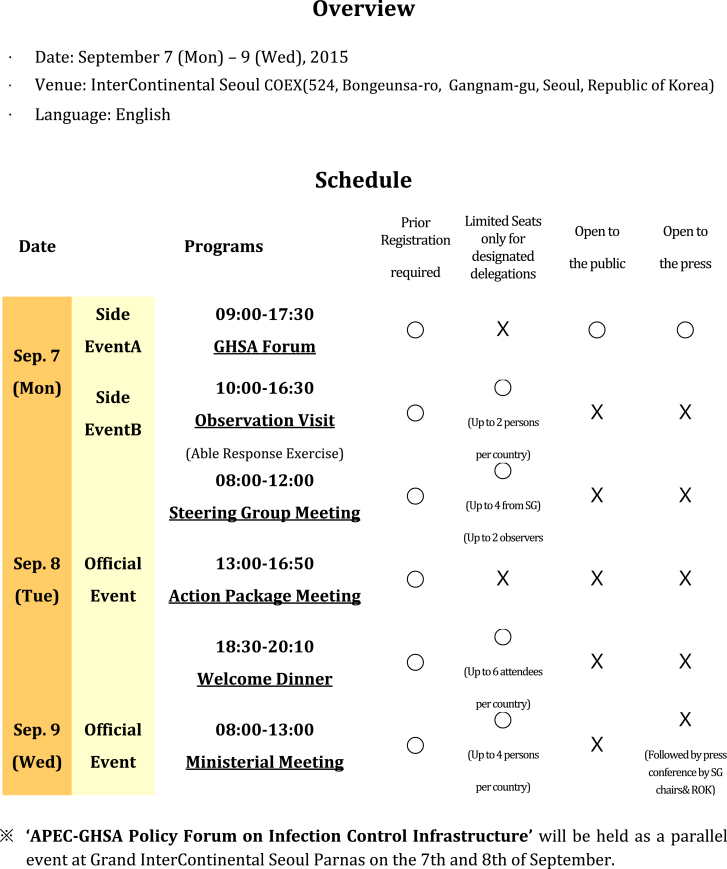
- At the 1st GHSA High Level Meeting in Washington, DC, it was decided that the Republic of Korea would host the 2nd GHSA High Level Meeting, which was held on September 7 to 9, 2015 in Seoul.
- A total of 50 nations along with major international organizations and non-state actors participated in the 2nd GHSA High Level Meeting.
- 2.1 Ministerial Level Meeting
- Korea proudly has hosted and welcomed the honorable two Ministers from relevant Ministries, such as the Ministry of Health, Foreign Affairs, Defense, Development, Agriculture, Interior, and National Security. It is crucial for high level officials from different Ministries to gather in one place in order to share the need for health security and reflect health security in each country's policy direction as a top priority.
- The Ministerial level Meeting was held in the morning of September 9. On the occasion of the 2nd Ministerial Meeting, the participating countries will issue a “Seoul Declaration of the GHSA” that will identify the collective vision, effective organization, and future direction of the GHSA.
- 2.2 Steering Group Meeting
- The Steering Group, chaired by Finland in 2015, is a group of nations responsible for overseeing the implementation of the GHSA commitments and Action Package activities as well as organizing the logistics of the GHSA. There will be 10 nations participating in this group in collaboration with 8 international organizations as advisors (three are permanent and five are cooperative) to facilitate activities and discussions.
• 10 Participating Nations: Canada, Chile, Finland, India, Indonesia, Italy, Kenya, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, the Republic of Korea, the United States.
• 8 Advisors: (3 Permanent Advisors) World Health Organization (WHO), Food & Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), World Organization for Animal Health (OIE), (5 Cooperative Advisors) Interpol, African Union, European Union, ECOWAS, World Bank Group.
- The Steering Group meeting was held in the morning of September 8. Up to four officials, including two senior level officials, from the Steering Group member countries are welcome to attend the meeting. Observation of non-Steering Group countries with the maximum of 2 persons, based on prior registration, is highly encouraged to enhance transparency and productivity of the meeting.
