Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effects of an arteriovenous fistula stenosis prevention program in patients receiving hemodialysis
- Haegyeong Lee, Gyuli Baek, Eunju Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):279-290. Published online August 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0101
- 1,246 View
- 142 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
To increase the efficiency of hemodialysis, an appropriate vascular pathway must be created, and its function must be maintained. This study aimed to identify the effects of an arteriovenous fistula (AVF) stenosis prevention program on upper muscular strength, blood flow, physiological indexes, and self-efficacy among patients receiving hemodialysis.
Methods
The participants were patients receiving hemodialysis at Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center in Daegu, Republic of Korea. They were divided into experimental and control groups based on the day of the week they received hemodialysis at the outpatient department and included 25 participants each. The study was conducted for 8 weeks.
Results
The AVF stenosis prevention program was effective in improving upper extremity muscle strength (F=15.23, p<0.001) and blood flow rate (F=36.00, p<0.001). As a result of the program, the phosphorus index level, which is a physiological indicator in hemodialysis patients, decreased (F=8.64, p<0.001). Encouragement and support through text messages and practice lists also resulted in an increase in self-efficacy (F=18.62, p<0.001).
Conclusion
The AVF stenosis prevention program in this study resulted in an increase in upper extremity muscle strength through grip strength exercises and was effective in preventing AVF stenosis by increasing the blood flow rate.
- Estimating the number of severe COVID-19 cases and COVID-19-related deaths averted by a nationwide vaccination campaign in Republic of Korea
- Ji Hae Hwang, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Jung Jang, Ryu Kyung Kim, Kil Hun Lee, Seon Kyeong Park, Sang Eun Lee, Chungman Chae, Sangwon Lee, Young Joon Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):164-172. Published online June 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0096
- 1,696 View
- 116 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 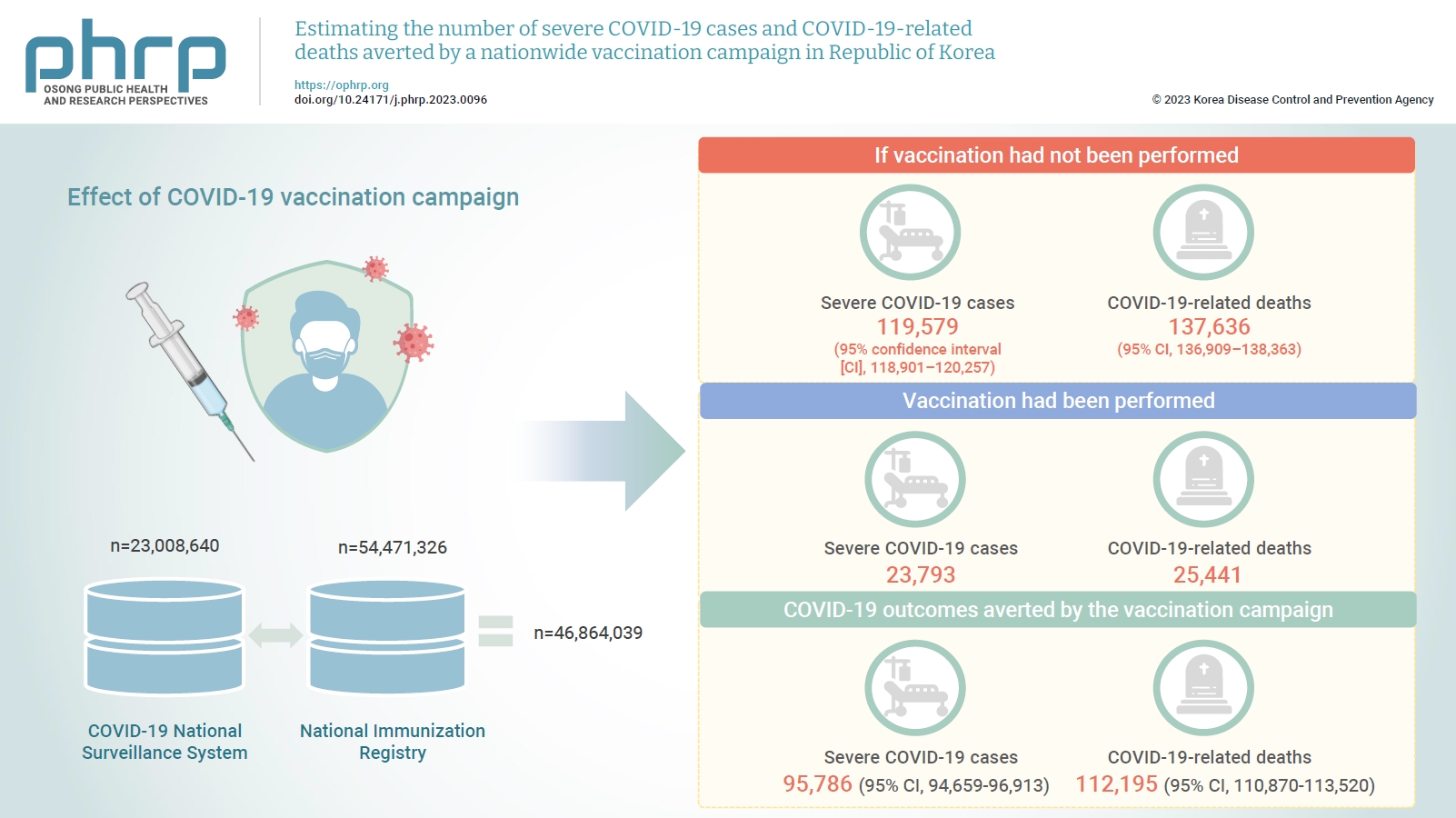
- Objectives
The Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency promotes vaccination by regularly providing information on its benefits for reducing the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). This study aimed to analyze the number of averted severe COVID-19 cases and COVID-19-related deaths by age group and quantify the impact of Republic of Korea’s nationwide vaccination campaign.
Methods
We analyzed an integrated database from the beginning of the vaccination campaign on February 26, 2021 to October 15, 2022. We estimated the cumulative number of severe cases and COVID-19-related deaths over time by comparing observed and estimated cases among unvaccinated and vaccinated groups using statistical modeling. We compared daily age-adjusted rates of severe cases and deaths in the unvaccinated group to those in the vaccinated group and calculated the susceptible population and proportion of vaccinated people by age.
Results
There were 23,793 severe cases and 25,441 deaths related to COVID-19. We estimated that 119,579 (95% confidence interval [CI], 118,901–120,257) severe COVID-19 cases and 137,636 (95% CI, 136,909–138,363) COVID-19-related deaths would have occurred if vaccination had not been performed. Therefore, 95,786 (95% CI, 94,659–96,913) severe cases and 112,195 (95% CI, 110,870–113,520) deaths were prevented as a result of the vaccination campaign.
Conclusion
We found that, if the nationwide COVID-19 vaccination campaign had not been implemented, the number of severe cases and deaths would have been at least 4 times higher. These findings suggest that Republic of Korea’s nationwide vaccination campaign reduced the number of severe cases and COVID-19 deaths. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Effectiveness of COVID-19 Bivalent Versus Monovalent mRNA Vaccines in the Early Stage of Bivalent Vaccination in Korea: October 2022 to January 2023
Ryu Kyung Kim, Young June Choe, Eun Jung Jang, Chungman Chae, Ji Hae Hwang, Kil Hun Lee, Ji Ae Shim, Geun-Yong Kwon, Jae Young Lee, Young-Joon Park, Sang Won Lee, Donghyok Kwon
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparative Effectiveness of COVID-19 Bivalent Versus Monovalent mRNA Vaccines in the Early Stage of Bivalent Vaccination in Korea: October 2022 to January 2023
- The COVID-19 pandemic and healthcare utilization in Iran: evidence from an interrupted time series analysis
- Monireh Mahmoodpour-Azari, Satar Rezaei, Nasim Badiee, Mohammad Hajizadeh, Ali Mohammadi, Ali Kazemi-Karyani, Shahin Soltani, Mehdi Khezeli
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):180-187. Published online June 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0041
- 1,365 View
- 66 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 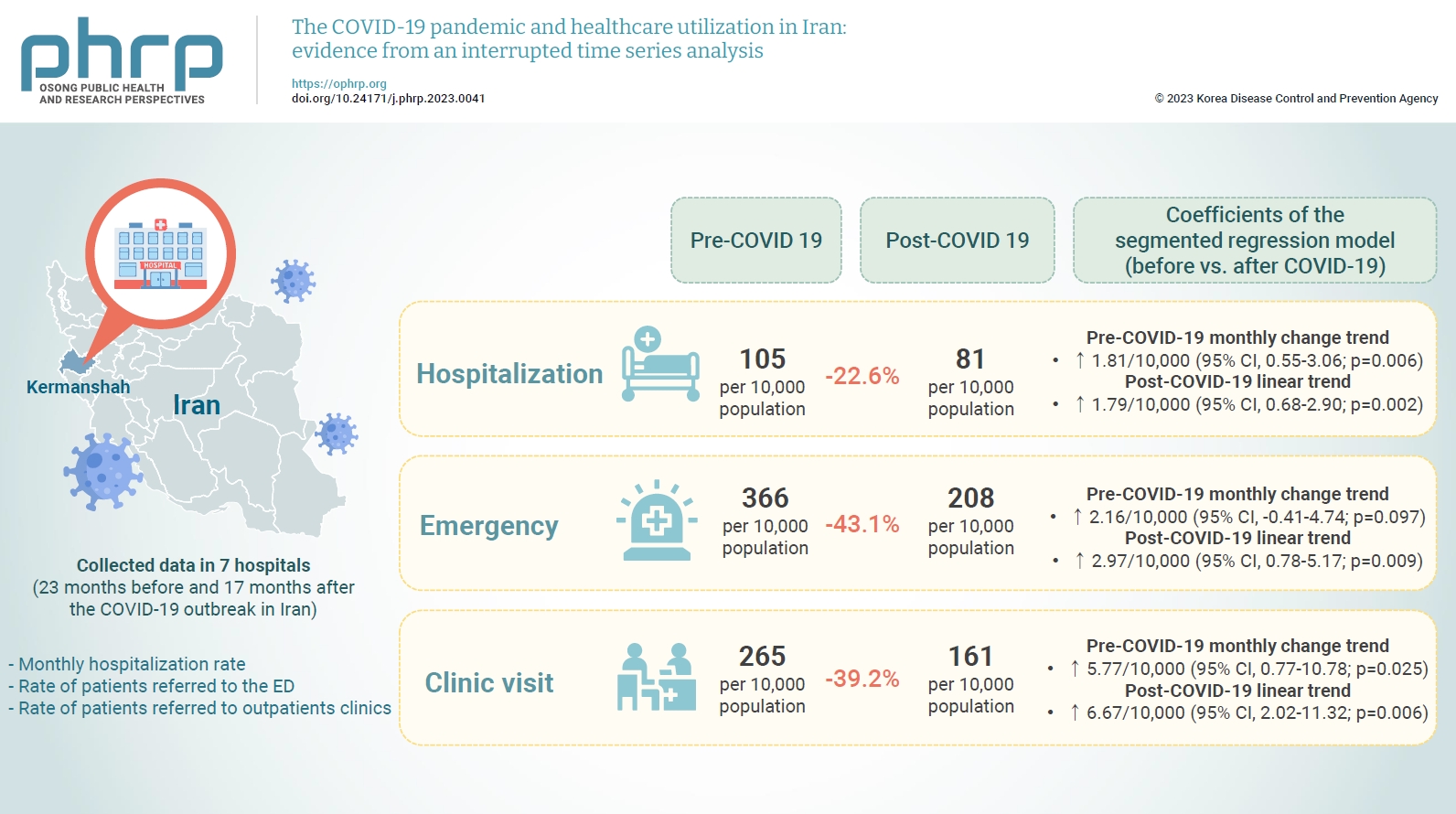
- Objectives
This study aimed to examine the effect of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak on the hospitalization rate, emergency department (ED) visits, and outpatient clinic visits in western Iran.
