Abstract
-
Objectives
- On February 26, 2021, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination was started for high-priority groups based on the recommendation of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices with 2 available COVID-19 vaccines (AstraZeneca and Pfizer-BioNTech) in Korea. This report provides a summary of adverse events following COVID-19 vaccination as of April 30, 2021.
-
Methods
- Adverse events following immunization are notifiable by medical doctors to the Korea Immunization Management System (KIMS) under the national surveillance system. We analyzed all adverse events reports following COVID-19 vaccination to the KIMS from February 26 to April 30, 2021.
-
Results
- In total, 16,196 adverse events following 3,586,814 administered doses of COVID-19 vaccines were reported in approximately 2 months (February 26 to April 30, 2021). Of these, 15,658 (96.7%) were non-serious adverse events, and 538 (3.3%) were serious adverse events, including 73 (0.5%) deaths. The majority of adverse events (n=13,063, 80.7%) were observed in women, and the most frequently reported adverse events were myalgia (52.2%), fever (44.9%), and headache (34.9%). Of the 73 deaths following the COVID-19 vaccination, none were related to the vaccines.
-
Conclusion
- By April 30, 3.6 million doses of the COVID 19 vaccine had been given in Korea, and the overwhelming majority of reports were for non-serious events. The Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency continues to monitor the safety of COVID-19 vaccination.
-
Keywords: Adverse event; COVID-19; Safety; Vaccines
Introduction
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a serious pandemic that has spread globally since it was first reported in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. As of May 1, 2021 in Korea, more than 114,000 people had confirmed infections and 1,831 had died of COVID-19 [1]. Globally, countries have implemented various control measures such as the use of masks, physical distancing, testing of exposed or symptomatic patients, or isolating infected individuals and their contacts to prevent the transmission of COVID-19. However, vaccines are needed to reduce the morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19, and achieving herd immunity through vaccination is a key strategy to prevent the spread of the virus [2,3].
- In 2020, various COVID-19 vaccines were developed based on different mechanisms of triggering an immune response. Currently, new mRNA vaccines, viral vector vaccines, and synthetic antigen vaccines have been developed and distributed worldwide for vaccination. Vaccination is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of infectious diseases; however, since vaccines are biological products, they might cause adverse events [4]. As reported in the clinical trials of the COVID-19 vaccines, adverse events following vaccination include pain, redness, and rashes at the site of injection and systemic reactions such as fever, myalgia, and headache. Anaphylaxis, although rare, was also reported [5–7].
- The Korea Immunization Management System (KIMS) integrates and manages the records of registration for vaccination and reported adverse events, and also manages vaccine distribution in Korea. The Ministry of Food and Drug Safety approved the AstraZeneca vaccine on February 10, 2021 and the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine on March 5, 2021. Shortly thereafter, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommended priority vaccination for healthcare personnel and vulnerable groups, including residents in nursing facilities and long-term care facilities.
- In Korea, medical doctors are required to report any adverse events following immunization (AEFIs) in accordance with the Infectious Diseases Control and Prevention Act [8]. This study collected and analyzed the data of adverse events after COVID-19 vaccination through the KIMS to identify the epidemiological characteristics of AEFIs and unexpected health problems.
Materials and Methods
- Adverse events after COVID-19 vaccination are monitored through the national passive monitoring system. AEFIs are primarily reported to local public health centers by medical doctors using the KIMS, a web-based reporting system. Serious events include intensive care unit admission, reports of death, adverse events of special interest, persistent or significant disabilities or incapacities, congenital anomaly/birth defects, and life-threatening adverse events.
- A total of 16,196 adverse events following vaccination with the AstraZeneca and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines were reported to the KIMS from February 26 to April 30, 2021; these adverse events were analyzed in this study. The AEFIs were examined by sex, age group, type of AEFIs, and type of vaccine. In addition, symptoms were analyzed including both non-serious and serious AEFIs. The chi-square test and SAS ver. 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) was used for the statistical analysis.
Results
- In total, 3,586,814 doses of COVID-19 vaccines were administered, and 16,196 adverse events were reported between February 26 and April 30, 2021. Of these, 15,658 (96.7%) were general adverse events, and 538 (3.3%) were serious adverse events. The report rates gradually decreased from 1.8% in the first week of vaccination to 0.3% in the eighth week (Figure 1).
- The rate of adverse events was 0.6% in women and 0.2% in men. The number of vaccinations was 2,279,364 (63.5%) in women, which were 1.7 times higher than that in men. The number of reported adverse events was also approximately 3 times higher in women than in men. The rate was highest in the age group of 18 to 29 years old at 2.9%, and the rate decreased as recipients’ age increased (Table 1).
- A total of 15,658 (96.7%) non-serious adverse events, including myalgia, fever, and headache, were reported, and 538 (3.3%) serious adverse events, including death and suspected anaphylaxis, were observed. Of all the adverse events, 13,968 were reported after AstraZeneca vaccines; 383 of these were serious adverse events including death and suspected anaphylaxis. The rate of adverse events after AstraZeneca vaccination was 7.7 per 1,000 doses, and the rate of serious adverse events, including death, was 0.2 per 1,000 doses. A total of 2,228 adverse events were reported after Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines, with 155 serious adverse events including deaths. The rate of adverse events after Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines was 1.3 per 1,000 doses, and the rate of serious adverse events, including death, was 0.09 per 1,000 doses.
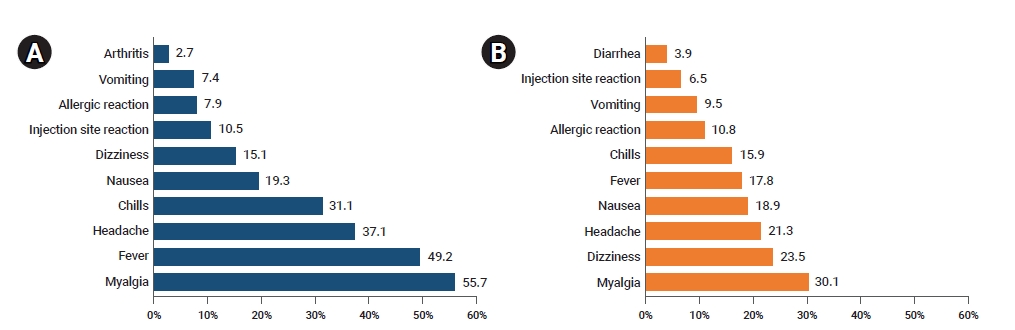
- Overall, the most frequently reported adverse events were myalgia (8,450, 52.2%), fever (7,274, 44.9%), and headache (5,660, 34.9%). The most frequently reported adverse events following vaccination with AstraZeneca vaccines included myalgia (7,780, 55.7%) followed by fever (6,878, 49.2%), and headache (5,185, 37.1%). The most frequently reported adverse events following vaccination with Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines were myalgia (670, 30.1%),dizziness (523, 23.5%), and headache (475, 21.3%), in decreasing order (Figure 2).
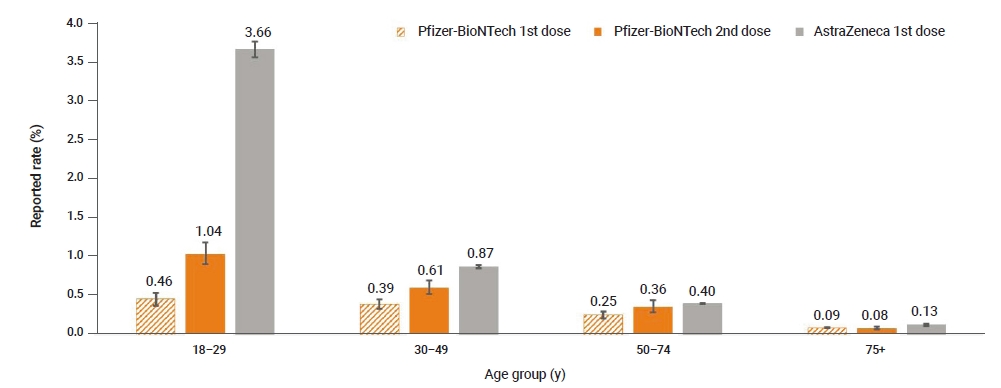
- A total of 1,550,412 first doses and 228,295 second doses of Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines were administered until April 30, 2021. The adverse event rate was higher after the second dose than after the first dose (first dose vs. second dose: 0.1%, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.10–0.11 and 0.3%, 95% CI, 0.25–0.29; respectively). Both COVID-19 vaccines showed higher adverse event rates among younger age groups (Figure 3).
