Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Association between the empirical dietary inflammatory index and musculoskeletal pain in community-dwelling older adults: a cross-sectional study
- Mahshid Rezaei, Zahra Tajary, Zahra Esmaeily, Atefeh Eyvazkhani, Shahrzad Daei, Marjan Mansouri Dara, Mohaddeseh Rezaei, Abolghassem Djazayeri, Ahmadreza Dorosty Motlagh
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(1):51-58. Published online February 20, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0194
- 1,988 View
- 69 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 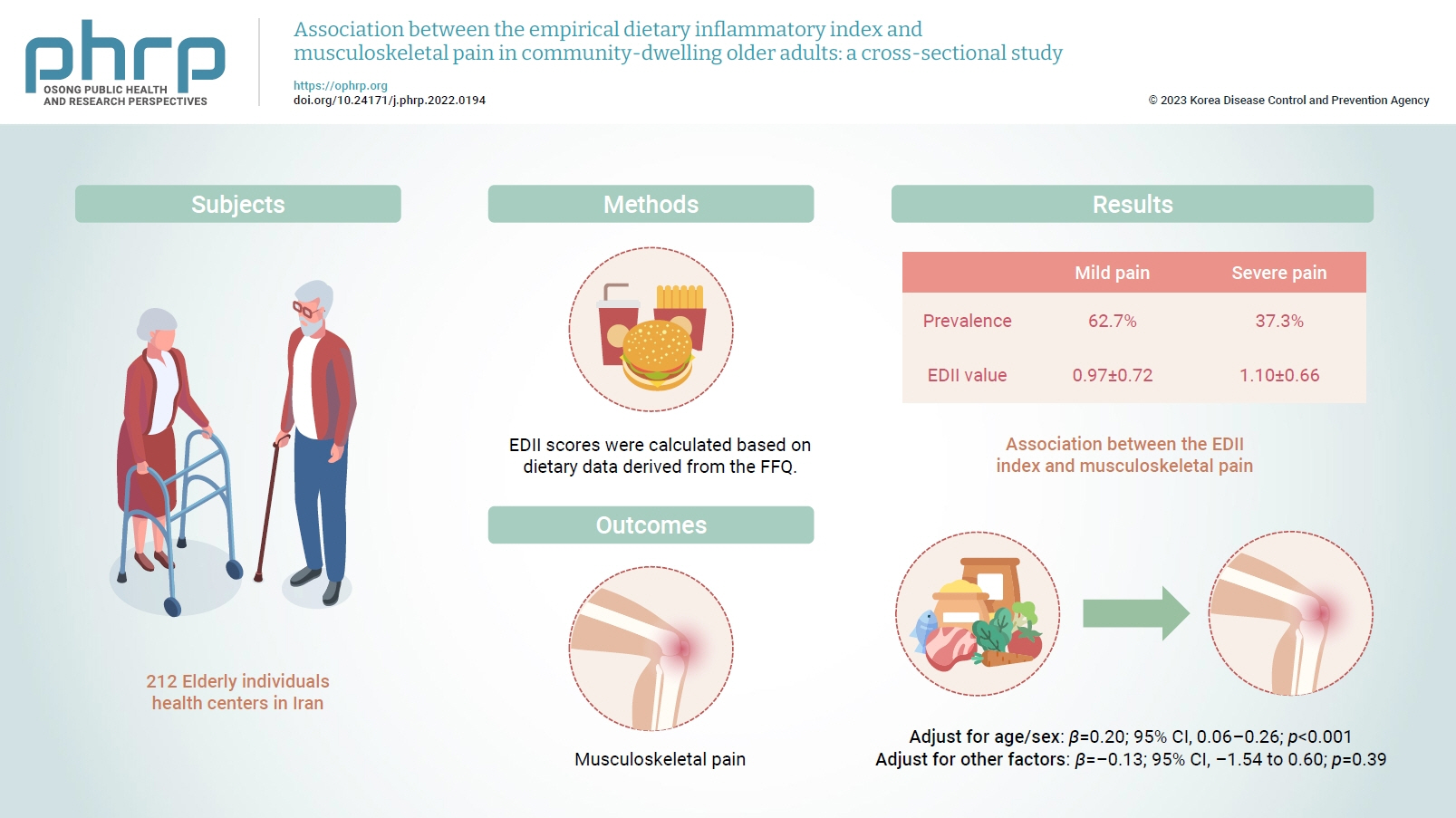
- Objectives
Inflammation has been proposed to be one of the main causes of musculoskeletal pain. Diet is a lifestyle factor that plays an important role in managing inflammation; thus, we assessed the inflammatory potential of diets using the empirical dietary inflammatory index (EDII) to investigate the relationship between diet and musculoskeletal pain.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 212 elderly individuals who were selected from health centers in Tehran, Iran. Dietary intake was evaluated using a valid and reliable 147-item food frequency questionnaire. To measure the intensity of pain, a visual analogue scale was used. Multiple linear regression was applied to assess the association between the EDII and musculoskeletal pain.
Results
In total, 62.7% and 37.3% of participants had mild and severe pain, respectively. The EDII values were 0.97±0.72 and 1.10±0.66, respectively, in those with mild and severe pain. A higher EDII score was associated with more intense musculoskeletal pain after adjusting for age and sex (β=0.20; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.06–0.26; p<0.001), but not after adjustment for other confounders (β=–0.13; 95% CI, –1.54 to 0.60; p=0.39).
Conclusion
Our findings indicated that higher dietary inflammation might not be associated with musculoskeletal pain in older adults. However, further investigations are required to confirm these findings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between dietary inflammatory index and musculoskeletal disorders in adults
Firoozeh Khamoushi, Davood Soleimani, Farid Najafi, Neshat Ahmadi, Neda Heidarzadeh-Esfahani, Bita Anvari, Ebrahim Shakiba, Yahya Pasdar
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between dietary inflammatory index and musculoskeletal disorders in adults
- Early Intervention Reduces the Spread of COVID-19 in Long-Term Care Facilities in the Republic of Korea
- Shin Young Park, Gawon Choi, Hyeyoung Lee, Na-young Kim, Seon-young Lee, Kyungnam Kim, Soyoung Shin, Eunsu Jang, YoungSin Moon, KwangHwan Oh, JaeRin Choi, Sangeun Lee, Young-Man Kim, Jieun Kim, Seonju Yi, Jin Gwack, Ok Park, Young Joon Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(4):259-264. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.4.16
- 6,438 View
- 146 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study describes the epidemiological characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) based on reported cases from long-term care facilities. As of April 20th, 2020, 3 long-term care facilities in a metropolitan area of South Korea had reported cases of COVID-19. These facilities’ employees were presumed to be the sources of infection. There were 2 nursing hospitals that did not report any additional cases. One nursing home had a total of 25 cases, with an attack rate of 51.4% (95% CI 35.6–67.0), and a fatality rate of 38.9% (95% CI 20.3–61.4) among residents. The results from this study suggest that early detection and maintenance of infection control minimizes the risk of rapid transmission.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and corresponding control measures on long-term care facilities: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Jun Zhang, Yushan Yu, Mirko Petrovic, Xiaomei Pei, Qing-Bao Tian, Lei Zhang, Wei-Hong Zhang
Age and Ageing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A scoping review of the impacts of COVID-19 physical distancing measures on vulnerable population groups
Lili Li, Araz Taeihagh, Si Ying Tan
Nature Communications.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Concentrated COVID-19 Outbreaks in Elderly Facilities in Suita City, Osaka Prefecture, Japan
Toshiyuki Shibata, Sawa Okano, Daisuke Onozuka, Etsuko Ohta, Satoshi Kutsuna
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2023; 20(20): 6926. CrossRef - Factors relating to intention of use non-face-to-face services among family caregivers of persons with dementia: A cross-sectional study
Myonghwa Park, Jinju Kim, Jihye Jung, Seonhwa Kim, Jinhee Lee, Dongyoung Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(4): 377. CrossRef - Staffing Levels and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths in Korean Nursing Homes
Jiyeon Lee, Juh Hyun Shin, Kyeong Hun Lee, Charlene A. Harrington, Sun Ok Jung
Policy, Politics, & Nursing Practice.2022; 23(1): 15. CrossRef - An Experience of the Early Stage of COVID-19 Outbreak in Nursing Homes in Gyeonggi Province, Korea
Gawon Choi, Na-young Kim, Seon-young Lee, Hae Deun Noh, Heeyoung Lee
Korean Journal of Clinical Geriatrics.2022; 23(1): 27. CrossRef - The implications of the COVID-19 pandemic for long term care facilities
Muh-Yong Yen, Jonathan Schwartz, Po-Ren Hsueh
Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases.2022; 35(4): 370. CrossRef - Health impact of the first and second wave of COVID-19 and related restrictive measures among nursing home residents: a scoping review
Marjolein E. A. Verbiest, Annerieke Stoop, Aukelien Scheffelaar, Meriam M. Janssen, Leonieke C. van Boekel, Katrien G. Luijkx
BMC Health Services Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology and clinical features of COVID-19 outbreaks in aged care facilities: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohammad Rashidul Hashan, Nicolas Smoll, Catherine King, Hannah Ockenden-Muldoon, Jacina Walker, Andre Wattiaux, Julieanne Graham, Robert Booy, Gulam Khandaker
EClinicalMedicine.2021; 33: 100771. CrossRef - Protecting Nursing Homes and Long-Term Care Facilities From COVID-19: A Rapid Review of International Evidence
Sally Hall Dykgraaf, Sethunya Matenge, Jane Desborough, Elizabeth Sturgiss, Garang Dut, Leslee Roberts, Alison McMillan, Michael Kidd
Journal of the American Medical Directors Associat.2021; 22(10): 1969. CrossRef - Dementia Risk among Coronavirus Disease Survivors: A Nationwide Cohort Study in South Korea
Hye-Yoon Park, In-Ae Song, Tak-Kyu Oh
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2021; 11(10): 1015. CrossRef
- Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and corresponding control measures on long-term care facilities: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Predictors Affecting the Elderly’s Use of Emergency Medical Services
- Ju Moon Park, Aeree Sohn
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(4):209-215. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.4.10
- 4,672 View
- 68 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Elderly adults are the demographic most likely to utilize emergency medical services (EMS). This study aimed to examine the difference in EMS utilization in subgroups of the elderly population by assessing the predictors for using EMS.
Methods Using both descriptive and logistic regression analyses, this study analyses data from the 2014 Korean Health Panel Survey (
n = 3,175).Results It was observed that certain predisposing factors such as age, sex, and marital status were significant predictors of EMS utilization. However, differences in EMS need do not fully account for the original differences observed between subgroups of elderly Koreans. While health status and disability were important predictors of elderly Koreans using EMS, place of residence did not account for subgroup differences. Nonetheless, place of residence remained particularly important predictors of EMS utilization for the elderly.
Conclusion Emergency needs and resource availability are 2 main determinants for elderly Koreans using EMS. In addition, it was observed that the demographic subgroup profile of unmarried/divorced/separated/widowed men who were aged 75 and older was least likely to utilize EMS. Improving their resource availability to meet their EMS needs should be a top priority for national policy making to narrow elderly population subgroup differences.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fatores associados às causas externas em idosos atendidos pelo serviço de atendimento móvel de urgência
Ana Angélica Oliveira de Brito, Beatriz Barros de Vasconcelos, Ana Maria Ribeiro dos Santos, Débora de Oliveira Lima, Maria Zélia de Araújo Madeira, Guilherme Guarino de Moura Sá, Julyanne dos Santos Nolêto, Rouslanny Kelly Cipriano de Oliveira
Revista Gaúcha de Enfermagem.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with external causes in elderly attended by the mobile emergency care service
Ana Angélica Oliveira de Brito, Beatriz Barros de Vasconcelos, Ana Maria Ribeiro dos Santos, Débora de Oliveira Lima, Maria Zélia de Araújo Madeira, Guilherme Guarino de Moura Sá, Julyanne dos Santos Nolêto, Rouslanny Kelly Cipriano de Oliveira
Revista Gaúcha de Enfermagem.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Medical and social factors influencing the utilization of healthcare services among older adults in Israel during the COVID-19 lockdown
Ohad Shaked, Liat Korn, Yair Shapiro, Moti Zwilling, Avi Zigdon
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Social Factors Contributing to Healthcare Service Requirements during the First COVID-19 Lockdown among Older Adults
Ohad Shaked, Liat Korn, Yair Shapiro, Avi Zigdon
Healthcare.2022; 10(10): 1854. CrossRef - Socio-demographic characteristics and their relation to medical service consumption among elderly in Israel during the COVID-19 lockdown in 2020 as compared to the corresponding period in 2019
Ohad Shaked, Liat Korn, Yair Shapiro, Gideon Koren, Avi Zigdon, Aviad Tur-Sinai
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(12): e0278893. CrossRef
- Fatores associados às causas externas em idosos atendidos pelo serviço de atendimento móvel de urgência
- Neighborhood Deprivation and Unmet Health Care Needs: A Multilevel Analysis of Older Individuals in South Korea
- Seung Eun Lee, Miyeon Yeon, Chul-Woung Kim, Tae-Ho Yoon, Dongjin Kim, Jihee Choi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(5):295-306. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.5.06
- 12,213 View
- 64 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives In this study the relationship between neighborhood deprivation and the unmet health care needs of elderly individuals (≥ 65 years) was examined. Some previous studies suggested that neighborhood characteristics affect access to health care, yet research on the unmet needs of older individuals is limited.
Methods Multilevel logistic regression analysis was used to assess the relationship of neighborhood-level factors with unmet health care needs due to costs, adjusting for individual-level factors, in individuals ≥ 65 years in the 2017 Korean Community Health Survey (
n = 63,388).Results There were 2.6% of elderly individuals who experienced unmet health care needs due to costs. Following adjustment for individual and neighborhood characteristics, the neighborhood deprivation in urban areas was found to have an inverse association with unmet needs (odds ratio = 0.50; 95% confidence interval = 0.24–1.06) for the most deprived quartile versus the least deprived quartile). However, in rural areas neighborhood deprivation was not a significant variable. Among the individual-level variables, household income was one of the strongest correlates with unmet needs in both urban and rural areas.
Conclusion The present findings suggest that targeted policy interventions reflecting both neighborhood and individual characteristics, should be implemented to reduce the unmet health care needs of elderly individuals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- What are the factors affecting older adults’ experience of unmet healthcare needs amid the COVID-19 pandemic in Korea?
Sujin Kim, Jongnam Hwang
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Linking neighbourhood safety and children's internalizing and externalizing problems: Mediating role of maternal depression
Youngmin Cho
Child & Family Social Work.2023; 28(4): 1089. CrossRef - Urban-Rural Differences in the Prevalence of Depressive Symptoms in Korean Adults
Ji-An Jeong, Sun A Kim, Jung Ho Yang, Min-Ho Shin
Chonnam Medical Journal.2023; 59(2): 128. CrossRef - PhaVIP: Phage VIrion Protein classification based on chaos game representation and Vision Transformer
Jiayu Shang, Cheng Peng, Xubo Tang, Yanni Sun
Bioinformatics.2023; 39(Supplement): i30. CrossRef - Dashboard to analyze associations of socio-economic and environmental inequality of regions with health indicators. Guidelines
A. A. Zelenina, S. A. Shalnova, S. A. Maksimov
Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention.2023; 22(7): 3652. CrossRef - The Older Persons' Index of Multiple Deprivation: Measuring the deprivation circumstances of older populations in Aotearoa New Zealand
Daniel J. Exeter, Michael Browne, Tommi Robinson-Chen, Jessie Colbert, Ngaire Kerse, Arier Lee
Health & Place.2022; 76: 102850. CrossRef - The Contribution of Material, Behavioral, Psychological, and Social-Relational Factors to Income-Related Disparities in Cardiovascular Risk Among Older Adults
Chiyoung Lee, Qing Yang, Eun-Ok Im, Eleanor Schildwachter McConnell, Sin-Ho Jung, Hyeoneui Kim
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2021; 36(4): E38. CrossRef - Association between community deprivation and practising health behaviours among South Korean adults: a survey-based cross-sectional study
Bich Na Jang, Hin Moi Youn, Doo Woong Lee, Jae Hong Joo, Eun-Cheol Park
BMJ Open.2021; 11(6): e047244. CrossRef
- What are the factors affecting older adults’ experience of unmet healthcare needs amid the COVID-19 pandemic in Korea?
- Factors Affecting Activity Limitation in the Elderly: Data Processed from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2016
- Jong-Hoon Moon
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(3):117-122. Published online June 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.3.02
- 5,630 View
- 42 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the sociodemographic characteristics, depression, and the health-related quality of life outcome, among the Korean elderly population, with and without activity limitation.
Methods The data used was drawn from the raw data of the seventh Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (
N = 8,150). There were 1,632 records for individuals aged 65 or older extracted from the seventh Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey database, 199 of those had missing responses (n = 1,433). Differences within the sociodemographic characteristic, the Patient Health Questionnaire-9, and the EuroQol-5 Dimension were analyzed using logistic regression analysis according to the presence or absence of activity limitation.Results The prevalence of activity limitation among the elderly individuals surveyed was 19.9%. In the unadjusted regression analysis, the odds ratios of all independent variables (age, gender, education level, type of region, family income, the Patient Health Questionnaire-9, all 5 domains of the EuroQol-5 Dimension) between the elderly individuals with and without activity limitation, were significant. Although, in the adjusted logistic regression analysis, it was observed that the only factors that were significantly associated with activity limitation were the Patient Health Questionnaire-9, EuroQol-5 Dimension, type of region, and family income.
Conclusion These findings demonstrated that activity limitation in elderly individuals is associated with the sociodemographic characteristics of family income and type of region of residence, as well as depression and the health-related quality of life outcome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Higher physical activity is associated with lower activity limitation: Cross-sectional analyses among the Spanish working population
R. López-Bueno, G.F. López-Sánchez, L. Smith, E. Sundstrup, L.L. Andersen, J.A. Casajús
Science & Sports.2023; 38(3): 247. CrossRef - Self-Reported Reasons for Activity Limitations According to Age and Sex in Community-Dwelling Stroke Survivors
Young-Ah Choi, Yeo Hyung Kim
Healthcare.2023; 11(10): 1420. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of health status and health service utilization patterns among rural and urban elderly populations in Hungary: a study on the challenges of unhealthy aging
Nora Kovacs, Peter Piko, Attila Juhasz, Csilla Nagy, Beatrix Oroszi, Zoltan Ungvari, Roza Adany
GeroScience.2023; 46(2): 2017. CrossRef - Associations between Depressive Symptoms and Satisfaction with Meaningful Activities in Community-Dwelling Japanese Older Adults
Michio Maruta, Hyuma Makizako, Yuriko Ikeda, Hironori Miyata, Atsushi Nakamura, Gwanghee Han, Suguru Shimokihara, Keiichiro Tokuda, Takuro Kubozono, Mitsuru Ohishi, Kounosuke Tomori, Takayuki Tabira
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(3): 795. CrossRef
- Higher physical activity is associated with lower activity limitation: Cross-sectional analyses among the Spanish working population
- Mediating and Moderating Effects in Ageism and Depression among the Korean Elderly: The Roles of Emotional Reactions and Coping Reponses
- Il-Ho Kim, Samuel Noh, Heeran Chun
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(1):3-11. Published online February 28, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.11.012
- 3,115 View
- 23 Download
- 27 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study evaluated the relationship between ageism and depression, exploring the stress-mediating and stress-moderating roles of emotional reactions and coping behaviors.
Methods
Data were from the 2013 Ageism and Health Study (n = 816), a cross-sectional survey of urban and rural community-dwelling seniors aged 60–89 years in South Korea. Participants with at least one experience of ageism reported on their emotional reactions and coping responses. The measure yielded two types of coping: problem-focused (taking formal action, confrontation, seeking social support) and emotion-focused (passive acceptance, emotional discharge).
Results
Although ageism was significantly associated with depressive symptoms (B = 0.27, p < 0.0001), the association was entirely mediated by emotional reactions such as anger, sadness, and powerlessness. Problem-focused coping, especially confrontation and social support, seemingly reduced the impact of emotional reactions on depression, whereas emotion-focused coping exacerbated the adverse effects.
Conclusion
These findings support the cultural characterization explanation of ageism and related coping processes among Korean elderly and suggest that regulating emotional reactions may determine the efficacy of coping with ageism. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Can Residents Access Leisure Spaces in Our City: Investigating the Leisure Space Distribution in Seoul, South Korea
Hyun-Young Jin, Junhee Cho, Yujin Kim, Lisa Lim
Leisure Sciences.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Reducing negative attitudes toward older adults and increasing advocacy for policies to support older adults: Bayesian analysis approach
Yuho Shimizu, Takaaki Hashimoto, Kaori Karasawa
Acta Psychologica.2023; 239: 103995. CrossRef - Changes in perceived ageism during the COVID-19 pandemic: impact on quality of life and mental well-being among Dutch adults aged 55 and older
Lotte P. Brinkhof, J. M. J. Murre, S. de Wit, H. J. Krugers, K. R. Ridderinkhof
Aging & Mental Health.2023; 27(12): 2490. CrossRef - Impact of a Nonfamilial Intergenerational Program With a Mobile Application on College Students’ Attitudes Toward Older Adults in Taiwan
Jeffrey Tsifan Tseng, Hsinyi Hsiao, Amy Pei-Lung Yu, Yi Chen
Journal of the Society for Social Work and Researc.2023; 14(2): 365. CrossRef - A phenomenological, intersectional understanding of coping with ageism and racism among older adults
Andrew T. Steward, Yating Zhu, Carson M. De Fries, Annie Zean Dunbar, Miguel Trujillo, Leslie Hasche
Journal of Aging Studies.2023; 67: 101186. CrossRef - Do we all perceive experiences of age discrimination in the same way? Cross-cultural differences in perceived age discrimination and its association with life satisfaction
M. Clara P. de Paula Couto, Jana Nikitin, Sylvie Graf, Helene H. Fung, Thomas M. Hess, Shyhnan Liou, Klaus Rothermund
European Journal of Ageing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Trajectory of Depressive Symptoms Across Years of Community Care Utilization Among Older Adults: A 14-Year Follow-up Study Using the ‘Korean Welfare Panel Survey’
Il-Ho Kim, Cheong-Seok Kim, Min-Hyeok Jeong
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(6): 495. CrossRef - Mitigating the Harmful Impact of Ageism among Older Individuals: The Buffering Role of Resilience Factors
Lotte P. Brinkhof, Sanne de Wit, Jaap M. J. Murre, K. Richard Ridderinkhof
Geriatrics.2023; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - Reducing ageism focusing on stereotype embodiment theory: Pre-registered study and Bayesian analysis approach
Yuho Shimizu
Experimental Results.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Self-Perceived Stigma and Quality of Life Among Urban Chinese Older Adults: The Moderating Role of Attitude Toward Own Aging and Traditionality
Tao Sun, Shu-E Zhang, Meng-yao Yan, Ting-hui Lian, Yi-qi Yu, Hong-yan Yin, Chen-xi Zhao, Yan-ping Wang, Xiao Chang, Ke-yu Ji, Si-yu Cheng, Xiao-he Wang, Xian-hong Huang, De-pin Cao
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - You’re Too Old for That! Ageism and Prescriptive Stereotypes in the Workplace
Elizabeth A Hanrahan, Courtney L Thomas, Lisa M Finkelstein, Mo Wang
Work, Aging and Retirement.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Ageism and Psychological Well-Being Among Older Adults: A Systematic Review
Hyun Kang, Hansol Kim
Gerontology and Geriatric Medicine.2022; 8: 233372142210870. CrossRef - The Subjective Experience of Ageism: The Perceived Ageism Questionnaire (PAQ)
Lotte P. Brinkhof, Sanne de Wit, Jaap M. J. Murre, Harm J. Krugers, K. Richard Ridderinkhof
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(14): 8792. CrossRef - Depressive Symptoms and Ageism among Nursing Home Residents: The Role of Social Support
Dongjuan Xu, Yaqi Wang, Ming Li, Meng Zhao, Zhenhua Yang, Kefang Wang
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(19): 12105. CrossRef - Coping Style, Insomnia, and Psychological Distress Among Persons With Gastrointestinal Cancer
Gaorong Lv, Di Zhao, Guopeng Li, Qing Wang, Miao Zhou, Yiming Gao, Xiangyu Zhao, Ping Li
Nursing Research.2022; 71(6): 450. CrossRef - Assessing knowledge and ageist attitudes and behaviors toward older adults among undergraduate nursing students
Mohammad Rababa, Tariq Al-Dwaikat, Maysa H. Almomani
Gerontology & Geriatrics Education.2021; 42(3): 347. CrossRef - Day-to-Day Variability in Subjective Age and Ageist Attitudes and Their Association With Depressive Symptoms
Ehud Bodner, Amit Shrira, Yaakov Hoffman, Yoav S Bergman, Shevaun Neupert
The Journals of Gerontology: Series B.2021; 76(5): 836. CrossRef - Association of nurses’ characteristics and level of knowledge with ageist attitudes toward older adults: a systematic review
Mohammad Rababa, Ammar M. Hammouri, Sami Al-Rawashdeh
Working with Older People.2021; 25(1): 21. CrossRef - Associations of perceived poor societal treatment among the oldest-old
M Knuutila, TE Lehti, H Karppinen, H Kautiainen, TE Strandberg, KH Pitkala
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2021; 93: 104318. CrossRef - Ageism and the Factors Affecting Ageism among Korean Nursing Students: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jiyeon Ha, Juah Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(4): 1798. CrossRef - Psychometrics of Persian Version of the Ageism Survey Among an Iranian Older Adult Population During COVID-19 Pandemic
Hamid Sharif Nia, Long She, Ratneswary Rasiah, Fatemeh Khoshnavay Fomani, Omolhoda Kaveh, Saeed Pahlevan Sharif, Lida Hosseini
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Global reach of ageism on older persons’ health: A systematic review
E-Shien Chang, Sneha Kannoth, Samantha Levy, Shi-Yi Wang, John E. Lee, Becca R. Levy, Antony Bayer
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(1): e0220857. CrossRef - The Role of Socio-demographics in Adoption of Religious–Spiritual and Other Coping Strategies Among Muslim Chronic Patients with Hepatitis C in Pakistan
Malik Muhammad Sohail, Saeed Ahmad, Fauzia Maqsood
Journal of Religion and Health.2020; 59(1): 234. CrossRef - Association of nurses' level of knowledge and attitudes to ageism toward older adults: Cross‐sectional study
Mohammad Rababa, Ammar M. Hammouri, Issa M. Hweidi, Julie L. Ellis
Nursing & Health Sciences.2020; 22(3): 593. CrossRef - How does ageism influence frailty? A preliminary study using a structural equation model
Bo Ye, Junling Gao, Hua Fu, Hao Chen, Wenjing Dong, Ming Gu
BMC Geriatrics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Ageism, Attitudes Toward Aging, and Body Satisfaction by Subjective Socioeconomic and Health Status Among Older Women
Haekyung Yu, Minsun Lee
Fashion & Textile Research Journal.2019; 21(5): 586. CrossRef - Where are we now in relation to determining the prevalence of ageism in this era of escalating population ageing?
Donna M. Wilson, Begoña Errasti-Ibarrondo, Gail Low
Ageing Research Reviews.2019; 51: 78. CrossRef
- Can Residents Access Leisure Spaces in Our City: Investigating the Leisure Space Distribution in Seoul, South Korea
- Comparison of Consensus on Life-sustaining Treatment of the Elderly in Care Facilities and Family Member Dyad
- Sunmi Lim, Seong Ae Hong, Hyun Sook Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2015;6(2):126-132. Published online April 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.02.003
- 2,737 View
- 15 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study is to compare the agreement in opinion between the elderly in care facilities and their family members regarding the life-sustaining treatment at the deathbed and to find out if the intentions of the elderly are being properly reflected in their deathbed treatment.
Methods
Data were collected from 85 elderly individuals at five care facilities in Chunkcheongnam-do and 85 family members. The data were collected with a self-administered questionnaire from July 22, 2013 to August 15, 2014. A total of 170 cases were analyzed using SPSS version 21.
Results
First, the family members' preference for life-sustaining treatment was higher than the patients' preference. The preference between the elderly and their family members regarding life-sustaining treatment was statistically significant with regards to oral nutrition, pain control through oral and anal administration, pain control through intravenous administration, transfusion, and admission to an intensive care unit. Second, looking at the agreement between elderly and guardians regarding life-sustaining treatment, there was significant concordance about general testing, oral nutrition, intravenous hydration, intravenous nutrition, antibiotic treatment for severe infection with low resiliency, admission to an intensive care unit, blood pressure increase medication use, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and tracheotomy.
Conclusion
It is essential for the medical staff to confirm agreement between the elderly and their family members regarding life-sustaining treatment, and if such a prior agreement is not feasible, the patient's intention should be considered more actionable than their family members. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of high-intensity care in intensive care units and its cost at the end of life among older people in South Korea between 2016 and 2019: a cross-sectional study of the health insurance review and assessment service national patient sample database
Yunji Lee, Minjeong Jo, Taehwa Kim, Kyoungsun Yun
BMJ Open.2021; 11(8): e049711. CrossRef - Effect of the Contents in Advance Directives on Individuals’ Decision-Making
Jae Yoon Park, Chi-Yeon Lim, Gloria Puurveen, Do Yeun Kim, Jae Hang Lee, Han Ho Do, Kyung Soo Kim, Kyung Don Yoo, Hyo Jin Kim, Yunmi Kim, Sung Joon Shin
OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.2020; 81(3): 436. CrossRef - Do medical oncology patients and their support persons agree about end‐of‐life issues?
Amy Waller, Alix Hall, Rob Sanson‐Fisher, Nicholas Zdenkowski, Charles Douglas, Justin Walsh
Internal Medicine Journal.2018; 48(1): 60. CrossRef - Preferences of older inpatients and their family caregivers for life-sustaining treatments in South Korea
Hyeyoung Hwang, Sook Ja Yang, Sarah Yeun-Sim Jeong
Geriatric Nursing.2018; 39(4): 428. CrossRef
- Analysis of high-intensity care in intensive care units and its cost at the end of life among older people in South Korea between 2016 and 2019: a cross-sectional study of the health insurance review and assessment service national patient sample database



 First
First Prev
Prev