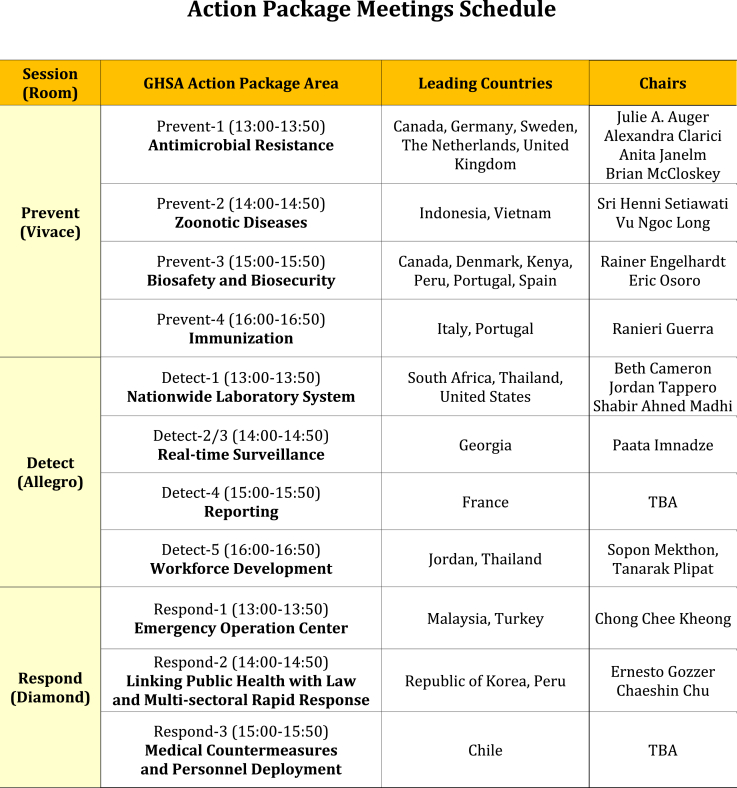
- 2.3 Action Package Meeting
- The GHSA provides concrete action plans for 1) prevention of avoidable epidemics, 2) early detection of threats, and 3) rapid and effective response against infectious disease outbreaks. The Action Packages are designed to accelerate progress toward these goals by facilitating regional and global collaboration toward specific GHSA objectives and targets. The Action Package Meeting was held in the afternoon of September 8 attended by all participating nations according to the following themes:
• 11 Action Packages of the GHSA:
– Prevent: ① Antimicrobial Resistance, ② Zoonotic Disease, ③ Biosafety and Biosecurity, ④ Immunization
– Detect: ① Real-Time Surveillance, ② Reporting, ③ National Laboratory System, ④ Workforce Development
– Respond: ① Emergency Operations Centers, ② Multi-sectoral Rapid Response, ③ Medical Countermeasures and Personnel Deployment
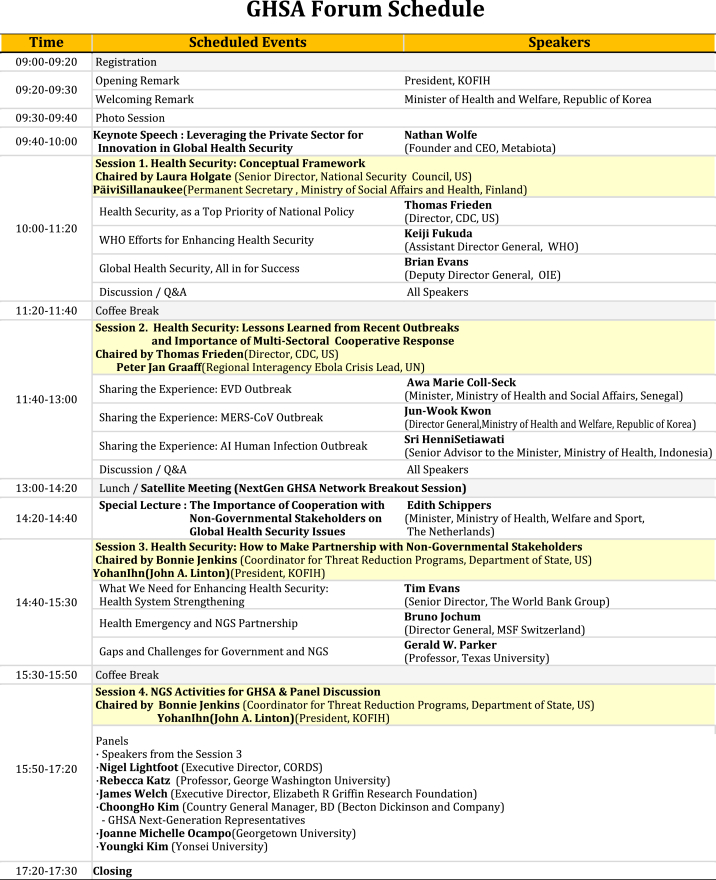
- 2.4 Side Event A: GHSA Forum ‘Partnership with Non-Governmental Stakeholders’
- On the occasion of the Second GHSA High Level Meeting, non-governmental stakeholders convened a whole-day conference on September 7 - bringing together civil society organizations, foundations, and government representatives - to discuss strategies to promote cooperation between governmental and non-governmental actors on sharing the vision of global health security.