Methods
We collected data on the monthly hospitalization rate, rate of patients referred to the ED, and rate of patients referred to outpatient clinics for a period of 40 months (23 months before and 17 months after the COVID-19 outbreak in Iran) from all 7 public hospitals in the city of Kermanshah. An interrupted time series analysis was conducted to examine the impact of COVID-19 on the outcome variables in this study.
Results
A statistically significant decrease of 38.11 hospitalizations per 10,000 population (95% confidence interval [CI], 24.93–51.29) was observed in the first month of the COVID-19 outbreak. The corresponding reductions in ED visits and outpatient visits per 10,000 population were 191.65 (95% CI, 166.63–216.66) and 168.57 (95% CI, 126.41–210.73), respectively. After the initial reduction, significant monthly increases in the hospitalization rate (an increase of 1.81 per 10,000 population), ED visits (an increase of 2.16 per 10,000 population), and outpatient clinic visits (an increase of 5.77 per 10,000 population) were observed during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusion
Our study showed that the utilization of outpatient and inpatient services in hospitals and clinics significantly declined after the COVID-19 outbreak, and use of these services did not return to pre-outbreak levels as of June 2021.
- Characteristics of Inpatients Who Survive Suicide Attempts
- Sang Mi Kim, Hyun-Sook Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(1):32-38. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.1.07
- 5,448 View
- 155 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The purpose of this study was to analyze the characteristics and factors affecting the survival of inpatients admitted following a suicide attempt.
Methods A total of 3,095 cases retrieved from the Korean National Hospital Discharge In-depth Injury Survey data (from 2011 to 2015) were grouped according to survival and death and analyzed using descriptive statistics chi-square and logistic regression analysis.
Results The following factors had statistically significant risks on reducing survival: female (OR = 2.352,
p < 0.001), 40–59 years old (OR = 0.606,p = 0.014), over 60 years old (OR = 0.186,p < 0.001), poisoning (OR = 0.474,p = 0.009), hanging (OR = 0.031,p < 0.001), jumping (OR = 0.144,p < 0.001), conflicts with family (OR = 2.851,p < 0.001), physical diseases (OR = 1.687,p = 0.046), mental health problems (OR = 2.693,p < 0.001), financial problems (OR = 3.314,p = 0.002), 2014 (OR = 2.498,p = < 0.001) and 2015 (OR = 2.942,p = 0.005).Conclusion The survival group that had a history of attempted suicide (high-risk suicide group), should be further characterized. It is necessary to identify the suicide methods and risk factors for suicide prevention management policies and to continuously expand the management policy according to these characteristics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Affecting Inpatients’ Mortality through Intentional Self-Harm at In-Hospitals in South Korea
Sulki Choi, Sangmi Kim, Hyunsook Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2023; 20(4): 3095. CrossRef - The economic burden of adolescent internet addiction: A Korean health cost case study
Robert W. Mead, Edward Nall
The Social Science Journal.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Loss to follow-up in a population-wide brief contact intervention to prevent suicide attempts - The VigilanS program, France
Larissa Djembi Fossi, Christophe Debien, Anne-Laure Demarty, Guillaume Vaiva, Antoine Messiah, Xenia Gonda
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(3): e0263379. CrossRef
- Factors Affecting Inpatients’ Mortality through Intentional Self-Harm at In-Hospitals in South Korea
- Effects of Physical Activity on Depression in Adults with Diabetes
- Deok-Ju Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(4):143-149. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.4.02
- 5,748 View
- 145 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The purpose of this study was to identify the current state of physical activity in adults with diabetes and to investigate the effect of physical activity on depression.
Methods The present study was conducted using data from the 2nd year of the 6th Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey. From the total of 7,550 individuals, 418 adults diagnosed with diabetes were selected as participants, and their physical activity and depression levels were examined.
Results The physical activity status of the participants showed that they did not usually engage in physical activities at work, and only a few participants were involved in moderate intensity physical leisure activity. Apart from walking for 10 minutes each day, which accounted for 1/3 of the participants, most of the participants did not engage in specific forms of exercise. An examination of the effects of physical activity on depression revealed that moderate intensity physical activity at work and leisure influenced depression. In terms of demographic characteristics, gender, occupation, income quintile, and subjective health status were all found to affect depression.
Conclusion For elderly (60 years or older) patients with diabetes, which accounted for the majority of the diabetic population, a systematic leisure program and professional education are necessary to help them to manage stress and depression in daily life. Additionally, provision of community and family support should encourage regular, moderate intensity exercise and promote lifestyle changes to encourage increased physical activity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of comorbid depression and associated factors among hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Hunan, China
Rehanguli Maimaitituerxun, Wenhang Chen, Jingsha Xiang, Atipatsa C. Kaminga, Xin Yin Wu, Letao Chen, Jianzhou Yang, Aizhong Liu, Wenjie Dai
BMC Psychiatry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Barriers & facilitators to physical activity in people with depression and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Pakistan: A qualitative study to explore perspectives of patient participants, carers and healthcare staff
Aatik Arsh, Saima Afaq, Claire Carswell, Karen Coales, Najma Siddiqi
Mental Health and Physical Activity.2023; 25: 100542. CrossRef - Moderating Effect of Grip Strength in the Association between Diabetes Mellitus and Depressive Symptomatology
Diogo Veiga, Miguel Peralta, Élvio R. Gouveia, Laura Carvalho, Jorge Encantado, Pedro J. Teixeira, Adilson Marques
Sports.2023; 12(1): 3. CrossRef - Modeling the effects of physical activity, education, health, and subjective wealth on happiness based on Indonesian national survey data
Bhina Patria
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Triad of impairment in older people with diabetes-reciprocal relations and clinical implications
A.H. Abdelhafiz, P.C. Davies, A.J. Sinclair
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 161: 108065. CrossRef - Association between exercise and health-related quality of life and medical resource use in elderly people with diabetes: a cross-sectional population-based study
Chien-Cheng Huang, Chien-Chin Hsu, Chong-Chi Chiu, Hung-Jung Lin, Jhi-Joung Wang, Shih-Feng Weng
BMC Geriatrics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Challenges and Strategies for Diabetes Management in Community-Living Older Adults
Alan J. Sinclair, Ahmed H. Abdelhafiz
Diabetes Spectrum.2020; 33(3): 217. CrossRef
- Prevalence of comorbid depression and associated factors among hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Hunan, China
- Treatment with Sofosbuvir and Daclatasvir (with or without Ribavirin) Improves Patient Reported Outcomes in Hepatitis C
- Lucas Pereira Jorge de Medeiros, Mario Barreto Correa Lima, Marcia Maria Amêndola Pires, Alessandra Mendonça Almeida Maciel, Renata Barboza Vianna Medeiros, Mariana Dermínio Donadel, Isabela Martins Becattini Pereira, Fábio Marchon Leão, Luiz Eduardo Amorim Correa Lima Pires, Helio Rzetelna, Carlos Eduardo Brandão-Mello
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(2):50-58. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.2.03
- 5,101 View
- 38 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives To evaluate the impact of 3 treatment regimens upon health-related quality of life and work productivity using patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in chronic hepatitis C infected patients: sofosbuvir (SOF) + daclatasvir (DCV); SOF + DCV + ribavirin (RBV); SOF + simeprevir (SMV).
Methods 4 questionnaires were used to evaluate PROs before, during and after treatment: Short Form-36 (SF-36), Chronic Liver Disease Questionnaire (CLDQ) - hepatitis C virus (HCV), Work Productivity and Activity Index, Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F).
Results Of the global sample of 55 patients included in this study; SOF + DCV (
n = 10); SOF + DCV + RBV (n = 29); SOF + SMV (n = 16) all had a statistically significant improvement in SF-36, CLDQ and FACIT-F scores during and post-treatment. No statistically significant differences in the PRO questionnaire values were observed between the distinct treatment regimens. The SOF and SMV patient groups presented higher mean PRO variations during and post-treatment, compared to the other groups: SF-36 functional capacity (16.1); SF-36 mental health (21.4); CLDQ activity (1.8); CLDQ emotional function (1.2); FACIT-F physical well-being (8.0); Total FACIT-F (21.6).Conclusion Treatment with SOF + DCV, with or without RBV, results in an improved PRO similar to treatment with SOF + SMV in chronic hepatitis C patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health-related quality of life in people receiving opioid agonist treatment and treatment for hepatitis C virus infection
Olav Dalgard, Alain H. Litwin, Oren Shibolet, Jason Grebely, Ronald Nahass, Frederick L. Altice, Brian Conway, Edward J. Gane, Anne F. Luetkemeyer, Cheng-Yuan Peng, David Iser, Isaias Noel Gendrano, Michelle M. Kelly, Barbara A. Haber, Heather Platt, Amy
Journal of Addictive Diseases.2023; 41(3): 213. CrossRef - Impact of sofosbuvir and daclastavir on health-related quality of life in patients co-infected with hepatitis C and human immunodeficiency virus
Evy Yunihastuti, Fhadilla Amelia, Arini Ika Hapsari, Bramantya Wicaksana, Veritea Natali, Alvina Widhani, Andri Sanityoso Sulaiman, Teguh Harjono Karjadi
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-related quality of life and fatigue in patients with chronic hepatitis C with therapy with direct-acting antivirals agents interferon-free
Raíssa Neves Fagundes, Lincoln Eduardo Villela Vieira de Castro Ferreira, Fábio Heleno de Lima Pace, Yury E. Khudyakov
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(8): e0237005. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of sofosbuvir-based pangenotypic direct-acting antiviral agents for chronic hepatitis C patients without genotype determination
Juan Li, Dong-Bo Wu, Wei Jiang, Xue-Bin Chen, Gui-Bao Xiao, Yong-Hong Wang, Meng-Lan Wang, Ya-Chao Tao, En-Qiang Chen
Medicine.2020; 99(43): e22726. CrossRef
- Health-related quality of life in people receiving opioid agonist treatment and treatment for hepatitis C virus infection
- Comparative Analysis of the Trends in Medical Utilization of Cancer Inpatients in Korea
- Hyun-Ju Lee, Sung-Soo Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(5):342-350. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.5.08
- 3,365 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Cancer has attracted worldwide attention. The incidence and prevalence are increasing, and it is the main cause of death. The purpose of this study was to identify the characteristics of hospitalized cancer patients.
Methods This study is a secondary data study using the Korean National Hospital Discharge In-depth Injury Survey Data conducted annually by the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Using these data, we extracted inpatients who principal diagnosis is cancer for nine years from 2005 to 2013.
Results According to the analysis, the annual trend of cancer inpatients is steadily increasing. In 2025, it is expected to increase to about 670,000 inpatients. A cancer diagnosis created a change in medical utilization depending on the characteristics of patients and hospital. Men are more at risk of cancer than women. The number of hospital beds and hospital days were inversely proportional to cancer inpatients. There was also a difference in the equity of medical utilization by region. Other cancer management policies should be based on sex.
Conclusion Populations between the ages of 45 and 64 years should be a priority in cancer policy. Because of the long-term hospitalization of patients with death as the outcome, a terminal cancer patient care facility is needed. These conclusions can provide a basis for various health policies.
- Quality of Life of Chronic Hepatitis C Patients and Its Associated Factors
- Hoo Jeung Cho, Euna Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(2):124-129. Published online April 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.2.04
- 4,719 View
- 30 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This study aimed to investigate the factors affecting the health-related quality of life (HRQOL) of patients with chronic hepatitis C (CHC).
Methods This study is based on a descriptive survey and involved 125 gastroenterology outpatients visiting a university hospital in South Korea as the participants. HRQOL was assessed using the Liver Disease Quality of Life 1.0, which consisted of Short Form-36 (SF-36) and the Liver Disease Targeted Scale. Data were collected from December 2015 to April 2016, which were then analyzed through multiple regression analysis.
Results HRQOL had a statistically significant correlation with age, sex, educational level, living type, employment status, monthly income level, and comorbidity status. This study showed that age > 51 years, female sex, high educational level, living alone, unemployment status, low monthly income, and presence of comorbidity had negative effects on the HRQOL of patients with CHC (R2 = 8.7%–34.6%).
