Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Factors affecting depression and health-related quality of life in the elderly during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Deok-Ju Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(6):520-529. Published online November 16, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0166
- 853 View
- 42 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
This study investigated changes in the health behaviors of the elderly due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), concerns due to COVID-19, depression, and healthrelated quality of life (HRQOL), and aimed to identify factors that affect depression and HRQOL in the elderly. Methods: This study was conducted using data from the 2021 Community Health Survey of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. From a total sample size of 229,242 individuals, 74,376 elderly people aged 65 or older were selected as subjects, and changes in health behaviors, concerns due to COVID-19, depression, and HRQOL were measured and analyzed. Results: The level of depression associated with sleep and fatigue was high. The lowest HRQOL was related to physical pain and discomfort, while the most common concerns were related to economic difficulties. Factors influencing depression included worries about infection and economic harm, while factors impacting HRQOL encompassed concerns about infection, economic harm, and criticism from others. Conclusion: If an infectious disease situation such as COVID-19 reoccurs in the future, it will be necessary to encourage participation in hybrid online and offline programs at senior welfare centers. This should also extend to community counseling institutions like mental health welfare centers. Additionally, establishing connections with stable senior job projects can help to mitigate the effects of social interaction restrictions, physical and psychological health issues, and economic difficulties experienced by the elderly.
- Quality of life in patients treated for COVID-19–associated mucormycosis at a tertiary care hospital
- Pragya Kumar, Rajath Rao UR, Nilanjan Roy, Deepika Agrawal, Shamshad Ahmad, Kranti Bhavana
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(2):119-128. Published online April 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0307
- 1,970 View
- 57 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)–associated mucormycosis (CAM) has emerged as a formidable infection in patients with COVID-19. The aggressive management of CAM affects quality of life (QOL); thus, this study was designed to assess the QOL in patients with CAM at a tertiary healthcare institution.
Methods
This cross-sectional study of 57 patients with CAM was conducted over 6 months using a semi-structured standard questionnaire (the abbreviated World Health Organization Quality of Life questionnaire [WHO-BREF]) and a self-rated improvement (SRI) scale ranging from 0 to 9. Cut-off values of ≤52 and <7 were considered to indicate poor QOL and poor improvement, respectively. The correlations of QOL and SRI scores were evaluated using Spearman rho values.
Results
In total, 27 patients (47.4%; 95% confidence interval [CI], 34.9%–60.1%) and 26 patients (45.6%; 95% CI, 33.4%–58.4%) had poor QOL and poor SRI scores, respectively. The overall median (interquartile range) QOL score was 52 (41–63). Headache (adjusted B, −12.3), localized facial puffiness (adjusted B , −16.4), facial discoloration (adjusted B, −23.4), loosening of teeth (adjusted B, −18.7), and facial palsy (adjusted B, −38.5) wer e significantly associated with the QOL score in patients with CAM.
Conclusion
Approximately 1 in 2 patients with CAM had poor QOL and poor improvement. Various CAM symptoms were associated with QOL in these patients. Early recognition is the key to optimal treatment, improved outcomes, and improved QOL in patients with CAM.
- Factors influencing quality of life in caregivers of adolescents with developmental disabilities
- Joung Woo Joung
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(4):298-307. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0158
- 2,148 View
- 60 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Caring for adolescents with developmental disabilities (DD) is stressful and challenging, and mothers usually provide care for these children in Korea. This study aimed to identify factors influencing quality of life (QoL) in mothers of adolescents with DD.
Methods
A predictive design was used. Data were collected from a web-based survey administered to a convenience sample of 154 mothers of adolescents with DD from October to November 2020. Data were analyzed using the t-test, analysis of variance, Pearson correlation coefficients, and multiple regression.
Results
Perceived health, depression, and family strength were significantly correlated with QoL. Multiple regression showed that family strength, perceived health, depression, and monthly household income influenced the participants’ QoL, and these factors accounted for 69.2% of variance in QoL. Family strength was the factor most strongly affecting QoL (β=0.39).
Conclusion
The study results indicate that health professionals and policy-makers need to pay attention to the overall QoL and physical and psychological health of mothers of adolescents with DD. Since our findings raise the importance of family strength in the QoL of this population, programs to improve family strength need to be implemented and strengthened. Interventions to improve perceived health and decrease depression should be applied, and knowledge on adolescent characteristics and changes should be delivered to caregivers when providing education and consultations. The findings will be helpful for developing educational and counseling programs for this population.
- Predictors of health-related quality of life in Koreans with cardiovascular disease
- Jung-Hye Lim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(1):62-70. Published online February 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0286
- 3,949 View
- 86 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 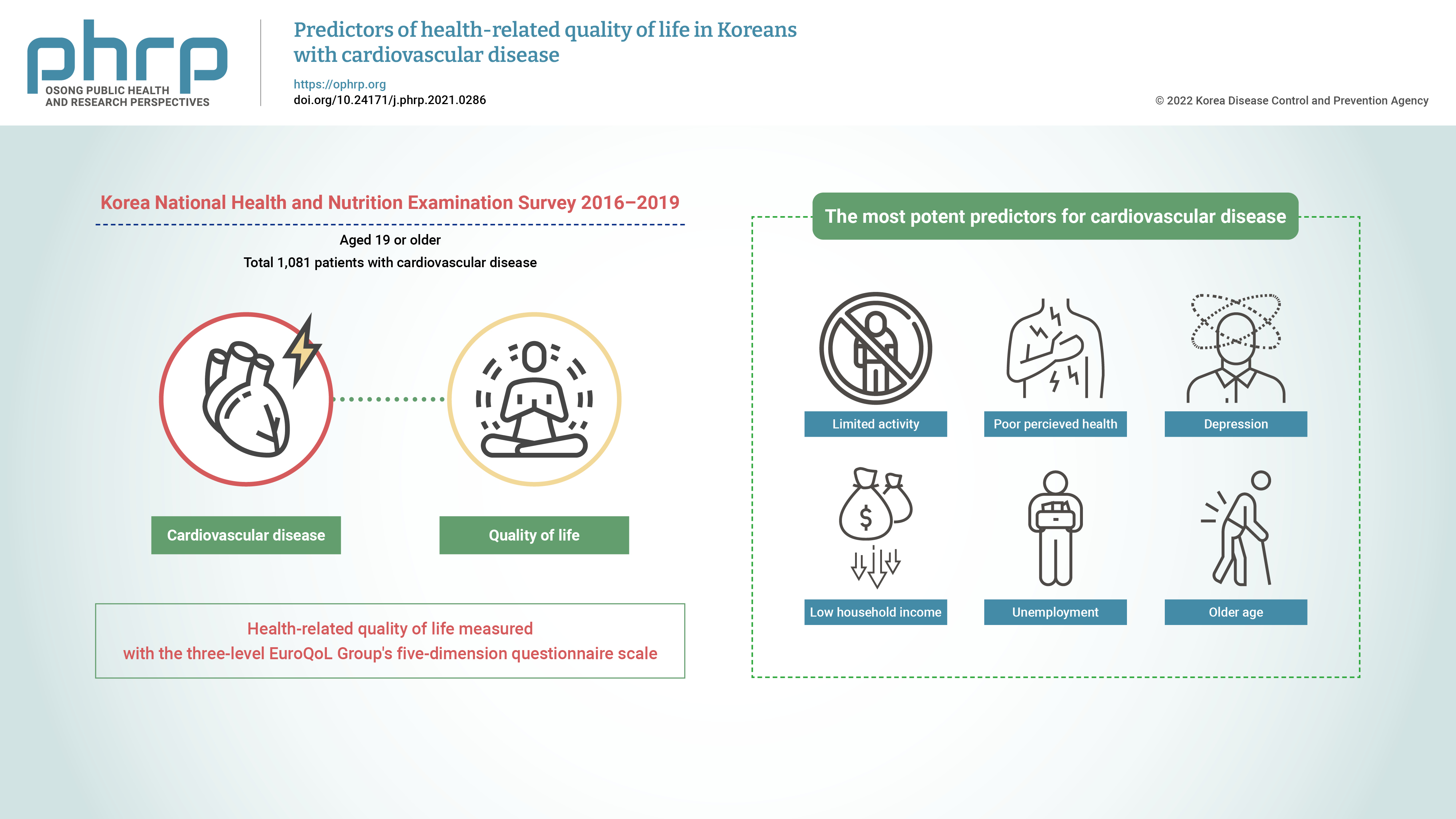
- Objectives
This study aimed to identify the predictors of health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in Korean adults with cardiovascular disease (CVD). Methods: This was a cross-sectional study with a stratified multistage probability sampling design. Data from the 2016 to 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (n=32,379) were used. Among the participants aged 19 years or older (n=25,995), 1,081 patients with CVD were extracted after excluding those with missing data and those who had cancer. The participants’ HRQoL was measured using the three-level EuroQoL Group’s five-dimension questionnaire (EQ-5D) scale. Data were analyzed using the t-test, one-way analysis of variance, and general linear regression for complex samples. Results: The most potent predictors of HRQoL in Korean adults with CVD were limited activity (β =−0.103, p <0.001), poor perceived health (β =−0.089, p <0.001), depression (β =−0.065, p<0.01), low household income (β=−0.033, p<0.05), unemployment (β=−0.023, p<0.05), and older age (β=−0.002, p<0.01), which explained 37.2% of the variance. Conclusion: Comprehensive interventions that address both physical and mental factors and social systems that provide financial help need to be implemented to improve the HRQoL of Korean adults with CVD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with health-related quality of life in patients with coronary heart disease
Febio Gutama, Melisa Intan Barliana, Irma Melyani Puspitasari
Pharmacia.2022; 69(3): 771. CrossRef
- Factors associated with health-related quality of life in patients with coronary heart disease
- Effects of activities of daily living-based dual-task training on upper extremity function, cognitive function, and quality of life in stroke patients
- Hee-Su An, Deok-Ju Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(5):304-313. Published online September 13, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0177
- 10,786 View
- 306 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of daily living dual-task training focused on improving attention and executive function of the upper extremities, cognitive function, and quality of life in stroke patients.
Methods
We included 30 stroke patients who were hospitalized between July 2020 and October 2020. They were divided into experimental and control groups through randomization. The experimental group performed 20 minutes of dual-task training and received 10 minutes of conventional occupational therapy, while the control group performed 20 minutes of single-task training and received 10 minutes of conventional occupational therapy. Both groups underwent their respective rehabilitation for 30 minutes per session, 5 times per week for 5 weeks.
Results
Both groups showed significant improvements in upper extremity function, cognitive function, and quality of life; the experimental group showed higher results for all items. A significant between-group difference was observed in the magnitude of the changes.
Conclusion
In stroke patients, dual-task training that combined attention and executive function with daily living activities was found to be meaningful, as it encouraged active participation and motivation. This study is expected to be used as a foundation for future interventions for stroke patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intervention and assessment of executive dysfunction in patients with stroke: A scoping review
Katsuya Sakai, Yuichiro Hosoi, Junpei Tanabe, Kathleen Bennett
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0298000. CrossRef - Occupation-based interventions to improve occupational performance and participation in the hospital setting: a systematic review
Gemma Wall, Stephen Isbel, Louise Gustafsson, Claire Pearce
Disability and Rehabilitation.2023; : 1. CrossRef - The effect of five activities daily living on improving cognitive function in ischemic stroke patients
Frana Andrianur, Dwi Prihatin Era, Arifin Hidayat, Ismansyah Ismansyah, Diah Setiani
Healthcare in Low-resource Settings.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Upper Limb Motor Rehabilitation on Cognition in Parkinson’s Disease: An Observational Study
Valentina Varalta, Elisa Evangelista, Anna Righetti, Giovanni Morone, Stefano Tamburin, Alessandro Picelli, Cristina Fonte, Michele Tinazzi, Ilaria Antonella Di Vico, Andreas Waldner, Mirko Filippetti, Nicola Smania
Brain Sciences.2022; 12(12): 1684. CrossRef
- Intervention and assessment of executive dysfunction in patients with stroke: A scoping review
- Validity and reliability of the Health-Related Quality of Life Instrument with 8 Items (HINT-8) in Korean breast cancer patients
- Juyoung Kim, Min-Woo Jo, Hyeon-Jeong Lee, Sei-Hyun Ahn, Byung Ho Son, Jong Won Lee, Sae Byul Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(4):254-263. Published online August 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0005
- 6,580 View
- 126 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
This study evaluated the validity and reliability of the Health-Related Quality of Life Instrument with 8 Items (HINT-8) in postoperative breast cancer patients in South Korea.
Methods
The study included 300 breast cancer patients visiting a tertiary hospital. We measured health-related quality of life (HRQoL) using the HINT-8, the 5-level EQ-5D version (EQ-5D-5L), and the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast (FACT-B). Discriminatory ability, known-group validity, and convergent validity were assessed. Reliability was evaluated with the Cohen kappa, weighted kappa, and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC).
Results
The EQ-5D-5L indexes (p<0.001) and EQ visual analogue scale (VAS) scores (p<0.001) were significantly higher in subjects with no problems in each item of the HINT-8 than in those with problems. The FACT-B total scores were also higher in subjects without problems on the HINT-8. Older age, lower education level, and comorbidities were associated with a lower HINT-8 index. The HINT-8 index was correlated with the EQ-5D-5L index and the EQ VAS, with correlation coefficients of 0.671 (p<0.001) and 0.577 (p<0.001), respectively. The correlation coefficients between the HINT-8 and the FACT-B ranged from 0.390 to 0.714. The ICC was 0.690 (95% confidence interval, 0.580–0.780).
Conclusion
The HINT-8 showed appropriate validity for capturing HRQoL in postoperative breast cancer patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health-related quality of life of premenopausal young breast cancer survivors undergoing endocrine therapy
Kyungmi Lee, Hye Suk Jun
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2024; 68: 102496. CrossRef - Smartphone application-based rehabilitation in patients with chronic respiratory and cardiovascular diseases
Chiwook Chung, Ah-Ram Kim, Dongbum Kim, Hee Kwon, Seong Ho Lee, Il-Young Jang, Min-Woo Jo, Do-Yoon Kang, Sei Won Lee
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Willingness to pay for integrative healthcare services to treat sleep disturbances: Evidence from a nationwide survey
Min Kyung Hyun
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2023; 58: 102223. CrossRef - Internal Structure of the Health-Related Quality of Life Instrument with 8-Items in a Nationally Representative Population
Eun-Hyun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(3): 359. CrossRef - Factors influencing health-related quality of life for young single-person households: the mediating effect of resilience
Soo Jin Lee, Sujin Lee, Xianglan Jin
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(3): 160. CrossRef - Smartphone application-based rehabilitation in patients with chronic respiratory and cardiovascular diseases: a randomised controlled trial study protocol
Chiwook Chung, Ah-Ram Kim, Il-Young Jang, Min-Woo Jo, Seongho Lee, Dongbum Kim, Hee Kwon, Do-Yoon Kang, Sei Won Lee
BMJ Open.2023; 13(9): e072698. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life among cancer patients and survivors and its relationship with current employment status
Woorim Kim, Kyu-Tae Han, Seungju Kim
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(5): 4547. CrossRef - Associations between Food Groups and Health-Related Quality of Life in Korean Adults
Shamirah Nabbosa, Sunghee Lee
Nutrients.2022; 14(17): 3643. CrossRef - Validity of the Health-Related Quality of Life Instrument with 8 Items (HINT-8) in the Korean Elderly: A Cross-Sectional Study
Seon-Ha Kim, Miok Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(3): 248. CrossRef
- Health-related quality of life of premenopausal young breast cancer survivors undergoing endocrine therapy
- Impact of fatigue on quality of life among breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy
- Fares Mohammed Saeed Muthanna, Mahmathi Karuppannan, Bassam Abdul Rasool Hassan, Ali Haider Mohammed
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(2):115-125. Published online April 29, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.12.2.09
- 7,764 View
- 271 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Fatigue is the most frequently reported symptom experienced by cancer patients and has a profound effect on their quality of life (QOL). The study aimed to determine the impact of fatigue on QOL among breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy and to identify the risk factors associated with severe fatigue incidence.
Methods
This was an observational prospective study carried out at multiple centers. In total, 172 breast cancer patients were included. The Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue Questionnaire was used to measure QOL, while the Brief Fatigue Inventory (BFI) was used to assess the severity of fatigue.
Results
The total average mean and standard deviation of QOL were 84.58±18.07 and 4.65±1.14 for BFI scores, respectively. A significant association between fatigue and QOL was found in linear and multiple regression analyses. The relationships between fatigue severity and cancer stage, chemotherapy dose delay, dose reduction, chemotherapy regimen, and ethnicity were determined using binary logistic regression analysis.
Conclusion
The findings of this study are believed to be useful for helping oncologists effectively evaluate, monitor, and treat fatigue related to QOL changes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Therapeutic Exercise Models on Cancer-Related Fatigue in Patients With Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis
Aida Herranz-Gómez, Ferran Cuenca-Martínez, Luis Suso-Martí, Clovis Varangot-Reille, Miriam Prades-Monfort, Joaquín Calatayud, Jose Casaña
Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation.2023; 104(8): 1331. CrossRef - Anatomical Sites OF Superficial Basal Cell Cancers Demonstrate Higher Rates of Mixed Histology
Zahid Sarfaraz Khan, Asim Muhammad, Muhammad Ataullah, Syeda Gulrukh Saba Shah, Tehmina Naushin, Hina Mir, Nabiha Naeem, Ziyad Ahmad, Sudhair Abbas Bangash, Irfan Ullah
Pakistan BioMedical Journal.2022; : 44. CrossRef - Glycated Albumin's Clinical Effectiveness in The Diabetes Diagnosis
Summeira Jabeen Shah, Hajira Ishaq, Hina Hakeem, Saima Shaheen, Sikandar Ali Khan, Sosan Rauf, Hina Mir, Sudhair Abbas Bangash, Muhammad Ali, Irfan Ullah
Pakistan BioMedical Journal.2022; : 176. CrossRef - Post stroke intervention trial in fatigue (POSITIF): Randomised multicentre feasibility trial
Gillian Mead, David Gillespie, Mark Barber, Allan House, Steff Lewis, Hannah Ensor, Simiao Wu, Trudie Chalder
Clinical Rehabilitation.2022; 36(12): 1578. CrossRef - Quality of Life and Its Associated Factors Among Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy at Oncology Hospitals in Vietnam After the Third Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic
Hanh TH Nguyen, Khanh Linh Duong, Son T Nguyen, Quy Trinh, Hao TL Hoang, Toan Q Phung, Hsiang-Wen Lin, Huong TL Nguyen
Cancer Management and Research.2022; Volume 14: 2429. CrossRef - Effects of traditional Chinese medicine exercise therapy on cancer-related fatigue, anxiety and sleep quality in cancer patients
Lihao Jiang, Ju Ouyang, Xianfeng Du
Medicine.2021; 100(44): e27681. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Therapeutic Exercise Models on Cancer-Related Fatigue in Patients With Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis
- Health-Related Quality of Life and its Associated Factors in COVID-19 Patients
- Morteza Arab-Zozani, Fatemah Hashemi, Hossein Safari, Mahmood Yousefi, Hosein Ameri
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(5):296-302. Published online October 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.5.05
- 13,138 View
- 482 Download
- 68 Web of Science
- 81 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) is one of the most important outcome measures for patients. The purpose of this study was to evaluate HRQoL and related factors in Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients.
Methods A total of 420 COVID-19 patients who had been discharged from hospital were selected using a systematic sampling. The EuroQol 5-dimensional-5 levels (EQ-5D-5L) questionnaire along with medical records of the patients were used to gather the data. The
t test and analysis of variance were employed to test the difference between mean EQ-5D-5L scores, and the BetaMix model was used to investigate factors associated with EQ-5D-5L scores.Results The mean score for the patients who completed the EQ-5D-5L questionnaire (
n = 409) was 0.6125. The EQ-5D-5L scores were significantly higher in males, patients with younger age, those with a low level of education, the employed, patients who worked in uncrowded workplaces, patients without diabetes, and those who were not admitted to intensive care unit. The BetaMix model showed that gender, age, education, employment status, having diabetes, heart failure, and admission to the intensive care unit were significant independent predictors of the EQ-5D-5L index values.Conclusion The mean score for EQ-5D-5L in COVID-19 patients was low in this study. Some of the factors, especially aging and having diabetes, should be considered in the aftercare of patients to improve their HRQoL.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Examining the Trajectory of Health-Related Quality of Life among Coronavirus Disease Patients
Jia Li, Juan P. Wisnivesky, Jenny J. Lin, Kirk N. Campbell, Liangyuan Hu, Minal S. Kale
Journal of General Internal Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-related quality of life among adults living with chronic non-communicable diseases in the Ho Municipality of Ghana: a health facility-based cross-sectional study
William Kwame Witts, Hubert Amu, Robert Kokou Dowou, Frank Oppong Kwafo, Luchuo Engelbert Bain
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A lifestyle adjustments program in long COVID-19 improves symptomatic severity and quality of life. A randomized control trial
A. Navas-Otero, A. Calvache-Mateo, I. Calles-Plata, G. Valenza-Peña, S. Hernández-Hernández, A. Ortiz-Rubio, MC Valenza
Patient Education and Counseling.2024; 122: 108180. CrossRef - Actividad física, independencia funcional y calidad de vida relacionada con la salud en los pacientes post COVID-19
J. Rodríguez-Castro, J. Betancourt-Peña
Fisioterapia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The influence of nutritional status and associated factors on the quality of life among COVID-19 patients in Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional study
Ahlam B. El Shikieri, Ahmad H. Hafiz, Opeyemi E. Adewumi, Oluwatobi E. Fijabi
Human Nutrition & Metabolism.2024; 36: 200262. CrossRef - Symptoms, Mental Health, and Quality of Life Among Patients After COVID-19 Infection: A Cross-sectional Study in Vietnam
Hai Nguyen Thanh, Duc Cap Minh, Hien Hoang Thu, Duc Nguyen Quang
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2024; 57(2): 128. CrossRef - Association of Pulmonary Function Test Abnormalities and Quality-of-Life Measures after COVID-19 Infection.
James Bradley, Qian Xu, Nikolas Touloumes, Eugene Lusciks, T'shura Ali, Emma C. Huang, James Chen, Shahab Ghafghazi, Forest W Arnold, Maiying Kong, Jiapeng Huang, Rodrigo Cavallazzi, Ahmed Abdelhaleem Mohamed Fawzy Abdelhaleem, Lucia Belen Puga Sanchez, R
The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, depression and related factors among COVID-19 patients during the fourth wave of the pandemic in Vietnam
Hoang Bac Nguyen, Thi Hong Minh Nguyen, Thi Hong Nhan Vo, Thi Cam Nhung Vo, Duc Nguyet Quynh Nguyen, Huu-Thinh Nguyen, Tuan-Ngan Tang, Thi-Hiep Nguyen, Van Trang Do, Quang Binh Truong
International Health.2023; 15(4): 365. CrossRef - One-year follow-up of depression, anxiety, and quality of life of Peruvian patients who survived COVID-19
Jeff Huarcaya-Victoria, Christoper A. Alarcon-Ruiz, William Barzola-Farfán, Claudia Cruzalegui-Bazán, Michaell Cabrejos-Espinoza, Gabriela Aspilcueta-Montoya, Feleydi Cornero-Quispe, Javier Salazar-Bellido, Beltrán Villarreal
Quality of Life Research.2023; 32(1): 139. CrossRef - Postdischarge pain, fatigue severity and quality of life in COVID-19 survivors
Esma DEMİRHAN, Sevgi ATAR, Günay ER, İpek OKUTAN, Ömer KURU
The European Research Journal.2023; 9(1): 57. CrossRef - Salud mental de cuidadores de niños con trastornos del neurodesarrollo durante la pandemia
Jorge Emiro Restrepo, Tatiana Castañeda-Quirama, Mónica Gómez-Botero, David Molina-González
Neurología Argentina.2023; 15(1): 28. CrossRef - The trend in quality of life of Chinese population: analysis based on population health surveys from 2008 to 2020
Dingyao Wang, Shitong Xie, Jing Wu, Bei Sun
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Post-discharge quality of life of COVID-19 patients at 1-month follow-up: A cross-sectional study in the largest tertiary care hospital of Bangladesh
Mohammad Mahfuzul Hoque, Ponkaj Kanti Datta, Kamalesh Chandra Basu, Muhammad Faizur Rahman, Mohammed Masudul Hassan Khan, Mohammad Mostafa Kamal, Reaz Mahmud, Kazi Ali Aftab, Ejrarul Alam Khan, Imran Mahmud, Rumana Sharmin, Md. Abdullah Saeed Khan, Mohamm
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(1): e0280882. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life and associated factors among COVID-19 individuals managed with Indian traditional medicine: A cross-sectional study from South India
Rajalakshmi Elumalai, Bhavani Shankara Bagepally, Manickam Ponnaiah, Tarun Bhatnagar, Suganya Barani, Poornima Kannan, Lakshmi Kantham, P. Sathiyarajeswaran, Sasikumar D
Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health.2023; 20: 101250. CrossRef - The influencing factors of health–related quality of life of the general population of Iran during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Maryam Shirvani Shiri, Hassan Karami, Hosein Ameri, Ali Akbari Sari, Maryam Tatari, Sara Emamgholipour, Somayeh Afshari
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life of COVID-19 Survivors Treated in Intensive Care Unit—Prospective Observational Study
Josipa Domazet Bugarin, Lenko Saric, Nikola Delic, Svjetlana Dosenovic, Darko Ilic, Ivana Saric, Sanda Stojanovic Stipic, Bozidar Duplancic
Journal of Intensive Care Medicine.2023; 38(8): 710. CrossRef - Pain and Clinical Presentation: A Cross-Sectional Study of Patients with New-Onset Chronic Pain in Long-COVID-19 Syndrome
Andrés Calvache-Mateo, Laura López-López, Javier Martín-Núñez, Alejandro Heredia-Ciuró, María Granados-Santiago, Araceli Ortiz-Rubio, Marie Carmen Valenza
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2023; 20(5): 4049. CrossRef - Evaluation and follow-up of pain, fatigue, and quality of life in COVID-19 patients
Sevda Adar, Petek Şarlak Konya, Ali İzzet Akçin, Ümit Dündar, Neşe Demirtürk
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(1): 40. CrossRef - Validation of the Slovakian Version of the “Post‑acute (Long) COVID‑19 Quality of Life Instrument” and Pilot Study
Romana Ulbrichtova, Peter Vysehradsky, Alica Bencova, Maria Tatarkova, Oto Osina, Viera Svihrova, Henrieta Hudeckova
Patient Preference and Adherence.2023; Volume 17: 1137. CrossRef - Quality of life in patients treated for COVID-19–associated mucormycosis at a tertiary care hospital
Pragya Kumar, Rajath Rao UR, Nilanjan Roy, Deepika Agrawal, Shamshad Ahmad, Kranti Bhavana
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(2): 119. CrossRef - Clinical characterization and factors associated with quality of life in Long COVID patients: Secondary data analysis from a randomized clinical trial
Mario Samper-Pardo, Sandra León-Herrera, Bárbara Oliván-Blázquez, Santiago Gascón-Santos, Raquel Sánchez-Recio, Gustavo Plaza-Manzano
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(5): e0278728. CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life for Jordanian-Recovered Individuals During Post-COVID-19 Era: A Cross-Sectional Study
Sawsan Abuhammad, Omar F Khabour, Karem H Alzoubi, Shaher Hamaideh, Basheer Y Khassawneh, Amat Al-Khaleq O Mehrass, Baha F Alsmadi, Abdelrahman M Ababneh
Patient Preference and Adherence.2023; Volume 17: 1303. CrossRef - Physical therapy management of an individual with post-COVID fatigue considering emotional health in an outpatient setting: A case report
Neeti Pathare, Dylan MacPhail
Physiotherapy Theory and Practice.2023; : 1. CrossRef - RETRACTED: Post-acute (long) COVID-19 quality of life: validation of the German version of (PAC19QoL) instrument
Srikanth Umakanthan, Mariam Monice, Salona Mehboob, Cheryl Linda Jones, Sam Lawrence
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Primary Allied Health Care in Patients Recovering From COVID-19 at 6-Month Follow-up: Dutch Nationwide Prospective Cohort Study
Anne I Slotegraaf, Marissa H G Gerards, Arie C Verburg, Marian A E de van der Schueren, Hinke M Kruizenga, Maud J L Graff, Edith H C Cup, Johanna G Kalf, Antoine F Lenssen, Willemijn M Meijer, Renée A Kool, Rob A de Bie, Philip J van der Wees, Thomas J Ho
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e44155. CrossRef - Predictors of fear control related to COVID-19 among older population: an investigation on COVID-19 risk perception and health related quality of life during the pandemic
Saeedeh Avazzadeh, Neda Gilani, Leila Jahangiry
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Post COVID-19 condition and health-related quality of life: a longitudinal cohort study in the Belgian adult population
Pierre Smith, Robby De Pauw, Dieter Van Cauteren, Stefaan Demarest, Sabine Drieskens, Laura Cornelissen, Brecht Devleesschauwer, Karin De Ridder, Rana Charafeddine
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Health and well-being of the Portuguese citizens: impacts of the COVID-19
Lara N. Ferreira, Luís N. Pereira, Pedro L. Ferreira
Journal of Patient-Reported Outcomes.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Qol among COVID-19 Patients in South India: A Tertiary Care Center Study: An Original Research
Sreedevi Janapareddi, Kiran S. Shankar, Mansi Mendiratta, Neha Chauhan, Sachin Kumar Jadhav, Divya Jahagirdar
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2023; 15(Suppl 1): S218. CrossRef - Cost-effectiveness of therapeutics for COVID-19 patients: a rapid review and economic analysis
Andrew Metry, Abdullah Pandor, Shijie Ren, Andrea Shippam, Mark Clowes, Paul Dark, Ronan McMullan, Matt Stevenson
Health Technology Assessment.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 Infection on Health-Related Quality of Life, Work Productivity and Activity Impairment by Symptom-Based Long COVID Status and Age in the US
Manuela Di Fusco, Joseph C. Cappelleri, Laura Anatale-Tardiff, Henriette Coetzer, Alon Yehoshua, Mary B. Alvarez, Kristen E. Allen, Thomas M. Porter, Laura Puzniak, Ashley S. Cha-Silva, Santiago M. C. Lopez, Xiaowu Sun
Healthcare.2023; 11(20): 2790. CrossRef - Post-COVID-19 fatigue and health-related quality of life in Saudi Arabia: a population-based study
Moath S. Al-Johani, Rehana Khalil, Yazeed A. Al-Mohaimeed, Omar M. Al-Mundarij, Abdulmajeed S. Al-Samani, Osama S. Al-saqry, Alwaleed A. Al-saawi, Ibrahim K. Al-dhali, Waleed A. Al-Essa
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Calidad de vida relacionada con la salud en chilenos de comunas vulnerables
Isabel Rada, Manuel S. Ortiz, Baltica Cabieses
Gaceta Sanitaria.2023; 37: 102328. CrossRef - One-year quality of life among post-hospitalization COVID-19 patients
Ignacio Pérez Catalán, Celia Roig Martí, Sergio Fabra Juana, Elena Domínguez Bajo, Germán Herrero Rodríguez, Ana Segura Fábrega, María Varea Villanueva, Sofía Folgado Escudero, María José Esteve Gimeno, Daniela Palomo de la Sota, Alejandro Cardenal Álvare
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Body Mass Index, Physical Activity and Quality of Life amongst Older People in Malaysia during COVID-19: A Cross-Sectional Analysis
Nor Safura Mohd Noor, Nur Kamilah Mohd Fauzy, Sakinah Harith, Wan Rohani Wan Taib, Rosliza Yahaya, Almira Sitasari, Furaida Khasanah
Malaysian Journal of Medicine and Health Sciences.2023; 19(6): 42. CrossRef - Quality of Life in Adolescents and Young Adults with Cleft Lip and Palate with and Without Speech Therapy During COVID-19
Zahra Moshtaghi Fard, Samira Aghadoost, Negin Moradi, Sarvin Sarmadi, Farnoosh Mohammadi, Naghmeh Bahrami
The Cleft Palate Craniofacial Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Health related quality of life in adults with asthma: a systematic review to identify the values of EQ-5D-5L instrument
Somayeh Afshari, Hosein Ameri, Rajab Ali Daroudi, Maryam Shiravani, Hassan Karami, Ali Akbari Sari
Journal of Asthma.2022; 59(6): 1203. CrossRef - Evaluation of perceived fears of COVID-19 virus infection and its relationship to health-related quality of life among patients with diabetes mellitus in Egypt during pandemic: a developing country single-center study
Mohamed Abdelghani, Mohamed G. Hamed, Amira Said, Eman Fouad
Diabetology International.2022; 13(1): 108. CrossRef - Post‐acute COVID‐19 syndrome (PCS) and health‐related quality of life (HRQoL)—A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Preeti Malik, Karan Patel, Candida Pinto, Richa Jaiswal, Raghavendra Tirupathi, Shreejith Pillai, Urvish Patel
Journal of Medical Virology.2022; 94(1): 253. CrossRef - Infección grave por SARS-CoV-2: valoración clínica y evaluación funcional biomecánica al mes del alta hospitalaria
A. Ezzeddine Angulo, J.M. Elía Martínez, V. Iñigo Huarte, I. Máñez Añón, J.M. Tenías Burillo, F. Peydro de Moya
Rehabilitación.2022; 56(2): 142. CrossRef - Quality of life and other patient-reported outcomes in adult Lebanese patients with type 2 diabetes during COVID-19 pandemic
E. Naous, M. Boulos, G. Sleilaty, A. A. Achkar, M.-H. Gannagé-Yared