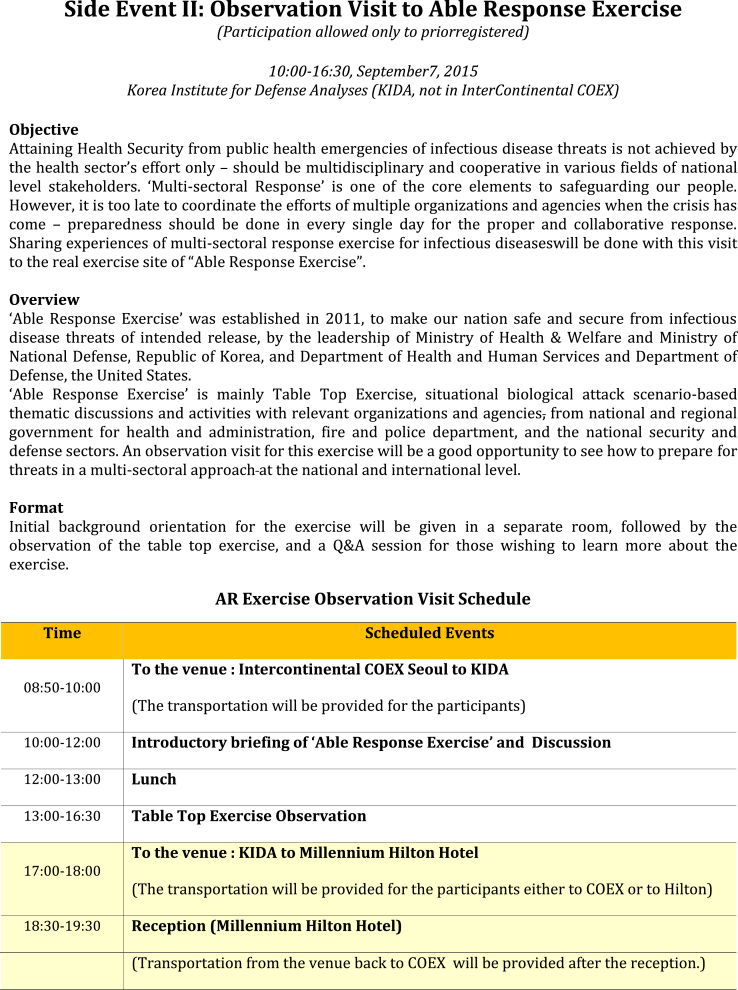
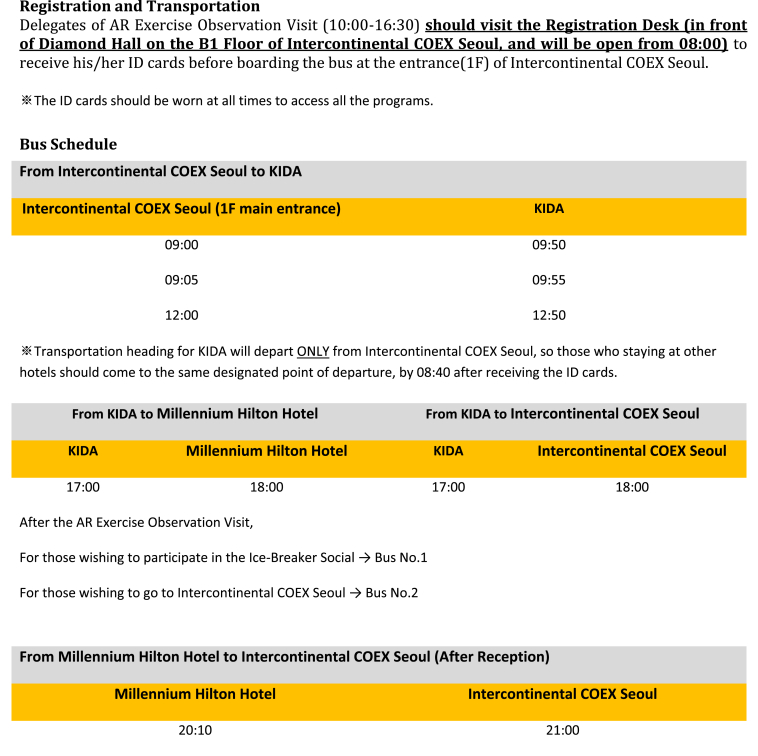
- 2.5 Side Event B: Observation Visit to the ‘Able Response Exercise’
- Able Response is an annual ROK-U.S. joint exercise designed to improve both countries' ability to prepare for and respond to a biological threat, regardless of the sources. This multi-sectoral exercise is a collaborative effort between the Ministries of National Defense and Health of both countries. It is a good example of a multi-sectoral rapid response system, which was held on the sidelines of the Second GHSA High Level Meeting. Taking this opportunity, the Republic of Korea, as a leading nation of Action Package Respond-2, ‘Multi-sectoral Rapid Response System’, presented an opportunity for countries to observe the Able Response collaborative exercise on September 7. The action package leaders and senior level officials of participating nations of Action Package - Respond 2 (Multi-sectoral Rapid Response), international organizations and the Steering Group countries are highly encouraged to join the observation visit.
