Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Psychiatric adverse events associated with the COVID-19 vaccines approved in the Republic of Korea: a systematic review
- Seungeun Ryoo, Miyoung Choi, Nam-Kyong Choi, Hyoung-Shik Shin, Jun Hee Woo, Byung-Joo Park, Sanghoon Oh
- Received October 31, 2023 Accepted January 16, 2024 Published online March 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0325 [Epub ahead of print]
- 463 View
- 28 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This systematic review evaluated psychiatric adverse events (AEs) following vaccination against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We included studies that reported or investigated psychiatric AEs in individuals who had received an approved COVID-19 vaccine in the Republic of Korea. Systematic electronic searches of Ovid-Medline, Embase, CENTRAL, and KoreaMed databases were conducted on March 22, 2023. Risk of bias was assessed using the Risk of Bias Assessment Tool for Non-randomized Studies 2.0. The study protocol was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (CRD42023449422). Of the 301 articles initially selected, 7 were included in the final analysis. All studies reported on sleep disturbances, and 2 highlighted anxiety-related AEs. Sleep disorders like insomnia and narcolepsy were the most prevalent AEs, while depression was not reported. Our review suggests that these AEs may have been influenced by biological mechanisms as well as the broader psychosocial context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Although this study had limitations, such as a primary focus on the BNT162b2 vaccine and an observational study design, it offered a systematic, multi-vaccine analysis that fills a critical gap in the existing literature. This review underscores the need for continued surveillance of psychiatric AEs and guides future research to investigate underlying mechanisms, identify risk factors, and inform clinical management.
- Predictors of outcomes 3 to 12 months after traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Younes Iderdar, Maryem Arraji, Nadia Al Wachami, Morad Guennouni, Karima Boumendil, Yassmine Mourajid, Noureddine Elkhoudri, Elmadani Saad, Mohamed Chahboune
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):3-17. Published online February 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0288
- 1,013 View
- 70 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 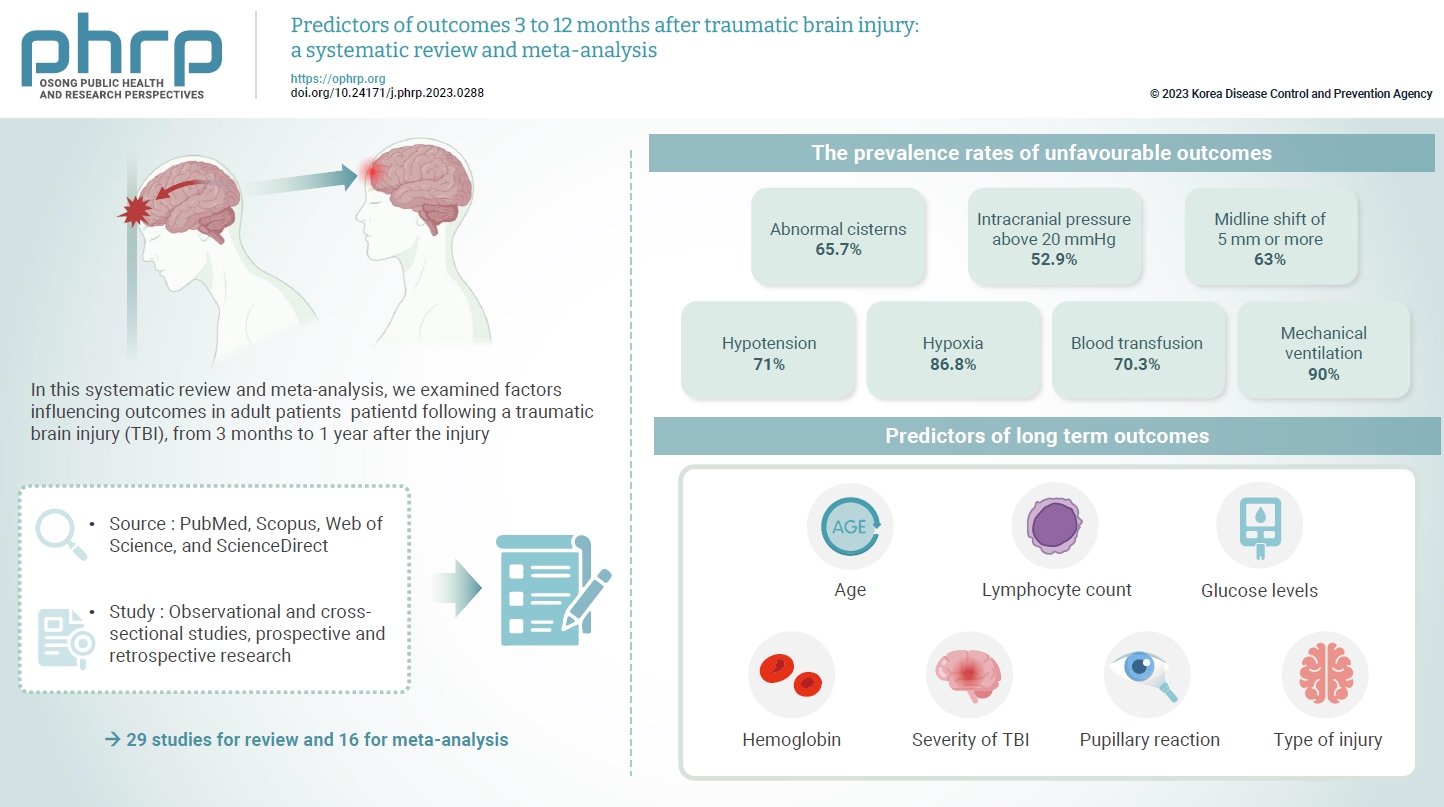
- The exact factors predicting outcomes following traumatic brain injury (TBI) remain elusive. In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we examined factors influencing outcomes in adult patients with TBI, from 3 months to 1 year after injury. A search of four electronic databases—PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and ScienceDirect—yielded 29 studies for review and 16 for meta-analysis, in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis guidelines. In patients with TBI of any severity, mean differences were observed in age (8.72 years; 95% confidence interval [CI], 4.77–12.66 years), lymphocyte count (−0.15 109/L; 95% CI, −0.18 to −0.11), glucose levels (1.20 mmol/L; 95% CI, 0.73–1.68), and haemoglobin levels (−0.91 g/dL; 95% CI, −1.49 to −0.33) between those with favourable and unfavourable outcomes. The prevalence rates of unfavourable outcomes were as follows: abnormal cisterns, 65.7%; intracranial pressure above 20 mmHg, 52.9%; midline shift of 5 mm or more, 63%; hypotension, 71%; hypoxia, 86.8%; blood transfusion, 70.3%; and mechanical ventilation, 90%. Several predictors were strongly associated with outcome. Specifically, age, lymphocyte count, glucose level, haemoglobin level, severity of TBI, pupillary reaction, and type of injury were identified as potential predictors of long-term outcomes.
- Spatiotemporal analysis of environmental and physiographic factors related to malaria in Bareilly district, India
- Shikhar Chaudhary, Biju Soman
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(2):123-132. Published online March 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0304
- 5,017 View
- 92 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 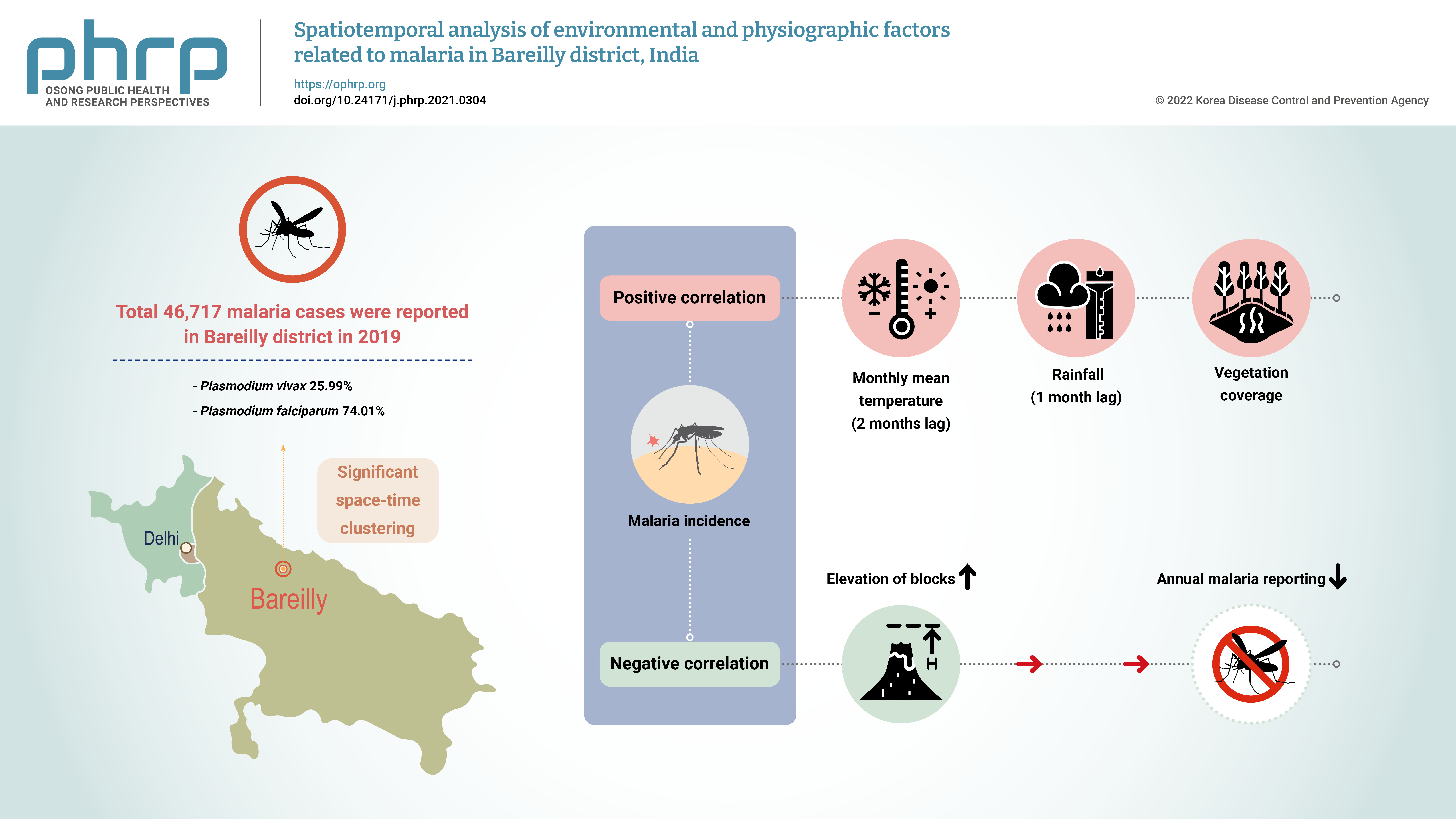
- Objectives
The aim of this study was to explore the spatiotemporal clustering of reported malaria cases and to study the effects of various environmental and physiographic factors on malaria incidence in Bareilly district, Uttar Pradesh, India. Methods: Malaria surveillance data were collected from the state health department and cleaned into an analyzable format. These data were analyzed along with meteorological, physiographic, and 2019 population data, which were obtained from the Indian Meteorological Department, National Aeronautics and Space Administration web portal, the Bhuvan platform of the Indian Space Research Organization, and the 2011 Census of India. Results: In total, 46,717 malaria cases were reported in Bareilly district in 2019, of which 25.99% were Plasmodium vivax cases and 74.01% were P. falciparum cases. The reported malaria cases in the district showed clustering, with significant spatial autocorrelation (Moran’s I value=0.63), and space-time clustering (p<0.01). A significant positive correlation was found between monthly malaria incidence and the monthly mean temperature (with a lag of 1−2 months) and rainfall (with a lag of 1 month). A significant negative correlation was detected between the elevation of blocks (i.e., intermediate-level administrative districts) and annual malaria reporting. Conclusion: The presence of space-time clustering of malaria cases and its correlation with meteorological and physiographic factors indicate that routine spatial analysis of the surveillance data could help control and manage malaria outbreaks in the district. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Digital health: trends, opportunities and challenges in medical devices, pharma and bio-technology
Naresh Kasoju, N. S. Remya, Renjith Sasi, S. Sujesh, Biju Soman, C. Kesavadas, C. V. Muraleedharan, P. R. Harikrishna Varma, Sanjay Behari
CSI Transactions on ICT.2023; 11(1): 11. CrossRef
- Digital health: trends, opportunities and challenges in medical devices, pharma and bio-technology
- Behavioral interventions for smoking cessation among adolescents: a rapid review and meta-analysis for the Korea Preventive Services Task Force
- Younglee Choi, Cheol Min Lee, Belong Cho, Eon Sook Lee, Seung-Won Oh, Naae Lee, Jae Moon Yun
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(3):177-186. Published online June 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0018
- 9,380 View
- 162 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of behavioral smoking cessation interventions among adolescents.
Methods
MEDLINE, CENTRAL, Embase, CINAHL, KoreaMed, and KMbase were searched from inception to June 2020. Systematic reviews (SRs) or meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were initially searched to perform a rapid SR. After selecting the final SR, RCTs after the publication year of the selected SR were searched. The primary outcome was smoking status after at least 6 months of follow-up, and the secondary outcome was smoking status at 4 weeks. Two reviewers independently assessed the selected studies’ quality using the Cochrane risk of bias tool. The meta-analysis utilized a Mantel-Haenszel fixed-effect model reporting the relative risk (RR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). The subgroup analysis utilized Cochrane’s Q.