Conclusion Based on the result of this study, intervention for patients with CHC needs to be developed to enhance their HRQOL. The findings can serve as a useful reference for nursing personnel in the development of therapeutic plans to upgrade the care of CHC patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and individual factors of quality of life of chronic liver disease patients at University of Gondar comprehensive specialized hospital, Northwest Ethiopia 2022
Eliud Teshome, Workagegnehu Hailu, Aynishet Adane, Endalkachew Belayneh Melese, Dessie Abebaw Angaw, Gebrekidan Ewnetu Tarekegn
Medicine.2023; 102(45): e35425. CrossRef - Risk factors of severe hepatotoxicity among HIV-1 infected individuals initiated on highly active antiretroviral therapy in the Northwest Region of Cameroon
Lem Edith Abongwa, Anthony Kebira Nyamache, Fokunang Charles, Judith Torimiro, Nshom Emmanuel, Irénée Domkam, Mbu Eyongetah, Beriyuy Jude, Fung Holgar Mua, Sama Bella, Tankou Colman Tamboh, Erna Charlene Moungang, Victorine Ngum, Paul Okemo
BMC Gastroenterology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cathepsin B and Plasma Kallikrein Are Reliable Biomarkers to Discriminate Clinically Significant Hepatic Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis-C Infection
Alexia de Cassia Oliveira Zanelatto, Gilmar de Souza Lacerda, Camila de Melo Accardo, Natalia Fonseca do Rosário, Andréa Alice da Silva, Guacyara Motta, Ivarne Luis dos Santos Tersariol, Analucia Rampazzo Xavier
Microorganisms.2022; 10(9): 1769. CrossRef - Impact of newer direct-acting antiviral drugs based on quality-adjusted life years: A prospective pharmacoeconomic study in hepatitis C patients
BhavyaH Vyas, NishitaH Darji, DevangA Rana, KaushalY Vyas, SupriyaD Malhotra
Perspectives in Clinical Research.2021; 12(2): 76. CrossRef - Exploring Perception of Chronic Hepatitis C: An Idiographic Case Study
Hana Arshad, Subha Malik
Pakistan Journal of Psychological Research.2020; 34(4): 735. CrossRef - Changes in Quality of Life of Chronic Hepatitis C Patients Participating in Clinical Trial
Hoo-Jeung CHO, Euna PARK
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2018; 30(5): 1725. CrossRef - Treatment with Sofosbuvir and Daclatasvir (with or without Ribavirin) Improves Patient Reported Outcomes in Hepatitis C
Lucas Pereira Jorge de Medeiros, Mario Barreto Correa Lima, Marcia Maria Amêndola Pires, Alessandra Mendonça Almeida Maciel, Renata Barboza Vianna Medeiros, Mariana Dermínio Donadel, Isabela Martins Becattini Pereira, Fábio Marchon Leão, Luiz Eduardo Amor
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2018; 9(2): 50. CrossRef - Quality of life in Brazilian patients with treated or untreated chronic hepatitis C
Cássio Marques Perlin, Vinicius Lins Ferreira, Helena Hiemisch Lobo Borba, Astrid Wiens, Cláudia Alexandra Pontes Ivantes, Luana Lenzi, Roberto Pontarolo
Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de São P.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical and individual factors of quality of life of chronic liver disease patients at University of Gondar comprehensive specialized hospital, Northwest Ethiopia 2022
- Evaluating Service Quality from Patients' Perceptions: Application of Importance–performance Analysis Method
- Rafat Mohebifar, Hana Hasani, Ameneh Barikani, Sima Rafiei
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(4):233-238. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2016.05.002
- 3,378 View
- 18 Download
- 40 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Providing high service quality is one of the main functions of health systems. Measuring service quality is the basic prerequisite for improving quality. The aim of this study was to evaluate the quality of service in teaching hospitals using importance–performance analysis matrix.
Methods
A descriptive–analytic study was conducted through a cross-sectional method in six academic hospitals of Qazvin, Iran, in 2012. A total of 360 patients contributed to the study. The sampling technique was stratified random sampling. Required data were collected based on a standard questionnaire (SERVQUAL). Data analysis was done through SPSS version 18 statistical software and importance–performance analysis matrix.
Results
The results showed a significant gap between importance and performance in all five dimensions of service quality (p < 0.05). In reviewing the gap, “reliability” (2.36) and “assurance” (2.24) dimensions had the highest quality gap and “responsiveness” had the lowest gap (1.97). Also, according to findings, reliability and assurance were in Quadrant (I), empathy was in Quadrant (II), and tangibles and responsiveness were in Quadrant (IV) of the importance–performance matrix.
Conclusion
The negative gap in all dimensions of quality shows that quality improvement is necessary in all dimensions. Using quality and diagnosis measurement instruments such as importance–performance analysis will help hospital managers with planning of service quality improvement and achieving long-term goals. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A New Model to Consolidate Long-Term Intersectoral Partnerships in Humanitarian and Social Crises Management
Anderson Nunes da Silva, Marcele Elisa Fontana
Public Organization Review.2024; 24(1): 27. CrossRef - Evaluation of outpatient service quality: What do patients and providers think?
Pouria Farrokhi, Aidin Aryankhesal, Rafat Bagherzadeh, Asgar Aghaei Hashjin
International Journal of Healthcare Management.2023; 16(3): 394. CrossRef - Assessing the Challenges and Opportunities of Agricultural Information Systems to Enhance Farmers’ Capacity and Target Rice Production in Indonesia
Agung Budi Santoso, Setia Sari Girsang, Budi Raharjo, Arlyna Budi Pustika, Yanter Hutapea, Mahargono Kobarsih, Agus Suprihatin, Erpina Delina Manurung, Deddy Romulo Siagian, Sidiq Hanapi, Tommy Purba, Dorkas Parhusip, Sri Wahyuni Budiarti, Yeyen Prestyani
Sustainability.2023; 15(2): 1114. CrossRef - Patients’ views on health promotion and disease prevention services provided by healthcare workers in a South African tertiary hospital
Herbert I. Melariri, Chester Kalinda, Moses J. Chimbari
BMC Health Services Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Telecommunication service quality analysis using integration of SIPA and modified Kano
Hanny Kanavika Rizky Munawar, Annisa Kesy Garside, Adhi Nugraha, Amelia Khoidir
Jurnal Sistem dan Manajemen Industri.2023; 7(1): 53. CrossRef - Identifying service quality gaps between patients and providers in a Native American outpatient clinic
Robert Dorsey, David Claudio, María A. Velázquez, Polly Petersen
BMC Health Services Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing the Utility and Patient Satisfaction of Virtual Retina Clinics During COVID-19 Pandemic
Leire Juaristi, Cristina Irigoyen, Jaione Chapartegui, Ane Guibelalde, Javier Mar
Clinical Ophthalmology.2022; Volume 16: 311. CrossRef - A social-media-based improvement index for urban renewal
Zhifang Wang, Hua Jie, Hongpeng Fu, Lu Wang, Hezhishi Jiang, Lu Ding, Yingjie Chen
Ecological Indicators.2022; 137: 108775. CrossRef - On the comparative use of social media data and survey data in prioritizing ecosystem services for cost-effective governance
Zhifang Wang, Hongpeng Fu, Yuqing Jian, Salman Qureshi, Hua Jie, Lu Wang
Ecosystem Services.2022; 56: 101446. CrossRef - Quality Assessment Methods of Hospital Services from the Viewpoint of Patients Based on Standard Assessment Models in Iran: A Narrative Review
Mehdi Rahimi, Fateme Solymani
Modern Care Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Responsiveness level and its effect on services quality from the viewpoints of the older adults hospitalized during COVID-19 pandemic
Ali Reza Yusefi, Esmat Rezabeigi Davarani, Salman Daneshi, Misagh Bastani, Gholamhossein Mehralian, Peivand Bastani
BMC Geriatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Ranking Hospital Hoteling Services from Patients’ Perspective Using Importance-Performance Analysis
Amir Karimkhany, Ehsan Zarei, Samira Arabi, Elahe Navvabi, Somayeh Anisi
Shiraz E-Medical Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Using the Kano model to associate the number of confirmed cases of COVID-19 in a population of 100,000 with case fatality rates: An observational study
Sheng-Yao Hsu, Tsair-Wei Chien, Yu-Tsen Yeh, Willy Chou
Medicine.2022; 101(37): e30648. CrossRef - Patient satisfaction with quality of care in public hospitals in Albania
Rezarta Kalaja, Marsida Krasniqi
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Crisis in the Health System and Quality of Healthcare in Economically Developed Countries
Magdalena Biel, Katarzyna Grondys, Ane-Mari Androniceanu
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 20(1): 469. CrossRef - An integrated approach for evaluating hospital service quality with linguistic preferences
Xiaobing Li, Zhen He
International Journal of Production Research.2021; 59(6): 1776. CrossRef - Rethinking health services operations to embrace patient experience of healthcare journey
Mahdi Mahdavi, Leila Doshmangir, Ebrahim Jaafaripooyan
The International Journal of Health Planning and M.2021; 36(6): 2020. CrossRef - A STUDY ON QUALITY OF SERVICES IN THE OUTPATIENT DEPARTMENT OF A MULTISPECIALTY TEACHING HOSPITAL
Nirmala Kumari, Keerthana Maria Pinto
GLOBAL JOURNAL FOR RESEARCH ANALYSIS.2021; : 117. CrossRef - Variation in compliance with safe surgery checklist in hospitals with different levels of patient safety culture
Saeed Asefzadeh, Sima Rafiei, Masoomeh Karimi
International Journal of Healthcare Management.2020; 13(sup1): 12. CrossRef - Assessment of Quality of Services Delivered to Iranian Patients with Cataract
Zahra Hashemi Dehaghi, Soad Mahfoozpour, Mahmoud Modiri, Fateme Alipour
Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Gap between patient expectation and perception during pharmacist–patient communication at community pharmacy
Myeong Gyu Kim, Na Eun Lee, Hyun Soon Sohn
International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy.2020; 42(2): 677. CrossRef - Validating Service Quality (SERVQUAL) in Healthcare: Measuring Patient Satisfaction Using their Perceptions in Jordan
Mohammed Shaker Ibrahim
Journal of Information & Knowledge Management.2020; 19(01): 2040021. CrossRef - Evaluating the environmental protection strategy of a printed circuit board manufacturer using a T fuzzy importance performance analysis with Google Trends
Kuen-Suan Chen, Kuo-Ping Lin, Li-Ju Lin
Expert Systems with Applications.2020; 156: 113483. CrossRef - Methodologies for Determining the Service Quality of the Intercity Rail Service Based on Users’ Perceptions and Expectations in Thailand
Sajjakaj Jomnonkwao, Thanapong Champahom, Vatanavongs Ratanavaraha
Sustainability.2020; 12(10): 4259. CrossRef - Patients’ Views on Service Quality in Selected Iranian Hospitals: An Importance-Performance Analysis
Ehsan Zarei, Ali Bagheri, Abbas Daneshkohan, Soheila Khodakarim
Shiraz E-Medical Journal.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of quality gaps in healthcare services using the SERVQUAL instrument and importance-performance analysis in medical intensive care: a prospective study at a medical center in Taiwan
Shu-Ju Lu, Hsiu-O Kao, Bao-Lin Chang, Shu-Ing Gong, Shu-Mei Liu, Shih-Chi Ku, Jih-Shuin Jerng
BMC Health Services Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Importance – Performance Analysis (IPA) of bus service attributes: A case study in a developing country
Javad Esmailpour, Kayvan Aghabayk, Mohammad Abrari Vajari, Chris De Gruyter
Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practic.2020; 142: 129. CrossRef - The Effect of Quality Service Towards Outpatients Satisfaction at Poasia Community Health Centre
Adryan Fristiohady, La Ode Muhammad Fitrawan, Yusniati Dwi Pemudi, Ruslin Ruslin, Sunandar Ihsan, Ruslan Ruslan, La Ode Muhammad Julian Purnama
Borneo Journal of Pharmacy.2020; 3(4): 270. CrossRef - Gap of services quality expectation and perception based on SERVQUAL model in the selected hospital outpatient clinics affiliated with Iran University of Medical Sciences
asgar Aghaei Hashjin, Pouria Farrokhi, Aidin Aryankhesal
Journal of Health Administration.2020; 23(3): 55. CrossRef - An empirical study of willingness to renewable energy installation using importance-performance analysis: the case of Taiwan
Wei-Chuan Chen, Wen-Kuo Chen, Chien-Wen Chen, Chien-Cheng Lo
Journal of Industrial and Production Engineering.2019; 36(7): 451. CrossRef - Assessing management performance of the national forest park using impact range-performance analysis and impact-asymmetry analysis
Pin-Zheng Chen, Wan-Yu Liu
Forest Policy and Economics.2019; 104: 121. CrossRef - Do patients really perceive better quality of service in private hospitals than public hospitals in India?
Swapnarag Swain
Benchmarking: An International Journal.2019; 26(2): 590. CrossRef - Percepción de los usuarios frente a la calidad de atención en salud del servicio de consulta externa según el modelo SERVQUAL
Angélica Viviana Boada-Niño, Adriana Mayeth Barbosa-López, Elisa Andrea Cobo-Mejía
Revista Investigación en Salud Universidad de Boya.2019; 6(1): 55. CrossRef - Application of the SERVQUAL model to evaluate the quality in the transportation service in Morelia, Mexico
Marco Alberto Valenzo-Jiménez, Daniel Adan Lazaro-López, Jaime Apolinar Martínez- Arroyo
DYNA.2019; 86(211): 64. CrossRef - Konya İlinde Bulunan Özel Hastanelerdeki Hizmet Kalitesinin Ölçülmesi: Akademik Personele Yönelik Araştırma
Büşra Güler, Saadettin Erhan Kesen
Selçuk Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Meslek Yükseko.2019; 22(2): 526. CrossRef - A Study on Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction in Nigerian Healthcare Sector
Rajasekhara Mouly Potluri, Gift Angiating
Journal of Industrial Distribution & Business.2018; 9(12): 7. CrossRef - Analysis of customer satisfaction in hospital by using Importance-Performance Analysis (IPA) and Customer Satisfaction Index (CSI)
Vembri Noor Helia, Cahya Putra Abdurrahman, Fety Ilma Rahmillah, S. Ma’mun, H. Tamura, M.R.A. Purnomo
MATEC Web of Conferences.2018; 154: 01098. CrossRef - Evaluating health service quality: using importance performance analysis
Azar Izadi, Younes Jahani, Sima Rafiei, Ali Masoud, Leila Vali
International Journal of Health Care Quality Assur.2017; 30(7): 656. CrossRef - Societal perception toward transportation modes based on online (Go-Jek) In Malang City
D M Buamona
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Sci.2017; 70: 012007. CrossRef - The Role of Subjective Culture on Consumer Perception towards Service Quality Delivery
Tiara Turay
Journal of Business and Social Review in Emerging .2016; 2(2): 175. CrossRef
- A New Model to Consolidate Long-Term Intersectoral Partnerships in Humanitarian and Social Crises Management
- Factors associated with health services utilization between the years 2010 and 2012 in Korea: using Andersen's Behavioral model
- Han-Kyoul Kim, Munjae Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(1):18-25. Published online February 28, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.11.007
- 3,258 View
- 29 Download
- 70 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to examine the factors associated with health services utilization using Andersen's behavioral model.
Methods
We collected Korea Health Panel data between the years 2010 and 2012 from the consortium of the National Health Insurance Service and the Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs, and analyzed the data to determine the outpatients and inpatients of health services utilization.
Results
Health services utilization was more significantly explained by predisposing and need factors than enabling factors. The outpatients were examined more specifically; sex, age, and marital status as predisposing factors, and chronic illness as a need factor were the variables that had significant effects on health-services-utilization experience. The inpatients were examined more specifically: sex, age, and marital status in predisposing factors; education level, economic activities, and insurance type in enabling factors; and chronic illness and disability status in need factors were the significant variables having greater effects on health-services-utilization experience.
Conclusion
This study suggests the practical implications for providing health services for outpatients and inpatients. Moreover, verifying the general characteristics of outpatients and inpatients by focusing on their health services utilization provides the baseline data for establishing health service policies and programs with regard to the recently increasing interest in health services. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and predictors of help-seeking behavior among post-partum women with urinary incontinence in China and Indonesia: A cross-sectional survey based on Andersen Help-Seeking Model
Surui Liang, Zhaoying Chen, Wenjun Tang, Esti Andarini, Lin Kou, Yan Li, Wenzhi Cai
Midwifery.2024; 128: 103885. CrossRef - Ethnic heterogeneity and healthcare utilization: The mediating role of poverty in Ghana
Opoku Adabor, Enock Kojo Ayesu
Review of Economics of the Household.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Health insurance and hospitalisation duration: empirical evidence from Ghana’s national health insurance scheme
Samuel Sekyi, James Dickson Fiagborlo, Gloria Essilfie
Cogent Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mental Health Services Utilization by the Population That Suffered Water Supply Interruption Following Mariana Dam Failure (Brazil)
Marcelo F. Dell’Aringa, Gabriel E. Correa-Oliveira, Francesco Della Corte, Luca Ragazzoni, Elaine S. Miranda, Ives Hubloue, Virginia Murray, Francesco Barone-Adesi
Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Use of Assistive Technologies and Alternative Means by Older People: The “Actional Model of Older People´s Coping with Health-Related Declines”
Diana Abri, Thomas Boll
Integrative Psychological and Behavioral Science.2023; 57(3): 960. CrossRef - Outpatient Service Use in Korean Older Adult Women with Degenerative Arthritis Based on Andersen’s Model
Soyoung Jang, Eunyoung E. Suh
Geriatrics.2023; 8(1): 9. CrossRef - Understanding Unmet Care Needs of Rural Older Adults with Chronic Health Conditions: A Qualitative Study
Dennis Asante, Craig S. McLachlan, David Pickles, Vivian Isaac
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2023; 20(4): 3298. CrossRef - Elderly people’s preferences for healthcare facilities in Shanghai: gender features and influencing factor analysis
Shangguang Yang, Luxue Liu, Chunlan Wang, Kevin Lo, Danyang Wang
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The efficient moral hazard effect of health insurance: Evidence from the consolidation of urban and rural resident health insurance in China
Yao Li, Lei Li, Junxia Liu
Social Science & Medicine.2023; 324: 115884. CrossRef - Use and impact of a novel nurse-led consultation model in a palliative care consultation service for terminally ill cancer patients in Taiwan: an 11-year observational study
Lian-Shin Lin, Ling-Hui Huang, Szu-Pei Chien, Chun-Li Wang, Lung-Chun Lee, Chung-Chieh Hu, Pi-Shan Hsu, Wei-Min Chu
Supportive Care in Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - System, institutional, and client-level factors associated with formal healthcare utilisation among older adults with low income under a social protection scheme in Ghana
Williams Agyemang-Duah, Dennis Asante, Joseph Oduro Appiah, Anthony Kwame Morgan, Isaac Verberk Mensah, Prince Peprah, Anthony Acquah Mensah
Archives of Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A qualitative investigation into pregnancy experiences and maternal healthcare utilisation among adolescent mothers in Nigeria
Christiana A. Alex-Ojei, Clifford O. Odimegwu, Lorretta F. C. Ntoimo
Reproductive Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Determinants of province-based health service utilization according to Andersen’ s Behavioral Model: a population-based spatial panel modeling study
Yu Xin, Xiaohui Ren
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Differences in healthcare service utilization between older adults with and without dementia: a cross-sectional study in Shandong, China
Yu Gao, Jingjie Sun, Wengui Zheng, Weiqin Cai, Qianqian Gao, Juncheng Lyu, Xiaomeng Zheng, Runguo Gao, Lihong Ji, Qi Jing
Journal of Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Contribution of private health services to universal health coverage in low and middle‐income countries: Factors affecting the use of private over public health services in Vietnam
Mai P. Nguyen, Amina Tariq, Reece Hinchcliff, Hoat N. Luu, Michael P. Dunne
The International Journal of Health Planning and M.2023; 38(6): 1613. CrossRef - Income and health insurance effects on modern health-seeking behaviours in rural Ghana: nature and extent of bias involved
Samuel Sekyi, Philip Kofi Adom, Emmanuel Agyapong Wiafe
International Journal of Social Economics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Health Care Utilization in Russia: Public Health Survey Findings
Arsen P. Davitadze, Ekaterina A. Aleksandrova, Alexandra V. Kupera, Tatiana I. Rodionova, Alina R. Khabibullina, Andrey A. Svistunov, Victor V. Fomin
ЗДОРОВЬЕ НАСЕЛЕНИЯ И СРЕДА ОБИТАНИЯ - ЗНиСО / PUBL.2023; : 7. CrossRef - Özel Sağlık Sigortasına Sahip Bireylerin Sağlık Hizmeti Kullanımının Değerlendirilmesi
Özden GÜDÜK, Emre İŞCİ, Mehveş TARIM
Adnan Menderes Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Fakül.2023; 7(3): 541. CrossRef - Understanding the Impact of Community Family Physician Contracting (CFPC) on Community Medical Resources Consumption: A Case Study from Beijing in China
Lele Li, Xiaotong He, Yifeng Xian, Tushar Singh
Health & Social Care in the Community.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Examining healthcare needs and decisions to seek health services among Venezuelan migrants living in Trinidad and Tobago using Andersen’s Behavioral Model
Nyla Lyons, Brendon Bhagwandeen
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gender differences in caregiver attitudes and unmet needs for activities of daily living (ADL) assistance among older adults with disabilities
Selin Woo, Ying Cui, Suyeon Kim, Mankyu Choi
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Social Gradient in Maternal Healthcare Utilization in Malawi: Analysis of Trends
Joe Maganga Zonda, Suchuan Yu
Journal of Asian and African Studies.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Heterogeneous effects of national health insurance scheme on healthcare utilisation: evidence from Ghana
Samuel Sekyi, Senia Nhamo, Edinah Mudimu
International Journal of Social Economics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Health Services Utilization among Older Adults in Pokhara Metropolitan City
Isha Karmacharya, Saruna Ghimire, Kshitiz Bhujel, Asmita Shrestha Dhauvadel, Shraddha Adhikari, Subash Baral, Naveen Shrestha
Journal of Aging & Social Policy.2022; 34(4): 568. CrossRef - Factors associated with the quality of mental health services and consumers' functionality using tertiary‐based services
Eric Badu, Anthony P. O'Brien, Rebecca Mitchell, Akwasi Osei
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2022; 58(2): 592. CrossRef - Health care utilization in very advanced ages: A study on predisposing, enabling and need factors
Daniela Brandão, Constança Paúl, Oscar Ribeiro
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2022; 98: 104561. CrossRef - Choosing a health behaviour theory or model for related research projects: a narrative review
Getahun K Beyera, Jane O’Brien, Steven Campbell
Journal of Research in Nursing.2022; 27(5): 436. CrossRef - The Urban-Rural Disparities and Associated Factors of Health Care Utilization Among Cancer Patients in China
Haipeng Wang, Xingxing Hua, Nengliang Yao, Nan Zhang, Jialin Wang, Roger Anderson, Xiaojie Sun
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of religious beliefs on bone graft selection for oral and maxillofacial surgery in Saudi Arabia
Ahmad Assari, Maram Hani, Hajar Qaid, Bushra Omar, Lamia Aleid
Journal of Stomatology, Oral and Maxillofacial Sur.2022; 123(5): e563. CrossRef - Effect of financial services access on health services utilisation among rural older adults in Ghana
Dennis Asante, Bismark Asante, Bismark Addai, Williams Agyemang‐Duah, Martinson Ankrah Twumasi
International Journal of Social Welfare.2022; 31(4): 492. CrossRef - The relationship between internal and external factors about the outpatients’ choice of hospital: A cross‐sectional study from Jiaxing City, China