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2022; 45(4): 763. CrossRef - Economic evaluations of inactivated COVID-19 vaccines in six Western Pacific and South East Asian countries and regions: A modeling study
Yawen Jiang, Dan Cai, Si Shi
Infectious Disease Modelling.2022; 7(1): 109. CrossRef - Psychological Symptoms in COVID-19 Patients: Insights into Pathophysiology and Risk Factors of Long COVID-19
Angel Yun-Kuan Thye, Jodi Woan-Fei Law, Loh Teng-Hern Tan, Priyia Pusparajah, Hooi-Leng Ser, Sivakumar Thurairajasingam, Vengadesh Letchumanan, Learn-Han Lee
Biology.2022; 11(1): 61. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life among COVID-19 individuals: A cross-sectional study in Tamil Nadu, India
Suganya Barani, Tarun Bhatnagar, Meenakumari Natarajan, Kumari Gayathri, Harshal Bhimrao Sonekar, Akhil Sasidharan, T.S. Selvavinayagam, Bhavani Shankara Bagepally
Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health.2022; 13: 100943. CrossRef - Evaluation of post-COVID health status using the EuroQol-5D-5L scale
Siddhi Hegde, Shreya Sreeram, Kaushik R Bhat, Vaishnavi Satish, Sujith Shekar, Mahesh Babu
Pathogens and Global Health.2022; 116(8): 498. CrossRef - European Respiratory Society statement on long COVID follow-up
Katerina M. Antoniou, Eirini Vasarmidi, Anne-Marie Russell, Claire Andrejak, Bruno Crestani, Marion Delcroix, Anh Tuan Dinh-Xuan, Venerino Poletti, Nicola Sverzellati, Michele Vitacca, Martin Witzenrath, Thomy Tonia, Antonio Spanevello
European Respiratory Journal.2022; 60(2): 2102174. CrossRef - Quality of life of COVID 19 patients after discharge: Systematic review
H. M. R. K. G. Nandasena, M. L. Pathirathna, A. M. M. P. Atapattu, P. T. S. Prasanga, Mohamed A Yassin
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(2): e0263941. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Poor Treatment Outcome among Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients in South Central, Ethiopia
Abdene Weya Kaso, Habtamu Endashaw Hareru, Taha Kaso, Gebi Agero, Mohd Saeed
BioMed Research International.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - The health-related quality of life in patients with post-COVID-19 after hospitalization: a systematic review
Eduardo Augusto Barbosa Figueiredo, Whesley Tanor Silva, Sabrina Pinheiro Tsopanoglou, Débora Fernandes de Melo Vitorino, Luciano Fonseca Lemos de Oliveira, Keity Lamary Souza Silva, Hiago Daniel Herédia Luz, Matheus Ribeiro Ávila, Lucas Fróis Fernandes d
Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropic.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality of life during COVID-19 pandemic: a community-based study in Dakahlia governorate, Egypt
Shorouk Mohsen, Ragaa El-Masry, Olfat Farag Ali, Doaa Abdel-Hady
Global Health Research and Policy.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality of life (QoL) among COVID-19 recovered healthcare workers in Bangladesh
Md Utba Rashid, Md Abdullah Saeed Khan, Koustuv Dalal, Soumik Kha Sagar, Mosharop Hossian, Sabrina Yesmin Barsha, Miah Md. Akiful Haque, Mohammad Ali Hossain, Mohammad Hayatun Nabi, Mohammad Delwer Hossain Hawlader
BMC Health Services Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - ASSESSMENT OF QUALITY OF LIFE AND EFFECTS IN RECOVERED AND VACCINATED COVID-19 POPULATION: A CROSS-SECTIONAL OBSERVATIONAL STUDY
VANLALFAKZELI, VARADHA PAYANGOTT, ABUBAKER SIDDIQ
International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutic.2022; : 1. CrossRef - The Persistent Symptoms and Decreased Quality of Life of COVID-19 Patients (A 3-month Follow-up after Discharge)
Nur Farhanah, Charles Budiman, Muchlis Achsan Udji Sofro, Budi Riyanto, Suharyo Hadisaputro, Muhammad Hussein Gasem
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(B): 1419. CrossRef - Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices Regarding “New Normal” Guidelines and Quality of Life Among Thai People During the COVID-19 Outbreak: An Online Cross-Sectional Survey
Pathavee Waewwab, Wirichada Pan-ngum, Sukhontha Siri, Bhophkrit Bhopdhornangkul, Wiriya Mahikul
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Patterns in the relationship between acute COVID-19/long COVID-19 and quality of life: A cross-sectional study of patients attending a tertiary care hospital in Turkey
Hakan Tuzun, Cansu Özbaş, Burkay Budak, Gizem Altunay, FN Baran Aksakal
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine.2022; 15(6): 274. CrossRef - The effect of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) according to gender on health-related quality of life
Betül ÇİFTÇİ
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2022; 5(4): 1030. CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life of Moroccan COVID-19 Survivors: A Case-Control Study
Asmaa Azizi, Doha Achak, Elmadani Saad, Abderraouf Hilali, Chakib Nejjari, Mohamed Khalis, Ibtissam Youlyouz-Marfak, Abdelghafour Marfak
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(14): 8804. CrossRef - Food Intake Changes and Their Impact on Quality of Life in Spanish Citizens with and without COVID-19 during Lockdown
María García-de-Miguel, Elisabet Huertas-Hoyas, Jorge Pérez-Corrales, Cristina Rodríguez-Rivas, Cristina García-Bravo, Sara García-Bravo, Lucía Rocío Camacho-Montaño
Healthcare.2022; 10(8): 1414. CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life and Its Socio-Demographic and Behavioural Correlates during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Estonia
Merili Tamson, Rainer Reile, Diana Sokurova, Kaire Innos, Eha Nurk, Kaia Laidra, Sigrid Vorobjov
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(15): 9060. CrossRef - Quality of life among patients with chronic non-communicable diseases during COVID-19 pandemic in Southern Ethiopia: A cross-sectional analytical study
Mohammed Ayalew, Bedilu Deribe, Siraj Hussen, Semira Defar, Abel Gedefaw
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Calidad de vida relacionada a la salud en personas con COVID-19, internados en un establecimiento hospitalario en el Callao.
Diana Karim Matta Solis
Revista Cuidado y Salud Pública.2022; 2(1): 56. CrossRef - Headache in Post-COVID-19 Patients: Its Characteristics and Relationship with the Quality of Life
Endang Mutiawati, Hendrix Indra Kusuma, Marhami Fahriani, Harapan Harapan, Syahrul Syahrul, Nasrul Musadir
Medicina.2022; 58(10): 1500. CrossRef - Quality of Life in COVID-19 Outpatients: A Long-Term Follow-Up Study
Vincent Tarazona, David Kirouchena, Pascal Clerc, Florence Pinsard-Laventure, Bastien Bourrion
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(21): 6478. CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life and Associated Factors Among Covid-19 Survivors. Experience from Ethiopian Treatment Centers
Abdene Weya Kaso, Hailmariam Getachew Tesema, Habtamu Endashaw Hareru, Taha Kaso, Zemachu Ashuro, Adugna Asefa Talemahu, Soressa Tafere Jore, Reta Kassa, Gebi Agero, Alemayehu Hailu
Infection and Drug Resistance.2022; Volume 15: 6143. CrossRef - Long COVID-19 and Health-Related Quality of Life of Mild Cases in Korea: 3-Months Follow-up of a Single Community Treatment Center
Hi Sun Soh, BeLong Cho
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-related quality of life in survivors of severe COVID-19 infection
Gabriele d’Ettorre, Paolo Vassalini, Vincenzo Coppolelli, Elio Gentilini Cacciola, Letizia Sanitinelli, Luca Maddaloni, Silvia Fabris, Claudio M. Mastroianni, Gabriella d’Ettorre, Giancarlo Ceccarelli
Pharmacological Reports.2022; 74(6): 1286. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 and effects of BNT162b2 on patient-reported outcomes: quality of life, symptoms, and work productivity among US adult outpatients
Manuela Di Fusco, Xiaowu Sun, Mary M. Moran, Henriette Coetzer, Joann M. Zamparo, Laura Puzniak, Mary B. Alvarez, Ying P. Tabak, Joseph C. Cappelleri
Journal of Patient-Reported Outcomes.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-related quality of life of children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes during the COVID-19 pandemic in Kuwait
Dalia Al-Abdulrazzaq, Doaa Khalifa, Taiba Alqaisi, Fatima Al-Juailla, Fouzeyah Othman, Sarah Qabazard, Hessa Al-Kandari