Results
Thirty-two RCTs (11,637 participants) from a single SR were meta-analyzed. After 6 months of follow-up, the intervention group had significantly higher abstinence rates (RR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.20−1.41; I2=26.46%). At 4 weeks of follow-up, the intervention group also had significantly higher abstinence rates (RR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.49–2.47; I2=0.00%). The subgroup analysis indicated a significant difference in the abstinence rate according to the study setting and the period between intervention completion and follow-up.
Conclusion
This review showed that adolescent behavioral smoking cessation intervention programs significantly increased abstinence rates compared to the usual care. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Healthcare Interventions on Smoking Cessation in Adolescents in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Narrative Review
Janhvi Thakur, Sonali G Choudhari
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-pharmacological interventions for smoking cessation: analysis of systematic reviews and meta-analyses
Tao Nian, Kangle Guo, Wendi Liu, Xinxin Deng, Xiaoye Hu, Meng Xu, Fenfen E, Ziyi Wang, Guihang Song, Kehu Yang, Xiuxia Li, Wenru Shang
BMC Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Behavioral Interventions for Smoking Cessation in Adolescents: Korea Preventive Services Task Force Guidance
Younglee Choi, Cheol Min Lee, Jae Moon Yun, Eon Sook Lee, Seung-Won Oh, Naae Lee, Belong Cho
Journal of the Korean Society for Research on Nico.2021; 12(1): 1. CrossRef - Tobacco Control Policy in Period of Epidemic “COVID 19”
Eon Sook Lee
Journal of the Korean Society for Research on Nico.2021; 12(1): 34. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Healthcare Interventions on Smoking Cessation in Adolescents in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Narrative Review
- COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Laboratory Findings, Comorbidities, and Clinical Outcomes Comparing Medical Staff versus the General Population
- Mina Ebrahimi, Amal Saki Malehi, Fakher Rahim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(5):269-279. Published online October 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.5.02
- 8,430 View
- 125 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material This review compared coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) laboratory findings, comorbidities, and clinical outcomes in patients from the general population versus medical staff to aid diagnosis of COVID-19 in a more timely, efficient, and accurate way. Electronic databases were searched up to 23rd March, 2020. The initial search yielded 6,527 studies. Following screening, 24 studies were included [18 studies (11,564 cases) of confirmed COVID-19 cases in the general public, and 6 studies (394 cases) in medical staff] in this review. Significant differences were observed in white blood cell counts (
p < 0.001), lymphocyte counts (p < 0.001), platelet counts (p = 0.04), procalcitonin levels (p < 0.001), lactate dehydrogenase levels (p < 0.001), and creatinine levels (p = 0.03) when comparing infected medical staff with the general public. The mortality rate was higher in the general population than in medical staff (8% versus 2%). This review showed that during the early stages of COVID-19, laboratory findings alone may not be significant predictors of infection and may just accompany increasing C-reactive protein levels, erythrocyte sedimentation rates, and lactate dehydrogenase levels. In the symptomatic stage, the lymphocyte and platelet counts tended to decrease. Elevated D-dimer fibrin degradation product was associated with poor prognosis.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- microRNA-185 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection through the Modulation of the Host’s Lipid Microenvironment
Nadine Ahmed, Magen E. Francis, Noreen Ahmed, Alyson A. Kelvin, John Paul Pezacki
Viruses.2023; 15(9): 1921. CrossRef - Protective action of natural and induced immunization against the occurrence of delta or alpha variants of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a test-negative case-control study
Giovanni Corrao, Matteo Franchi, Federico Rea, Danilo Cereda, Antonio Barone, Catia Rosanna Borriello, Petra Giulia Della Valle, Michele Ercolanoni, Ida Fortino, Jose Jara, Olivia Leoni, Francesco Mazziotta, Elisabetta Pierini, Giuseppe Preziosi, Marcello
BMC Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Balancing Benefits and Harms of COVID-19 Vaccines: Lessons from the Ongoing Mass Vaccination Campaign in Lombardy, Italy
Giovanni Corrao, Federico Rea, Matteo Franchi, Danilo Cereda, Antonio Barone, Catia Rosanna Borriello, Giulia Petra Della Valle, Michele Ercolanoni, Jose Jara, Giuseppe Preziosi, Manuel Maffeo, Francesco Mazziotta, Elisabetta Pierini, Francesco Lecis, Pie
Vaccines.2022; 10(4): 623. CrossRef - Vulnerability Predictors of Post-Vaccine SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Disease—Empirical Evidence from a Large Population-Based Italian Platform
Giovanni Corrao, Matteo Franchi, Danilo Cereda, Francesco Bortolan, Olivia Leoni, Catia Rosanna Borriello, Petra Giulia Della Valle, Marcello Tirani, Giovanni Pavesi, Antonio Barone, Michele Ercolanoni, Jose Jara, Massimo Galli, Guido Bertolaso
Vaccines.2022; 10(6): 845. CrossRef - Factors associated with severe or fatal clinical manifestations of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection after receiving the third dose of vaccine
Giovanni Corrao, Matteo Franchi, Danilo Cereda, Francesco Bortolan, Olivia Leoni, Jose Jara, Giuseppina Valenti, Giovanni Pavesi
Journal of Internal Medicine.2022; 292(5): 829. CrossRef - Role of multiresolution vulnerability indices in COVID-19 spread in India: a Bayesian model-based analysis
Rupam Bhattacharyya, Anik Burman, Kalpana Singh, Sayantan Banerjee, Subha Maity, Arnab Auddy, Sarit Kumar Rout, Supriya Lahoti, Rajmohan Panda, Veerabhadran Baladandayuthapani
BMJ Open.2022; 12(11): e056292. CrossRef - A novel multi-omics-based highly accurate prediction of symptoms, comorbid conditions, and possible long-term complications of COVID-19
Debmalya Barh, Sandeep Tiwari, Bruno Silva Andrade, Marianna E. Weener, Aristóteles Góes-Neto, Vasco Azevedo, Preetam Ghosh, Kenneth Blum, Nirmal Kumar Ganguly
Molecular Omics.2021; 17(2): 317. CrossRef - Clinical and laboratory factors associated with coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid‐19): A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Le Huu Nhat Minh, Ali Ahmed‐Fouad Abozaid, Nam Xuan Ha, Loc Le Quang, Abdelrahman Gamil Gad, Ranjit Tiwari, Tran Nhat‐Le, Dinh Kim Quyen, Balqees AL‐Manaseer, Nguyen Dang Kien, Nguyen Lam Vuong, Ahmad Helmy Zayan, Le Huu Hanh Nhi, Kadek Agus Surya Dila, J
Reviews in Medical Virology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiologic and Clinic Characteristics of the First Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Hospitalized Patients from Galați County
Mihaela-Camelia Vasile, Anca-Adriana Arbune, Gabriela Lupasteanu, Constantin-Marinel Vlase, George-Cosmin Popovici, Manuela Arbune
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(18): 4210. CrossRef - Human Amniotic Fluid for the Treatment of Hospitalized, Symptomatic, and Laboratory-verified SARS-CoV-2 Patients
Mojgan Barati, Fakher Rahim
The Open Biology Journal.2021; 9(1): 36. CrossRef - Stratification of the risk of developing severe or lethal Covid-19 using a new score from a large Italian population: a population-based cohort study
Giovanni Corrao, Federico Rea, Flavia Carle, Salvatore Scondotto, Alessandra Allotta, Vito Lepore, Antonio D'Ettorre, Cinzia Tanzarella, Patrizia Vittori, Sabrina Abena, Marica Iommi, Liana Spazzafumo, Michele Ercolanoni, Roberto Blaco, Simona Carbone, Cr
BMJ Open.2021; 11(11): e053281. CrossRef
- microRNA-185 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection through the Modulation of the Host’s Lipid Microenvironment
- Contact Transmission of COVID-19 in South Korea: Novel Investigation Techniques for Tracing Contacts
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(1):60-63. Published online February 28, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.1.09
- 45,333 View
- 1,053 Download
- 120 Web of Science
- 115 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In the epidemiological investigation of an infectious disease, investigating, classifying, tracking, and managing contacts by identifying the patient’s route are important for preventing further transmission of the disease. However, omissions and errors in previous activities can occur when the investigation is performed through only a proxy interview with the patient. To overcome these limitations, methods that can objectively verify the patient’s claims (medical facility records, Global Positioning System, card transactions, and closed-circuit television) were used for the recent ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 contact investigations in South Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Privacy risk in contact tracing systems
Janine L. Spears, Ali Padyab
Behaviour & Information Technology.2023; 42(2): 174. CrossRef - The role of data platforms in COVID-19 crisis: a smart city perspective
Laura-Diana Radu, Daniela Popescul
Aslib Journal of Information Management.2023; 75(6): 1033. CrossRef - Feasibility of digital contact tracing in low-income settings – pilot trial for a location-based DCT app
Eric Handmann, Sia Wata Camanor, Mosoka P. Fallah, Neima Candy, Davidetta Parker, André Gries, Thomas Grünewald
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidence of rheumatic diseases during the COVID-19 pandemic in South Korea
Soo Min Ahn, Seongho Eun, Sunghwan Ji, Seokchan Hong, Chang-Keun Lee, Bin Yoo, Ji Seon Oh, Yong-Gil Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(2): 248. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 molecular diagnostic point-of-care testing based on loop-mediated isothermal amplification: A prospective, single-center validation study
Sung Hun Moon, Sang-Chul Kim, Byung Woo Kim, Gwan-Jin Park, Hyun-Seok Chai, Young Min Kim, Hee Sung Kim, Hee Sue Park
Heliyon.2023; 9(3): e14564. CrossRef - Contact Tracing With District-Based Trajectories
Kiki Adhinugraha, Wenny Rahayu, Nasser Allheeib
International Journal of Data Warehousing and Mini.2023; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - La pandemia de COVID-19 en Brasil: epidemiología e impactos del negacionismo
Pedro Rodrigues Curi Hallal, Bruno Pereira Nunes
Revista de Estudios Brasileños.2023; 9(19): 15. CrossRef - Identification and comparison of pandemic-to-symptom networks of South Korea and the United States
Mijeong Park, Deachul Seo, Ji Geun Kim, Gayeon Lee, Larkin S. McReynolds, Lawrence Amsel, Hyunjung Yang, Young-Hoon Kim, Sanghoon Han, Soo Hyun Park, Juyoen Hur
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Detecting mpox infection in the early epidemic: an epidemiologic investigation of the third and fourth cases in Korea
Taeyoung Kim, Eonjoo Park, Jun Suk Eun, Eun-young Lee, Ji Won Mun, Yunsang Choi, Shinyoung Lee, Hansol Yeom, Eunkyoung Kim, Jongmu Kim, Jihyun Choi, Jinho Ha, Sookkyung Park
Epidemiology and Health.2023; 45: e2023040. CrossRef - COVID-19 conscience tracing: mapping the moral distances of coronavirus
David Shaw
Journal of Medical Ethics.2022; 48(8): 530. CrossRef - Bio-safety and bio-security: A major global concern for ongoing COVID-19 pandemic
Saud Ali Al Shehri, AM Al-Sulaiman, Sarfuddin Azmi, Sultan S. Alshehri
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2022; 29(1): 132. CrossRef - Perceived sources of occupational burn-out and embitterment among front-line health workers for COVID-19 control in Gyeonggi province, South Korea: a qualitative study
Bee-Ah Kang, Sijoung Kwon, Myoungsoon You, Heeyoung Lee
Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2022; 79(4): 245. CrossRef - COVID-19 vaccine willingness and hesitancy among residents in Qatar: a quantitative analysis based on machine learning
Muhammad Hafizh, Yousif Badri, Sakib Mahmud, Amir Hafez, Pilsung Choe
Journal of Human Behavior in the Social Environmen.2022; 32(7): 899. CrossRef - A resposta da Coreia do Sul à pandemia de COVID-19: lições aprendidas e recomendações a gestores
Thais Regis Aranha Rossi, Catharina Leite Matos Soares, Gerluce Alves Silva, Jairnilson Silva Paim, Lígia Maria Vieira-da-Silva
Cadernos de Saúde Pública.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Self-Injurious Behavior Rate in the Short-Term Period of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Korea
Se Jin Park, Soo Jung Rim, Minkyung Jo, Min Geu Lee, Gyurin Kim, Subin Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cost-effectiveness of interventions for the prevention and control of COVID-19: Systematic review of 85 modelling studies
Lihui Zhou, Wenxin Yan, Shu Li, Hongxi Yang, Xinyu Zhang, Wenli Lu, Jue Liu, Yaogang Wang
Journal of Global Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things (AI-IoT) Technologies in Response to COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review
Junaid Iqbal Khan, Jebran Khan, Furqan Ali, Farman Ullah, Jamshid Bacha, Sungchang Lee
IEEE Access.2022; 10: 62613. CrossRef - An Experience of the Early Stage of COVID-19 Outbreak in Nursing Homes in Gyeonggi Province, Korea
Gawon Choi, Na-young Kim, Seon-young Lee, Hae Deun Noh, Heeyoung Lee
Korean Journal of Clinical Geriatrics.2022; 23(1): 27. CrossRef - Likely community transmission of COVID-19 infections between neighboring, persistent hotspots in Ontario, Canada
Eliseos J. Mucaki, Ben C. Shirley, Peter K. Rogan
F1000Research.2022; 10: 1312. CrossRef - Unwillingness to cooperate with COVID-19 contact tracing in Japan
M. Machida, H. Kikuchi, T. Kojima, I. Nakamura, R. Saito, T. Nakaya, T. Hanibuchi, T. Takamiya, Y. Odagiri, N. Fukushima, S. Amagasa, H. Watanabe, S. Inoue
Public Health.2022; 210: 34. CrossRef - The effectiveness of COVID-19 testing and contact tracing in a US city
Xutong Wang, Zhanwei Du, Emily James, Spencer J. Fox, Michael Lachmann, Lauren Ancel Meyers, Darlene Bhavnani
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Contact Tracing Strategies for COVID-19 Prevention and Containment: A Scoping Review
Bolanle Adefowoke Ojokoh, Benjamin Aribisala, Oluwafemi A. Sarumi, Arome Junior Gabriel, Olatunji Omisore, Abiola Ezekiel Taiwo, Tobore Igbe, Uchechukwu Madukaku Chukwuocha, Tunde Yusuf, Abimbola Afolayan, Olusola Babalola, Tolulope Adebayo, Olaitan Afola
Big Data and Cognitive Computing.2022; 6(4): 111. CrossRef - Epidemiology and Outcome of Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrests during the COVID-19 Pandemic in South Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses
Jae Hwan Kim, Chiwon Ahn, Myeong Namgung
Yonsei Medical Journal.2022; 63(12): 1121. CrossRef - Perceived barriers to the process of COVID-19 control among frontline healthcare workers in South Korea: a qualitative study
Sijoung Kwon, Bee-Ah Kang, Myoungsoon You, Heeyoung Lee
BMJ Open.2022; 12(12): e063899. CrossRef - Response System for and Epidemiological Features of COVID-19 in Gyeongsangnam-do Province in South Korea
Yu Mi Wi, Su Jin Lim, Si-Ho Kim, Seungjin Lim, Su Jin Lee, Byung-Han Ryu, Sun In Hong, Oh-Hyun Cho, Kyunglan Moon, Kyung-Wook Hong, Sunjoo Kim, In-Gyu Bae
Clinical Infectious Diseases.2021; 72(4): 661. CrossRef - Impact of Public Health Interventions on Seasonal Influenza Activity During the COVID-19 Outbreak in Korea
Hyunju Lee, Heeyoung Lee, Kyoung-Ho Song, Eu Suk Kim, Jeong Su Park, Jongtak Jung, Soyeon Ahn, Eun Kyeong Jeong, Hyekyung Park, Hong Bin Kim
Clinical Infectious Diseases.2021; 73(1): e132. CrossRef - The utility of video technology and enhanced infection control in reducing COVID-19 disease burden in a custodial setting
Larissa H Unruh, Sadhana Dharmapuri, Kenneth Soyemi
American Journal of Infection Control.2021; 49(6): 852. CrossRef - Will the COVID-19 pandemic boost access to personal health care records? Smartphone data access to tackle the modern pandemic
Charles Edmund Breeze, Charlotte Murkin, Matt Lechner
BMJ Innovations.2021; 7(1): 243. CrossRef - Spatial variability in reproduction number and doubling time across two waves of the COVID-19 pandemic in South Korea, February to July, 2020
Eunha Shim, Amna Tariq, Gerardo Chowell
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2021; 102: 1. CrossRef - The experience of contact tracing in Singapore in the control of COVID-19: highlighting the use of digital technology
Sean Han Sheng Lai, Camelia Qian Ying Tang, Asok Kurup, Gowreeson Thevendran
International Orthopaedics.2021; 45(1): 65. CrossRef - Structural Racism in the COVID-19 Pandemic: Moving Forward
Maya Sabatello, Mary Jackson Scroggins, Greta Goto, Alicia Santiago, Alma McCormick, Kimberly Jacoby Morris, Christina R. Daulton, Carla L. Easter, Gwen Darien
The American Journal of Bioethics.2021; 21(3): 56. CrossRef - Privacy concerns can explain unwillingness to download and use contact tracing apps when COVID-19 concerns are high
Eugene Y. Chan, Najam U. Saqib
Computers in Human Behavior.2021; 119: 106718. CrossRef - Reduction in mobility and COVID-19 transmission
Pierre Nouvellet, Sangeeta Bhatia, Anne Cori, Kylie E. C. Ainslie, Marc Baguelin, Samir Bhatt, Adhiratha Boonyasiri, Nicholas F. Brazeau, Lorenzo Cattarino, Laura V. Cooper, Helen Coupland, Zulma M. Cucunuba, Gina Cuomo-Dannenburg, Amy Dighe, Bimandra A.
Nature Communications.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - State of the Art in Adoption of Contact Tracing Apps and Recommendations Regarding Privacy Protection and Public Health: Systematic Review
Katarzyna Kolasa, Francesca Mazzi, Ewa Leszczuk-Czubkowska, Zsombor Zrubka, Márta Péntek
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2021; 9(6): e23250. CrossRef - Genomic investigation of the coronavirus disease-2019 outbreak in the Republic of Korea
Jeong-Min Kim, Sung Yong Park, Daesang Lee, Jun-Sub Kim, Youngjoon Park, Jin Gwack, Mi Young Kim, Dong Hyun Song, Seong Tae Jeong, Yoon-Seok Chung, Cheon Kwon Yoo, Ha Youn Lee, Myung-Guk Han
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Test, Trace, and Put on the Blockchain?: A Viewpoint Evaluating the Use of Decentralized Systems for Algorithmic Contact Tracing to Combat a Global Pandemic
Moritz Platt, Anton Hasselgren, Juan Manuel Román-Belmonte, Marcela Tuler de Oliveira, Hortensia De la Corte-Rodríguez, Sílvia Delgado Olabarriaga, E Carlos Rodríguez-Merchán, Tim Ken Mackey
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2021; 7(4): e26460. CrossRef - Decrease in hospital admissions for respiratory diseases during the COVID-19 pandemic: a nationwide claims study
Kyungmin Huh, Young-Eun Kim, Wonjun Ji, Dong Wook Kim, Eun-Joo Lee, Jong-Hun Kim, Ji-Man Kang, Jaehun Jung
Thorax.2021; 76(9): 939. CrossRef - A simple model for the total number of SARS-CoV-2 infections on a national level
N. Blanco, K. A. Stafford, M. C. Lavoie, A. Brandenburg, M. W. Górna, M. Merski
Epidemiology and Infection.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Malaysia’s Health Systems Response to COVID-19
Zen Yang Ang, Kit Yee Cheah, Md. Sharif Shakirah, Weng Hong Fun, Jailani Anis-Syakira, Yuke-Lin Kong, Sondi Sararaks
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(21): 11109. CrossRef - Managing Pandemics with Health Informatics: Successes and Challenges
Mujeeb A. Basit, Christoph U. Lehmann, Richard J. Medford
Yearbook of Medical Informatics.2021; 30(01): 017. CrossRef - When robots contribute to eradicate the COVID-19 spread in a context of containment
Naila Aziza Houacine, Habiba Drias
Progress in Artificial Intelligence.2021; 10(4): 391. CrossRef - Best Practice Guidance for Digital Contact Tracing Apps: A Cross-disciplinary Review of the Literature
James O'Connell, Manzar Abbas, Sarah Beecham, Jim Buckley, Muslim Chochlov, Brian Fitzgerald, Liam Glynn, Kevin Johnson, John Laffey, Bairbre McNicholas, Bashar Nuseibeh, Michael O'Callaghan, Ian O'Keeffe, Abdul Razzaq, Kaavya Rekanar, Ita Richardson, And
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2021; 9(6): e27753. CrossRef - Implementing Public Health Strategies—The Need for Educational Initiatives: A Systematic Review
Amir Khorram-Manesh, Maxim A. Dulebenets, Krzysztof Goniewicz
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(11): 5888. CrossRef - Lessons from non-pharmaceutical interventions on the first wave of COVID-19 in the Asia Pacific region
Dongil Ahn
Journal of Global Health Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Modeling the early temporal dynamics of viral load in respiratory tract specimens of COVID-19 patients in Incheon, the Republic of Korea
Ah-Young Lim, Hae-Kwan Cheong, Yoon Ju Oh, Jae Kap Lee, Jae Bum So, Hyun Jin Kim, Boram Han, Sung Won Park, Yongsun Jang, Chang Yong Yoon, Yun Ok Park, Jong-Hun Kim, Jin Yong Kim
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2021; 108: 428. CrossRef - Contact Tracing Apps: Lessons Learned on Privacy, Autonomy, and the Need for Detailed and Thoughtful Implementation
Katie Hogan, Briana Macedo, Venkata Macha, Arko Barman, Xiaoqian Jiang
JMIR Medical Informatics.2021; 9(7): e27449. CrossRef - Using Mobile Phone Data to Estimate the Relationship between Population Flow and Influenza Infection Pathways
Qiushi Chen, Michiko Tsubaki, Yasuhiro Minami, Kazutoshi Fujibayashi, Tetsuro Yumoto, Junzo Kamei, Yuka Yamada, Hidenori Kominato, Hideki Oono, Toshio Naito
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(14): 7439. CrossRef - Effective COVID-19 Control: A Comparative Analysis of the Stringency and Timeliness of Government Responses in Asia
Shu Chen, Lei Guo, Taghred Alghaith, Di Dong, Mohammed Alluhidan, Mariam M. Hamza, Christopher H. Herbst, Xinqi Zhang, Gabrielle Charis Alano Tagtag, Yi Zhang, Nahar Alazemi, Rana Saber, Reem Alsukait, Shenglan Tang
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(16): 8686. CrossRef - Analysis of the factors affecting the adoption and compliance of the NHS COVID-19 mobile application: a national cross-sectional survey in England
Marcus Panchal, Sukhpreet Singh, Esther Rodriguez-Villegas
BMJ Open.2021; 11(8): e053395. CrossRef - Management of the COVID-19 Pandemic in the Republic of Korea from the Perspective of Governance and Public-Private Partnership
Woojin Kim, Tae Yong Jung, Susann Roth, Woochong Um, Changsoo Kim
Yonsei Medical Journal.2021; 62(9): 777. CrossRef - Pilot Evaluations of Two Bluetooth Contact Tracing Approaches on a University Campus: Mixed Methods Study
Tyler Shelby, Tyler Caruthers, Oren Y Kanner, Rebecca Schneider, Dana Lipnickas, Lauretta E Grau, Rajit Manohar, Linda Niccolai
JMIR Formative Research.2021; 5(10): e31086. CrossRef - Efficient Contact Tracing for pandemics using blockchain
Nida Bari, Usman Qamar, Ayesha Khalid
Informatics in Medicine Unlocked.2021; 26: 100742. CrossRef - Policy Review and Modeling Analysis of Mitigation Measures for Coronavirus Disease Epidemic Control, Health System, and Disease Burden, South Korea
Hae-Young Kim, In-Hwan Oh, Jacob Lee, Jeong-Yeon Seon, Woo-Hwi Jeon, Jae Seok Park, Sung-Il Nam, Niket Thakkar, Prashanth Selvaraj, Jessica McGillen, Daniel Klein, Scott Braithwaite, Anna Bershteyn, Seung Heon Lee
Emerging Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Experiences and Lessons Learned from COVID-19 Pandemic Management in South Korea and the V4 Countries
Gergő Túri, Attila Virág
Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease.2021; 6(4): 201. CrossRef - Likely community transmission of COVID-19 infections between neighboring, persistent hotspots in Ontario, Canada
Eliseos J. Mucaki, Ben C. Shirley, Peter K. Rogan
F1000Research.2021; 10: 1312. CrossRef - Cost-Effectiveness of Interventions for the Prevention and Control of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Lihui Zhou, Wenxin Yan, Shu Li, Hongxi Yang, Xinyu Zhang, Wenli Lu, Jue Liu, Yaogang WANG
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness for the Response to COVID-19: The MERS Outbreak Containment Procedures
Hae-Wol Cho
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2020; 11(1): 1. CrossRef - COVID-19, Australia: Epidemiology Report 5: Reporting week ending 19:00 AEDT 29 February 2020
Olivia Williams
Communicable Diseases Intelligence.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The global community needs to swiftly ramp up the response to contain COVID-19
Dale Fisher, Annelies Wilder-Smith
The Lancet.2020; 395(10230): 1109. CrossRef - Experts’ request to the Spanish Government: move Spain towards complete lockdown
Oriol Mitjà, Àlex Arenas, Xavier Rodó, Aurelio Tobias, Joe Brew, José M Benlloch
The Lancet.2020; 395(10231): 1193. CrossRef - Maximizing the Calm before the Storm: Tiered Surgical Response Plan for Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19)
Samuel Wade Ross, Cynthia W. Lauer, William S. Miles, John M. Green, Britton A Christmas, Addison K. May, Brent D. Matthews
Journal of the American College of Surgeons.2020; 230(6): 1080. CrossRef - Coronavirus Disease-19: Summary of 2,370 Contact Investigations of the First 30 Cases in the Republic of Korea
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2020; 11(2): 81. CrossRef - Only strict quarantine measures can curb the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak in Italy, 2020
Henrik Sjödin, Annelies Wilder-Smith, Sarah Osman, Zia Farooq, Joacim Rocklöv
Eurosurveillance.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Governance, technology and citizen behavior in pandemic: Lessons from COVID-19 in East Asia
Rajib Shaw, Yong-kyun Kim, Jinling Hua
Progress in Disaster Science.2020; 6: 100090. CrossRef - Sub-National Allocation of COVID-19 Tests: An Efficiency Criterion with an Application to Italian Regions
Christelle Baunez, Mickael Degoulet, Stephane Luchini, Patrick Pintus, Miriam Teschl
SSRN Electronic Journal .2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The COVID-19 pandemic: a moment for exposure science
Nicole C. Deziel, Joseph G. Allen, Paul T. J. Scheepers, Jonathan I. Levy
Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidem.2020; 30(4): 591. CrossRef - National Response to COVID-19 in the Republic of Korea and Lessons Learned for Other Countries
Juhwan Oh, Jong-Koo Lee, Dan Schwarz, Hannah L. Ratcliffe, Jeffrey F. Markuns, Lisa R. Hirschhorn
Health Systems & Reform.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Containing COVID-19 Among 627,386 Persons in Contact With the Diamond Princess Cruise Ship Passengers Who Disembarked in Taiwan: Big Data Analytics
Chi-Mai Chen, Hong-Wei Jyan, Shih-Chieh Chien, Hsiao-Hsuan Jen, Chen-Yang Hsu, Po-Chang Lee, Chun-Fu Lee, Yi-Ting Yang, Meng-Yu Chen, Li-Sheng Chen, Hsiu-Hsi Chen, Chang-Chuan Chan
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2020; 22(5): e19540. CrossRef - COVID-19 and MERS Infections in Healthcare Workers in Korea
Seong-Kyu Kang
Safety and Health at Work.2020; 11(2): 125. CrossRef - How we should respond to the Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 outbreak: A German perspective
F. Jung, V. Krieger, F.T. Hufert, J.-H. Küpper
Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation.2020; 74(4): 363. CrossRef - WHAT HAS THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC TAUGHT US ABOUT ADOPTING PREVENTIVE MEASURES?
Adriana Cristina de Oliveira, Thabata Coaglio Lucas, Robert Aldo Iquiapaza
Texto & Contexto - Enfermagem.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID-19: when should quarantine be enforced?
Chris T Bauch, Madhur Anand
The Lancet Infectious Diseases.2020; 20(9): 994. CrossRef - COVID-19–We urgently need to start developing an exit strategy
Eskild Petersen, Sean Wasserman, Shui-Shan Lee, Unyeong Go, Allison H. Holmes, Seif Al-Abri, Susan McLellan, Lucille Blumberg, Paul Tambyah
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2020; 96: 233. CrossRef - COVID-19: the virus in the control of culture?
Lincoln Lopes Ferreira, Antonio Carlos P. Chagas, Wanderley M. Bernardo
Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira.2020; 66(3): 242. CrossRef - Evaluating How Smartphone Contact Tracing Technology Can Reduce the Spread of Infectious Diseases: The Case of COVID-19
Enrique Hernandez-Orallo, Pietro Manzoni, Carlos Tavares Calafate, Juan-Carlos Cano
IEEE Access.2020; 8: 99083. CrossRef - Development and Utilization of a Rapid and Accurate Epidemic Investigation Support System for COVID-19
Young Joon Park, Sang Yun Cho, Jin Lee, Ikjin Lee, Won-Ho Park, Seungmyeong Jeong, Seongyun Kim, Seokjun Lee, Jaeho Kim, Ok Park
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2020; 11(3): 118. CrossRef - How could we improve the national projects in health and demography after coronavirus pandemic?
N. A. Avxentyev, V. S. Nazarov, N. N. Sisigina
Voprosy Ekonomiki.2020; (6): 22. CrossRef - Public Health Emergency and Crisis Management: Case Study of SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak
Hemin Choi, Wonhyuk Cho, Min-Hyu Kim, Joon-Young Hur
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2020; 17(11): 3984. CrossRef - COVID-19 data sources: evaluation of map applications and analysis of behavior changes in Europe’s population
Vít Pászto, Jaroslav Burian, Karel Macků
Geografie.2020; 125(2): 171. CrossRef - The impact of COVID-19 and strategies for mitigation and suppression in low- and middle-income countries
Patrick G. T. Walker, Charles Whittaker, Oliver J. Watson, Marc Baguelin, Peter Winskill, Arran Hamlet, Bimandra A. Djafaara, Zulma Cucunubá, Daniela Olivera Mesa, Will Green, Hayley Thompson, Shevanthi Nayagam, Kylie E. C. Ainslie, Sangeeta Bhatia, Samir
Science.2020; 369(6502): 413. CrossRef - Public health initiatives from hospitalized patients with COVID-19, China
Chenkai Zhao, Yueqin Xu, Xu Zhang, Yaping Zhong, Li Long, Wenzhi Zhan, Tingting Xu, Chen Zhan, Yuehan Chen, Jinghai Zhu, Wei Xiao, Miao He
Journal of Infection and Public Health.2020; 13(9): 1229. CrossRef - COVID-19 in South Korea
Jun Yong Choi
Postgraduate Medical Journal.2020; 96(1137): 399. CrossRef - COVID-19 Pandemic and Burden of Non-Communicable Diseases: An Ecological Study on Data of 185 Countries
M. Reza Azarpazhooh, Negar Morovatdar, Abolfazl Avan, Thanh G Phan, Afshin A. Divani, Nawaf Yassi, Saverio Stranges, Brian Silver, José Biller, Masoud Tokazebani Belasi, Sepideh Kazemi Neya, Bita Khorram, Asher Frydman, Yongchai Nilanont, Elisa Onorati, M
Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases.2020; 29(9): 105089. CrossRef - Effect of Underlying Comorbidities on the Infection and Severity of COVID-19 in Korea: a Nationwide Case-Control Study
Wonjun Ji, Kyungmin Huh, Minsun Kang, Jinwook Hong, Gi Hwan Bae, Rugyeom Lee, Yewon Na, Hyoseon Choi, Seon Yeong Gong, Yoon-Hyeong Choi, Kwang-Pil Ko, Jeong-Soo Im, Jaehun Jung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Innovative countermeasures can maintain cancer care continuity during the coronavirus disease-2019 pandemic in Korea
Soohyeon Lee, Ah-reum Lim, Min Ja Kim, Yoon Ji Choi, Ju Won Kim, Kyong Hwa Park, Sang Won Shin, Yeul Hong Kim
European Journal of Cancer.2020; 136: 69. CrossRef - Role of Chest CT in Resource-Driven Healthcare Systems
Natalie L. Demirjian, Brandon K. K. Fields, Ali Gholamrezanezhad
American Journal of Roentgenology.2020; 215(3): W36. CrossRef - Contact Tracing during Coronavirus Disease Outbreak, South Korea, 2020
Young Joon Park, Young June Choe, Ok Park, Shin Young Park, Young-Man Kim, Jieun Kim, Sanghui Kweon, Yeonhee Woo, Jin Gwack, Seong Sun Kim, Jin Lee, Junghee Hyun, Boyeong Ryu, Yoon Suk Jang, Hwami Kim, Seung Hwan Shin, Seonju Yi, Sangeun Lee, Hee Kyoung K
Emerging Infectious Diseases.2020; 26(10): 2465. CrossRef - Health policy and leadership models during the COVID-19 pandemic: A review
Maria Nicola, Catrin Sohrabi, Ginimol Mathew, Ahmed Kerwan, Ahmed Al-Jabir, Michelle Griffin, Maliha Agha, Riaz Agha
International Journal of Surgery.2020; 81: 122. CrossRef - Lessons From South Korea’s Covid-19 Policy Response
Jongeun You
The American Review of Public Administration.2020; 50(6-7): 801. CrossRef - Nationwide Results of COVID-19 Contact Tracing in South Korea: Individual Participant Data From an Epidemiological Survey
Seung Won Lee, Woon Tak Yuh, Jee Myung Yang, Yoon-Sik Cho, In Kyung Yoo, Hyun Yong Koh, Dominic Marshall, Donghwan Oh, Eun Kyo Ha, Man Yong Han, Dong Keon Yon
JMIR Medical Informatics.2020; 8(8): e20992. CrossRef - The COVID-19 pandemic: critical issues and perspectives for infectious disease prevention in Africa
Ayodele Oluwaseun Ajayi
Infection Ecology & Epidemiology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID-19
Osakpolor Ogbebor, Zaw Min, Tariq Cheema, Nitin Bhanot
Critical Care Nursing Quarterly.2020; 43(4): 343. CrossRef Awareness of Health Professionals on COVID-19 and Factors Affecting It Before and During Index Case in North Shoa Zone, Ethiopia, 2020
Ayele Abebe, Abinet Mekuria, Awraris Balchut
Infection and Drug Resistance.2020; Volume 13: 2979. CrossRef- COVID-19: Weighing the Endeavors of Nations, with Time to Event Analysis
Shine Stephen, Alwin Issac, Jaison Jacob, VR Vijay, Rakesh Vadakkethil Radhakrishnan, Nadiya Krishnan
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2020; 11(4): 149. CrossRef - Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) diagnostic technologies: A country-based retrospective analysis of screening and containment procedures during the first wave of the pandemic
Brandon K.K. Fields, Natalie L. Demirjian, Ali Gholamrezanezhad
Clinical Imaging.2020; 67: 219. CrossRef - Journey to the East: COVID-19 Lessons From the East
Samuel S. Y. Wang
Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health.2020; 32(8): 513. CrossRef - COVID-19 healthcare demand and mortality in Sweden in response to non-pharmaceutical mitigation and suppression scenarios
Henrik Sjödin, Anders F Johansson, Åke Brännström, Zia Farooq, Hedi Katre Kriit, Annelies Wilder-Smith, Christofer Åström, Johan Thunberg, Mårten Söderquist, Joacim Rocklöv
International Journal of Epidemiology.2020; 49(5): 1443. CrossRef - Lessons learnt from easing COVID-19 restrictions: an analysis of countries and regions in Asia Pacific and Europe
Emeline Han, Melisa Mei Jin Tan, Eva Turk, Devi Sridhar, Gabriel M Leung, Kenji Shibuya, Nima Asgari, Juhwan Oh, Alberto L García-Basteiro, Johanna Hanefeld, Alex R Cook, Li Yang Hsu, Yik Ying Teo, David Heymann, Helen Clark, Martin McKee, Helena Legido-Q
The Lancet.2020; 396(10261): 1525. CrossRef - Natural outbreaks and bioterrorism: How to deal with the two sides of the same coin?
Lionel Koch, Anne-Aurelie Lopes, Avelina Maiguy, Sophie Guillier, Laurent Guillier, Jean-Nicolas Tournier, Fabrice Biot
Journal of Global Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Retour d’expérience sur Covisan : un dispositif médicosocial pour casser les chaînes de transmission de la Covid-19
J. Pernet, H. de Bonnières, C. Breton, V. Hirsch, J.S. Molitor, D. Boutolleau, R. Piarroux, P. Hausfater
Annales françaises de médecine d’urgence.2020; 10(4-5): 306. CrossRef - Retour d’expérience sur la réorganisation d’un service d’urgence de centre hospitalo-universitaire en réponse à l’épidémie de Covid-19
M. Drogrey, J. Pernet, P. Hausfater
Annales françaises de médecine d’urgence.2020; 10(4-5): 233. CrossRef - Evaluating the Effectiveness of COVID-19 Bluetooth-Based Smartphone Contact Tracing Applications
Enrique Hernández-Orallo, Carlos T. Calafate, Juan-Carlos Cano, Pietro Manzoni
Applied Sciences.2020; 10(20): 7113. CrossRef - COVID-19 testing and infection surveillance: Is a combined digital contact-tracing and mass-testing solution feasible in the United States?
Devin Skoll, Jennifer C. Miller, Leslie A. Saxon
Cardiovascular Digital Health Journal.2020; 1(3): 149. CrossRef - Delay-adjusted age- and sex-specific case fatality rates for COVID-19 in South Korea: Evolution in the estimated risk of mortality throughout the epidemic
A.T. Newall, R.N.F. Leong, A. Nazareno, D.J. Muscatello, J.G. Wood, W.J. Kim
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2020; 101: 306. CrossRef - Heralding the Digitalization of Life in Post-Pandemic East Asian Societies
Calvin Wai-Loon Ho, Karel Caals, Haihong Zhang
Journal of Bioethical Inquiry.2020; 17(4): 657. CrossRef Intensive Care Unit Capacity and Its Associated Risk Factors During the COVID-19 Surge in the Republic of Korea: Analysis Using Nationwide Health Claims Data
Seung Heon Lee, So-Youn Park, Jeong-Yeon Seon, Woo-Hwi Jeon, Sung Il Nam, Jong-Hak Park, Jae Seok Park, Hae-Young Kim, Niket Thakkar, Prashanth Selvaraj, Anna Bershteyn, In-Hwan Oh
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy.2020; Volume 13: 2571. CrossRef- The Facts, Fallacies and Uncertainties about Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Tow Keang Lim
Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore.2020; 49(6): 343. CrossRef - Digital contact tracing technologies in epidemics: a rapid review
Andrew Anglemyer, Theresa HM Moore, Lisa Parker, Timothy Chambers, Alice Grady, Kellia Chiu, Matthew Parry, Magdalena Wilczynska, Ella Flemyng, Lisa Bero
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Initial estimates of COVID-19 infections in hospital workers in the United States during the first wave of pandemic
Junaid A. Razzak, Junaid A. Bhatti, Muhammad Ramzan Tahir, Omrana Pasha-Razzak, Oathokwa Nkomazana
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(12): e0242589. CrossRef - Effective Control of COVID-19 in South Korea: Cross-Sectional Study of Epidemiological Data
Gwang Hun Jeong, Hyo Jeong Lee, Jinhee Lee, Jun Young Lee, Keum Hwa Lee, Young Joo Han, Sojung Yoon, Seohyun Ryu, Da Kyung Kim, Myung Bae Park, Jae Won Yang, Maria Effenberger, Michael Eisenhut, Sung Hwi Hong, Andreas Kronbichler, Ramy Abou Ghayda, Jae Il
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2020; 22(12): e22103. CrossRef - Evidence of Long-Distance Droplet Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 by Direct Air Flow in a Restaurant in Korea
Keun-Sang Kwon, Jung-Im Park, Young Joon Park, Don-Myung Jung, Ki-Wahn Ryu, Ju-Hyung Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Why many countries failed at COVID contact-tracing — but some got it right
Dyani Lewis
Nature.2020; 588(7838): 384. CrossRef - The Serial Interval of COVID-19 in Korea: 1,567 Pairs of Symptomatic Cases from Contact Tracing
Kwan Hong, Sujin Yum, Jeehyun Kim, Byung Chul Chun
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - A Public Platform for Virtual IoT-Based Monitoring and Tracking of COVID-19
Younchan Jung, Ronnel Agulto
Electronics.2020; 10(1): 12. CrossRef - The feasibility of organ transplantation during the COVID-19 outbreak: experiences from South Korea
Juhan Lee, Eun Jin Kim, Kyong Ihn, Jae Geun Lee, Dong Jin Joo, Myoung Soo Kim, Soon Il Kim, Yu Seun Kim, Kyu Ha Huh
Korean Journal of Transplantation.2020; 34(4): 257. CrossRef
- Privacy risk in contact tracing systems
- Natural Infection with Rabies Virus: A Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Study of Human Brains
- Firouzeh Farahtaj, Leila Alizadeh, Alireza Gholami, Alireza Tahamtan, Sadegh Shirian, Maryam Fazeli, Amir Sasan Mozaffari Nejad, Ali Gorji, Hamid Mahmoudzadeh Niknam, Amir Ghaemi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(1):6-11. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.1.03
- 7,217 View
- 244 Download
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Despite all the efforts and increased knowledge of rabies, the exact mechanisms of infection and mortality from the rabies virus are not well understood. To understand the mechanisms underlying the pathogenicity of rabies virus infection, it is crucial to study the tissue that the rabies virus naturally infects in humans.
