Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Factors associated with the timely diagnosis of malaria and the utilization of types of healthcare facilities: a retrospective study in the Republic of Korea
- HyunJung Kim, Sangwoo Tak, So-dam Lee, Seongwoo Park, Kyungwon Hwang
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(2):159-167. Published online April 16, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0349
- 336 View
- 14 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 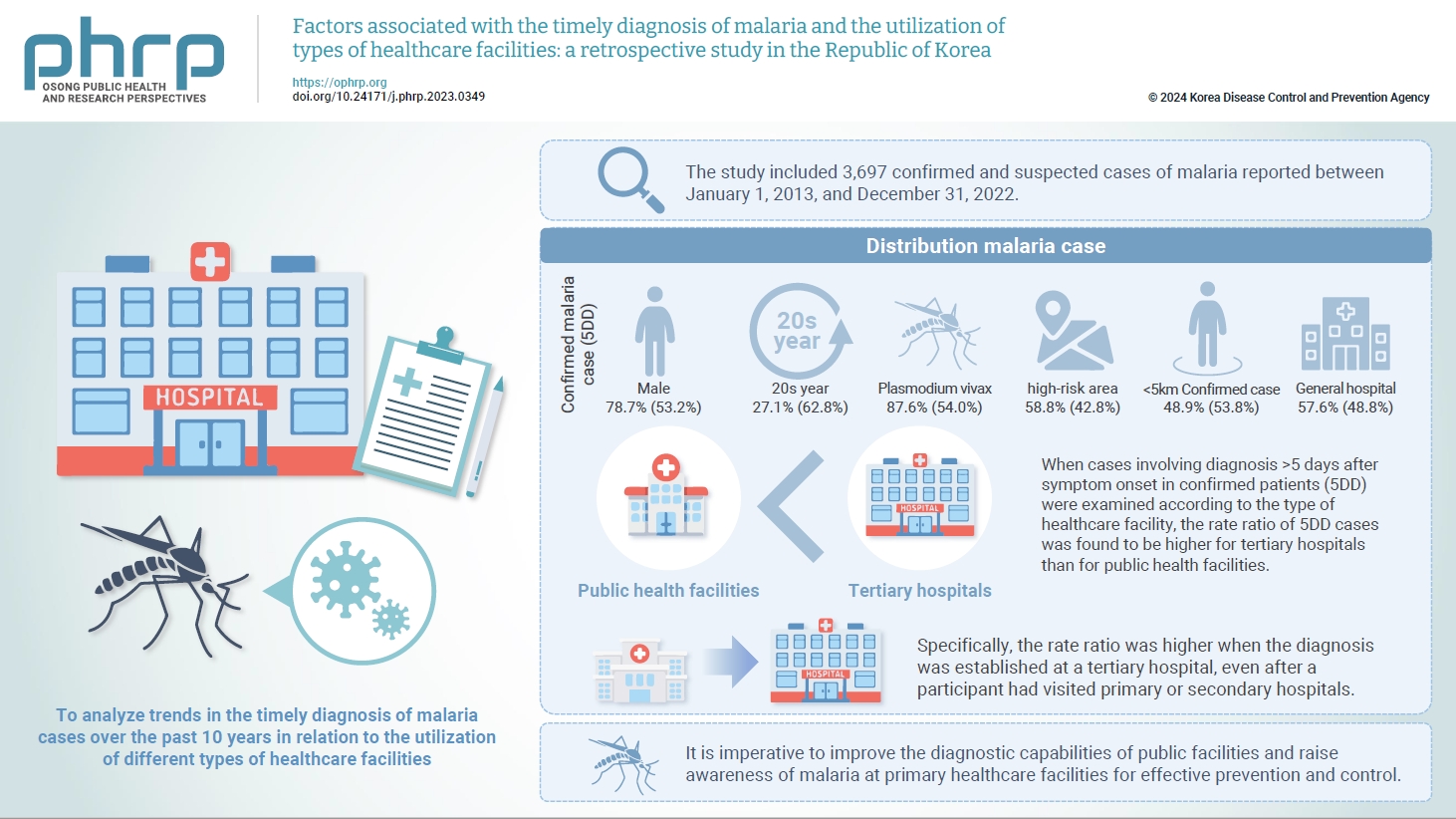
- Objectives
This study aimed to analyze trends in the timely diagnosis of malaria cases over the past 10 years in relation to the utilization of different types of healthcare facilities.
Methods
The study included 3,697 confirmed and suspected cases of malaria reported between January 1, 2013, and December 31, 2022, in the national integrative disease and healthcare management system. Some cases lacking a case report or with information missing from the case report were excluded from the analysis. A generalized linear model with a Poisson distribution was constructed to estimate rate ratios and 95% confidence intervals adjusted for other variables, such as distance.
Results
When cases involving diagnosis >5 days after symptom onset in confirmed patients (5DD) were examined according to the type of healthcare facility, the rate ratio of 5DD cases was found to be higher for public health facilities than for tertiary hospitals. Specifically, the rate ratio was higher when the diagnosis was established at a tertiary hospital, even after a participant had visited primary or secondary hospitals. In an analysis adjusted for the distance to each participant’s healthcare facility, the results did not differ substantially from the results of the crude analysis.
Conclusion
It is imperative to improve the diagnostic capabilities of public facilities and raise awareness of malaria at primary healthcare facilities for effective prevention and control.
- Trends of legionellosis reported in Jeju Province, Republic of Korea, 2015–2022
- Juyoung Park, Jong-Myon Bae
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):321-327. Published online August 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0145
- 1,208 View
- 99 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
The number of reported cases of Legionnaires’ disease (LD) in the Republic of Korea surged nationally in 2016; however, in 2022, this number was higher in Jeju Province than the previous national peak. A descriptive epidemiological study was conducted to analyze trends in the incidence of reported LD cases in Jeju Island from 2015 to 2022.
Methods
The data for this study were obtained from case reports submitted to the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency through its Disease and Health Integrated Management System. The selection criteria were cases or suspected cases of LD reported among Jeju residents between 2015 and 2022. The 95% confidence interval of the crude incidence rate was calculated using the Poisson distribution.
Results
Since 2020, the incidence rate of LD in Jeju has risen sharply, showing a statistically significant difference from the national incidence rate. A particular medical institution in Jeju reported a significant number of LD cases. Screening with the urine antigen test (UAT) also increased significantly.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate that the rapid increase in cases of LD in Jeju Province since 2020 was due to the characteristics of medical-care use among Jeju residents, which were focused on a specific medical institution. According to their clinical practice guidelines, this medical institution conducted UATs to screen patients suspected of pneumonia.
- Delays in the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis during the COVID-19 outbreak in the Republic of Korea in 2020
- Jiyeon Yang, Yunhyung Kwon, Jaetae Kim, Yoojin Jang, Jiyeon Han, Daae Kim, Hyeran Jeong, Hyekyung Park, Eunhye Shim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(5):293-303. Published online September 23, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0063
- 7,416 View
- 188 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 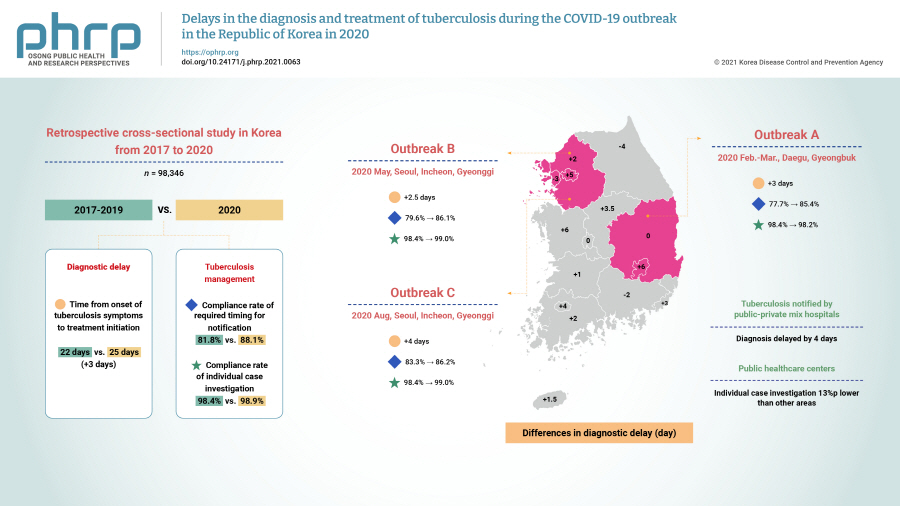
- Objectives
We investigated the impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on tuberculosis (TB) management in the Republic of Korea (ROK).