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Updated APLAR consensus statements on care for patients with rheumatic diseases during the COVID‐19 pandemic
Lai‐Shan Tam, Yoshiya Tanaka, Rohini Handa, Zhanguo Li, Jose Paulo Lorenzo, Worawit Louthrenoo, Catherine Hill, Kevin Pile, Philip C. Robinson, Leonila F. Dans, Li Yang Hsu, Sang‐Min Lee, Jiacai Cho, A. T. M. Tanveer Hasan, Babur Salim, Saba Samreen, Syah
International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases.2021; 24(6): 733. CrossRef - Physical and mental health complications post-COVID-19: Scoping review
Sanaz Shanbehzadeh, Mahnaz Tavahomi, Nasibeh Zanjari, Ismail Ebrahimi-Takamjani, Somayeh Amiri-arimi
Journal of Psychosomatic Research.2021; 147: 110525. CrossRef - Avoiding Trouble Ahead: Lessons Learned and Suggestions for Economic Evaluations of COVID-19 Vaccines
Chris Painter, Wanrudee Isaranuwatchai, Juthamas Prawjaeng, Hwee Lin Wee, Brandon Wen Bing Chua, Vinh Anh Huynh, Jing Lou, Fang Ting Goh, Nantasit Luangasanatip, Wirichada Pan-Ngum, Wang Yi, Hannah Clapham, Yot Teerawattananon
Applied Health Economics and Health Policy.2021; 19(4): 463. CrossRef - Protocol for the economic evaluation of COVID-19 pandemic response policies
Brandon Wen Bing Chua, Vinh Anh Huynh, Jing Lou, Fang Ting Goh, Hannah Clapham, Yot Teerawattananon, Hwee Lin Wee
BMJ Open.2021; 11(9): e051503. CrossRef - Quality of life of COVID-19 recovered patients in Bangladesh
Mohammad Delwer Hossain Hawlader, Md. Utba Rashid, Md. Abdullah Saeed Khan, Tasnim Ara, Mohammad Hayatun Nabi, Miah Md. Akiful Haque, Kazi Farhana Matin, Mohammad Ali Hossain, Mahfil Ara Rahman, Mosharop Hossian, Shuvajit Saha, Ridwana Maher Manna, Md. Ye
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(10): e0257421. CrossRef - Investigating the COVID-19 related behaviors in the public transport system
Fatemeh Bakhtari Aghdam, Homayoun Sadeghi-Bazargani, Kavous Shahsavarinia, Fatemeh Jafari, Leila Jahangiry, Neda Gilani
Archives of Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Covid-19 on health-related quality of life of patients: A structured review
Ak Narayan Poudel, Shihua Zhu, Nicola Cooper, Paul Roderick, Nisreen Alwan, Carolyn Tarrant, Nida Ziauddeen, Guiqing Lily Yao, Prasenjit Mitra
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(10): e0259164. CrossRef - Comprehensive and long-term surveys of COVID-19 sequelae in Japan, an ambidirectional multicentre cohort study: study protocol
Kensuke Nakagawara, Ho Namkoong, Hideki Terai, Katsunori Masaki, Takae Tanosaki, Kyoko Shimamoto, Ho Lee, Hiromu Tanaka, Satoshi Okamori, Hiroki Kabata, Shotaro Chubachi, Shinnosuke Ikemura, Hirofumi Kamata, Hiroyuki Yasuda, Ichiro Kawada, Makoto Ishii, Y
BMJ Open Respiratory Research.2021; 8(1): e001015. CrossRef - Determinants of quality of life among COVID-19 patients in Southwestern region of Bangladesh
Md. Injamul Haq Methun, M. Sheikh Giash Uddin, Iqramul Haq, Md. Asaduzzaman Noor, Md. Jakaria Habib, Md. Ismail Hossain, Ahmed Abdus Saleh Saleheen, Sutopa Roy, Shatabdi Shamrita Ume, Md. Rukonozzaman Rukon, Md. Amit Hasan, Md. Jahangir Alam
Indian Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 74: 15. CrossRef - Evaluation of health-related quality of life of Covid-19 patients: a hospital-based study in South Central Ethiopia
Abdene Weya Kaso, Gebi Agero, Zewdu Hurisa, Taha Kaso, Helen Ali Ewune, Alemayehu Hailu
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiovascular diseases, social and demographic factors, and quality of life in convalescents of COVID-19-associated pneumonia three months after hospital discharge
O.A. Guskova, E.I. Yaroslavskaya, B.Yu. Prilenskii, T.I. Petelina
Profilakticheskaya meditsina.2021; 24(11): 36. CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life Among COVID-19 Individuals: A Cross-Sectional Study in Tamil Nadu, India, 2020
Suganya Barani, Tarun Bhatnagar, Meenakumari Natarajan, Kumari Gayathri, Harshal Sonekar, Akhil Sasidharan, T S Selvavinayagam, Bhavani Shankara Bagepally
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Ayurveda and Yoga in the management of SARS-CoV-2: Two case reports
RajaRam Mahto, Arshath Jyothi, Aparna Dileep, Archana Shukla, Aleena Gauri
Journal of Ayurveda Case Reports.2020; 3(4): 127. CrossRef
- Examining the Trajectory of Health-Related Quality of Life among Coronavirus Disease Patients
- Factors Influencing Self-Rated Oral Health in Elderly People Residing in the Community: Results from the Korea Community Health Survey, 2016
- Jong-Hoon Moon, Sung-Jin Heo, Jin-Hwa Jung
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(4):245-250. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.4.14
- 5,825 View
- 92 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The aim of this study was to examine the factors influencing perceived oral health in elderly individuals residing in the community.
Methods This study used raw data from the Korea community health survey, 2016. Of the 64,223 participants that were elderly (aged ≥ 65 years), 61,280 (95.4%) were included for analysis. Self-rated oral health was the dependent variable and 6 independent variables including age, gender, type of area of residence (metropolitan or provincial), educational level, income, and living status with spouse were assessed. Oral function was studied based on mastication, pronunciation, and use of dentures, and oral health behavior included brushing teeth after breakfast, after lunch, after dinner, and before sleep). The EQ-5D questionnaire measured health-related quality of life (mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort and anxiety/depression).
Results Among the general characteristics, age, gender, educational level, income, and living status with spouse were the factors that affected self-rated oral health. Mastication, pronunciation, use of dentures, and brushing after lunch, dinner, and before sleep were the factors that influenced self-rated oral function. All domains of the EQ-5D (pain/discomfort, mobility, self-care, usual activities, and anxiety/depression) were factors that affected self-rated oral health.
Conclusion The results of the current investigation suggest that the development of management and education strategies for oral health promotion in the elderly, should focus on improving oral function and oral health behavior, taking into account the socio-economic and demographic characteristics that have been shown to be associated with poor self-rated oral function.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Older adults’ perceptions of oral health and its influence on general health: A deductive direct content analysis
Maria Snogren, Irene Eriksson, Maria Browall, Kristina Ek
Nordic Journal of Nursing Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Oral health status and behavior in elderly Koreans with periodontal disease
Sae‐Rom Lee, Mi Ah Han, Jong Park, So Yeon Ryu, So Yeong Kim
Journal of Public Health Dentistry.2022; 82(4): 378. CrossRef - Oral health-related quality of life, probable depression and probable anxiety: evidence from a representative survey in Germany
André Hajek, Hans-Helmut König
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with Self‐reported Oral Health Among Community-Dwelling Older Adults in a Rural Province of Thailand
Yaowapa Chantaraboot, Nithimar Sermsuti-anuwat
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2022; Volume 15: 2111. CrossRef - Self-rated oral health among elderly patients attending a university dental hospital in Thailand: a telephone-based cross-sectional survey study
Nithimar Sermsuti-anuwat, Narongrit Nampikul, Rawitsara Suwannimit, Weerachon Panthueng
PeerJ.2022; 10: e14191. CrossRef
- Older adults’ perceptions of oral health and its influence on general health: A deductive direct content analysis
- Health-Related Quality of Life Based on Comorbidities Among Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease
- Jieun Cha, Dallong Han
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(4):194-200. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.4.08
- 6,492 View
- 137 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The aim of this study was to investigate comorbidities in patients with end-stage renal disease, and to compare health-related quality of life (HRQOL) according to the type, and number of comorbidities.