Mingming Yu, Guoyang Zhao, Dan Tang
Health Science Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing health service utilization among mothers for under-five children: A cross-sectional study in Khulna district of Bangladesh
Shahinur Akter, A. K. M. Anisur Rahman
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(9): e0274449. CrossRef - Unmet health care needs: factors predicting satisfaction with health care services among community-dwelling Canadians living with neurological conditions
Tamara Chambers-Richards, Batholomew Chireh, Carl D’Arcy
BMC Health Services Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Joint modelling of health insurance, healthcare utilisation, healthcare expenditure and health status: Evidence from Ghana
Samuel Sekyi
Cogent Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - District division administrative disaggregation data framework for monitoring leaving no one behind in the National Health Insurance Fund of Sudan: achieving sustainable development goals in 2030
Ashraf Mansour, Nithat Sirichotiratana, Chukiat Viwatwongkasem, Mahmud Khan, Samrit Srithamrongsawat
International Journal for Equity in Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Gender Differences in Health Care Utilization Among the Elderly
Gordana Gajovic, Katarina Janicijevic, Dragana Andric, Olivera Djurovic, Svetlana Radevic
Serbian Journal of Experimental and Clinical Resea.2021; 22(3): 195. CrossRef - Financial Innovation in Digital Payment with WeChat towards Electronic Business Success
Yuk Ming Tang, Ka Yin Chau, Luchen Hong, Yun Kit Ip, Wan Yan
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Comm.2021; 16(5): 1844. CrossRef - The determinants of caregiver use and its costs for elderly inpatients in Korea: a study applying Andersen’s behavioral model of health care utilization and replacement cost method
Jennifer Ivy Kim, Sukil Kim
BMC Health Services Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - SAĞLIK HİZMETLERİ KULLANIMINI ETKİLEYEN FAKTÖRLERİN PANEL VERİ ANALİZİ İLE BELİRLENMESİ
Faruk YILMAZ, Canser BOZ, Özgür İNCE
Mehmet Akif Ersoy Üniversitesi İktisadi ve İdari B.2021; 8(2): 577. CrossRef - Determinants of Healthcare Use Based on the Andersen Model: A Systematic Review of Longitudinal Studies
André Hajek, Benedikt Kretzler, Hans-Helmut König
Healthcare.2021; 9(10): 1354. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Adherence to Follow-up Among Patients with Depressive Disorders in a Collaborative Care Program in Iran
Atefeh Mohammadjafari, Maryam Tabatabaee, Vandad Sharifi, Fattaneh Abdi Masouleh, Farid Abolhassani
Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Behavioral Scien.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Health service utilisation among African migrants in China: a nationwide cross-sectional study
Ming Zhou Xiong, Peizhen Zhao, Xia Zou, Brian Hall, Honghua Cao, Cheng Wang
BMJ Open.2021; 11(9): e046746. CrossRef - Effect of Religious Beliefs on Bone Graft Selection for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery in Saudi Arabia
Ahmad Assari, Maram Hani, Hajar Qaid, Bushra Omar, Lamia Aleid
SSRN Electronic Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Inequity in palliative care service full utilisation among patients with advanced cancer: a retrospective Cohort study
Daniela D’Angelo, Marco Di Nitto, Diana Giannarelli, Ileana Croci, Roberto Latina, Anna Marchetti, Caterina Magnani, Chiara Mastroianni, Michela Piredda, Marco Artico, Maria Grazia De Marinis
Acta Oncologica.2020; 59(6): 620. CrossRef - Unmet Medical Needs of Patients with Benign Prostate Enlargement
Munjae Lee, Sewon Park, Mankyu Choi, Kyu-Sung Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(4): 895. CrossRef - Predictors of healthcare utilisation among poor older people under the livelihood empowerment against poverty programme in the Atwima Nwabiagya District of Ghana
Williams Agyemang-Duah, Charles Peprah, Francis Arthur-Holmes
BMC Geriatrics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Patient-perceived service needs and health care utilization in people with type 2 diabetes
Yunxia Ni, Suzhen Liu, Jiping Li, Simin Li, Ting Dong
Medicine.2020; 99(21): e20322. CrossRef - Outpatient Visits among Older Adults Living Alone in China: Does Health Insurance and City of Residence Matter?
Jianyun Wang, Yaolin Pei, Renyao Zhong, Bei Wu
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2020; 17(12): 4256. CrossRef - The healthcare seeking behaviour of adult patients with asthma at Chitungwiza Central Hospital, Zimbabwe
Pisirai Ndarukwa, Moses J. Chimbari, Elopy N. Sibanda, Tafadzwa Madanhire
Asthma Research and Practice.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Inequality in Health Services for Internal Migrants in China: A National Cross-Sectional Study on the Role of Fund Location of Social Health Insurance
Qiang Yao, Chaojie Liu, Ju Sun
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2020; 17(17): 6327. CrossRef - Perceptions of Health Care Use in Germany during the COVID-19 Pandemic
André Hajek, Freia De Bock, Lothar H. Wieler, Philipp Sprengholz, Benedikt Kretzler, Hans-Helmut König
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2020; 17(24): 9351. CrossRef - Household wealth and maternal health: evidence from Ghana
Christian Kwaku Osei, Edward Nketiah-Amponsah, Monica Puoma Lambon-Quayefio
International Journal of Social Economics.2020; 48(1): 63. CrossRef - eHealth literacy and beliefs about medicines among Taiwanese college students: cross-sectional study (Preprint)
Chiao Ling Huang, Chia-Hsun Chiang, Shu Ching Yang
JMIR Medical Informatics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of hospital readmissions in internal medicine patients: Application of Andersen's Model
Sıdıka Kaya, Gulay Sain Guven, Seda Aydan, Onur Toka
The International Journal of Health Planning and M.2019; 34(1): 370. CrossRef - Pathways to mental health treatment in Ghana: Challenging biomedical methods from herbal- and faith-healing perspectives
Eric Badu, Rebecca Mitchell, Anthony Paul O’Brien
International Journal of Social Psychiatry.2019; 65(6): 527. CrossRef - Factors influencing healthcare use among poor older females under the Livelihood Empowerment Against Poverty programme in Atwima Nwabiagya District, Ghana
Williams Agyemang-Duah, Justice Kufour Owusu-Ansah, Charles Peprah
BMC Research Notes.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Emergency Department Utilization among Underserved African American Older Adults in South Los Angeles
Mohsen Bazargan, James Smith, Sharon Cobb, Lisa Barkley, Cheryl Wisseh, Emma Ngula, Ricky Thomas, Shervin Assari
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2019; 16(7): 1175. CrossRef - Factors associated with the intention to use adult preventive health services in Taiwan
Yi‐Lin Hsieh, Fang‐Hsin Lee, Shu‐Chuan Chen, Jing‐Shia Tang
Public Health Nursing.2019; 36(5): 631. CrossRef - Gender differences in health expenditure determinants: A follow-up study
Cecilia Quercioli, Francesca Nisticò, Gabriele Messina, Mauro Maccari, Massimo Barducci, Giovanni Carriero, Nicola Nante
Health Care for Women International.2019; 40(1): 33. CrossRef - Prevalence and Patterns of Health Care Use Among Poor Older People Under the Livelihood Empowerment Against Poverty Program in the Atwima Nwabiagya District of Ghana
Williams Agyemang-Duah, Charles Peprah, Francis Arthur-Holmes
Gerontology and Geriatric Medicine.2019; 5: 233372141985545. CrossRef - Who Uses The Health Services More? A Descriptive Study of Excessive Users’ Profile and Causes
Golnoosh Aghili, Masoud Ferdosi, Mohammadreza Rezayatmand, Abbas Feizbakhsh, Hamid Reza Dehghani
Health Scope.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Treatment Retention Among Patients Participating in Coordinated Specialty Care for First-Episode Psychosis: a Mixed-Methods Analysis
Jane E. Hamilton, Devika Srivastava, Danica Womack, Ashlie Brown, Brian Schulz, April Macakanja, April Walker, Mon-Ju Wu, Mark Williamson, Raymond Y. Cho
The Journal of Behavioral Health Services & Resear.2019; 46(3): 415. CrossRef - The predictors of treatment pathways to mental health services among consumers in Ghana
Anna Korley Nartey, Eric Badu, Peter Agyei‐Baffour, Naomi Gyamfi, Maxwell Preprah Opoku, Anthony Paul O'Brien, Rebecca Mitchell
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2019; 55(2): 300. CrossRef - Catastrophic Health Expenditures and Its Inequality in Households with Cancer Patients: A Panel Study
Munjae Lee, Kichan Yoon
Processes.2019; 7(1): 39. CrossRef - Patients’ perspectives regarding hospital visits in the universal health coverage system of Thailand: a qualitative study
Apichai Wattanapisit, Udomsak Saengow
Asia Pacific Family Medicine.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The Health and Retirement Study: Analysis of Associations Between Use of the Internet for Health Information and Use of Health Services at Multiple Time Points
Hyunju Shim, Jennifer Ailshire, Elizabeth Zelinski, Eileen Crimmins
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2018; 20(5): e200. CrossRef - Associations of eHealth Literacy With Health Services Utilization Among College Students: Cross-Sectional Study
Yi Fang Luo, Shu Ching Yang, An-Sing Chen, Chia-Hsun Chiang
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2018; 20(10): e283. CrossRef - Type 2 diabetes, healthcare expenditures and its correlation with anthropometric factors and physical activity: 18-month follow-up in a Brazilian city
Monique Yndawe Castanho Araujo, Bruna Camilo Turi, Dayane Cristina Queiroz, Izabela dos Santos Ferro, Carolina Rodrigues Bortolatto, Jamile Sanches Codogno
Motriz: Revista de Educação Física.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental hygienist attendance and its covariates in an ageing Swedish cohort
Anne N. Åstrøm, Gunnar Ekbäck, Sven Ordell, Stein A. Lie, Ferda Gulcan
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2017; 125(6): 487. CrossRef - Experiences with out-patient hospital service utilisation among older persons in the Asante Akyem North District- Ghana
Jonathan Bayuo
BMC Health Services Research.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prevalence and predictors of help-seeking behavior among post-partum women with urinary incontinence in China and Indonesia: A cross-sectional survey based on Andersen Help-Seeking Model
- Nurse-Perceived Patient Adverse Events depend on Nursing Workload
- Jeong-Hee Kang, Chul-Woung Kim, Sang-Yi Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(1):56-62. Published online February 28, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.10.015
- 2,848 View
- 18 Download
- 37 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to investigate the correlation between nursing workload and nurse-perceived patient adverse events.
Methods
A total of 1,816 nurses working in general inpatient units of 23 tertiary general hospitals in South Korea were surveyed, and collected data were analyzed through multilevel logistic regression analysis.
Results
Among variables related to nursing workload, the non-nursing task experience had an influence on all four types of patient adverse events. Nurses with non-nursing tasks experienced patient adverse events—falls [odds ratio (OR) = 1.31], nosocomial infections (OR = 1.23), pressure sores (OR = 1.16), and medication errors (OR = 1.23)—more often than occasionally. In addition, when the bed to nurse ratio was higher, nurses experienced cases of pressure sores more often (OR = 1.35). By contrast, nurses who said the nursing workforce is sufficient were less likely than others to experience cases of pressure sores (OR = 0.78). Hospitals with a relatively high proportion of nurses who perceived the nursing workforce to be sufficient showed a low rate of medication error (OR = 0.28).