- In total, 173 events of suspected anaphylaxis were reported: 139 and 34 events after administration of AstraZeneca and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines, respectively.
- The age of the 73 subjects who died after vaccination ranged from 25 to 95 years (median, 82 years). Thirty-five (47.9%) of the deaths were in women, and most deaths occurred in elderly recipients or those with underlying medical conditions. In cases of deaths, provincial rapid investigation teams and the injury investigation committee thoroughly evaluated the causality between vaccination and death through epidemiological investigations using medical records, death certificates, and autopsy results. No associations between death and vaccination have been identified as of April 30, 2021.
Discussion
- In Korea, 2 types of COVID-19 vaccines (AstraZeneca, Pfizer-BioNTech) are currently available, and as of April 30, 2021, a total of 3,586,814 doses were administered. The rate of adverse events as reported through the KIMS, the national passive monitoring system, was approximately 0.5%. During the first few months of the COVID-19 vaccination campaign in Korea, certain priority groups such as health care personnel and vulnerable people have been a focus for vaccination efforts. Therefore, it might be too early to evaluate adverse events after vaccination. However, as shown in clinical trials and data from other countries, most of the reported adverse events (97%) were non-serious events comprising local and systemic reactions, including myalgia, headache, fever, and pain at the injection site [5,6].
- Most of the 73 deaths reported after COVID-19 vaccination occurred in the elderly or those with underlying diseases. AEFIs were more frequently reported after the second dose than after the first dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. This is similar to the findings of the clinical trial [7]. However, no second-dose data for AstraZeneca vaccines are yet available due to the early stage of the vaccination campaigns.
- There are some limitations of this study, as follows. First, the number of adverse events reported by medical doctors may be an underestimation, as only data of patients who visited medical institutions due to adverse events were included. Moreover, the number of reports may also increase due to the growing interest in adverse events with the introduction of new vaccines.
- The Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency is monitoring and investigating AEFIs to assess any unexpected health problems due to COVID-19 vaccinations. We note that all findings in this paper are from the first few preliminary months of the national vaccination program. It is important for healthcare providers to report AEFIs and participate in epidemiological investigations to support operational decisions around the vaccine roll-out.
Article information
-
Ethics Approval
Given the current activity was conducted and authorized by the public health authority; and the purpose was to disseminate information to the public, the current study was exempted by the ethical board review.
-
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
-
Funding
None.
-
Availability of Data
The data used in this study is protected under the Personal Information Protection Act.
-
Authors’ Contributions
Conceptualization: HO, YKL; Data curation: EKK, YL, EL, TEK; Formal analysis: IH, HO; Investigation: YL, TEK, EL, EKK, HO; Methodology: HO, IH, YKL; Validation: YKL; Writing–original draft: HO, YKL; Writing–review & editing: all authors.
-
Additional Contributions
We thank the relevant ministries, including the Ministry of Interior and Safety; cities and provinces, medical staffs in health centers, and medical facilities for their effort in responding to the vaccine safety monitoring.
Figure 1.
Doses administered and the reported rates of adverse events per week, February 26 to April 30, 2021.
We added the first 2 days of vaccination campaign (February 26–February 27, 2021) to the first week. Similarly, the very last week of this paper included only 6 days (April 25–30, 2021). As the last week of this paper will be a slight undercount as more data may be reported in the coming days, the very right bar is indicated in a light color. COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019.

Figure 2.(A) Frequent symptoms and signs of adverse events following AstraZeneca coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination. (B) Frequent symptoms and signs of adverse events following Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination.