Methods
This retrospective cross-sectional study used nationwide ROK TB notification data (98,346 cases) from 2017 to 2020. The median time from the onset of TB symptoms to treatment initiation and the compliance rates with the required timing for notification and individual case investigations were measured and compared across periods and regions affected by the COVID-19 epidemic.
Results
TB diagnosis during the COVID-19 pandemic was delayed. The median time to TB treatment initiation (25 days) in 2020 increased by 3 days compared to that of the previous 3 years (22 days) (p<0.0001). In the outbreak in Seoul, Incheon, and Gyeonggi province during August, the time to TB diagnosis was 4 days longer than in the previous 3 years (p=0.0303). In the outbreak in Daegu and Gyeongbuk province from February to March 2020, the compliance rate with the required timing for individual case investigations was 2.2%p points lower than in other areas in 2020 (p=0.0148). For public health centers, the rate was 13%p lower than in other areas (80.3% vs. 93.3%, p=0.0003).
Conclusion
TB diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic in the ROK were delayed nationwide, especially for patients notified by public-private mix TB control hospitals. TB individual case investigations were delayed in regional COVID-19 outbreak areas (Daegu and Gyeongbuk province), especially in public health centers. Developing strategies to address this issue will be helpful for sustainable TB management during future outbreaks. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Review of the Impact of Patent Medicine Vendors in Driving Community Tuberculosis Case Finding in the COVID-19 Pandemic in Nigeria
Arinze Emmanuel Ajogwu, Onwubiko Iheanyichukwu Samuel, Nnanyelugo Longinus Ochike, Uzoma Chidinma Ajegbo, Chinedu Paschal Maduka
Matrix Science Medica.2024; 8(2): 33. CrossRef - Tuberculosis: Republic of Korea, 2021
Jinsoo Min, Hyung Woo Kim, Ju Sang Kim
Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases.2023; 86(1): 67. CrossRef - Prevalence and associated factors of diabetes mellitus among patients with tuberculosis in South Korea from 2011 to 2018: a nationwide cohort study
Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Jeong Mi Seo, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang
BMJ Open.2023; 13(3): e069642. CrossRef - Increased Healthcare Delays in Tuberculosis Patients During the First Wave of COVID-19 Pandemic in Korea: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study
Jinsoo Min, Yousang Ko, Hyung Woo Kim, Hyeon-Kyoung Koo, Jee Youn Oh, Yun-Jeong Jeong, Hyeon Hui Kang, Kwang Joo Park, Yong Il Hwang, Jin Woo Kim, Joong Hyun Ahn, Yangjin Jegal, Ji Young Kang, Sung-Soon Lee, Jae Seuk Park, Ju Sang Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Time trend prediction and spatial–temporal analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Guizhou Province, China, during 2014–2020
Wang Yun, Chen Huijuan, Liao Long, Lu Xiaolong, Zhang Aihua
BMC Infectious Diseases.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-world association of adherence with outcomes and economic burden in patients with tuberculosis from South Korea claims data
Sun-Hong Kwon, Jin Hyun Nam, Hye-Lin Kim, Hae-Young Park, Jin-Won Kwon
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Tuberculosis Case Notification and Treatment Outcomes in Eswatini
Hloniphile Victory Masina, I-Feng Lin, Li-Yin Chien
International Journal of Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in incidences of newly notified tuberculosis in Jeju Province, Korea, 2017-2021
Jinhee Kim, Nam-Hun Kang, Jong-Myon Bae
Journal of Medicine and Life Science.2022; 19(3): 103. CrossRef
- A Review of the Impact of Patent Medicine Vendors in Driving Community Tuberculosis Case Finding in the COVID-19 Pandemic in Nigeria
- Influence of Socioeconomic Status, Comorbidity, and Disability on Late-stage Cancer Diagnosis
- Bo Ram Park, So Young Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Hyung Kook Yang, Jong Hyock Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(4):264-270. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.4.06
- 3,992 View
- 39 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Understanding factors affecting advanced stage at diagnosis is vital to improve cancer outcomes and overall survival. We investigated the factors affecting later-stage cancer diagnosis.
Methods Patients completed self-reported questionnaires. We collected cancer stage data from medical records review. Logistic regression analyses were performed to identify factors associated with later stage cancer at diagnosis by gender.
Results In total, 1,870 cancer patients were included in the study; 55.8% were men, 31.1% had more than one comorbid condition, and 63.5% had disabilities. About half of the patients were smokers, and drank alcohol, and 58.0% were diagnosed at an advanced stage. By cancer type, lung and liver cancers (both genders), prostate (men), colorectal, cervical, and thyroid cancer (women) were more likely to be diagnosed at a later stage. After controlling for socioeconomic factors, comorbidity (odds ratio [OR], 1.48 in men) and disability (OR, 1.64 in men and 1.52 in women) remained significantly associated with late-stage diagnosis.
Conclusion In this nationwide study, using combined information from patients and medical records, we found that male patients with comorbidities or disabilities, and female patients with disabilities were more likely to have advanced stage cancer at diagnosis. Targeted approaches by cancer type and health conditions are recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with late diagnosis of cervical cancer at two national referral hospitals, Kenya 2017: A case control study
Valerian Mwenda, Martin Mwangi, Gladwell Gathecha, Joseph Kibachio, Robert Too, Zeinab Gura, Marleen Temmerman
Gynecologic Oncology Reports.2024; 52: 101355. CrossRef - Obstacles dans le dépistage du cancer du sein chez les personnes ayant un handicap
Sylvia Mazellier, Rajeev Ramanah, Catherine Guldenfels, Carole Mathelin
Bulletin du Cancer.2022; 109(2): 185. CrossRef - Cancer Disparities Experienced by People with Disabilities
Rosemary B. Hughes, Susan Robinson-Whelen, Carly Knudson
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(15): 9187. CrossRef - Prognostic factors and survival analysis of Hurthle cell carcinoma: A population-based study
Bailey M. Humphreys, Kelvin O. Memeh, Alex Funkhouser, Tanaz M. Vaghaiwalla
Surgery.2022; 172(5): 1379. CrossRef - Disparities in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Bile Duct Cancer in People with Disabilities: A National Cohort Study in South Korea
Seon Mee Park, So Young Kim, Kyoung Eun Yeob, Dong Wook Shin, Joung-Ho Han, Jong Heon Park, Jong Hyock Park
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(24): 16625. CrossRef - Impact of comorbidity assessment methods to predict non-cancer mortality risk in cancer patients: a retrospective observational study using the National Health Insurance Service claims-based data in Korea
Sanghee Lee, Yoon Jung Chang, Hyunsoon Cho
BMC Medical Research Methodology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Disparities in the Diagnosis, Treatment, and Survival Rate of Cervical Cancer among Women with and without Disabilities
Jin Young Choi, Kyoung Eun Yeob, Seung Hwa Hong, So Young Kim, Eun-Hwan Jeong, Dong Wook Shin, Jong Heon Park, Gil-won Kang, Hak Soon Kim, Jong Hyock Park, Ichiro Kawachi
Cancer Control.2021; 28: 107327482110552. CrossRef - Gynecologic Care in Women With Down Syndrome
Anna J. B. Smith, Jeremy Applebaum, Edward J. Tanner, George T. Capone
Obstetrics & Gynecology.2020; 136(3): 518. CrossRef
- Factors associated with late diagnosis of cervical cancer at two national referral hospitals, Kenya 2017: A case control study
- Identification of Dengue Type 1 Virus (DENV-1) in Koreans Traveling Abroad
- Young Eui Jeong, Yeon Hee Kim, Jung Eun Cho, Myung Guk Han, Young Ran Ju
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2011;2(1):34-40. Published online June 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2011.04.002
- 2,856 View
- 16 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To date, no indigenous dengue virus (DENV) transmissions have been reported in Korea. However, imported dengue infections have been diagnosed in travelers returning from endemic areas. This study presents the first virological evidence of travel-associated DENV importation into South Korea.
Methods
From January 2004 to June 2006, a total of 278 serum samples from 245 patients with suspected dengue fever were tested using the Panbio Dengue Duo IgM/IgG Rapid Strip Test. We selected 11 of the early symptomatic-phase sera that were negative for IgM and retrospectively studied them by virus isolation and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.
Results
All 11 serum samples were found to be DENV positive by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and viruses were successfully isolated from seven of the 11 serum samples. All the isolates were identified as DENV serotype-1.