Methods A total of 250 adults undergoing hemodialysis were recruited at local clinics. HRQOL was measured using the 12-item Medical Outcomes Study Short Form questionnaire. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, analysis of variance, and
t test.Results Around 70.8% of patients with end stage renal disease had 1 or more comorbidities, and the most common comorbidities were hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. HRQOL was significantly different based on the number of comorbidities (F = 9.83,
p < 0.001). The effect of comorbidities on the scores for mental health domains of the HRQOL questionnaire was not conclusive compared with the scores for the physical domain which were conclusive. Among the comorbidities, diabetes was associated with a lower quality of life.Conclusion The customized management of diabetic and hypertensive patients is necessary for the early detection and prevention of chronic kidney disease, and slowing the progression of renal disease and managing cardiovascular risk factors is essential.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Testosterone deficiency in men with end stage renal disease and kidney transplantation: a narrative review
Nicholas A. Deebel, Ashley N. Matthew, Justin Loloi, Ari P. Bernstein, Nannan Thirumavalavan, Ranjith Ramasamy
International Journal of Impotence Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality of Life in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis and Its Affecting Factors in a Hemodialysis Unit of General Hospital Denpasar
Agustina Nila Yuliawati, Pande Made Desy Ratnasari, Ni Luh Putu Satria Maharani
Borneo Journal of Pharmacy.2023; 6(3): 320. CrossRef - The Effect of Chronic Kidney Disease or End-stage Kidney Disease on Perioperative Outcomes and Healthcare Utilization in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery
Yung Lee, Léa Tessier, Audrey Jong, Adelia Padoan, Yasith Samarasinghe, Tyler McKechnie, Amber O. Molnar, Michael Walsh, Aristithes Doumouras, Jerry Dang, Matthew Kroh, Dennis Hong
Obesity Surgery.2023; 33(5): 1476. CrossRef - Navigating through the haemostatic paradox in kidney failure: A practical overview
Jessica Caruana, Nicoletta Riva, Kevin Vella, Andrew Davenport, Alexander Gatt
British Journal of Haematology.2023; 202(2): 230. CrossRef - IgA nephropathy in adults with epidermolysis bullosa
Manrup K Hunjan, Ajoy Bardhan, Natasha Harper, Dario Leonardo Balacco, Gerald Langman, Vijay Suresh, Adrian Heagerty
Clinical and Experimental Dermatology.2023; 48(8): 920. CrossRef - Comorbid Conditions in Kidney Transplantation: Outcome Analysis at King Abdulaziz Medical City
Abdulrahman R Al Tamimi, Bader A Aljaafri, Fahad Alhamad, Sultan Alhoshan, Awatif Rashidi, Basayel Dawsari, Ziad A Aljaafri
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Duration of Hemodialysis and its Impact on Quality of Life
Bushra Akram, Hafiz Shafique Ahmad, Muhammad Tahsin Akhtar, Ahmad Bilal, Khizra Iqbal
Pakistan Journal of Health Sciences.2023; : 31. CrossRef - Association between heart failure and arteriovenous access patency in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis
Andrea T. Fisher, Bianca Mulaney-Topkar, Brian M. Sheehan, Manuel Garcia-Toca, Ehab Sorial, Michael D. Sgroi
Journal of Vascular Surgery.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Health Literacy and Change in Health-Related Quality of Life in Dialysed Patients
Ivana Skoumalova, Andrea Madarasova Geckova, Jaroslav Rosenberger, Maria Majernikova, Peter Kolarcik, Daniel Klein, Andrea F. de Winter, Jitse P. van Dijk, Sijmen A. Reijneveld
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(2): 620. CrossRef - Physical Activity and Health-Related Quality of Life of Patients on Hemodialysis with Comorbidities: A Cross-Sectional Study
Yu-Hui Wu, Yu-Juei Hsu, Wen-Chii Tzeng
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(2): 811. CrossRef - Disease Knowledge, Self-Efficacy, and Quality of Life in Patient With Hypertensive Nephropathy
Yen-Yen Chen, Mei-Chen Lee, Shu-Fang Vivienne Wu, Yueh-Min Liu, Hui-Mei Chen
Clinical Nursing Research.2022; 31(6): 1179. CrossRef - The mediating effect of self‐efficacy in the relationship between mental health and quality of life in patients with hypertensive nephrology
Mei‐Chen Lee, Yen‐Yen Chen, Chun‐Yi Tai, Shu‐Fang Vivienne Wu
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2022; 78(9): 2827. CrossRef - The relationship between grip strength with health-related quality of life and mortality in hemodialysis patients
Clara S. A. Sugizaki, Hellen C. N. Rodrigues, Jéssica F. M. Ivo, Ana T. V. S. Freitas, Maria L. F. Stringhini, Sérgio A. R. Paiva, Marcos F. Minicucci, Maria R. G. Peixoto, Nara A. Costa
Nutrire.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting Quality of Life in Hemodialysis Patients
Ade Yonata, Nurul Islamy, Achmad Taruna, Lukman Pura
International Journal of General Medicine.2022; Volume 15: 7173. CrossRef - Health related quality of life of patients undergoing in-centre hemodialysis in Rwanda: a cross sectional study
Gloria Shumbusho, Celestin Hategeka, Marianne Vidler, Jules Kabahizi, Marla McKnight
BMC Nephrology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Short Form-6 Dimension (SF-6D) Validity and Reliability in Hemodialysis Patients
Anisa Zulfa Fatihah, Tri Murti Andayani, Nanang Munif Yasin
JURNAL FARMASI DAN ILMU KEFARMASIAN INDONESIA.2021; 8(2): 150. CrossRef
- Testosterone deficiency in men with end stage renal disease and kidney transplantation: a narrative review
- Impact of Cognitive Aging on Health-Related Quality of Life in Menopausal Women
- Kyoung Suk Lee, Mi Sook Jung, Mijung Kim, Kyeongin Cha, Eunyoung Chung
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(4):185-193. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.4.07
- 6,004 View
- 107 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Menopause is a well-known risk factor for accelerating cognitive aging in women. This study aimed to assess differences in cognitive function and health-related quality of life (HRQOL) according to menopausal status to determine whether the menopause significantly affects the relationship between cognitive function and HRQOL.
Methods This was a cross-sectional comparative study with a convenience sample of 178 Korean women including 89 naturally menopausal women (65 ± 10 years) and 89 non-menopausal women (45 ± 8 years) who met the eligibility criteria and completed neuropsychological tests and self-report questionnaires about their HRQOL, cognitive function, depression, and sleep quality. Multiple regression analyses were performed within and between groups according to menopausal status.
Results Menopausal women had significantly worse scores on neuropsychological performance and HRQOL than non-menopausal women. A better neuropsychological performance (β = 0.34) was solely associated with a better HRQOL in menopausal women, whilst socioeconomic variables were associated with HRQOL in non-menopausal women.
Conclusion Menopause is an important risk factor for HRQOL, and the association between cognition and HRQOL may differ according to menopausal status. When developing programs for target groups to improve daily functioning and HRQOL, healthcare professionals need to pay more attention to this relationship.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Brain volumetric changes in menopausal women and its association with cognitive function: a structured review
Nur Zuliani Ramli, Mohamad Fairuz Yahaya, Nur Azlina Mohd Fahami, Hanani Abdul Manan, Meharvan Singh, Hanafi Ahmad Damanhuri
Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Brain volumetric changes in menopausal women and its association with cognitive function: a structured review
- A Study on the Physical Activities, Mental Health, and Health-Related Quality of Life of Osteoarthritis Patients
- Deok-Ju Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(6):368-375. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.6.07
- 6,011 View
- 235 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The purpose of this study was to investigate the physical activities, mental health, and health-related quality of life (HRQOL) of osteoarthritis patients.
Methods This study was conducted using data from the first year of the 7th Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey. There were 8,150 participants included in the survey, and 665 participants had been diagnosed with osteoarthritis. This study analyzed the measurements of physical activities, depression, and HRQOL in participants with osteoarthritis.
Results The mean age of the participants was 67 ± 9.9 years and 83.1% were female. Participants rarely engaged in work-related physical activity, and engaged in leisure-related physical activities infrequently. Most of the participants (85.9%) did not do regular exercise, but 1/3 of the participants walked for over 10 minutes a day. “Pain/discomfort” had the least impact upon HRQOL, and among the depression subcategories, “difficult to sleep and tiredness” had the most impact. Multiple logistic regression analysis showed that an adverse HRQOL score was statistically significantly associated with “location changes/physical activities” (
p < 0. 01), “depression” (p < 0.001) and “age” (p < 0.001).Conclusion Exercise programs should be in place which are manageable in everyday life for the elderly (> 65 years). Changes in daily routine so that patients become more active, should be supported by the family and community, together with assistance in managing psychological problems such as depression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and Predictors of Depression in Women with Osteoarthritis: Cross-Sectional Analysis of Nationally Representative Survey Data
Ananya Ravi, Elisabeth C. DeMarco, Sarah Gebauer, Michael P. Poirier, Leslie J. Hinyard
Healthcare.2024; 12(5): 502. CrossRef - A scalable 12-week exercise and education programme reduces symptoms and improves function and wellbeing in people with hip and knee osteoarthritis
Jemma L. Smith, Aidan Q. Innes, Danielle S. Burns, Davina Deniszczyc, James Selfe, Stephen MacConville, Kevin Deighton, Benjamin M. Kelly
Frontiers in Rehabilitation Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Special Issue on Biomechanical and Biomedical Factors of Knee Osteoarthritis
Hanatsu Nagano
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(22): 11807. CrossRef - Investigation on the association between diabetes distress and productivity among patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus in the primary healthcare institutions
Yingqi Xu, Gabrielle Yin Yern Tong, Joyce Yu-Chia Lee
Primary Care Diabetes.2020; 14(5): 538. CrossRef
- Prevalence and Predictors of Depression in Women with Osteoarthritis: Cross-Sectional Analysis of Nationally Representative Survey Data
- Factors Affecting Activity Limitation in the Elderly: Data Processed from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2016
- Jong-Hoon Moon
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(3):117-122. Published online June 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.3.02
- 5,651 View
- 43 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The aim of this study was to compare the sociodemographic characteristics, depression, and the health-related quality of life outcome, among the Korean elderly population, with and without activity limitation.
Methods The data used was drawn from the raw data of the seventh Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (
N = 8,150). There were 1,632 records for individuals aged 65 or older extracted from the seventh Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey database, 199 of those had missing responses (n = 1,433). Differences within the sociodemographic characteristic, the Patient Health Questionnaire-9, and the EuroQol-5 Dimension were analyzed using logistic regression analysis according to the presence or absence of activity limitation.Results The prevalence of activity limitation among the elderly individuals surveyed was 19.9%. In the unadjusted regression analysis, the odds ratios of all independent variables (age, gender, education level, type of region, family income, the Patient Health Questionnaire-9, all 5 domains of the EuroQol-5 Dimension) between the elderly individuals with and without activity limitation, were significant. Although, in the adjusted logistic regression analysis, it was observed that the only factors that were significantly associated with activity limitation were the Patient Health Questionnaire-9, EuroQol-5 Dimension, type of region, and family income.
Conclusion These findings demonstrated that activity limitation in elderly individuals is associated with the sociodemographic characteristics of family income and type of region of residence, as well as depression and the health-related quality of life outcome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Higher physical activity is associated with lower activity limitation: Cross-sectional analyses among the Spanish working population
R. López-Bueno, G.F. López-Sánchez, L. Smith, E. Sundstrup, L.L. Andersen, J.A. Casajús
Science & Sports.2023; 38(3): 247. CrossRef - Self-Reported Reasons for Activity Limitations According to Age and Sex in Community-Dwelling Stroke Survivors
Young-Ah Choi, Yeo Hyung Kim
Healthcare.2023; 11(10): 1420. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of health status and health service utilization patterns among rural and urban elderly populations in Hungary: a study on the challenges of unhealthy aging
Nora Kovacs, Peter Piko, Attila Juhasz, Csilla Nagy, Beatrix Oroszi, Zoltan Ungvari, Roza Adany
GeroScience.2023; 46(2): 2017. CrossRef - Associations between Depressive Symptoms and Satisfaction with Meaningful Activities in Community-Dwelling Japanese Older Adults
Michio Maruta, Hyuma Makizako, Yuriko Ikeda, Hironori Miyata, Atsushi Nakamura, Gwanghee Han, Suguru Shimokihara, Keiichiro Tokuda, Takuro Kubozono, Mitsuru Ohishi, Kounosuke Tomori, Takayuki Tabira
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(3): 795. CrossRef
- Higher physical activity is associated with lower activity limitation: Cross-sectional analyses among the Spanish working population
- The Effects of Restricted Physical Activity on Health-Related Quality of Life in Adult Patients with Depression
- Deok-Ju Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(2):85-92. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.2.07
- 7,051 View
- 79 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The objective was to identify restricted physical activity in patients with depression, and to determine the effects of that restricted activity, on their health-related quality of life (HRQOL).
Methods Data was analysed from Year 1 of the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VII-1). From a total sample of 8,150 subjects, 277 adults aged ≥19 years who were diagnosed with depression were selected. The results were derived using restricted activity and HRQOL data measured from the subjects.
Results Most of the participants were females ≥ 50 years old. HRQOL scores were high in the “self-care” dimension and low in the “pain/discomfort” and “anxiety/depression” dimensions. Their restricted activity due to illness in the past year, led to increases in participants being bedridden or absent from work. Many participants reported being bedridden for more than 3 months. A higher number of absences owing to illness in the past year, and longer durations of being bedridden, had a negative impact on HRQOL. Age, marital status, educational level, income level, and occupation were the sociodemographic variables that had an impact on HRQOL.
Conclusion Patients with depression experiencing stress in their daily lives should take measures to avoid illness and pain that may lead to them becoming bedridden, and employ lifestyle habits with support from families and community health promotion centres, where mental health counselling can be accessed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Childhood trauma, inflammatory biomarkers and the presence of a current depressive episode: Is there a relationship in subjects from a population study?
Leonardo Carvalho Oliveira, Natália Wirowski, Pedro Borges de Souza, Andressa Schneider Lobato, Karen Jansen, Taiane de Azevedo Cardoso, Thaíse Campos Mondin, Jean Pierre Oses, Flávio Kapczinski, Luciano Dias de Mattos Souza, Ricardo Azevedo da Silva, Fer
Journal of Psychiatric Research.2023; 158: 255. CrossRef - The Relationship between Physical Activity and Health-Related Quality of Life in Korean Adults: The Eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Mun-Gyu Jun, Se-Hyeon Han
Healthcare.2023; 11(21): 2861. CrossRef
- Childhood trauma, inflammatory biomarkers and the presence of a current depressive episode: Is there a relationship in subjects from a population study?
- Treatment with Sofosbuvir and Daclatasvir (with or without Ribavirin) Improves Patient Reported Outcomes in Hepatitis C
- Lucas Pereira Jorge de Medeiros, Mario Barreto Correa Lima, Marcia Maria Amêndola Pires, Alessandra Mendonça Almeida Maciel, Renata Barboza Vianna Medeiros, Mariana Dermínio Donadel, Isabela Martins Becattini Pereira, Fábio Marchon Leão, Luiz Eduardo Amorim Correa Lima Pires, Helio Rzetelna, Carlos Eduardo Brandão-Mello
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(2):50-58. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.2.03
- 5,103 View
- 38 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives To evaluate the impact of 3 treatment regimens upon health-related quality of life and work productivity using patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in chronic hepatitis C infected patients: sofosbuvir (SOF) + daclatasvir (DCV); SOF + DCV + ribavirin (RBV); SOF + simeprevir (SMV).
Methods 4 questionnaires were used to evaluate PROs before, during and after treatment: Short Form-36 (SF-36), Chronic Liver Disease Questionnaire (CLDQ) - hepatitis C virus (HCV), Work Productivity and Activity Index, Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F).
Results Of the global sample of 55 patients included in this study; SOF + DCV (
n = 10); SOF + DCV + RBV (n = 29); SOF + SMV (n = 16) all had a statistically significant improvement in SF-36, CLDQ and FACIT-F scores during and post-treatment. No statistically significant differences in the PRO questionnaire values were observed between the distinct treatment regimens. The SOF and SMV patient groups presented higher mean PRO variations during and post-treatment, compared to the other groups: SF-36 functional capacity (16.1); SF-36 mental health (21.4); CLDQ activity (1.8); CLDQ emotional function (1.2); FACIT-F physical well-being (8.0); Total FACIT-F (21.6).Conclusion Treatment with SOF + DCV, with or without RBV, results in an improved PRO similar to treatment with SOF + SMV in chronic hepatitis C patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health-related quality of life in people receiving opioid agonist treatment and treatment for hepatitis C virus infection
Olav Dalgard, Alain H. Litwin, Oren Shibolet, Jason Grebely, Ronald Nahass, Frederick L. Altice, Brian Conway, Edward J. Gane, Anne F. Luetkemeyer, Cheng-Yuan Peng, David Iser, Isaias Noel Gendrano, Michelle M. Kelly, Barbara A. Haber, Heather Platt, Amy
Journal of Addictive Diseases.2023; 41(3): 213. CrossRef - Impact of sofosbuvir and daclastavir on health-related quality of life in patients co-infected with hepatitis C and human immunodeficiency virus
Evy Yunihastuti, Fhadilla Amelia, Arini Ika Hapsari, Bramantya Wicaksana, Veritea Natali, Alvina Widhani, Andri Sanityoso Sulaiman, Teguh Harjono Karjadi
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-related quality of life and fatigue in patients with chronic hepatitis C with therapy with direct-acting antivirals agents interferon-free
Raíssa Neves Fagundes, Lincoln Eduardo Villela Vieira de Castro Ferreira, Fábio Heleno de Lima Pace, Yury E. Khudyakov
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(8): e0237005. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of sofosbuvir-based pangenotypic direct-acting antiviral agents for chronic hepatitis C patients without genotype determination
Juan Li, Dong-Bo Wu, Wei Jiang, Xue-Bin Chen, Gui-Bao Xiao, Yong-Hong Wang, Meng-Lan Wang, Ya-Chao Tao, En-Qiang Chen
Medicine.2020; 99(43): e22726. CrossRef
- Health-related quality of life in people receiving opioid agonist treatment and treatment for hepatitis C virus infection



 First
First Prev
Prev