Conclusion
The study suggested that the high level of nursing workload in South Korea increases the possibility of patient adverse events. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Stepped-Wedge Cluster-Randomized Controlled Trial of a Multi-interventional Approach for Fall Prevention
Zhila Najafpour, Mohammad Arab, Arash Rashidian, Kamran Shayanfard, Mehdi Yaseri, Somayeh Biparva-Haghighi
Quality Management in Health Care.2024; 33(2): 77. CrossRef - Examining Barriers and Perceptions in Reporting Medication Administration Errors among Nurses at the Tertiary Care Hospitals in Peshawar Pakistan
Muhammad Anwar, Dildar Muhammad, Bakhtayar Ali Shah, Sumayya Shah, Asad Ullah, Sumaira Bibi
NURSEARCHER (Journal of Nursing & Midwifery Scienc.2024; : 25. CrossRef - Nursing care complexity as a predictor of adverse events in patients transferred from ICU to hospital ward after general surgery
Betül Güven, Serpil Topçu, Elif Hamarat, Birgül Ödül Özkaya, Ayten Güreşci Zeydan
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2024; 82: 103637. CrossRef - A phenomenological study of the experiences of nurses working in integrated nursing care wards in Korea
Young-mi Cho, Sun-hui Kim
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the causes and consequences of non-nursing tasks among nurses in Jordan: An in-depth qualitative investigation
Ayman Abed Aldarawsheh, Ahmad Saifan, Murad Adnan Sawalha, Enas A. Assaf, Intima Alrimawi, Rami A. Elshatarat, Zyad T. Saleh, Wesam T. Almagharbeh, Nermen A. Mohamed, Mudathir M. Eltayeb
Applied Nursing Research.2024; : 151791. CrossRef - Association of nursing hours with cognitive function, balance, and dependency level of stroke patients
Haneul Lee, Kyounga Lee, Seon‐Heui Lee
Nursing Open.2023; 10(3): 1735. CrossRef - Technological innovation for workload allocation in nursing care management: an integrative review
Maria Alejandra Galiano, Maria Elisa Moreno Fergusson, William J. Guerrero, Maria Francisca Muñóz, Germán A. Ortiz Basto, Juan Sebastián Cardenas Ramírez, Maryory Guevara Lozano, Ana Larraín Sundt
F1000Research.2023; 12: 104. CrossRef - What are the predictors and costs of nurse absenteeism at select multicenter government hospitals? A cross-sectional study
Hashem Al Ismail, Nawal H. Herzallah, Sultan T. Al-Otaibi
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Left behind: Exploring the concerns of emergency department staff when personnel are utilised for inter-hospital transfer
Clare Walters, Vicki Cope, Martin P.R. Hopkins
International Emergency Nursing.2023; 69: 101298. CrossRef - Technological innovation for workload allocation in nursing care management: an integrative review
Maria Alejandra Galiano, Maria Elisa Moreno Fergusson, William J. Guerrero, Maria Francisca Muñóz, Germán A. Ortiz Basto, Juan Sebastián Cardenas Ramírez, Maryory Guevara Lozano, Ana Larraín Sundt
F1000Research.2023; 12: 104. CrossRef - Nurses’ Perceptions of the Clinical Decision Support System Effect on Patient Safety
Reem N. AL-Dossary
Safety.2023; 9(4): 86. CrossRef - Spanish Version of the Scale “Eventos Adversos Associados às Práticas de Enfermagem” (EAAPE): Validation in Nursing Students
Antonio Martínez-Sabater, Carlos Saus-Ortega, Mónica Masiá-Navalon, Elena Chover-Sierra, María Luisa Ballestar-Tarín
Nursing Reports.2022; 12(1): 112. CrossRef - Relation between mental workload and hospital infection in the ICU
Ravenna Leite da Silva, Luiz Bueno da Silva, Aryelle Nayra Azevedo Silva
Work.2022; 73(3): 915. CrossRef - The Impact of Performance of Non-Nursing Tasks on the Attitudes of Nursing Students toward Nursing Profession
Ibrahim Rawhi Ayasreh, Ferial Hayajneh, Rana Al Awamleh
Nurse Media Journal of Nursing.2022; 12(2): 151. CrossRef - Identification of Predictive Nursing Workload Factors: A Six Sigma Approach
Marcos Buestan, Cinthia Perez
Sustainability.2022; 14(20): 13169. CrossRef - Burnout and patient safety: A discriminant analysis of paediatric nurses by low to high managerial support
Haitham Khatatbeh, Annamária Pakai, Dorina Pusztai, Szilvia Szunomár, Noémi Fullér, Gyula Kovács Szebeni, Adrienn Siket, Miklós Zrínyi, András Oláh
Nursing Open.2021; 8(2): 982. CrossRef - Major educational factors associated with nursing adverse events by nursing students undergoing clinical practice: A descriptive study
Hui Li, Xiangping Kong, Lulu Sun, Yuanyuan Zhu, Bo Li
Nurse Education Today.2021; 98: 104738. CrossRef - Accuracy of documented administration times for intravenous antimicrobial drugs and impact on dosing decisions
Stephanie A. Roydhouse, Jane E. Carland, Deborah S. Debono, Melissa T. Baysari, Stephanie E. Reuter, Alice J. Staciwa, Anmol P. K. Sandhu, Richard O. Day, Sophie L. Stocker
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2021; 87(11): 4273. CrossRef - Factors associated with length of stay and death in tube‐fed patients: A cross‐sectional multicentre study
Leticia Alves Freitas, Alex Luís Fagundes, Patrícia Rezende do Prado, Marta Cristiane Alves Pereira, Adriane Pinto de Medeiros, Ligia Menezes de Freitas, Thalyta Cardoso Alux Teixeira, Janine Koepp, Rhanna Emanuela Fontenele Lima de Carvalho, Fernanda Rap
Nursing Open.2021; 8(5): 2509. CrossRef - Patient safety. Factors for and perceived consequences of nursing errors by nursing staff in home care services
Deborah Elisabeth Jachan, Ursula Müller‐Werdan, Nils Axel Lahmann
Nursing Open.2021; 8(2): 755. CrossRef - Nurses’ perception of patient safety culture and its relationship with adverse events: a national questionnaire survey in Iran
Edris Kakemam, Hojatolah Gharaee, Mohamad Reza Rajabi, Milad Nadernejad, Zahra Khakdel, Pouran Raeissi, Rohollah Kalhor
BMC Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of changes in nursing work environment, non-professional tasks, and nursing care left undone with nurse job outcomes and quality of care: A panel study
Xu Liu, Jiali Liu, Ke Liu, Judith Gedney Baggs, Jun Wang, Jing Zheng, Yan Wu, Mengqi Li, Liming You
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2021; 115: 103860. CrossRef - Relationships among Non-Nursing Tasks, Nursing Care Left Undone, Nurse Outcomes and Medical Errors in Integrated Nursing Care Wards in Small and Medium-Sized General Hospitals
Ju-Young Park, Jee-In Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(1): 27. CrossRef - Covid-19 Effects on the Mental Workload and Quality of Work Life in Iranian Nurses
Kiana Nikeghbal, Bahram Kouhnavard, Ali Shabani, Zahra Zamanian
Annals of Global Health.2021; 87(1): 79. CrossRef - Dimensioning of nursing team at neonatal intensive care unit: real versus ideal / Dimensionamento de enfermagem em unidade de terapia intensiva neonatal: real versus ideal
Aline Patrícia Vicente Franco, Beatriz Pera De Almeida Hamasaki, Luciana Renata De Puiz, Gisele Hespanhol Dorigan, Ariane Polidoro Dini, Elenice Valentim Carmona
Revista de Pesquisa Cuidado é Fundamental Online.2021; 13: 1536. CrossRef - Safety Performance in Acute Medical Care: A Qualitative, Explorative Study on the Perspectives of Healthcare Professionals
Lina Heier, Donia Riouchi, Judith Hammerschmidt, Nikoloz Gambashidze, Andreas Kocks, Nicole Ernstmann
Healthcare.2021; 9(11): 1543. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Web-Based Pediatric Readmission Risk Assessment Tool
Thom Taylor, Danielle Altares Sarik, Daria Salyakina
Hospital Pediatrics.2020; 10(3): 246. CrossRef - Design and application of time series algorithm model in information assisted sensing system of nursing measurement in neurology
Meirong Liu, Miaoxia Wang, Quanyuan He, Mingyuan Yin
Measurement.2020; 162: 107894. CrossRef - Nurse-staffing level and quality of acute care services: Evidence from cross-national panel data analysis in OECD countries
Arshia Amiri, Tytti Solankallio-Vahteri
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2019; 6(1): 6. CrossRef - Nurses' Perceptions Regarding Disclosure of Patient Safety Incidents in Korea: A Qualitative Study
Eun Young Choi, Jeehee Pyo, Minsu Ock, Sang-il Lee
Asian Nursing Research.2019; 13(3): 200. CrossRef - Occupational stress and cognitive failure of nurses and associations with self‐reported adverse events: A national cross‐sectional survey
Edris Kakemam, Roholla Kalhor, Zahra Khakdel, Ali Khezri, Sancia West, Denis Visentin, Michelle Cleary
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2019; 75(12): 3609. CrossRef - Analysis of factors related to the mental workload of nurses during interaction through nursing care in the intensive care unit
Hany Wihardja, Rr. Tutik Sri Hariyati, Dewi Gayatri
Enfermería Clínica.2019; 29: 262. CrossRef - Hospital nursing organizational factors, nursing care left undone, and nurse burnout as predictors of patient safety: A structural equation modeling analysis
Xu Liu, Jing Zheng, Ke Liu, Judith Gedney Baggs, Jiali Liu, Yan Wu, Liming You
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2018; 86: 82. CrossRef - An Exploration of Contributing Factors to Patient Safety
Inga M. Zadvinskis, Pamela J. Salsberry, Esther M. Chipps, Emily S. Patterson, Laura A. Szalacha, Kathryn A. Crea
Journal of Nursing Care Quality.2018; 33(2): 108. CrossRef - Mental Workload and Its Determinants among Nurses in One Hospital in Kermanshah City, Iran
Ehsan Bakhshi, Adel Mazlomi, Seyed Mostafa Hoseini
Journal of Occupational Hygiene Engineering.2017; 3(4): 53. CrossRef - Análise de eventos adversos em pacientes internados em unidade de terapia intensiva
Daniela Benevides Ortega, Maria D’Innocenzo, Lucia Marta Giunta da Silva, Elena Bohomol
Acta Paulista de Enfermagem.2017; 30(2): 168. CrossRef - The Association of Nursing Workloads, Organizational, and Individual Factors with Adverse Patient Outcome
Majid Bagheri Hossein Abadi, Hesam Akbari, Hamed Akbari, Mohammad Gholami-Fesharaki, Mohammad Ghasemi
Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
- A Stepped-Wedge Cluster-Randomized Controlled Trial of a Multi-interventional Approach for Fall Prevention
- Phenotypic Assays to Determine Virulence Factors of Uropathogenic
Escherichia coli (UPEC) Isolates and their Correlation with Antibiotic Resistance Pattern - Mohsen Tabasi, Mohammad Reza Asadi Karam, Mehri Habibi, Mir Saeed Yekaninejad, Saeid Bouzari
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2015;6(4):261-268. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.08.002
- 3,493 View
- 21 Download
- 50 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Urinary tract infection caused by uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) strains is one of the most important infections in the world. UPEC encode widespread virulence factors closely related with pathogenesis of the bacteria. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the presence of different phenotypic virulence markers in UPEC isolates and determine their correlation with antibiotic resistance pattern.
Methods
UPEC isolates from patients with different clinical symptoms of UTI were collected and screened for biofilm and hemolysin production, mannose resistant, and mannose sensitive hemagglutination (MRHA and MSHA, respectively). In addition, antimicrobial resistance pattern and ESBL-producing isolates were recorded.
Results
Of the 156 UPEC isolates, biofilm and hemolysin formation was seen in 133 (85.3%) and 53 (34%) isolates, respectively. Moreover, 98 (62.8%) and 58 (37.2%) isolates showed the presence of Types 1 fimbriae (MSHA) and P fimbriae (MRHA), respectively. Our results also showed a relationship between biofilm formation in UPEC isolated from acute cystitis patients and recurrent UTI cases. Occurrence of UTI was dramatically correlated with the patients' profiles. We observed that the difference in antimicrobial susceptibilities of the biofilm and nonbiofilm former isolates was statistically significant. The UPEC isolates showed the highest resistance to ampicillin, tetracycline, amoxicillin, and cotrimoxazole. Moreover, 26.9% of isolates were ESBL producers.
Conclusion
This study indicated that there is a relationship between the phenotypic virulence traits of the UPEC isolates, patients' profiles, and antibiotic resistance. Detection of the phenotypic virulence factors could help to improve understanding of pathogenesis of UPEC isolates and better medical intervention. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multi-drug-resistant Escherichia coli in adult male patients with enlarged prostate attending general hospitals in Benue state
Cornelius Iwodi, Grace M. Gberikon, Innocent Okonkwo Ogbonna, Emmanuel O. Agada
Brazilian Journal of Microbiology.2024; 55(1): 447. CrossRef - Phylogenetic analysis, biofilm formation, antimicrobial resistance and relationship between these characteristics in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Talieh Mostaghimi, Abazar Pournajaf, Ali Bijani, Mohsen Mohammadi, Mehdi Rajabnia, Mehrdad Halaji
Molecular Biology Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Type 1 fimbrial phase variation in multidrug-resistant asymptomatic uropathogenic Escherichia coli clinical isolates upon adherence to HTB-4 cells
Arunita Ghosh, Mandira Mukherjee
Folia Microbiologica.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Characteristics of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases (ESBLs)-Producing Escherichia coli in Bloodstream Infection
Rongrong Li, Huaming Xu, Hao Tang, Jilu Shen, Yuanhong Xu
Infection and Drug Resistance.2023; Volume 16: 2043. CrossRef - Phenotypic Detection of Virulence Factors of Uropathogenic Enterobacteriaceae
Betu Rama Soujanya, G.S. Banashankari
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2023; 17(2): 931. CrossRef - Uropathogenic bacteria and deductive genomics towards antimicrobial resistance, virulence, and potential drug targets
Aaima Amin, Ramisha Noureen, Ayesha Iftikhar, Annam Hussain, Wadi B. Alonazi, Hafiz Muhammad Zeeshan Raza, Ifra Ferheen, Muhammad Ibrahim
International Microbiology.2023; 27(1): 325. CrossRef - Regarding the prospects of using Lactobacillus-based probiotics, D-mannose and cranberry extracts in therapy of urinary tract infections
O. A. Gromova, I. Yu. Torshin
Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproduction.2023; 17(4): 485. CrossRef - The Impact of Gold Nanoparticle Susceptibility on Drug Resistance Phenotypes in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Iman Hosseinpour, Leila Fozouni, Morteza Khademi, Mehdi Movaghari, Mohammad Mehdi Akhoondi
Journal of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Dis.2023; 11(3): 155. CrossRef - Biofilm Formation by Escherichia coli Isolated from Urinary Tract Infections from Aguascalientes, Mexico
Flor Yazmín Ramírez Castillo, Alma Lilian Guerrero Barrera, Josée Harel, Francisco Javier Avelar González, Philippe Vogeleer, José Manuel Arreola Guerra, Mario González Gámez
Microorganisms.2023; 11(12): 2858. CrossRef - Detection of Adhesion Encoding Genes, Antibacterial Susceptibility Test and Biofilm Formation of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Urinary Tract Infections in Children
Rezvan Goodarzi, Rasoul Yousefimashouf, Iraj Sedighi, Abbas Moradi, Fatemeh Nouri, Mohammad Taheri
Journal of Advances in Medical and Biomedical Rese.2022; 30(1): 1. CrossRef - A global systematic review and meta-analysis on correlation between biofilm producers and non-biofilm producers with antibiotic resistance in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Mitra Garousi, Sina Monazami Tabar, Hosein Mirazi, Parnia Asgari, Paniz Sabeghi, Astireh Salehi, Azad Khaledi, Mohammad Ghenaat Pisheh Sanani, Hossein Karballaei Mirzahosseini
Microbial Pathogenesis.2022; 164: 105412. CrossRef - Antibiotic resistance, phylogenetic typing, and virulence genes profile analysis of uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from patients in southern Iraq
Mohammed Allami, Masoumeh Bahreini, Mohammad Reza Sharifmoghadam
Journal of Applied Genetics.2022; 63(2): 401. CrossRef - Phylogenetic Group Distribution of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli and Related Antimicrobial Resistance Pattern: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review
Mehrdad Halaji, Amirhossein Fayyazi, Mehdi Rajabnia, Donya Zare, Abazar Pournajaf, Reza Ranjbar
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Genotypic assay to determine some virulence factors of Uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) isolates
Tsahel H. Al-Dulaimi, Ilham A Bunyan, Thikra A. Banimuslem
International journal of health sciences.2022; : 1593. CrossRef - Demonstrating the utility of Escherichia coli asymptomatic bacteriuria isolates’ virulence profile towards diagnosis and management—A preliminary analysis
Lalitha Maniam, Kumutha Malar Vellasamy, Hassan Mahmood Jindal, Vallikannu Narayanan, Mahmoud Danaee, Jamuna Vadivelu, Vinod Pallath, Abdelazeem Mohamed Algammal
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(5): e0267296. CrossRef - Urine Microscopy Score and Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio at Presentation are Good Biomarkers of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Upper Urinary Tract Infection when Assessed in Correlation with Virulence Factors of Escherichia coli and Blood Group Secret
Shanmugapriya Thiagarajan, Selvaraj Stephen, Santosh Kumar, Priscilla Charles, Sarangapani Kanagamuthu, Stanley Ambroise, Pragasam Viswanathan, Palanivel Chinnakali, Rajesh Nachiappa Ganesh
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2022; 16(2): 1074. CrossRef - Association between Virulence Factors and Antimicrobial Resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates from North Kerala
Ramya Kumaran, R.V. Geetha, Sabitha Baby
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2022; 16(2): 867. CrossRef - Molecular Characterization and Mutational Analysis of Fluoroquinolones and Tetracycline Resistant Genes of Escherichia coli Isolated from UTI Patients
Sadiq Azam, Nauman Khan, Noor Rehman, Ibrar khan, Amjad Ali, Muhammad Asghar, Azam Hayat, Gulesehra Mujib, Anila Farid
Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns of Escherichia coli from Urine Isolates
Taher I. Mahmod Shailabi, Osama H. Aldeeb, Abdullah F. Almaedani, Elham O. Borwis, Samar A. Amer
Al-Mukhtar Journal of Sciences.2022; 37(4): 372. CrossRef - Possible Relationship of Novel Phylogenetic Structure With Antimicrobial Resistance, Biofilm Formation, and Hemolytic Activity in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC)
Batoul Rahimifard, Vahid Soheili, Gholamreza Hashemitabar, Mahdi Askari Badouei
International Journal of Enteric Pathogens.2022; 10(3): 98. CrossRef - Virulence genes and phylogenetic groups of uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates from patients with urinary tract infection and uninfected control subjects: a case-control study
Seyedeh Elham Rezatofighi, Mahsa Mirzarazi, Mansour Salehi
BMC Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance of uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) isolated from urinary tract infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Gabriel Kambale Bunduki, Eva Heinz, Vincent Samuel Phiri, Patrick Noah, Nicholas Feasey, Janelisa Musaya
BMC Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Biofilm Formation and Virulence Genes and Association with Antibiotic Resistance Patterns of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Strains in Southwestern Iran
Mostafa Boroumand, Asghar Sharifi, Mohammad Amin Ghatei, Mohsen Sadrinasab
Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The urobiome, urinary tract infections, and the need for alternative therapeutics
Jennifer Jones, Craig P. Murphy, Roy D. Sleator, Eamonn P. Culligan
Microbial Pathogenesis.2021; 161: 105295. CrossRef - Clinical cases, drug resistance, and virulence genes profiling in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Ali Hozzari, Payam Behzadi, Parisa Kerishchi Khiabani, Mohammad Sholeh, Niloofar Sabokroo
Journal of Applied Genetics.2020; 61(2): 265. CrossRef Prevalence of Virulence Genes and Their Association with Antimicrobial Resistance Among Pathogenic E. coli Isolated from Egyptian Patients with Different Clinical Infections
Rehab Mahmoud Abd El-Baky, Reham Ali Ibrahim, Doaa Safwat Mohamed, Eman Farouk Ahmed, Zeinab Shawky Hashem
Infection and Drug Resistance.2020; Volume 13: 1221. CrossRefIn-vitro Investigation of Antibiotics Efficacy Against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Biofilms and Antibiotic Induced Biofilm Formation at Sub-Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Ciprofloxacin
Zara Rafaque, Nasira Abid, Nida Liaquat, Pashmina Afridi, Saima Siddique, Safia Masood, Sehrish Kanwal, Javid Iqbal Dasti
Infection and Drug Resistance.2020; Volume 13: 2801. CrossRef- Relationship between Virulence and Resistance among Gram-Negative Bacteria
Virginio Cepas, Sara M. Soto
Antibiotics.2020; 9(10): 719. CrossRef - In Vitro and In Vivo Biological Activity of Berberine Chloride against Uropathogenic E. coli Strains Using Galleria mellonella as a Host Model
Giulio Petronio Petronio, Marco Alfio Cutuli, Irene Magnifico, Noemi Venditti, Laura Pietrangelo, Franca Vergalito, Antonella Pane, Giovanni Scapagnini, Roberto Di Marco
Molecules.2020; 25(21): 5010. CrossRef - Study of virulence factors and antibiotic susceptibility pattern of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli
Mahendraswamy B Hiremath, R Lava
Indian Journal of Microbiology Research.2020; 7(4): 330. CrossRef - Virulence factors of uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) and correlation with antimicrobial resistance
Chhaya Shah, Ratna Baral, Bijay Bartaula, Lok Bahadur Shrestha
BMC Microbiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcome of acute urinary tract infections caused by uropathogenic Escherichia coli with phenotypically demonstrable virulence factors
Unnimaya Pullanhi, Sadia Khan, Vivek Vinod, Karthika Mohan, Anil Kumar
Annals of African Medicine.2019; 18(3): 138. CrossRef - Urinary tract infection: Pathogenicity, antibiotic resistance and development of effective vaccines against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Mohammad Reza Asadi Karam, Mehri Habibi, Saeid Bouzari
Molecular Immunology.2019; 108: 56. CrossRef - Systematic analysis of research on D-mannose and the prospects for its use in recurrent infections of the urinary tract in women of reproductive age
O. A. Gromova, I. Yu. Torshin, N. K. Tetruashvili
Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproduction.2019; 13(2): 119. CrossRef - Evaluation of pap and sfa Genes Relative Frequency P and S Fimbriae Encoding of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Hospitals and Medical Laboratories; Yasuj City, Southwest Iran
Mostafa Boroumand, Asghar Sharifi, Leila Manzouri, Seyed Sajjad Khoramrooz, Seyed Abdolmajid Khosravani
Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Extended spectrum β-lactamase producing uropathogenic Escherichia coli and the correlation of biofilm with antibiotics resistance in Nepal
Raju Shrestha, Santosh Khanal, Pramod Poudel, Karan Khadayat, Sajani Ghaju, Anita Bhandari, Sunil Lekhak, Narayan Dutt Pant, Manisha Sharma, Bishnu P. Marasini
Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Genotyping and Molecular Characterization of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases-Producing Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli in and Around Coimbatore District, Tamil Nadu, India
Mylsamy Muraleetharan, Thirumoorthy Viswanathan
Urological Science.2019; 30(6): 244. CrossRef - Investigation of P Fimbriae Presence in Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Urine Samples in Human, and Their Antibacterial Resistance
Emel Inegol Paykoc, Suheyla Turkyilmaz
Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - An evaluation of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli isolates in urinary tract infections from Aguascalientes, Mexico: cross-sectional study
Flor Y. Ramírez-Castillo, Adriana C. Moreno-Flores, Francisco J. Avelar-González, Francisco Márquez-Díaz, Josée Harel, Alma L. Guerrero-Barrera
Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential Mechanisms Underlying the Increased Excitability of the Bladder Afferent Pathways in Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
Doo Sang Kim
Urogenital Tract Infection.2018; 13(2): 26. CrossRef - Distribution of virulence genes and their association with antimicrobial resistance among uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates from Iranian patients
Yalda Malekzadegan, Reza Khashei, Hadi Sedigh Ebrahim-Saraie, Zahra Jahanabadi
BMC Infectious Diseases.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Important Virulence Factors and Related Genes in Uropathogenic E. coli and their Relation to Fluoroquinolone Resistance
Noha Mohammad Gohar, Hanaa Fathy Aly, Magda Ibrahim Ayoub
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2018; 12(3): 1393. CrossRef - Clonal and Virulence Distribution of UropathogenicEscherichia coliIsolated from Children in Korea
Dong Ho Kim, Chul Hee Choi
Journal of Bacteriology and Virology.2017; 47(1): 54. CrossRef - An Epidemiological Study on the Prevalence and Antibiotic Resistance Patterns of Bacteria Isolated from Urinary Tract Infections in Central Iran
Fahimeh Ghanbari, Farzad Khademi, Shirin Saberianpour, Mojtaba Shahin, Nafiseh Ghanbari, Kourosh Naderi, Tahereh Motalebi-Rad
Avicenna Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infe.2017; 4(3): 42214. CrossRef - Correlation Between hlyA and cnf1 Virulent Genes with Antibiotic Resistance and non-ESBLs Escherichia coli Isolates Collected from Patient with Urinary Tract Infections in Kerman, Iran
Zahra Hashemizadeh, Davood Kalantar-Neyestanaki, Shahla Mansouri
Archives of Pediatric Infectious Diseases.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Antibiotic Resistance Profile of Enterobacteria Involved in Urinary Infections in Bamako, Mali
Amadou Hamadoun Babana
MOJ Biology and Medicine.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Phenotypic and Molecular Characterization of some Virulence Factors in Multidrug Resistance Escherichia coli Isolated from Different Clinical Infections in Iraq
Ahmed Abduljabbar Ja Aljanaby, Qassim Mmuhsin Hashi Alfaham
American Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Bio.2017; 7(2): 65. CrossRef - Emerging nanotechnology based strategies for diagnosis and therapeutics of urinary tract infections: A review
M.S. Kumar, A.P. Das
Advances in Colloid and Interface Science.2017; 249: 53. CrossRef - Effects of single and combined use of bacteriophages and antibiotics to inactivate Escherichia coli
Nádia Valério, Cristiana Oliveira, Vânia Jesus, Tatiana Branco, Carla Pereira, Catarina Moreirinha, Adelaide Almeida
Virus Research.2017; 240: 8. CrossRef - Crystal Structures of Acyclic Nucleoside Phosphonates in Complex with Escherichia coli Hypoxanthine Phosphoribosyltransferase
Wai Soon Eng, Dana Hocková, Petr Špaček, Ondřej Baszczyňski, Zlatko Janeba, Lieve Naesens, Dianne T. Keough, Luke W. Guddat
ChemistrySelect.2016; 1(19): 6267. CrossRef
- Multi-drug-resistant Escherichia coli in adult male patients with enlarged prostate attending general hospitals in Benue state
- A Study on the Characteristics of Infrequent and Frequent Outpatients Visiting Korean Traditional Medical Facilities
- Jinwon Yoon, Haemo Park, Chaeshin Chu, Sung-Yong Choi, Kibum Lee, Sundong Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2015;6(3):170-183. Published online June 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.06.001
- 2,618 View
- 17 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was intended to analyze the characteristics of infrequent and frequent outpatients visiting Korean medical facilities, and find the related variables of frequent users.
Methods
The data source was the Report on the Usage and Consumption of Korean Medicine (2011) published by the Ministry of Health and Welfare and Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. We analyzed outpatient data using SAS 9.2.
Results
As much as 46.6% of the patients used Korean medical services over 11 times in 3 months. The proportion of frequent users increased depending on age, and their proportion was high in the low-income and low-education group. People with musculoskeletal disease, stroke, hypertension, and obesity were more likely to use Korean medical services. In general, patients were satisfied with their treatment, with frequent outpatients being more satisfied than infrequent outpatients. In logistic regression analysis, age and musculoskeletal disease were significant determinants of frequency of use of Korean medical services.
Conclusion
Age, musculoskeletal disease, and specific diseases were highly associated with frequent Korean medical utilization. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Identifying the Relationship between the Korean Medicine and Western Medicine in Factors Affecting Medical Service Use
Young-eun Choi, Chul-woung Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(9): 1697. CrossRef - Association between subjective health status and frequency of visits to acupuncture clinic: A cross-sectional study
Takumi Kayo, Masao Suzuki, Ryuji Kato, Naoto Ishizaki, Tadamichi Mitsuma, Fumihiko Fukuda, Vijay S. Gc
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(11): e0277686. CrossRef - Characteristics of Herbal Medicine Users and Adverse Events Experienced in South Korea: A Survey Study
Soobin Jang, Kyeong Han Kim, Seung-Ho Sun, Ho-Yeon Go, Eun-Kyung Lee, Bo-Hyoung Jang, Yong-Cheol Shin, Seong-Gyu Ko
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medic.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Utilization Patterns of Korean Medicine: An Analysis of the National Health Insurance Cohort Database from 2002 to 2013
Sunju Park, In-Hwan Oh, Bo-Hyoung Jang, Minjung Park, YongCheol Shin, Kanghee Moon, Seong-Gyu Ko
The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medic.2016; 22(10): 824. CrossRef
- Identifying the Relationship between the Korean Medicine and Western Medicine in Factors Affecting Medical Service Use
- Determinants of the Length of Stay in Stroke Patients
- Sang Mi Kim, Sung Wan Hwang, Eun-Hwan Oh, Jung-Kyu Kang
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2013;4(6):329-341. Published online December 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2013.10.008
- 3,175 View
- 13 Download
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The study objective was to identify the factors that influence the length of stay (LOS) in hospital for stroke patients and to provide data for managing hospital costs by managing the LOS.
Methods
This study used data from the Discharge Injury Survey of the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which included 17,364 cases from 2005 to 2008.
Result
The LOS for stroke, cerebral infarction, intracerebral hemorrhage, and subarachnoid hemorrhage was 18.6, 15.0, 28.9, and 25.3 days, respectively. Patients who underwent surgery had longer LOS. When patients were divided based on whether they had surgery, there was a 2.4-time difference in the LOS for patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage, 2.0-time difference for patients with cerebral infarction, and 1.4-time difference for patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. The emergency route of admission and other diagnosis increased LOS, whereas hypertension and diabetic mellitus reduced LOS.
Conclusion
In the present rapidly changing hospital environments, hospitals approach an efficient policy for LOS, to maintain their revenues and quality of assessment. If LOS is used as the indicator of treatment expenses, there is a need to tackle factors that influence the LOS of stroke patients for each disease group who are divided based on whether surgery is performed or not for the proper management of the LOS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Teleneurocritical Care for Patients with Large Vessel Occlusive Ischemic Stroke Treated by Thrombectomy
Nick M. Murray, Scott Marshall, Robert Hoesch, Kyle Hobbs, Shawn Smith, Dean Roller, Katherine Thomas, Kevin Meier, Adrian Puttgen
Neurocritical Care.2023; 38(3): 650. CrossRef - Association Between Race and Length of Stay Among Stroke Patients: The National US Emergency Departments Data Set
Karan Patel, Kamil Taneja, Jared Wolfe, Joseph V. Campellone, Mudassir Farooqui, Santiago Ortega‐Gutierrez, James E. Siegler
Stroke: Vascular and Interventional Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Can HRV Predict Prolonged Hospitalization and Favorable or Unfavorable Short-Term Outcome in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke?
Joanna Aftyka, Jacek Staszewski, Aleksander Dębiec, Aleksandra Pogoda-Wesołowska, Jan Żebrowski
Life.2023; 13(4): 856. CrossRef - Does the Implementation of a National Health Insurance Program Result in Rationing Care for Ischemic Stroke Management? Analysis of the Indonesian National Health Insurance Program
Lisda Amalia
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy.2023; Volume 16: 455. CrossRef - Teleneurocritical care is associated with equivalent billable charges to in-person neurocritical care for patients with acute stroke
Nick M. Murray, Katherine Thomas, Dean Roller, Scott Marshall, Julie Martinez, Robert Hoesch, Kyle Hobbs, Shawn Smith, Kevin Meier, Adrian Puttgen
Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare.2023; : 1357633X2311661. CrossRef - Systematic Review of Resource Use and Costs in the Hospital Management of Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Steven Mulackal Thomas, Yarin Reindorp, Brandon R. Christophe, Edward Sander Connolly
World Neurosurgery.2022; 164: 41. CrossRef - Relationship between time of referral for physiotherapy and length of stay after stroke in a Nigerian tertiary hospital: a retrospective study
A. Aderonmu Joseph, O. Obembe Adebimpe
Bulletin of Faculty of Physical Therapy.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting length of stay in patients admitted to stroke rehabilitation with severe and moderate levels of functional impairments
Alejandro García-Rudolph, Blanca Cegarra, Eloy Opisso, Josep María Tormos, Montserrat Bernabeu, Joan Saurí
Medicine.2020; 99(43): e22423. CrossRef - Propensity score matching analysis on inpatient period differences of hemorrhagic stroke survivors depending on medical insurance coverage
Sang-Mi Kim, Young Kim, Seong-A Lee
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2019; 8(2): 67. CrossRef - Does service heterogeneity have an impact on acute hospital length of stay in stroke? A UK-based multicentre prospective cohort study
Michelle Tørnes, David McLernon, Max Bachmann, Stanley Musgrave, Elizabeth A Warburton, John F Potter, Phyo Kyaw Myint
BMJ Open.2019; 9(4): e024506. CrossRef - Can differences in length of stay between Dutch university hospitals and other hospitals be explained by patient characteristics? A cross-sectional study
Janine Ghielen, Sezgin Cihangir, Karin Hekkert, Ine Borghans, Rudolf Bertijn Kool
BMJ Open.2019; 9(2): e021851. CrossRef - The Factors Associated with the Fatal Outcome of Stroke
Andjela Milojevic Samanovic, Dragan Milovanovic, Vladimir Gajic, Aleksandar Raskovic, Dragan Milojevic
Serbian Journal of Experimental and Clinical Resea.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating the Duration of Hospitalization and Its Related Factors Among Stroke Patients
Maedeh Majidi Shad, Alia Saberi, Maryam Shakiba, Shademan Rezamasouleh
Caspian Journal of Neurological Sciences.2018; 4(15): 169. CrossRef - Racial differences in recurrent ischemic stroke risk and recurrent stroke case fatality
Karen C. Albright, Lei Huang, Justin Blackburn, George Howard, Michael Mullen, Vera Bittner, Paul Muntner, Virginia Howard
Neurology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Subacute Phase of Stroke
Hyunkyu Jeon, Min Kyun Sohn, Minsoo Jeon, Sungju Jee
Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine.2017; 41(4): 556. CrossRef - Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Patients Admitted to Intensive Care in Australia and New Zealand: A Multicenter Cohort Analysis of In-Hospital Mortality Over 15 Years
Andrew A. Udy, Chelsey Vladic, Edward Robert Saxby, Jeremy Cohen, Anthony Delaney, Oliver Flower, Matthew Anstey, Rinaldo Bellomo, David James Cooper, David V. Pilcher
Critical Care Medicine.2017; 45(2): e138. CrossRef
- Teleneurocritical Care for Patients with Large Vessel Occlusive Ischemic Stroke Treated by Thrombectomy
- The Impact of Emergency Room Utilization by Depression Patients on Medical Treatment Expense in Korea
- Hyun Sook Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2013;4(5):240-245. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2013.09.007
- 2,716 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To investigate the determinants of total medical expense for depression patients admitted through the emergency room (ER).
Methods
Data were selected from the Korean National Health Insurance sample data for 2009. SPSS version 18 was used for the statistical analysis such as descriptive analysis, correlation analysis, and multiple regression analysis. Data included 1203 cases admitted through the ER with ICD-10 codes (F31–F39).
Results
In the multiple regression analysis, significant variables affecting total payment were gender (p < 0.001), age (p < 0.001), main illness (p < 0.001), course of admission to the ER (p < 0.05), and length of stay (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
It is necessary to build a long-term program and system for high-risk depression groups. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The economic burden of adolescent internet addiction: A Korean health cost case study
Robert W. Mead, Edward Nall
The Social Science Journal.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Towards Actualizing the Value Potential of Korea Health Insurance Review and Assessment (HIRA) Data as a Resource for Health Research: Strengths, Limitations, Applications, and Strategies for Optimal Use of HIRA Data
Jee-Ae Kim, Seokjun Yoon, Log-Young Kim, Dong-Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2017; 32(5): 718. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on Total Payment of Mental and Behavioral Disorders Patients Admitted through the Emergency Room: Focusing on Main & Sub Sick
Hyun-Sik Choi, Hyun-Sook Lee
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(10): 562. CrossRef
- The economic burden of adolescent internet addiction: A Korean health cost case study



 First
First Prev
Prev