Methods Cerebellum brain tissue from 9 human post mortem cases from Iran, who had been infected with rabies virus, were examined histopathologically and immunohistochemically to evaluate the innate immune responses against the rabies virus.
Results Histopathological examination revealed inflammation of the infected cerebellum and immunohistochemical analyses showed an increased immunoreactivity of heat shock protein 70, interleukin-6, interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, caspase-3, caspase-9, toll-like receptor3 and toll-like receptor4 in the infected brain tissue.
Conclusion These results indicated the involvement of innate immunity in rabies infected human brain tissue, which may aggravate the progression of this deadly disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Systematic development of immunohistochemistry protocol for large cryosections-specific to non-perfused fetal brain
Karthika Pandurangan, Jaikishan Jayakumar, Stephen Savoia, Reetuparna Nanda, S. Lata, E. Harish Kumar, Suresh S., Sudha Vasudevan, Chitra Srinivasan, Jayaraj Joseph, Mohanasankar Sivaprakasam, Richa Verma
Journal of Neuroscience Methods.2024; 405: 110085. CrossRef - Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Neurodegeneration of Neurotropic Viral Infection
Prapimpun Wongchitrat, Theerawut Chanmee, Piyarat Govitrapong
Molecular Neurobiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Biosensor as an alternative diagnostic method for rabies virus detection: A literature review
Milad Zandi, Sajad Zandi, Ramin Mohammadi, Parastoo Hosseini, Samane Teymouri, Saber Soltani, Azadeh Rasouli
Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry.2022; 69(4): 1348. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical diagnosis of human infectious diseases: a review
Hamadou Oumarou Hama, Gérard Aboudharam, Rémi Barbieri, Hubert Lepidi, Michel Drancourt
Diagnostic Pathology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Rabies Virus-Infected Human and Canine Brains
Pulleri Kandi Harsha, Sathyanarayanan Ranganayaki, Gowri Yale, Gourav Dey, Kiran K. Mangalaparthi, Anusha Yarlagadda, B. K. Chandrasekhar Sagar, Anita Mahadevan, M. M. Srinivas Bharath, Reeta S. Mani
Neurochemical Research.2022; 47(6): 1610. CrossRef - A rare fatal case of rabies coexisting with COVID-19
RabiNarayan Hota, Shalendra Singh, Rakesh Sharma, Pallavi Khandare
Journal of Acute Disease.2022; 11(3): 129. CrossRef - Enhancement of immune responses by co-stimulation of TLR3 - TLR7 agonists as a potential therapeutics against rabies in mouse model
Firouzeh Farahtaj, Alireza Gholami, Mohammad Sadeq Khosravy, Safoora Gharibzadeh, Hamid Mahmoudzadeh Niknam, Amir Ghaemi
Microbial Pathogenesis.2021; 157: 104971. CrossRef - Establishment of Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neurons—A Promising In Vitro Model for a Molecular Study of Rabies Virus and Host Interaction
Thanathom Chailangkarn, Nathiphat Tanwattana, Thanakorn Jaemthaworn, Sira Sriswasdi, Nanchaya Wanasen, Sithichoke Tangphatsornruang, Kantinan Leetanasaksakul, Yuparat Jantraphakorn, Wanapinun Nawae, Penpicha Chankeeree, Porntippa Lekcharoensuk, Boonlert L
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(21): 11986. CrossRef - Beneficial and Detrimental Effects of Regulatory T Cells in Neurotropic Virus Infections
Malgorzata Ciurkiewicz, Vanessa Herder, Andreas Beineke
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(5): 1705. CrossRef - Characterization of the Th17 profile immune response in cases of human rabies transmitted by dogs and its interference in the disease pathogenesis.
L.B. Santos, F. Guedes, S.M. Achkar, M.I.S. Duarte, I.S.S. Katz, S.R. Silva, E.R. Fernandes
Journal of Neuroimmunology.2020; 344: 577263. CrossRef - Quantitative proteomics leads to identify dog brain proteins involved in rabies virus infection: implication in understanding viral pathophysiology
Suchismita Behera, Rajesh Raghunath Pharande, R. Rajendra Reddy, Sharmila B. Majee, Sandeepan Mukherjee, Amol Ratnakar Suryawanshi
Journal of Proteins and Proteomics.2020; 11(4): 241. CrossRef - Feral dog bite causing paralytic rabies: Difficult diagnosis and failure of prevention
Hussein Algahtani, Bader Shirah, Emna Chtourou, Osama Abuhawi, Nawal Abdelghaffar, Mohammad Alshehri
Saudi Journal for Health Sciences.2020; 9(3): 260. CrossRef
- Systematic development of immunohistochemistry protocol for large cryosections-specific to non-perfused fetal brain
- The Prevalence of
CYP2B6 Gene Polymorphisms in Malaria-endemic Population of Timor in East Nusa Tenggara Indonesia - Linawati Hananta, Indwiani Astuti, Ahmad Hamim Sadewa, Josephine Alice, Jontari Hutagalung, Mustofa
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(4):192-196. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.4.08
- 5,661 View
- 48 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The
CYP2B6 is one of the most polymorphicCYP genes in humans that has the potential to modify the pharmacological and toxicological responses to clinically important drugs such as antimalarial artemisinin and its derivatives. The aim of the study was to determine the frequency ofCYP2B6 polymorphisms in Timor malaria endemic area, East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia where Artemisin-based Combination Therapy (ACT) has been used to treat uncomplicated malaria.Methods A total of 109 healthy subjects were participated in this study.
CYP2B6*4, *6 and*9 polymorphisms were analyzed using PCR-RFLP to confirm the SNPs prevalence of 516G>T and 785A>G in exon 4 and 5.Results There were 96 subjects included in the analysis. In the exon 4 of
CYP2B6 516G>T, the frequency of the T mutation was 37.5% (39/96), and the wildtype 27.1% (26/96). In the exon 5,CYP2B6 785A>G mutant was detected in 29.2% (28/96) of individuals, and the wildtype allele in 35.4% (34/96). The frequency ofCYP2B6*9 (516G>T),CYP2B6*4 (785A>G) andCYP2B6*6 (516G>T and 785A>G) were 40.6%, 29.2% and 22.9%, respectively. The prevalence of theseCYP2B6 gene polymorphisms in Timorian ethnic were higher than that in Malay, Han Chinese, Indian, and Egyptian populations.Conclusion The prevalence of these
CYP2B6 516G>T and 785A>G polymorphisms in Timorian ethnic is higher than that in other populations. These polymorphisms may affect the metabolism of artemisinin and its derivatives.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Allelic variants of CYP2B6 gene expression and its implication on the pathogenesis of malaria among a cohort of outpatients in North-Central Nigeria
Olalere Shittu, Mobolanle Oladipo Oniya, Titus Adeniyi Olusi
Open Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Leveraging Mann–Whitney U test on large-scale genetic variation data for analysing malaria genetic markers
Kah Yee Tai, Jasbir Dhaliwal, Vinod Balasubramaniam
Malaria Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Frequency of CYP2B6 Alleles in Major Iranian Ethnicities, Affecting Response to Efavirenz
Parham Mardi, Bahareh Tavakoli-Far, Samira Sheibani Nia, Roshanak Jazayeri, Massoud Houshmand, Nadeem Sheikh
Genetics Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Phenotyping Study of Cyclophosphamide 4-Hydroxylation in Malay Cancer Patients
Yesi Ihdina Fityatal Hasanah, Yahdiana Harahap, Denni Joko Purwanto
Drug Design, Development and Therapy.2021; Volume 15: 305. CrossRef - CYP2B6 Functional Variability in Drug Metabolism and Exposure Across Populations—Implication for Drug Safety, Dosing, and Individualized Therapy
Immaculate M. Langmia, Katja S. Just, Sabrina Yamoune, Jürgen Brockmöller, Collen Masimirembwa, Julia C. Stingl
Frontiers in Genetics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The correlation between the level of 3-hydroxypropyl mercapturic acid, CYP2B6 polymorphisms, and hematuria occurrences after cyclophosphamide administration and its bioanalytical methods: A systematic review
Yahdiana Harahap, Farhan Nurahman, Denni Joko Purwanto, Arry Yanuar
Heliyon.2021; 7(10): e08126. CrossRef - Frequencies of CYP2B6∗4,∗5, and ∗6 Alleles within an Iranian Population (Mazandaran)
Mohammad Bagher Hashemi-Soteh, Elaheh Hosseini, Shokoufeh Fazelnia, Faramarz Ghasemian-Sorbeni, Sara Madahian, Mohammad Reza Shiran, Hafiz Ishfaq Ahmad
Genetics Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - In vitro and in silico Determination of the Interaction of Artemisinin with Human Serum Albumin
S. Ginosyan, H. Grabski, S. Tiratsuyan
Molecular Biology.2020; 54(4): 586. CrossRef - A Review of Danshen Combined with Clopidogrel in the Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease
Zhaojian Zhang, Yu Wang, Wangxiao Tan, Siwei Wang, Jinghua Liu, Xiao Liu, Xiaoying Wang, Xiumei Gao
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medic.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef
- Allelic variants of CYP2B6 gene expression and its implication on the pathogenesis of malaria among a cohort of outpatients in North-Central Nigeria
- How do Sexual Identity, and Coming Out Affect Stress, Depression, and Suicidal Ideation and Attempts Among Men Who Have Sex With Men in South Korea?
- Byonghee Cho, Aeree Sohn
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(5):281-288. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2016.09.001
- 3,297 View
- 28 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the status of sexual identity, perceived stigma, stress, depression, and suicidal ideation and attempts. It also examined how sexual identity and “coming out” affect stress, depression, and suicidal ideation and attempts.
Methods
Suicidal ideation, psychological health status, and health-related behaviors were assessed using the Internet to maximize the confidentiality of the participants, men who have sex with men (MSM). The data were collected from a total of 873 MSM aged between 19 years and 59 years in 2014.
Results
Only 20.9% of the MSM had come out (18.0% voluntarily and 2.9% by others). The prevalences of perceived stress and depression among MSM were 46.7% and 42.7%, respectively, compared with 20.1% and 7.4% among general men. Approximately 32% of the MSM reported any suicidal ideation, and 3.3% had attempted suicide in the past year. The likelihood of suicidal ideation was significantly associated with being age 30–39 years [odds ratio (OR) = 1.8], high school or less (OR = 1.6), having been outed (OR = 5.2), feeling stressed (OR = 1.8), and feeling depressed (OR = 12.4) after sociodemographic factors and other perceptions were controlled for.
Conclusion
The present study provides evidence that MSM are at an elevated risk for suicidal ideation and attempts with high stress and depression. Some risk factors were specific to being gay or bisexual in a hostile environment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Stress of being outed to parents, LGBTQ family support, and depressive symptoms among sexual and gender diverse youth
Peter S. McCauley, Alexander J. Del Farno, Antonia E. Caba, Benton M. Renley, Shaylynne Shuler, Lisa A. Eaton, Ryan J. Watson
Journal of Research on Adolescence.2024; 34(1): 205. CrossRef - High Interest in the Use of mHealth Platform for HIV Prevention among Men Who Have Sex with Men in Nepal
Kamal Gautam, Kiran Paudel, Ali Ahmed, Manisha Dhakal, Jeffrey A Wickersham, Krishna C Poudel, Sherry Pagoto, Bibhav Acharya, Keshab Deuba, Pablo K Valente, Roman Shrestha
Journal of Community Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Age Differences in the Associations Between Outness and Suicidality Among LGBTQ+ Youth
Brian A. Feinstein, Ethan H. Mereish, Mary Rose Mamey, Cindy J. Chang, Jeremy T. Goldbach
Archives of Suicide Research.2023; 27(2): 734. CrossRef - Psychological Status of Men Who Have Sex with Men during COVID-19: An Online Cross-Sectional Study in Western China
Bing Lin, Jiaxiu Liu, Wei He, Haiying Pan, Xiaoni Zhong
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2023; 20(2): 1333. CrossRef - Social capital, perceived stress, and mental health of men who have sex with men in China: A cross-sectional study
Xiaoyue Zhang, Ying Zhou, Kaili Zhang
Frontiers in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - HIV-related stigma, depression and suicidal ideation among HIV-positive MSM in China: a moderated mediation model
Jiaqi Fu, Xu Chen, Zhenwei Dai, Yiman Huang, Weijun Xiao, Hao Wang, Mingyu Si, Yijin Wu, Ling Zhang, Shu Jing, Xin Liu, Fei Yu, Guodong Mi, Xiao-You Su
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Related Knowledge and Stigma among Men Who Have Sex with Men in the Republic of Korea from 2012 to 2022
Aeree Sohn
Healthcare.2023; 11(24): 3135. CrossRef - HIV-Related Stigma, Sexual Identity, and Depressive Symptoms Among MSM Living With HIV in China: A Moderated Mediation Modeling Analysis
Tianyue Mi, Guanghua Lan, Xueying Yang, Xiaoming Li, Shan Qiao, Zhiyong Shen, Yuejiao Zhou
American Journal of Men's Health.2022; 16(2): 155798832210875. CrossRef - Sexual Minority Stigma, Sexual Orientation Concealment, Social Support and Depressive Symptoms Among Men Who have Sex with Men in China: A Moderated Mediation Modeling Analysis
Changmian Ding, Xiangfan Chen, Wei Wang, Bin Yu, Huimin Yang, Xiaoyan Li, Shumin Deng, Hong Yan, Shiyue Li
AIDS and Behavior.2020; 24(1): 8. CrossRef - TRANSNATIONAL INTEREST CONVERGENCE AND GLOBAL KOREA AT THE EDGE OF RACE AND QUEER EXPERIENCES
Patrick S. Thomsen
Du Bois Review: Social Science Research on Race.2020; 17(2): 411. CrossRef - Is Perceived Stigma in Clinical Settings Associated With Poor Health Status Among New York City’s Residents of Color?
Prabal De, Alexis Pozen, Henna Budhwani
Medical Care.2019; 57(12): 960. CrossRef - Comparison of depression and anxiety between HIV-negative men who have sex with men and women (MSMW) and men who have sex with men only (MSMO): a cross-sectional study in Western China
Ying Hu, Xiao-ni Zhong, Bin Peng, Yan Zhang, Hao Liang, Jiang-hong Dai, Juying Zhang, Xiao-hua Zhong, Ai-long Huang
BMJ Open.2019; 9(1): e023498. CrossRef - Transgender Women's Experiences with Stigma, Trauma, and Attempted Suicide in the Dominican Republic
Henna Budhwani, Kristine R. Hearld, Adrienne N. Milner, Rebecca Charow, Elaine M. McGlaughlin, Mayra Rodriguez‐Lauzurique, Santo Rosario, Robert Paulino‐Ramirez
Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior.2018; 48(6): 788. CrossRef - The Reciprocal Relationship between Suicidality and Stigma
Bernardo Carpiniello, Federica Pinna
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Fallen Flowers
Hae-Wol Cho, Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2016; 7(5): 279. CrossRef
- Stress of being outed to parents, LGBTQ family support, and depressive symptoms among sexual and gender diverse youth
- Epidemiological and Clinical Features of People with Malta Fever in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Mahmood Moosazadeh, Roja Nikaeen, Ghasem Abedi, Motahareh Kheradmand, Saeid Safiri
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(3):157-167. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2016.04.009
- 3,351 View
- 22 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Numerous studies have reported the epidemiological and clinical features of Malta fever incidence in Iran. Review and synthesis of the related literature through meta-analysis can provide an appropriate measurement for aforementioned indices. Therefore, the present study aimed to determine the epidemiological and clinical features of people with Malta fever in Iran.
Methods
The required documents were obtained through searching national and international databases. In each study, standard deviation of the indices was calculated using binomial distribution formulas. Finally, the heterogeneity index was determined between studies using Cochran (Q) and I2 tests.
Results
Combining the results of 47 articles in the meta-analysis indicated that 57.6% (55.02–60.1%) and 42.3% (49.8–44.9%) of the patients were male and female, respectively. Most of the patients lived in rural areas; 68.4% (63.6–73.2%) compared to 31.4% (26.7–36.3%). In addition, 20.8% (17.4–24.2%) of the patients were ranchers and farmers, 16.9% (14.5–19.4%) were students, and 31.6% (27–36.2%) were housewives. Of the patients studies, 50.5% (35.6–65.2%) experienced contact with animals and 57.1% (46.4–67.9%) used unpasteurized dairy products. Fever, joint pain, and sweating were detected among 65.7% (53.7–77.8%) and 55.3% (44.4–66.2%), respectively.
Conclusion
The present study revealed that the frequency of male patients with brucellosis was considerably more than that of female patients. The number of patients with Malta fever in rural areas was significantly more than in urban areas. High-risk behavior, unprotected contact with animals, and using unpasteurized dairy products were among the most significant factors affecting Malta fever incidence in Iran. Fever, joint pain, and sweating were detected among most of the patients with Malta fever. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A study of rural populations’ knowledge, attitude, and practice about brucellosis: a descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study
Zahra Montaseri, Zahra Mohebi, Rahil Masoumi, Azizallah Dehghan, Mostafa Bijani
BMC Research Notes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic significance of hematological parameters in brucellosis
Mehmet Çelik, Mehmet Reşat Ceylan, Deniz Altındağ, Nevin Güler Dinçer, Sevil Alkan
Journal of Clinical Medicine of Kazakhstan.2023; 20(1): 50. CrossRef - Presence of Brucella spp. in Milk and Dairy Products: A Comprehensive Review and Its Perspectives
Md. Sadequl Islam, Md. Ariful Islam, Md. Moshiur Rahman, Khaleda Islam, Md. Mominul Islam, Md. Murtuza Kamal, Md. Nazrul Islam, Gianfranco Picone
Journal of Food Quality.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Predicting of Bacteremia in Patients with Brucellosis Using Machine Learning Methods
Mehmet ÇELİK, Mehmet Reşat CEYLAN, Deniz ALTINDAĞ, Sait Can YÜCEBAŞ, Nevin GÜLER DİNCER, Sevil ALKAN
Journal of Contemporary Medicine.2023; 13(3): 459. CrossRef - Toponyms in dermatology
Heera Ramesh, Sachin Somashekar
Indian Journal of Dermatology.2022; 67(3): 279. CrossRef - Brucella pleurisy: An extremely rare complication of brucellosis
Ahmad Alikhani, Hamideh Abbaspour Kasgari, Haadi Majidi, Zahra Nekoukar
Clinical Case Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Design and validation of brucellosis prevention questionnaire focused on animal vaccination
Farhad Bahadori, Fazlollah Ghofranipour, Saeideh Ghaffarifar, Reza Ziaei
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Forecasting the monthly incidence rate of brucellosis in west of Iran using time series and data mining from 2010 to 2019
Hadi Bagheri, Leili Tapak, Manoochehr Karami, Zahra Hosseinkhani, Hamidreza Najari, Safdar Karimi, Zahra Cheraghi, Esteban Tlelo-Cuautle
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(5): e0232910. CrossRef - Epidemiologically characteristics of human brucellosis and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of Brucella melitensis in Hinggan League of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
Hai-Tao Yuan, Cheng-Ling Wang, Li-Na Liu, Dan Wang, Dan Li, Zhen-Jun Li, Zhi-Guo Liu
Infectious Diseases of Poverty.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Brucellosis: Evaluation of Two Hundred and Ten Cases with Different Clinical Features
Esma Eroglu, Bahar Kandemir
Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore.2020; 49(7): 462. CrossRef - A comparison of three data mining time series models in prediction of monthly brucellosis surveillance data
Nasrin Shirmohammadi‐Khorram, Leili Tapak, Omid Hamidi, Zohreh Maryanaji
Zoonoses and Public Health.2019; 66(7): 759. CrossRef - Human brucellosis caused by raw dairy products: A review on the occurrence, major risk factors and prevention
Maryam Dadar, Youcef Shahali, Adrian M. Whatmore
International Journal of Food Microbiology.2019; 292: 39. CrossRef - Epidemiological, Clinical and Paraclinical Evaluation of Recorded Cases with Brucellosis in Kermanshah Province Health Center 2012 - 2016
Hossein Hatami, Ali Ramezankhani, Farahnaz Shekarchi
Journal of Kermanshah University of Medical Scienc.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiological, risk factors, clinical, and laboratory features of brucellosis in the Southwest of Iran within 2009–2015
Mahmood Nabavi, Hossein Hatami, Hedayatollah Jamaliarand
International Journal of Preventive Medicine.2019; 10(1): 108. CrossRef - Meta-Analysis of the Changes of Peripheral Blood T Cell Subsets in Patients with Brucellosis
Rongjiong Zheng, Songsong Xie, Shaniya Niyazi, Xiaobo Lu, Lihua Sun, Yan Zhou, Yuexin Zhang, Kai Wang
Journal of Immunology Research.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Epidemiology and Clinical Manifestations of Human Brucellosis in China
Rongjiong Zheng, Songsong Xie, Xiaobo Lu, Lihua Sun, Yan Zhou, Yuexin Zhang, Kai Wang
BioMed Research International.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - The clinical features of 590 patients with brucellosis in Xinjiang, China with the emphasis on the treatment of complications
Bin Jia, Fengbo Zhang, Ying Lu, Wenbao Zhang, Jun Li, Yuexin Zhang, Jianbing Ding, Mazin Barry
PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.2017; 11(5): e0005577. CrossRef
- A study of rural populations’ knowledge, attitude, and practice about brucellosis: a descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study
- Comparison of Three Different Methods for Detection of IL28 rs12979860 Polymorphisms as a Predictor of Treatment Outcome in Patients with Hepatitis C Virus
- Abolfazl Fateh, Mohammadreza Aghasadeghi, Seyed D. Siadat, Farzam Vaziri, Farzin Sadeghi, Roohollah Fateh, Hossein Keyvani, Alireza H. Tasbiti, Shamsi Yari, Angila Ataei-Pirkooh, Seyed H. Monavari
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(2):83-89. Published online April 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.11.004
- 3,038 View
- 19 Download
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the specificity, sensitivity, cost, and turn-around time of three methods of gene polymorphism analysis and to study the relationship between IL28B rs12979860 and SVR rate to pegIFN-α/RVB therapy among patients with chronic hepatitis C.
Methods
A total of 100 samples from chronic hepatitis C patients were analyzed in parallel using the three methods: direct sequencing, real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS)-PCR.
Results
The different profiles for IL28B rs12979860 alleles (CC, CT, and TT) obtained with PCR-RFLP, ARMS-PCR, and direct sequencing were consistent among the three methods. Prevalence of rs12979860 genotypes CC, CT and TT in HCV genotype 1a was 10(19.6%), 35(68.6%), and six (11.8%), respectively, and in HCV genotype 31, it was 13(26.5%), 31(63.3%), and five (10.2%), respectively. No significant difference was seen between rs12979860 genotype and HCV genotype (p = 0.710).
Conclusion
Screening by ARMS – PCR SNOP detection represents the most efficient and reliable method to determine HCV polymorphisms in routine clinical practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multiplex Snapshot Minisequencing for the Detection of Common PAH Gene Mutations in Iranian Patients with Phenylketonuria
Pegah Namdar Aligoodarzi, Golale Rostami, Seyed Reza Kazemi Nezhad, Mohammad Hamid
Iranian Biomedical Journal.2023; 27(1): 46. CrossRef - Expression of TRIM56 gene in SARS-CoV-2 variants and its relationship with progression of COVID-19
Rezvan Tavakoli, Pooneh Rahimi, Mojtaba Hamidi-Fard, Sana Eybpoosh, Delaram Doroud, Iraj Ahmadi, Enayat Anvari, Mohammadreza Aghasadeghi, Abolfazl Fateh
Future Virology.2023; 18(9): 563. CrossRef - Performance of the tetra-primer PCR technique compared to PCR-RFLP in the search for rs12979860 (C/T) and rs8099917 (T/G) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the IFNL4 gene
Ellen Hochleitner Souza Kindermann, Karoline Rodrigues Campos, Adele Caterino-de-Araujo
Revista do Instituto Adolfo Lutz.2023; 82: 1. CrossRef - Glioblastoma as a Novel Drug Repositioning Target: Updated State
Hamed Hosseinalizadeh, Ammar Ebrahimi, Ahmad Tavakoli, Seyed Hamidreza Monavari
Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry.2023; 23(11): 1253. CrossRef - Prevalence of Human Cytomegalovirus Infection in Iranian Prostate Cancer Patients
Ehsan Alborzi, Ahmad Tavakoli, Seyed Jalal Kiani, Saied Ghorbani, Davod Javanmard, Milad Sabaei, Maryam Fatemipour, Seyed Hamidreza Monavari
Iranian Journal of Medical Microbiology.2023; 17(4): 379. CrossRef - MicroRNAs Profiling in HIV, HCV, and HIV/HCV Co-Infected Patients
Mohsen Moghoofei, Sohrab Najafipour, Shayan Mostafaei , Ahmad Tavakoli , Farah Bokharaei-Salim , Saied Ghorbani, Davod Javanmard, Hadi Ghaffari , Seyed Hamidreza Monavari
Current HIV Research.2021; 19(1): 27. CrossRef - Occult hepatitis C virus infection in hemophilia patients and its correlation with interferon lambda 3 and 4 polymorphisms
Amir Hossein Nafari, Ahmad Ayadi, Zahra Noormohamadi, Fatemeh Sakhaee, Farzam Vaziri, Seyed Davar Siadat, Abolfazl Fateh
Infection, Genetics and Evolution.2020; 79: 104144. CrossRef - Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay Using the Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Technique in the Detection of Prosthetic Joint Infections: A Multi-Centered Study
Ataollah Moshirabadi, Mohammad Razi, Peyman Arasteh, Mohammad Mahdi Sarzaeem, Saman Ghaffari, Saied Aminiafshar, Kami Hosseinian Khosroshahy, Fatemeh Maryam Sheikholeslami
The Journal of Arthroplasty.2019; 34(2): 359. CrossRef - One-Step ARMS-PCR for the Detection of SNPs—Using the Example of the PADI4 Gene
Ehnert, Linnemann, Braun, Botsch, Leibiger, Hemmann, Nussler
Methods and Protocols.2019; 2(3): 63. CrossRef - Epstein–Barr virus and risk of breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohammad Farahmand, Seyed Hamidreza Monavari, Zabihollah Shoja, Hadi Ghaffari, Mehdi Tavakoli, Ahmad Tavakoli
Future Oncology.2019; 15(24): 2873. CrossRef - Modeling suggests that microliter volumes of contaminated blood caused an outbreak of hepatitis C during computerized tomography
Eyal Shteyer, Louis Shekhtman, Tal Zinger, Sheri Harari, Inna Gafanovich, Dana Wolf, Hefziba Ivgi, Rima Barsuk, Ilana Dery, Daniela Armoni, Mila Rivkin, Rahul Pipalia, Michal Cohen Eliav, Yizhak Skorochod, Gabriel S. Breuer, Ran Tur-kaspa, Yonit Weil Wien
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(1): e0210173. CrossRef - Correlation of CD81 and SCARB1 polymorphisms on virological responses in Iranian patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1
Milad Nafari, Shiva Irani, Farzam Vaziri, Safoora Gharibzadeh, Fatemeh Sakhaee, Mohammad Khazeni, Naser Kalhor, Fatemeh Rahimi Jamnani, Seyed Davar Siadat, Abolfazl Fateh
Infection, Genetics and Evolution.2018; 62: 296. CrossRef - First detection of human hepegivirus-1 (HHpgV-1) in Iranian patients with hemophilia
Yazdan Bijvand, Mohammad Reza Aghasadeghi, Fatemeh Sakhaee, Parviz Pakzad, Farzam Vaziri, Alireza Azizi Saraji, Fatemeh Rahimi Jamnani, Seyed Davar Siadat, Abolfazl Fateh
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of TRIM5 and TRIM22 polymorphisms on treatment responses in Iranian patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection
Setareh Mobasheri, Nazanin Irani, Abbas Akhavan Sepahi, Fatemeh Sakhaee, Fatemeh Rahimi Jamnani, Farzam Vaziri, Seyed Davar Siadat, Abolfazl Fateh
Gene.2018; 676: 95. CrossRef - Data Mining and Machine Learning Algorithms Using IL28B Genotype and Biochemical Markers Best Predicted Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis C
Hend Ibrahim Shousha, Abubakr Hussein Awad, Dalia Abdelhamid Omran, Mayada Mohamed Elnegouly, Mahasen Mabrouk
Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases.2018; 71(1): 51. CrossRef - IL28B rs12980275 and HLA rs4273729 genotypes as a powerful predictor factor for rapid, early, and sustained virologic response in patients with chronic hepatitis C
Parvaneh Sedighimehr, Shiva Irani, Fatemeh Sakhaee, Farzam Vaziri, Mohammadreza Aghasadeghi, Seyed Mehdi Sadat, Fatemeh Rahimi Jamnani, Abolfazl Fateh, Seyed Davar Siadat
Archives of Virology.2017; 162(1): 181. CrossRef - Comparison of Direct Sequencing, Real-Time PCR-High Resolution Melt (PCR-HRM) and PCR-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) Analysis for Genotyping of Common Thiopurine Intolerant Variant Alleles NUDT15 c.415C>T and TPMT c.719A>G (TPMT*3C)
Wai-Ying Fong, Chi-Chun Ho, Wing-Tat Poon
Diagnostics.2017; 7(2): 27. CrossRef - Effect of IL15 rs10833 and SCARB1 rs10846744 on virologic responses in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with pegylated interferon-α and ribavirin
Sahar Sadeghi, Mehdi Davari, Esmaeil Asli, Safoora Gharibzadeh, Farzam Vaziri, Fatemeh Rahimi Jamnani, Abolfazl Fateh, Seyed Davar Siadat
Gene.2017; 630: 28. CrossRef - High platelet count and high probability of CALR detection in myeloproliferative neoplasms
Reza Shirzad, Zari Tahan-nejad, Javad Mohamadi-asl, Mohammad Seghatoleslami, Ahmad Ahmadzadeh, Amal Saki Malehi, Najmaldin Saki
Comparative Clinical Pathology.2017; 26(1): 25. CrossRef - A comparative study of various methods for detection of IL28B rs12979860 in chronic hepatitis C
Seyed Hamidreza Monavari, Roohollah Fateh, Farzam Vaziri, Fatemeh Rahimi Jamnani, Enayat Anvari, Farzin Sadeghi, Parviz Afrough, Ava Behrouzi, Fatemeh Sakhaee, Sepideh Meidaninikjeh, Hamidreza Mollaie, Alireza Hadizadeh Tasbiti, Shamsi Yari, Maryam Sadegh
Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory In.2017; 77(4): 247. CrossRef - EGFR rs11506105 and IFNL3 SNPs but not rs8099917 are strongly associated with treatment responses in Iranian patients with chronic hepatitis C
M Asnavandi, M Zargar, F Vaziri, F R Jamnani, S Gharibzadeh, A Fateh, S D Siadat
Genes & Immunity.2017; 18(3): 144. CrossRef - Genetic Variation in Interleukin-28B and Response to Peg-IFNα-2a/RBV Combination Therapy in Patients with Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Farah Bokharaei-Salim, Mostafa Salehi-Vaziri, Farzin Sadeghi, Khadijeh Khanaliha, Maryam Esghaei, Seyed Hamidreza Monavari, Seyed Moayed Alavian, Shahin Fakhim, Hossein Keyvani
Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
- Multiplex Snapshot Minisequencing for the Detection of Common PAH Gene Mutations in Iranian Patients with Phenylketonuria
- Modeling Chagas Disease at Population Level to Explain Venezuela's Real Data
- Gilberto González-Parra, Benito M. Chen-Charpentier, Moises Bermúdez
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2015;6(5):288-301. Published online October 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.09.001
- 2,609 View
- 15 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
In this paper we present an age-structured epidemiological model for Chagas disease. This model includes the interactions between human and vector populations that transmit Chagas disease.
Methods
The human population is divided into age groups since the proportion of infected individuals in this population changes with age as shown by real prevalence data. Moreover, the age-structured model allows more accurate information regarding the prevalence, which can help to design more specific control programs. We apply this proposed model to data from the country of Venezuela for two periods, 1961–1971, and 1961–1991 taking into account real demographic data for these periods.
Results
Numerical computer simulations are presented to show the suitability of the age-structured model to explain the real data regarding prevalence of Chagas disease in each of the age groups. In addition, a numerical simulation varying the death rate of the vector is done to illustrate prevention and control strategies against Chagas disease.
Conclusion
The proposed model can be used to determine the effect of control strategies in different age groups. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A description of the epidemiological dynamics of Chagas disease via mathematical modeling
Rafael Lozada-Yavina, Carolina Marchant, Beatriz Cancino-Faure, Erix W. Hernández-Rodríguez, Fernando Córdova-Lepe
Acta Tropica.2023; 243: 106930. CrossRef - Mathematical modeling and numerical simulations of Zika in Colombia considering mutation
Diego F. Aranda L., Gilberto González-Parra, Tommaso Benincasa
Mathematics and Computers in Simulation.2019; 163: 1. CrossRef - Modeling Chagas disease in Chile: From vector to congenital transmission
Mauricio Canals, Dante Cáceres, Sergio Alvarado, Andrea Canals, Pedro E. Cattan
Biosystems.2017; 156-157: 63. CrossRef
- A description of the epidemiological dynamics of Chagas disease via mathematical modeling
- TEM and SHV Genes in
Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Cockroaches and Their Antimicrobial Resistance Pattern - Abbas Doosti, Mohammad Pourabbas, Asghar Arshi, Mohammad Chehelgerdi, Hamidreza Kabiri
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2015;6(1):3-8. Published online February 28, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2014.10.011
- 2,990 View
- 47 Download
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a gram-negative rod bacterium, a known cause of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia and is an important hospital-acquired pathogen that causes severe morbidity and mortality. The aim of this study was to identify the TEM and SHV genes in K. pneumoniae isolated from cockroaches obtained from hospitals.
Methods
In this study, 250 cockroaches were collected from different hospitals in the province of Chaharmahal Va Bakhtiari, which is located in southwest Iran. The samples were examined for the presence of K. pneumoniae by plating onto a combination of culture media, and the antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of isolated K. pneumoniae from samples were evaluated using the disk diffusion test. In addition, from the culture, genomic bacterial DNA was extracted, and sequence-specific targets (TEM and SHV genes) were amplified using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method.
Results
Out of 250 cockroach samples collected from various hospitals, 179 samples (71.60%) were positive for K. pneumoniae. PCR reaction was performed using specific oligonucleotide primers (TEM-F, TEM-R and SHV-F, SHV-R) for the amplification of each gene, and amplified products were visualized on 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. Of all the specimens amplified by PCR in this research, 32 samples (17.87%) were positive for TEM and 15 samples (8.37%) were positive for SHV.
Conclusion
Detection of TEM and SHV genes using molecular methods and their pattern of antimicrobial resistance can provide useful information about the epidemiology of and risk factors associated with K. pneumoniae infection. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Novel adjuvant nano-vaccine induced immune response against Acinetobacter baumannii
Tohid Piri-Gharaghie, Abbas Doosti, Seyed Abbas Mirzaei
AMB Express.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Virulence factors, antibiotic resistance patterns, and molecular types of clinical isolates of Klebsiella Pneumoniae
Mitra Ahmadi, Reza Ranjbar, Payam Behzadi, Taher Mohammadian
Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy.2022; 20(3): 463. CrossRef - Detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae antibiotic-resistant genes: An impending source of multidrug resistance dissemination through raw food
Kashaf Junaid, Hasan Ejaz, Sonia Younas, Awadh Alanazi, Humaira Yasmeen, Abdul Rehman
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2022; 29(5): 3347. CrossRef -
First Report of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (
bla
CTX-M1
) and Colistin Resistance Gene
mcr-1
in E. coli of Lineage ST648 from Cockroaches in Tunisia
Sarrah Landolsi, Rachid Selmi, Linda Hadjadj, Asma Ben Haj Yahia, Kaouther Ben Romdhane, Lilia Messadi, Jean Marc Rolain, Courtney J. Robinson
Microbiology Spectrum.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Phenotypic and genotypic detection of extended spectrum beta lactamase enzyme in Klebsiella pneumoniae
Aso Bakr Mohammed, Khanda Abdullateef Anwar, Monica Cartelle Gestal
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(9): e0267221. CrossRef - Virulence factors and antibiotic resistance properties of Streptococcus species isolated from hospital cockroaches
Mohammad Chehelgerdi, Reza Ranjbar
3 Biotech.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Putative novel B-cell vaccine candidates identified by reverse vaccinology and genomics approaches to control Acinetobacter baumannii serotypes
Sheida Beiranvand, Abbas Doosti, Seyed Abbas Mirzaei
Infection, Genetics and Evolution.2021; 96: 105138. CrossRef - Molecular epidemiology of Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in a paediatric hospital in China
Bingjie Wang, Fen Pan, Chun Wang, Wantong Zhao, Yan Sun, Tiandong Zhang, Yingying Shi, Hong Zhang
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2020; 93: 311. CrossRef Fecal Carriage and Molecular Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae from Inpatient Children in a Pediatric Hospital of Shanghai
Qi Xu, Fen Pan, Yan Sun, Chun Wang, Yingying Shi, Tiandong Zhang, Fangyuan Yu, Hong Zhang
Infection and Drug Resistance.2020; Volume 13: 4405. CrossRef- Contamination of Cockroaches (Insecta: Blattaria) by Medically Important Bacteriae: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Hassan Nasirian, Michael Rust
Journal of Medical Entomology.2019; 56(6): 1534. CrossRef - Competition assays between ESBL-producing E. coli and K. pneumoniae isolates collected from Lebanese elderly: An additional cost on fitness
Nourhane Hafza, Caren Challita, Iman Dandachi, Mounir Bousaab, Elias Dahdouh, Ziad Daoud
Journal of Infection and Public Health.2018; 11(3): 393. CrossRef - Synthesis, characterization, antiproliferative, and antimicrobial activity of osmium(II) half-sandwich complexes
Joel M. Gichumbi, Holger B. Friedrich, Bernard Omondi, Kovashnee Naicker, Moganavelli Singh, Hafizah Y. Chenia
Journal of Coordination Chemistry.2018; 71(2): 342. CrossRef - Relationship between β-lactamase production and resistance phenotype in Klebsiella pneumoniae strains
Jeongjin Kim, Tian Ding, Juhee Ahn
FEMS Microbiology Letters.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - First Report of German Cockroaches (Blattella germanica) as Reservoirs of CTX-M-15 Extended-Spectrum-β-Lactamase- and OXA-48 Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Batna University Hospital, Algeria
Lotfi Loucif, Djamila Gacemi-Kirane, Zineb Cherak, Naima Chamlal, Nadia Grainat, Jean-Marc Rolain
Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy.2016; 60(10): 6377. CrossRef
- Novel adjuvant nano-vaccine induced immune response against Acinetobacter baumannii
- Exposure to Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and the Risk of Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Jae-Hong Park, Eun Shil Cha, Yousun Ko, Myung-Sil Hwang, Jin-Hwan Hong, Won Jin Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2014;5(2):77-84. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2014.02.001
- 3,288 View
- 26 Download
- 24 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study extended and updated a meta-analysis of the association between exposure to dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) and the risk of breast cancer.
Methods
We reviewed the published literature on exposure to DDE and breast cancer risk to update a meta-analysis from 2004. The total of 35 studies included 16 hospital-based case–control studies, 11 population-based case–control studies, and 10 nested case–control studies identified through keyword searches in the PubMed and EMBASE databases.
Results
The summary odds ratio (OR) for the identified studies was 1.03 (95% confidence interval 0.95–1.12) and the overall heterogeneity in the OR was observed (I2 = 40.9; p = 0.006). Subgroup meta-analyses indicated no significant association between exposure to DDE and breast cancer risk by the type of design, study years, biological specimen, and geographical region of the study, except from population-based case–control studies with estimated DDE levels in serum published in 1990s.
Conclusion
Existing studies do not support the view that DDE increases the risk of breast cancer in humans. However, further studies incorporating more detailed information on DDT exposure and other potential risk factors for breast cancer are needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Causes and Risk Factors of Breast Cancer, What Do We Know for Sure? An Evidence Synthesis of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Borghild Løyland, Ida Hellum Sandbekken, Ellen Karine Grov, Inger Utne
Cancers.2024; 16(8): 1583. CrossRef - Validation and green profile assessment of a binary solvent liquid phase microextraction method for the determination of chlorbenside and fenobucarb in lake and wastewater samples by GC–MS
Dotse Selali Chormey
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2023; 30(15): 44697. CrossRef - Putative interactions between transthyretin and endosulfan II and its relevance in breast cancer
Saurabh Sharma, Lakshay Malhotra, Paromita Mukherjee, Navneet Kaur, Thammineni Krishanlata, Chittur V. Srikanth, Vandana Mishra, Basu Dev Banerjee, Abdul Samath Ethayathulla, Radhey Shyam Sharma
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2023; 235: 123670. CrossRef - Exposure to Organochlorine Pesticides and Female Breast Cancer Risk According to Molecular Receptors Expression: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Epidemiological Evidence
Rodrigo Ugalde-Resano, Brenda Gamboa-Loira, Ángel Mérida-Ortega, Alma Rincón-Rubio, Gisela Flores-Collado, Maricela Piña-Pozas, Lizbeth López-Carrillo
Current Environmental Health Reports.2023; 10(4): 442. CrossRef - Mosquito control exposures and breast cancer risk: analysis of 1071 cases and 2096 controls from the Ghana Breast Health Study
Naomie Olivos, Jim E. Banta, Rhonda Spencer-Hwang, Daniel Ansong, Laura E. Beane Freeman, Joe-Nat Clegg-Lamptey, Beatrice Wiafe-Addai, Lawrence Edusei, Ernest Adjei, Nicholas Titiloye, Florence Dedey, Francis Aitpillah, Joseph Oppong, Verna Vanderpuye, Er
Breast Cancer Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Endocrine disrupting chemicals and breast cancer: a systematic review of epidemiological studies
Murphy Lam Yim Wan, Vanessa Anna Co, Hani El-Nezami
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2022; 62(24): 6549. CrossRef - Epidemiology beyond its limits
Lauren E. McCullough, Maret L. Maliniak, Avnika B. Amin, Julia M. Baker, Davit Baliashvili, Julie Barberio, Chloe M. Barrera, Carolyn A. Brown, Lindsay J. Collin, Alexa A. Freedman, David C. Gibbs, Maryam B. Haddad, Eric W. Hall, Sarah Hamid, Kristin R. V
Science Advances.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasma concentrations of chlorinated persistent organic pollutants and their predictors in the general population of Algiers, Algeria
El Hadia Mansouri, Mohamed Reggabi
Emerging Contaminants.2021; 7: 35. CrossRef - Association between type 2 diabetes and exposure to chlorinated persistent organic pollutants in Algeria: A case-control study
El Hadia Mansouri, Mohamed Reggabi
Chemosphere.2021; 264: 128596. CrossRef - Extraction of Chlorobenzenes and PCBs from Water by ZnO Nanoparticles
Yuntao Zhang, Ran Chen, Jim E. Riviere, Jeffrey Comer
Processes.2021; 9(10): 1764. CrossRef - Two Cases of Possible Familial Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in a Family with Extensive History of Cancer
Marisa J.L. Aitken, Christopher B. Benton, Ghayas C. Issa, Koji Sasaki, Musa Yilmaz, Nicholas J. Short
Acta Haematologica.2021; 144(5): 585. CrossRef - In utero DDT exposure and breast density before age 50
Nickilou Y. Krigbaum, Piera M. Cirillo, Julie D. Flom, Jasmine A. McDonald, Mary Beth Terry, Barbara A. Cohn
Reproductive Toxicology.2020; 92: 85. CrossRef - DDT exposure during pregnancy and DNA methylation alterations in female offspring in the Child Health and Development Study
Hui-Chen Wu, Barbara A. Cohn, Piera M. Cirillo, Regina M. Santella, Mary Beth Terry
Reproductive Toxicology.2020; 92: 138. CrossRef - Prediagnostic serum concentrations of organochlorine pesticides and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A nested case–control study in the Norwegian Janus Serum Bank Cohort
Dazhe Chen, Tom K. Grimsrud, Hilde Langseth, Dana B. Barr, Bryan A. Bassig, Aaron Blair, Kenneth P. Cantor, Marilie D. Gammon, Qing Lan, Nathaniel Rothman, Lawrence S. Engel
Environmental Research.2020; 187: 109515. CrossRef - Global trends in pesticides: A looming threat and viable alternatives
Akanksha Sharma, Ananya Shukla, Kriti Attri, Megha Kumar, Puneet Kumar, Ashish Suttee, Gurpal Singh, Ravi Pratap Barnwal, Neha Singla
Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety.2020; 201: 110812. CrossRef - Exposure to Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals and Risk of Breast Cancer
Louisane Eve, Béatrice Fervers, Muriel Le Romancer, Nelly Etienne-Selloum
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(23): 9139. CrossRef - Breast Cancer and Exposure to Organochlorines in the CECILE Study: Associations with Plasma Levels Measured at the Time of Diagnosis and Estimated during Adolescence
Delphine Bachelet, Marc-André Verner, Monica Neri, Émilie Cordina Duverger, Corinne Charlier, Patrick Arveux, Sami Haddad, Pascal Guénel
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2019; 16(2): 271. CrossRef - Risk of breast cancer and adipose tissue concentrations of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides: a hospital-based case-control study in Chinese women
Wenlong Huang, Yuanfang He, Jiefeng Xiao, Yuanni Huang, Anna Li, Meirong He, Kusheng Wu
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2019; 26(31): 32128. CrossRef - Serum levels of Organochlorine Pesticides and Breast Cancer Risk in Iranian Women
Parisa Paydar, Gholamreza Asadikaram, Hossein Fallah, Hamid Zeynali Nejad, Hamed Akbari, Moslem Abolhassani, Vahid Moazed, Payam Khazaeli, Mahmoud Reza Heidari
Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxico.2019; 77(4): 480. CrossRef - DDT exposure in early childhood and female breast cancer: Evidence from an ecological study in Taiwan
Simon Chang, Sonia El-Zaemey, Jane Heyworth, Meng-chi Tang
Environment International.2018; 121: 1106. CrossRef - Chiral pharmaceuticals: Environment sources, potential human health impacts, remediation technologies and future perspective
Yaoyu Zhou, Shikang Wu, Hao Zhou, Hongli Huang, Jia Zhao, Yaocheng Deng, Hua Wang, Yuan Yang, Jian Yang, Lin Luo
Environment International.2018; 121: 523. CrossRef - Organochlorine pesticides accumulation and breast cancer: A hospital-based case–control study
Ting-Ting He, An-Jun Zuo, Ji-Gang Wang, Peng Zhao
Tumor Biology.2017; 39(5): 101042831769911. CrossRef - Correlation between toxic organochlorine pesticides and breast cancer
SA Eldakroory, DA El Morsi, RH Abdel-Rahman, S Roshdy, MS Gouida, EO Khashaba
Human & Experimental Toxicology.2017; 36(12): 1326. CrossRef - Breast cancer and persistent organic pollutants (excluding DDT): a systematic literature review
Tafzila Akter Mouly, Leisa-Maree Leontjew Toms
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2016; 23(22): 22385. CrossRef
- Causes and Risk Factors of Breast Cancer, What Do We Know for Sure? An Evidence Synthesis of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- Obesity and Asian Americans in the United States: Systematic Literature Review
- Sanggon Nam
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2013;4(4):187-193. Published online August 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2013.06.001
- 2,796 View
- 20 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Obesity is one of the most serious health problems in the world today. Asian Americans are usually less overweight and obese than African Americans and Hispanic Americans, but the rate of obesity in Asian Americans is still increasing, especially in younger generations. This research examines Asian American obesity using existing research, as a means of finding the need for greater emphasis on Asian American obesity intervention research.
Methods
In this research literature review, Asian American obesity using existing research as a means of finding the need for greater emphasis on Asian American obesity intervention research is examined. A systematic review is done in order to find Asian American obesity research, due to the minimal amount of existing studies. In total, there were only nine papers which were not duplicates and which still met the criteria for inclusion, from an initial 106 papers.
Results
There is very little research on obesity in Asian Americans. Although the rate of obesity among Asian Americans is increasing, there are few related articles, projects, and surveys, and there is little information. There is a need for more specific and in-depth analysis of Asian American obesity. Asian Americans are associated with a lower waist circumference (WC) and BMI, while Hawaiian/Pacific Islanders are associated with a higher WC and BMI. Typically, Asian Americans who were born in the United States (US) tend to be overweight and more obese than those born in foreign countries.
Conclusion
Based on this literature review, it is concluded that there is a shortage of Asian American obesity research, even though there is an evident need for particular obesity intervention programs that target Asian Americans. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Southern California Asian Americans and the Obesity Epidemic: A Qualitative Study to Improve Understanding and Cultural Competence
Alyssa Mae Carlos, Kathleen Doll
American Journal of Health Education.2023; 54(6): 463. CrossRef - The posterior tibial artery free flap for head and neck reconstruction
Alexandra E. Kejner
Current Opinion in Otolaryngology & Head & Neck Su.2022; 30(5): 358. CrossRef - Heterogeneity in Obesity Prevalence Among Asian American Adults
Nilay S. Shah, Cecily Luncheon, Namratha R. Kandula, Sadiya S. Khan, Liping Pan, Cathleen Gillespie, Fleetwood Loustalot, Jing Fang
Annals of Internal Medicine.2022; 175(11): 1493. CrossRef - Fruit and Vegetable Consumption Behavior Among Asian Americans: A Thematic Analysis
Chia-Liang Dai, Manoj Sharma, Taj Haider, Hema Sunchu
Journal of Primary Care & Community Health.2021; 12: 215013272098477. CrossRef - The effect of racial discrimination on mental and physical health: A propensity score weighting approach
Shanting Chen, Allen B. Mallory
Social Science & Medicine.2021; 285: 114308. CrossRef - Ethnic Enclaves and Pregnancy and Behavior Outcomes Among Asian/Pacific Islanders in the USA
Andrew D. Williams, Lynne C. Messer, Jenna Kanner, Sandie Ha, Katherine L. Grantz, Pauline Mendola
Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities.2020; 7(2): 224. CrossRef - Developing a Socioculturally Nuanced Systems Model of Childhood Obesity in Manhattan’s Chinese American Community via Group Model Building
Ewelina Swierad, Terry T.-K. Huang, Ellis Ballard, Karen Flórez, Sheng Li
Journal of Obesity.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Healthy Living Behaviors Among Chinese–American Preschool-Aged Children: Results of a Parent Survey
Virginia Rall Chomitz, Alison Brown, Victoria Lee, Aviva Must, Kenneth Kwan Ho Chui
Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health.2018; 20(4): 926. CrossRef - Obesity Prevention Behaviors in Asian Indian Adolescent Girls: A Pilot Study
Annie Thomas, Linda Janusek
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2018; 42: 9. CrossRef - Filipinos Fit and Trim - A feasible and efficacious DPP-based intervention trial
Melinda S. Bender, Bruce A. Cooper, Elena Flowers, Raymond Ma, Shoshana Arai
Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications.2018; 12: 76. CrossRef - The neighborhood environment and obesity: Understanding variation by race/ethnicity
Michelle S. Wong, Kitty S. Chan, Jessica C. Jones-Smith, Elizabeth Colantuoni, Roland J. Thorpe, Sara N. Bleich
Preventive Medicine.2018; 111: 371. CrossRef - STRIVE, San Diego! Methodology of a Community-Based Participatory Intervention to Enhance Healthy Dining at Asian and Pacific Islander Restaurants
Sarah Oropeza, Mary Grace Sadile, Chantine Nguyen Phung, Moana Cabiles, Sandy Spackman, Myleen Abuan, Fe Seligman, Maria Rosario Araneta
Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior.2018; 50(3): 297. CrossRef - Geographic differences in obesity prevalence and its risk factors among Asian Americans: findings from the 2013–2014 California Health Interview Survey
Shaoqing Gong, Kesheng Wang, Ying Li, Arsham Alamian
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - American Heart Association’s Ideal Cardiovascular Health Metrics in Under-Represented Asian Americans
Freda Patterson, Guo Zhang, Adam Davey, Yin Tan, Grace X. Ma
Journal of Community Health.2016; 41(6): 1282. CrossRef - Genes and the intergenerational transmission of BMI and obesity
Timothy J. Classen, Owen Thompson
Economics & Human Biology.2016; 23: 121. CrossRef
- Southern California Asian Americans and the Obesity Epidemic: A Qualitative Study to Improve Understanding and Cultural Competence



 First
First Prev
Prev