Conclusion
We successfully isolated seven DENV serotype-1 strains for the first time in South Korea from imported infections. Considering that the vector mosquito, Aedes albopictus, already exists in South Korea, we propose that a vector surveillance program for dengue is urgently needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Genotypic persistence of dengue virus in the Philippines
Ma. Jowina Galarion, Brian Schwem, Coleen Pangilinan, Angelo dela Tonga, Joy Ann Petronio-Santos, Erlinda delos Reyes, Raul Destura
Infection, Genetics and Evolution.2019; 69: 134. CrossRef - Neutralization of Acidic Intracellular Vesicles by Niclosamide Inhibits Multiple Steps of the Dengue Virus Life Cycle In Vitro
Eunhye Jung, Sangwoo Nam, Hyeryeon Oh, Sangmi Jun, Hyun-Joo Ro, Baek Kim, Meehyein Kim, Yun Young Go
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Seroprevalence of Dengue Virus Antibody in Korea
Ji Hyen Lee, Han Wool Kim, Kyung-Hyo Kim
Pediatric Infection & Vaccine.2018; 25(3): 132. CrossRef - Circulating Genotypes of Dengue-1 Virus in South West India, 2014–2015
Shetty Pooja, Sasidharanpillai Sabeena, Bhaskar Revti, Ramachandran Sanjay, Aithal Anjali, Kumar Rajendra, Sushama Aswathyraj, Dsouza Giselle, Maity Hindol, Govindakarnavar Arunkumar
Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases.2017; 70(6): 663. CrossRef - WITHDRAWN: A disease around the corner
Hae-Wol Cho, Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - A Disease Around the Corner
Hae-Wol Cho, Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2016; 7(1): 1. CrossRef - Prevalence of Neutralizing Antibodies to Japanese Encephalitis Virus among High-Risk Age Groups in South Korea, 2010
Eun Ju Lee, Go-Woon Cha, Young Ran Ju, Myung Guk Han, Won-Ja Lee, Young Eui Jeong, Nagendra R Hegde
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(1): e0147841. CrossRef - Laboratory-acquired dengue virus infection by needlestick injury: a case report, South Korea, 2014
Changhwan Lee, Eun Jung Jang, Donghyok Kwon, Heun Choi, Jung Wan Park, Geun-Ryang Bae
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - A Pan-Dengue Virus Reverse Transcription-Insulated Isothermal PCR Assay Intended for Point-of-Need Diagnosis of Dengue Virus Infection by Use of the POCKIT Nucleic Acid Analyzer
Yun Young Go, R. P. V. Jayanthe Rajapakse, Senanayake A. M. Kularatne, Pei-Yu Alison Lee, Keun Bon Ku, Sangwoo Nam, Pin-Hsing Chou, Yun-Long Tsai, Yu-Lun Liu, Hsiao-Fen Grace Chang, Hwa-Tang Thomas Wang, Udeni B. R. Balasuriya, M. J. Loeffelholz
Journal of Clinical Microbiology.2016; 54(6): 1528. CrossRef - Comparison of the Epidemiological Aspects of Imported Dengue Cases between Korea and Japan, 2006–2010
Young Eui Jeong, Won-Chang Lee, Jung Eun Cho, Myung-Guk Han, Won-Ja Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2016; 7(1): 71. CrossRef - Complete Genome Sequences of Three Clinical Isolates of Dengue Virus Serotype 1 from South Korean Travelers
Yun Young Go, Eunhye Jung, Young Eui Jeong, Udeni B. R. Balasuriya
Genome Announcements.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Four Serological Tests for Detecting Antibodies to Japanese Encephalitis Virus after Vaccination in Children
Go Woon Cha, Jung Eun Cho, Young Ran Ju, Young-Jin Hong, Myung Guk Han, Won-Ja Lee, Eui Yul Choi, Young Eui Jeong
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2014; 5(5): 286. CrossRef - Dengue virus type 1 clade replacement in recurring homotypic outbreaks
Boon-Teong Teoh, Sing-Sin Sam, Kim-Kee Tan, Jefree Johari, Meng-Hooi Shu, Mohammed Bashar Danlami, Juraina Abd-Jamil, NorAziyah MatRahim, Nor Muhammad Mahadi, Sazaly AbuBakar
BMC Evolutionary Biology.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - Travel-Associated Chikungunya Cases in South Korea during 2009–2010
Go Woon Cha, Jung Eun Cho, Eun Ju Lee, Young Ran Ju, Myung Guk Han, Chan Park, Young Eui Jeong
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2013; 4(3): 170. CrossRef - The Road Less Traveled
Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2011; 2(1): 1. CrossRef
- Genotypic persistence of dengue virus in the Philippines



 First
First Prev
Prev