Second GHSA High Level Meeting in Seoul
- Global health security is a shared responsibility that cannot be achieved by a single sector of government or a single nation alone. Its success depends upon collaboration among the health and security Ministries of all countries. The Second GHSA High Level Meeting in Seoul is an important step to make this effort more productive and concrete. To that end, the Republic of Korea kindly asks for active participation and cooperation from countries across the globe.
- 3.1 Steering Group Meeting
- 120 experts from 10 steering group countries and 8 international organization participated in the meeting. Action package assessment tool was finalized with 5 pilot country on-site assessment in Georgia, Peru, Uganda, Portugal, United Kingdom. Dr. Junwook Kwon (Ministry of ROK) and Ambassador Bonnie Jenkins (Department of State) presented Non-Governmental Stakeholders and next generation leaders' activities. Seoul Declaration was discussed, and next chairmanship was taken by Indonesia.
- 3.2 Action Package Meeting
- 120 experts from 30 countries participated in the 11 Action Package Meeting. All the section was reviewed the past year's progress report and discussed on the next 5-year plan. ROK was involved in 3 Action Package and plan to actively participate in up to 9 Action Packages.
- 3.3 Ministerial Meeting
- About 400 delegates attended. Seoul Declaration was adopted. Speeches were on health security and multi-sectoral cooperation by the minister of ROK. The speech suggested that Health security and multi-sectoral response be priority in the national agenda and that transparency and rapid information sharing is important and that enhance global collaboration system. Seoul Declaration was adopted based on GHSA vision and Action Packages. The thematic discussion was engaged by 6 countries: Sweden, Netherlands, UK, China, Finland and Indonesia. Ministerial comments were conducted by 12 countries (Australia, Kenya, USA, Italy, Germany, Spain, Switzerland, Georgia, Chile, Norway, Vietnam and Japan. The Netherlands announce to host the next high-level meeting in 2016 1, 2.
- Conflicts of interest
- The authors have nothing to declare.
Results
- 1. http://www.ghsa2015seoul.kr/en.
- 2. http://www.ghsa2015seoul.kr/SeoulDeclaration.pdf.
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Financing health system elements in Africa: A scoping review
Humphrey Cyprian Karamagi, David Njuguna, Solyana Ngusbrhan Kidane, Herve Djossou, Hillary Kipchumba Kipruto, Aminata Binetou-Wahebine Seydi, Juliet Nabyonga-Orem, Diane Karenzi Muhongerwa, Kingsley Addai Frimpong, Benjamin Musembi Nganda, Masoud Behzadif
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(9): e0291371. CrossRef - Évaluation des capacités de détection des menaces infectieuses aux points d’entrée au Bénin
Vincent Dossou Sodjinou, Lamidhi Salami, Ahoumènou Paul Ayelo, Edgard-Marius Dona Ouendo
Santé Publique.2022; Vol. 34(2): 263. CrossRef - The Sustainable Development Goals and the Global Health Security Agenda: exploring synergies for a sustainable and resilient world
Sulzhan Bali, Jessica Taaffe
Journal of Public Health Policy.2017; 38(2): 257. CrossRef













 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite