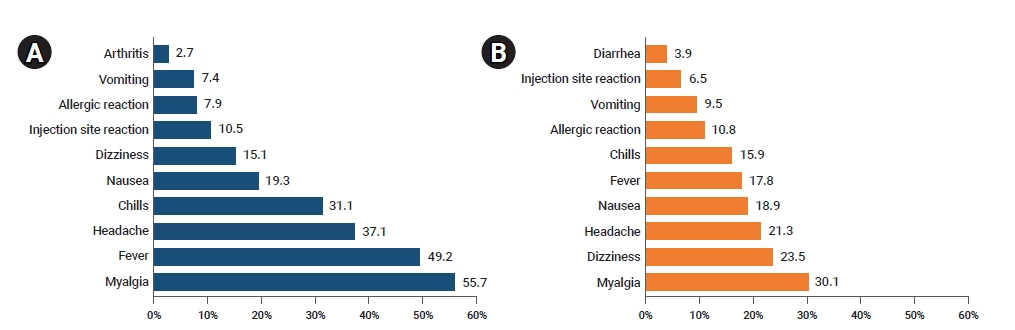
Figure 3.Reported adverse event rates following coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination by age group.
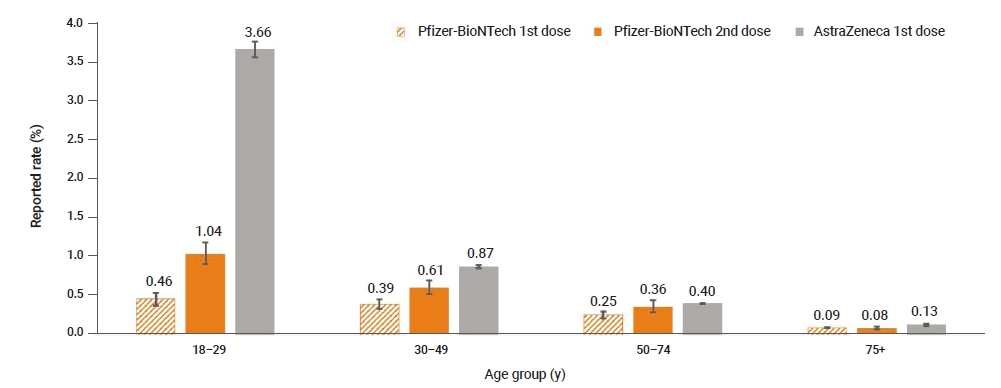
Table 1.Reports of adverse events following COVID-19 vaccination, by recipients’ sex, age group, and type of vaccine: Republic of Korea, February 26, 2021 to April 30, 2021 (as of May 1, 2021)
|
Variable |
Vaccination doses (n=3,586,814) |
Adverse events reporteda) (%) (n=16,196)
|
p-valued)
|
|
Non-serious adverse eventsb) (n=15,658) |
Serious adverse eventsc)
|
|
Death (n=73) |
Anaphylaxis (n=173) |
Others (n=292) |
|
Sex |
|
|
|
|
|
<0.001 |
|
Male |
1,307,450 (36.5) |
2,968 (19.0) |
38 (52.1) |
30 (17.3) |
97 (33.2) |
|
|
Female |
2,279,364 (63.5) |
12,690 (81.0) |
35 (47.9) |
143 (82.7) |
195 (66.8) |
|
|
Age (y) |
|
|
|
|
|
<0.001 |
|
18–29 |
180,115 (5.0) |
5,198 (33.2) |
1 (1.4) |
35 (20.2) |
33 (11.3) |
|
|
30–49 |
698,354 (19.5) |
5,583 (35.7) |
1 (1.4) |
88 (50.9) |
75 (25.7) |
|
|
50–74 |
939,634 (26.2) |
3,499 (22.3) |
15 (20.5) |
31 (17.9) |
80 (27.4) |
|
|
≥75 |
1,768,711 (49.3) |
1,378 (8.8) |
56 (76.7) |
19 (11.0) |
104 (35.6) |
|
|
AstraZeneca vaccine |
|
|
|
|
|
NA |
|
1st dose |
1,807,921 (50.4) |
13,585 (86.8) |
44 (60.3) |
139 (80.3) |
200 (68.5) |
|
|
2nd dose |
186 (0.01) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
Pfizer-BioNTech |
|
|
|
|
|
<0.001 |
|
1st dose |
1,550,412 (43.2) |
1,471 (9.4) |
28 (38.4) |
33 (19.1) |
87 (29.8) |
|
|
2nd dose |
228,295 (6.4) |
602 (3.8) |
1 (1.4) |
1 (0.6) |
5 (1.7) |
|
References
- 1. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA). Press release: updates on COVID-19 in Republic of Korea [Internet]. Cheongju: KDCA; 2021 May 1 [cited 2021 May 6]. Available from: http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/en/tcmBoardView.do?brdId=12&brdGubun=125&dataGubun=&ncvContSeq=5302&contSeq=5302&board_id=&gubun=.
- 2. Jung J. Preparing for the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) vaccination: evidence, plans, and implications. J Korean Med Sci 2021;36:e59.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. World Health Organization (WHO). COVID-19 vaccines: safety surveillance manual. Geneva: WHO; 2020.
- 4. World Health Organization (WHO). Immunization safety surveillance: guidelines for immunization programme managers on surveillance of adverse events following immunization. 3rd ed. Manila: WHO Regional Office for the Western Pacific; 2016.
- 5. Gee J, Marquez P, Su J, et al. First month of COVID-19 vaccine safety monitoring-United States, December 14, 2020-January 13, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021;70:283−8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA). Coronavirus vaccine: weekly summary of Yellow Card reporting. MHRA; 2021 May 27 [cited 2021 Jun 1]. Available from: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/coronavirus-covid-19-vaccine-adverse-reactions/coronavirus-vaccine-summary-of-yellow-card-reporting.
- 7. Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med 2020;383:2603−15.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA). Adverse events following COVID-19 immunization management guidelines. Cheongju: KDCA; 2021.
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

- A prospective cohort study protocol: monitoring and surveillance of adverse events following heterologous booster doses of Oxford AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine in previous recipients of two doses of Sinopharm or Sputnik V vaccines in Iran
Shahin Soltani, Behzad Karami Matin, Mohammad Mehdi Gouya, Sayed Mohsen Zahraei, Ghobad Moradi, Omid Chehri, Moslem Soofi, Mehdi Moradinazar, Fatemeh Khosravi Shadmani, Mahsa Kalantari, Hamidreza Khajeha, Mohammad Hassan Emamian, Farid Najafi
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Herpes Zoster Reactivation After mRNA and Adenovirus-Vectored Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccination: Analysis of National Health Insurance Database
Jin Gu Yoon, Young-Eun Kim, Min Joo Choi, Won Suk Choi, Yu Bin Seo, Jaehun Jung, Hak-Jun Hyun, Hye Seong, Eliel Nham, Ji Yun Noh, Joon Young Song, Woo Joo Kim, Dong Wook Kim, Hee Jin Cheong
The Journal of Infectious Diseases.2023; 228(10): 1326. CrossRef - Safety and effectiveness of BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine in adolescents
Young June Choe, Seonju Yi, Insob Hwang, Jia Kim, Young-Joon Park, Eunhee Cho, Myoungyoun Jo, Hyunju Lee, Eun Hwa Choi
Vaccine.2022; 40(5): 691. CrossRef - Direct and Indirect Associations of Media Use With COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy in South Korea: Cross-sectional Web-Based Survey
Minjung Lee, Myoungsoon You
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2022; 24(1): e32329. CrossRef - Self-Reported COVID-19 Vaccines’ Side Effects among Patients Treated with Biological Therapies in Saudi Arabia: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study
Lama T AlMutairi, Wesal Y Alalayet, Sondus I Ata, Khalidah A Alenzi, Yazed AlRuthia
Vaccines.2022; 10(6): 977. CrossRef - COVID-19 vaccine safety monitoring in Republic of Korea from February 26, 2021 to October 31, 2021
Insob Hwang, Kyeongeun Park, Tae Eun Kim, Yunhyung Kwon, Yeon-Kyeng Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2021; 12(6): 396. CrossRef
 , Eun Kyeong Kim
, Eun Kyeong Kim , Insob Hwang
, Insob Hwang , Tae Eun Kim
, Tae Eun Kim , Yeon-kyeong Lee
, Yeon-kyeong Lee , Eunju Lee
, Eunju Lee , Yeon-Kyeng Lee
, Yeon-Kyeng Lee







 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite