Most download
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Most download
Most-download articles are from the articles published in 2022 during the last three month.
Original Article
- Risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 transmission during a movie theater outbreak in Incheon in the Republic of Korea, November 2021: a retrospective study
- Hye Young Lee, Young-Joon Park, Sang-Eun Lee, Han-Na Yoo, Il-Hwan Kim, Jin Sun No, Eun-Jin Kim, Jungyeon Yu, Sanghwan Bae, Mi Yu
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):45-55. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0269
- 10,579 View
- 325 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 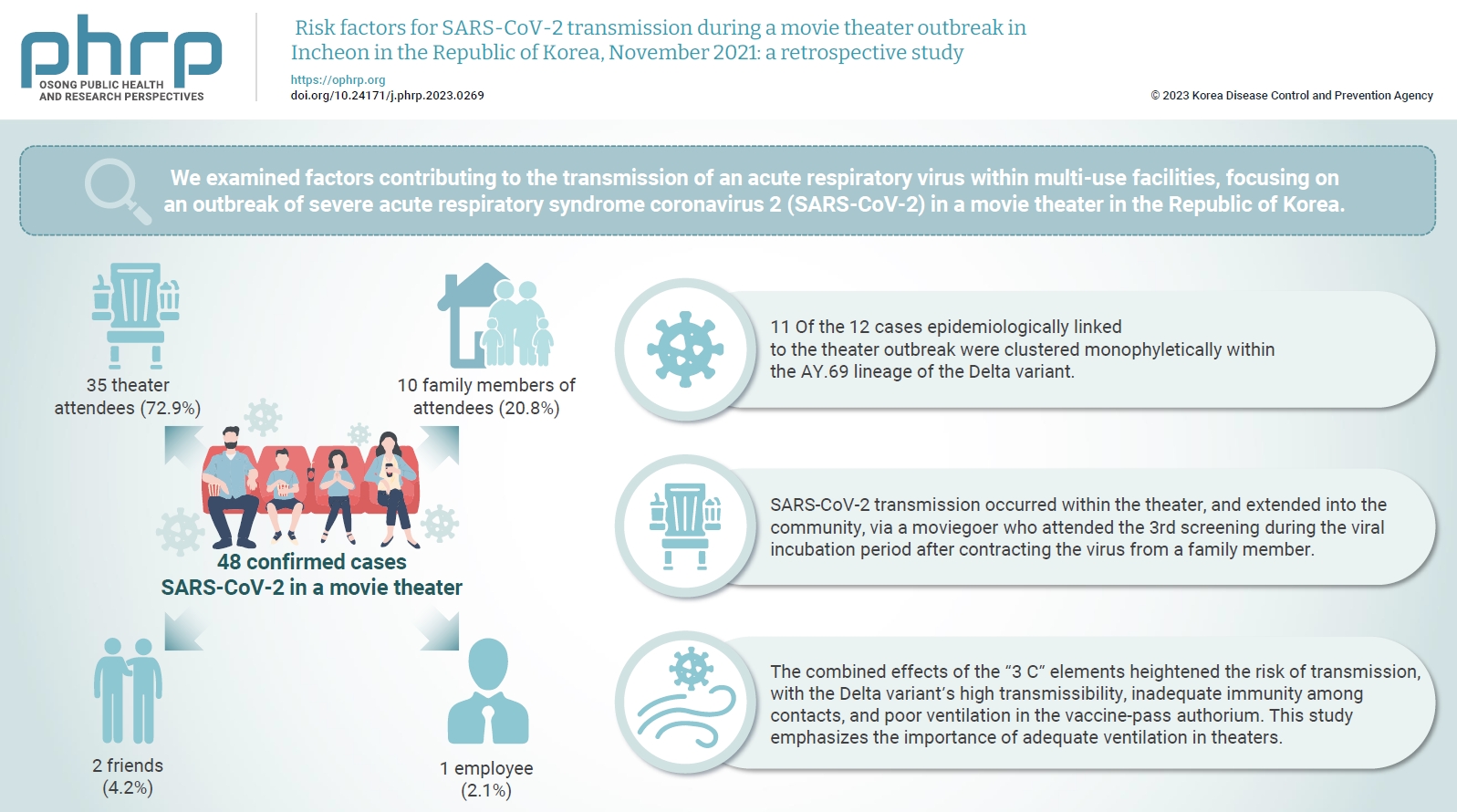
- Objectives
We examined factors contributing to the transmission of an acute respiratory virus within multi-use facilities, focusing on an outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in a movie theater in the Republic of Korea. Methods: This retrospective cohort study involved a descriptive analysis of 48 confirmed cases. Logistic regression was applied to a cohort of 80 theater attendees to identify risk factors for infection. The infection source and transmission route were determined through gene sequencing data analysis. Results: Of the 48 confirmed cases, 35 were theater attendees (72.9%), 10 were family members of attendees (20.8%), 2 were friends (4.2%), and 1 was an employee (2.1%). Among the 80 individuals who attended the 3rd to 5th screenings of the day, 35 became infected, representing a 43.8% attack rate. Specifically, 28 of the 33 third-screening attendees developed confirmed SARSCoV-2, constituting an 84.8% attack rate. Furthermore, 11 of the 12 cases epidemiologically linked to the theater outbreak were clustered monophyletically within the AY.69 lineage. At the time of the screening, 35 individuals (72.9%) had received 2 vaccine doses. However, vaccination status did not significantly influence infection risk. Multivariate analysis revealed that close contacts had a 15.9-fold higher risk of infection (95% confidence interval, 4.37–78.39) than casual contacts. Conclusion: SARS-CoV-2 transmission occurred within the theater, and extended into the community, via a moviegoer who attended the 3rd screening during the viral incubation period after contracting the virus from a family member. This study emphasizes the importance of adequate ventilation in theaters.
Editorial
- What are the strategies for national health security in preparation for the next pandemic?
- Jong-Koo Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):1-2. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2024.0056
- 580 View
- 158 Download
Commentary
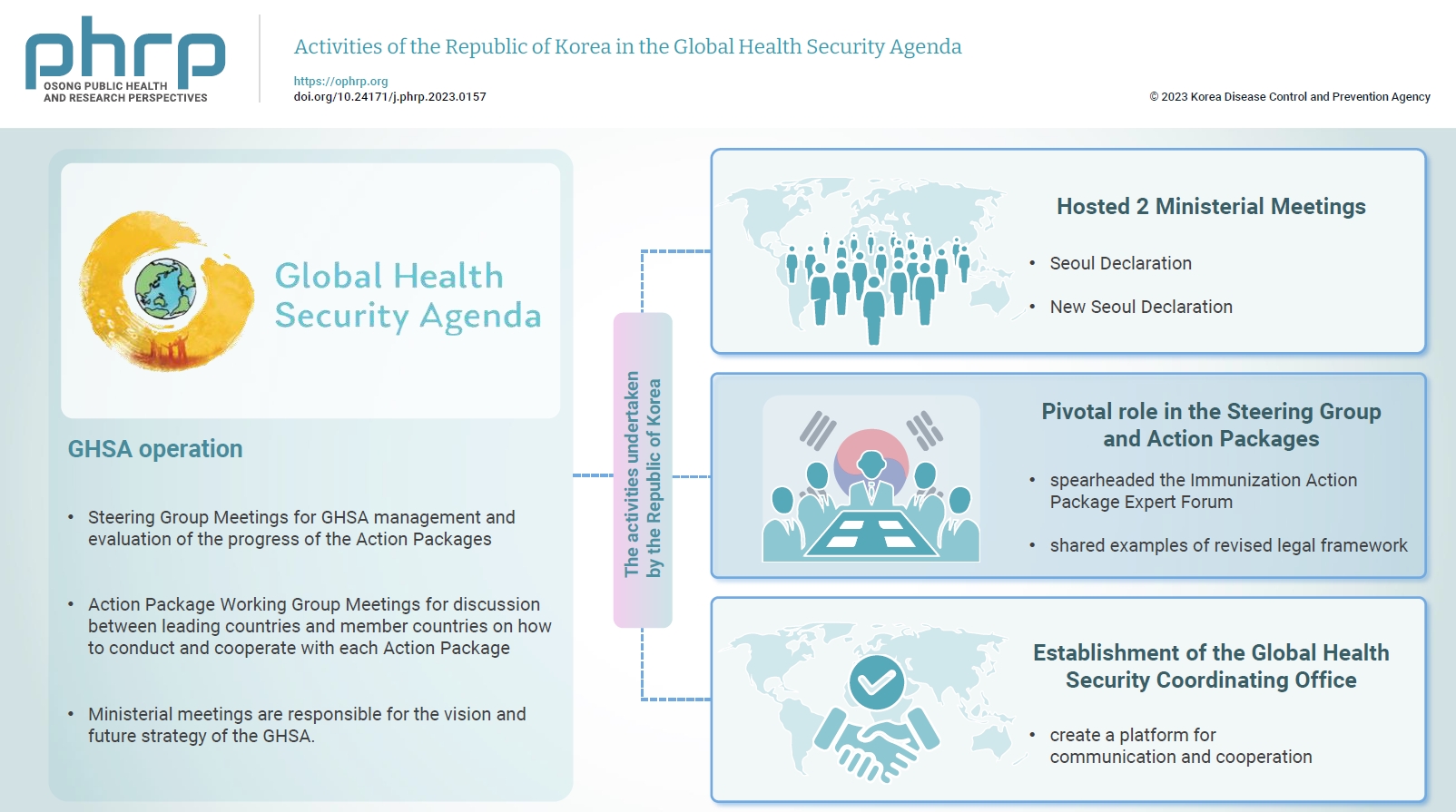
- Activities of the Republic of Korea in the Global Health Security Agenda
- Gang Lip Kim, Sookhyun Lee, So Yoon Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):90-93. Published online February 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0157
- 582 View
- 141 Download
Review Article
- Predictors of outcomes 3 to 12 months after traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Younes Iderdar, Maryem Arraji, Nadia Al Wachami, Morad Guennouni, Karima Boumendil, Yassmine Mourajid, Noureddine Elkhoudri, Elmadani Saad, Mohamed Chahboune
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):3-17. Published online February 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0288
- 1,044 View
- 72 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 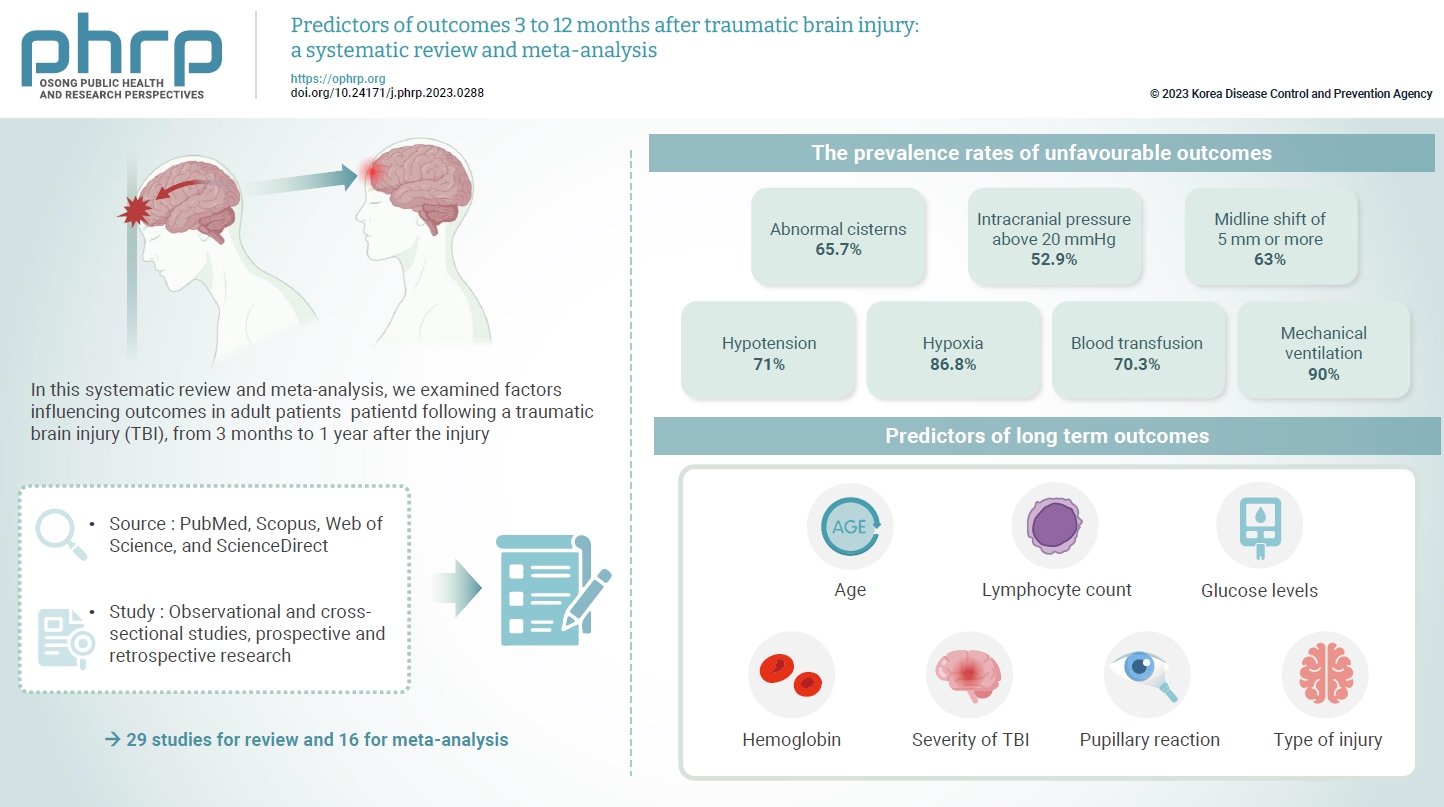
- The exact factors predicting outcomes following traumatic brain injury (TBI) remain elusive. In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we examined factors influencing outcomes in adult patients with TBI, from 3 months to 1 year after injury. A search of four electronic databases—PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and ScienceDirect—yielded 29 studies for review and 16 for meta-analysis, in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis guidelines. In patients with TBI of any severity, mean differences were observed in age (8.72 years; 95% confidence interval [CI], 4.77–12.66 years), lymphocyte count (−0.15 109/L; 95% CI, −0.18 to −0.11), glucose levels (1.20 mmol/L; 95% CI, 0.73–1.68), and haemoglobin levels (−0.91 g/dL; 95% CI, −1.49 to −0.33) between those with favourable and unfavourable outcomes. The prevalence rates of unfavourable outcomes were as follows: abnormal cisterns, 65.7%; intracranial pressure above 20 mmHg, 52.9%; midline shift of 5 mm or more, 63%; hypotension, 71%; hypoxia, 86.8%; blood transfusion, 70.3%; and mechanical ventilation, 90%. Several predictors were strongly associated with outcome. Specifically, age, lymphocyte count, glucose level, haemoglobin level, severity of TBI, pupillary reaction, and type of injury were identified as potential predictors of long-term outcomes.
Editorial
- How to transform the medical care system after the COVID-19 pandemic
- Jong-Koo Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(6):439-440. Published online December 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0382
- 611 View
- 152 Download
Original Articles
- Developing a national surveillance system for stroke and acute myocardial infarction using claims data in the Republic of Korea: a retrospective study
- Tae Jung Kim, Hak Seung Lee, Seong-Eun Kim, Jinju Park, Jun Yup Kim, Jiyoon Lee, Ji Eun Song, Jin-Hyuk Hong, Joongyub Lee, Joong-Hwa Chung, Hyeon Chang Kim, Dong-Ho Shin, Hae-Young Lee, Bum Joon Kim, Woo-Keun Seo, Jong-Moo Park, Soo Joo Lee, Keun-Hwa Jung, Sun U. Kwon, Yun-Chul Hong, Hyo-Soo Kim, Hyun-Jae Kang, Juneyoung Lee, Hee-Joon Bae
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):18-32. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0248
- 927 View
- 58 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 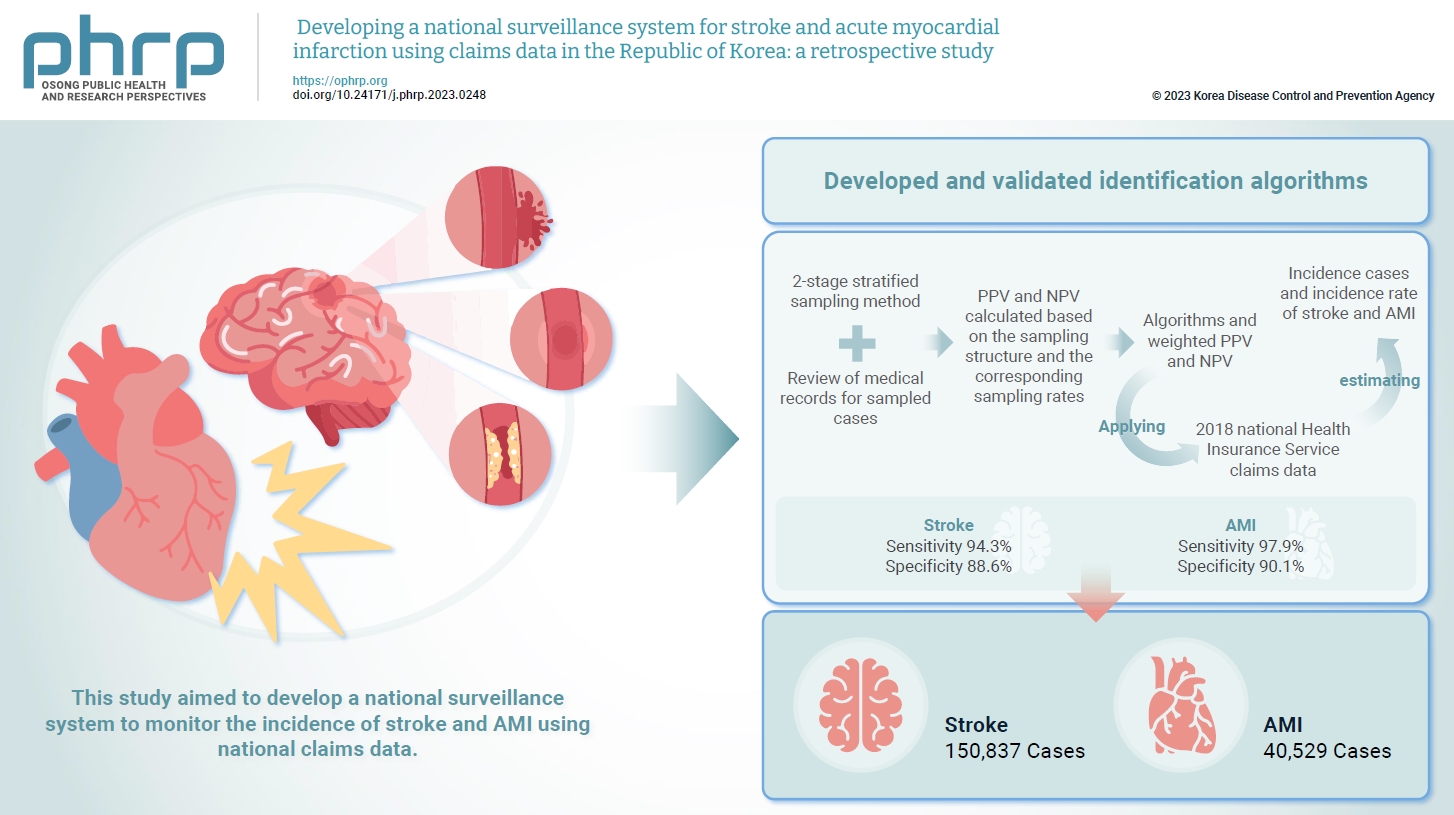
- Objectives
Limited information is available concerning the epidemiology of stroke and acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in the Republic of Korea. This study aimed to develop a national surveillance system to monitor the incidence of stroke and AMI using national claims data. Methods: We developed and validated identification algorithms for stroke and AMI using claims data. This validation involved a 2-stage stratified sampling method with a review of medical records for sampled cases. The weighted positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated based on the sampling structure and the corresponding sampling rates. Incident cases and the incidence rates of stroke and AMI in the Republic of Korea were estimated by applying the algorithms and weighted PPV and NPV to the 2018 National Health Insurance Service claims data. Results: In total, 2,200 cases (1,086 stroke cases and 1,114 AMI cases) were sampled from the 2018 claims database. The sensitivity and specificity of the algorithms were 94.3% and 88.6% for stroke and 97.9% and 90.1% for AMI, respectively. The estimated number of cases, including recurrent events, was 150,837 for stroke and 40,529 for AMI in 2018. The age- and sex-standardized incidence rate for stroke and AMI was 180.2 and 46.1 cases per 100,000 person-years, respectively, in 2018. Conclusion: This study demonstrates the feasibility of developing a national surveillance system based on claims data and identification algorithms for stroke and AMI to monitor their incidence rates.
- Impact of long COVID-19 on posttraumatic stress disorder as modified by health literacy: an observational study in Vietnam
- Han Thi Vo, Tien Duc Dao, Tuyen Van Duong, Tan Thanh Nguyen, Binh Nhu Do, Tinh Xuan Do, Khue Minh Pham, Vinh Hai Vu, Linh Van Pham, Lien Thi Hong Nguyen, Lan Thi Huong Le, Hoang Cong Nguyen, Nga Hoang Dang, Trung Huu Nguyen, Anh The Nguyen, Hoan Van Nguyen, Phuoc Ba Nguyen, Hoai Thi Thanh Nguyen, Thu Thi Minh Pham, Thuy Thi Le, Thao Thi Phuong Nguyen, Cuong Quoc Tran, Kien Trung Nguyen
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):33-44. Published online February 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0261
- 766 View
- 55 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 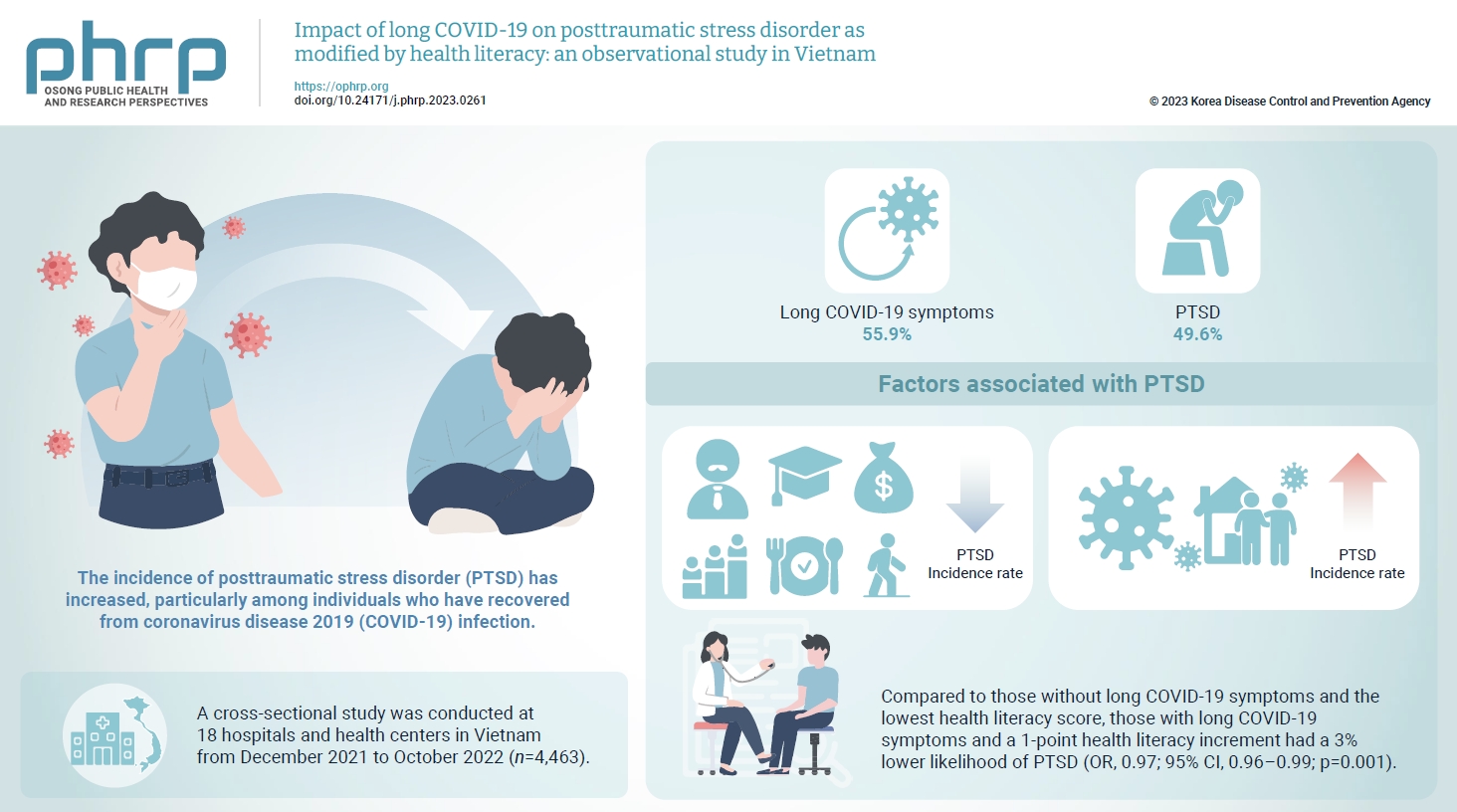
- Objectives
The prevalence of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) has increased, particularly among individuals who have recovered from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection. Health literacy is considered a “social vaccine” that helps people respond effectively to the pandemic. We aimed to investigate the association between long COVID-19 and PTSD, and to examine the modifying role of health literacy in this association. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted at 18 hospitals and health centers in Vietnam from December 2021 to October 2022. We recruited 4,463 individuals who had recovered from COVID-19 infection for at least 4 weeks. Participants provided information about their sociodemographics, clinical parameters, health-related behaviors, health literacy (using the 12-item short-form health literacy scale), long COVID-19 symptoms and PTSD (Impact Event Scale-Revised score of 33 or higher). Logistic regression models were used to examine associations and interactions. Results: Out of the study sample, 55.9% had long COVID-19 symptoms, and 49.6% had PTSD. Individuals with long COVID-19 symptoms had a higher likelihood of PTSD (odds ratio [OR], 1.86; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.63–2.12; p<0.001). Higher health literacy was associated with a lower likelihood of PTSD (OR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.97–0.99; p=0.001). Compared to those without long COVID-19 symptoms and the lowest health literacy score, those with long COVID-19 symptoms and a 1-point health literacy increment had a 3% lower likelihood of PTSD (OR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.96–0.99; p=0.001). Conclusion: Health literacy was found to be a protective factor against PTSD and modified the negative impact of long COVID-19 symptoms on PTSD.
Review Article
- Strategies to combat Gram-negative bacterial resistance to conventional antibacterial drugs: a review
- Priyanka Bhowmik, Barkha Modi, Parijat Roy, Antarika Chowdhury
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):333-346. Published online October 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0323
- 2,156 View
- 173 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- The emergence of antimicrobial resistance raises the fear of untreatable diseases. Antimicrobial resistance is a multifaceted and dynamic phenomenon that is the cumulative result of different factors. While Gram-positive pathogens, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium difficile, were previously the most concerning issues in the field of public health, Gram-negative pathogens are now of prime importance. The World Health Organization’s priority list of pathogens mostly includes multidrug-resistant Gram-negative organisms particularly carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales, carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. The spread of Gram-negative bacterial resistance is a global issue, involving a variety of mechanisms. Several strategies have been proposed to control resistant Gram-negative bacteria, such as the development of antimicrobial auxiliary agents and research into chemical compounds with new modes of action. Another emerging trend is the development of naturally derived antibacterial compounds that aim for targets novel areas, including engineered bacteriophages, probiotics, metal-based antibacterial agents, odilorhabdins, quorum sensing inhibitors, and microbiome-modifying agents. This review focuses on the current status of alternative treatment regimens against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria, aiming to provide a snapshot of the situation and some information on the broader context.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy of new generation biosorbents for the sustainable treatment of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes from polluted waste effluent
Barkha Madhogaria, Sangeeta Banerjee, Atreyee Kundu, Prasanta Dhak
Infectious Medicine.2024; 3(1): 100092. CrossRef - Evaluation of Plant-Based Silver Nanoparticles for Antioxidant Activity and Promising Wound-Healing Applications
Maria Qubtia, Shazia Akram Ghumman, Sobia Noreen, Huma Hameed, Shazia Noureen, Rizwana Kausar, Ali Irfan, Pervaiz Akhtar Shah, Hafsa Afzal, Misbah Hameed, Mohammad Raish, Maria Rana, Ajaz Ahmad, Katarzyna Kotwica-Mojzych, Yousef A. Bin Jardan
ACS Omega.2024; 9(10): 12146. CrossRef
- Efficacy of new generation biosorbents for the sustainable treatment of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes from polluted waste effluent
Original Articles
- Epidemiological analysis and prevention strategies in response to a shigellosis cluster outbreak: a retrospective case series in an alternative school in the Republic of Korea, 2023
- Yeongseo Ahn, Sunmi Jin, Gemma Park, Hye Young Lee, Hyungyong Lee, Eunkyung Shin, Junyoung Kim, Jaeil Yoo, Yuna Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):68-76. Published online February 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0298
- 974 View
- 51 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 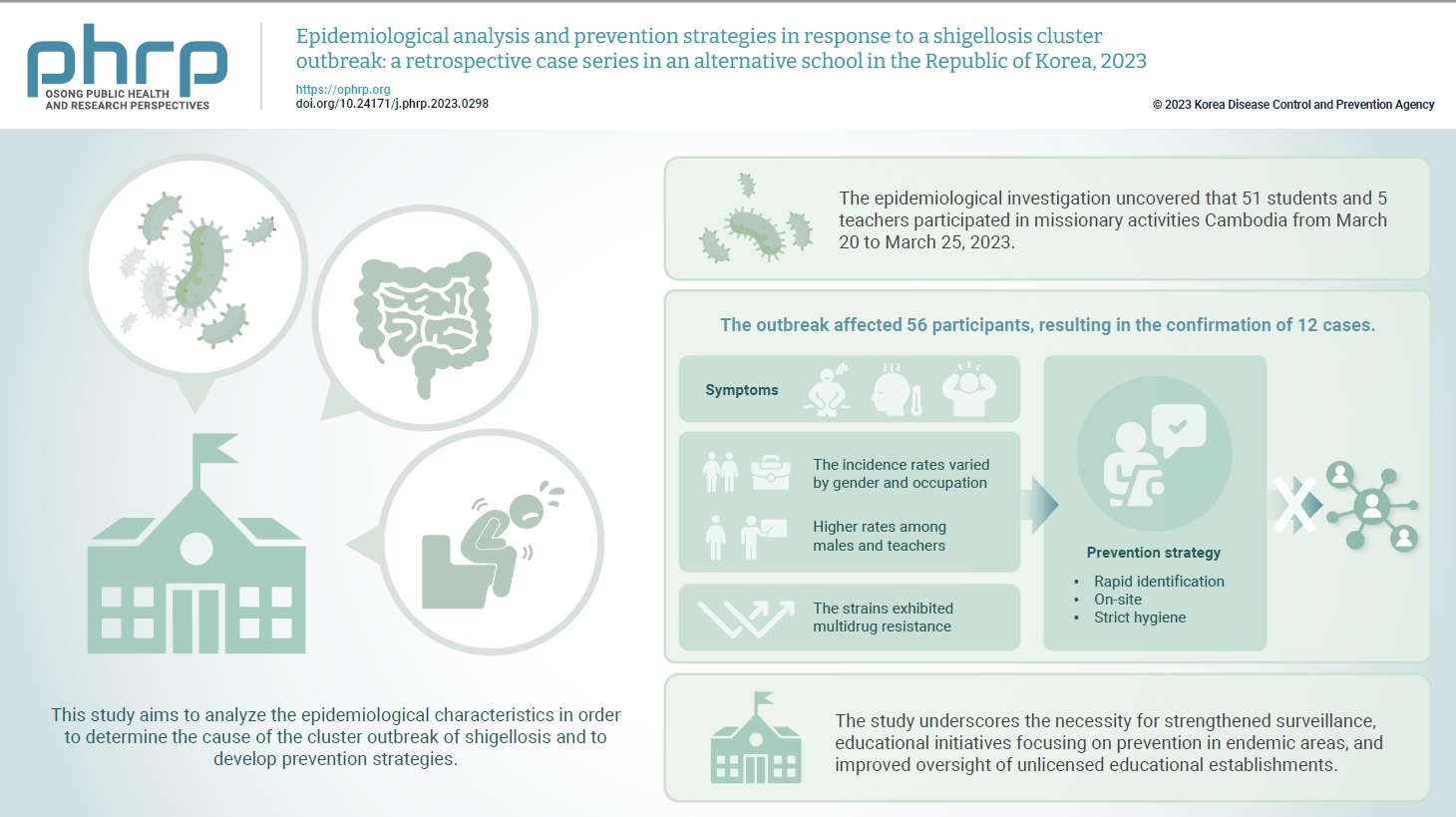
- Objectives
In March 2023, an alternative school in the Republic of Korea reported 12 cases of shigellosis. This study aims to analyze the epidemiological characteristics in order to determine the cause of the cluster outbreak of shigellosis and to develop prevention strategies. Methods: This study focused on 12 patients with confirmed Shigella infection and investigated their demographics, clinical features, epidemiology, diagnostics, and antimicrobial susceptibility. Following the identification of Shigella, we conducted follow-up rectal smear cultures to manage patients, implementing isolation and control measures. Results: This study investigated the emergence of multidrug-resistant Shigella following missionary activities in Cambodia, documenting a cluster infection within an alternative school in Daejeon, the Republic of Korea. The outbreak affected 56 participants, resulting in the confirmation of 12 cases. The incidence rates varied by gender and occupation, with higher rates among males and teachers. All 12 cases demonstrated multidrug resistance. Challenges included delayed pathogen confirmation and suboptimal adherence to isolation criteria. The incident prompted revisions in the criteria for isolation release, focusing on symptom resolution. The study underscores the necessity for strengthened surveillance, educational initiatives focusing on prevention in endemic areas, and improved oversight of unlicensed educational establishments. Conclusion: Successful response strategies included swift situation assessment, collaborative efforts, effective infection control measures, and modified criteria for isolation release. Continued surveillance of multidrug-resistant strains is recommended, especially in regions with a high prevalence.
- Prevalence, multidrug resistance, and biofilm formation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from fish mariculture environments in Cat Ba Island, Vietnam
- Kim Cuc Thi Nguyen, Phuc Hung Truong, Hoa Truong Thi, Xuan Tuy Ho, Phu Van Nguyen
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):56-67. Published online February 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0181
- 805 View
- 49 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 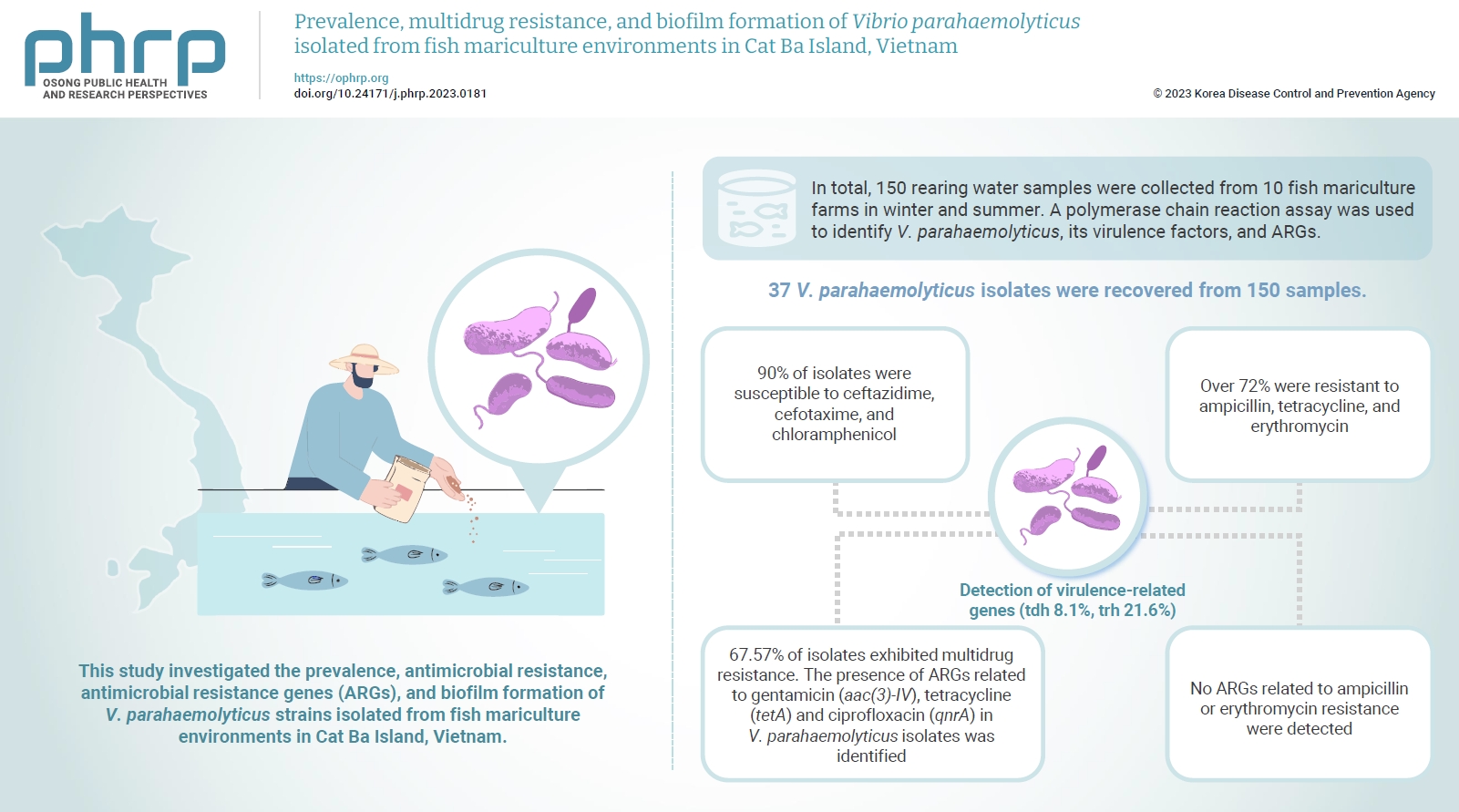
- Objectives
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is a major foodborne pathogen in aquatic animals and a threat to human health worldwide. This study investigated the prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs), and biofilm formation of V. parahaemolyticus strains isolated from fish mariculture environments in Cat Ba Island, Vietnam. Methods: In total, 150 rearing water samples were collected from 10 fish mariculture farms in winter and summer. A polymerase chain reaction assay was used to identify V. parahaemolyticus, its virulence factors, and ARGs. The antimicrobial resistance patterns and biofilm formation ability of V. parahaemolyticus strains were investigated using the disk diffusion test and a microtiter plate-based crystal violet method, respectively. Results: Thirty-seven V. parahaemolyticus isolates were recovered from 150 samples. The frequencies of the tdh and trh genes among V. parahaemolyticus isolates were 8.1% and 21.6%, respectively. More than 90% of isolates were susceptible to ceftazidime, cefotaxime, and chloramphenicol, but over 72% were resistant to ampicillin, tetracycline, and erythromycin. Furthermore, 67.57% of isolates exhibited multidrug resistance. The presence of ARGs related to gentamicin (aac(3)-IV), tetracycline (tetA) and ciprofloxacin (qnrA) in V. parahaemolyticus isolates was identified. Conversely, no ARGs related to ampicillin or erythromycin resistance were detected. Biofilm formation capacity was detected in significantly more multidrug-resistant isolates (64.9%) than non-multidrug-resistant isolates (18.9%). Conclusion: Mariculture environments are a potential source of antibiotic-resistant V. parahaemolyticus and a hotspot for virulence genes and ARGs diffusing to aquatic environments. Thus, the prevention of antibiotic-resistant foodborne vibriosis in aquatic animals and humans requires continuous monitoring.
- Menstrual hygiene management and its determinants among adolescent girls in low-income urban areas of Delhi, India: a community-based study
- Suneela Garg, Nidhi Bhatnagar, Mongjam Meghachandra Singh, Saurav Basu, Amod Borle, Yamini Marimuthu, Falak Azmi, Yomri Dabi, Indu Bala
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(4):273-281. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0127
- 3,493 View
- 253 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Menstrual hygiene management (MHM) in developing countries is linked to human rights, social justice, and the education and empowerment of young girls. The objective of this study was to assess menstrual hygiene practices and their determinants among adolescent girls, including school dropouts, and the effects of pad distribution programs in urban resettlement areas of Delhi, India.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted from March 2019 to February 2020 in urban resettlement colonies and 2 villages of Delhi among 1,130 adolescent girls aged 10 to 19 years, who were interviewed face to face.
Results
In total, 954 participants (84.4%) used only disposable sanitary pads, 150 (13.3%) used both sanitary pads and cloths, and 26 (2.3%) used only cloths (n=1,130). Most school-going girls utilized the scheme for pad distribution, but only two-thirds of the girls who were out of school utilized the scheme. In the adjusted analysis, girls with lower educational status, those who had dropped out of school, and those from the Muslim religious community were more likely to use cloths for MHM.
Conclusion
More than 4 out of 5 adolescent girls in Delhi in low-income neighborhoods preferred sanitary pads for MHM. The government free pad scheme reached near-universal utilization among school-going girls (97%), but the subsidized pad scheme for girls who did not attend school was insufficiently utilized (75%). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Associated with Exclusive Use of Hygienic Methods during Menstruation among Adolescent Girls (15–19 Years) in Urban India: Evidence from NFHS-5
Doli Roy, Nuruzzaman Kasemi, Manik Halder, Malasree Majumder
Heliyon.2024; 10(8): e29731. CrossRef - Menstrual Hygiene Problems and Challenges Faced by Adolescent Females in Rural Areas: A Narrative Review
Vijiya Kashyap, Sonali G Choudhari
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Perceived difficulties in maintaining menstrual hygiene practices among indigenous adolescents during seasonal water scarcity periods in Bandarban hill district of Bangladesh: A cross-sectional study
Imdadul Haque Talukdar, M.A. Rifat, Plabon Sarkar, Nobonita Saha, Mesfin Kassaye Tessma, Md. Ibrahim Miah
International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental.2023; 254: 114268. CrossRef - Menstrual hygiene practices among adolescent women in rural India: a cross-sectional study
Aditya Singh, Mahashweta Chakrabarty, Shivani Singh, Rakesh Chandra, Sourav Chowdhury, Anshika Singh
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Factors Associated with Exclusive Use of Hygienic Methods during Menstruation among Adolescent Girls (15–19 Years) in Urban India: Evidence from NFHS-5
- Chronic kidney disease in Indonesia: evidence from a national health survey
- Puti Sari Hidayangsih, Dwi Hapsari Tjandrarini, Noor Edi Widya Sukoco, Nikson Sitorus, Ika Dharmayanti, Feri Ahmadi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(1):23-30. Published online February 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0290
- 3,234 View
- 233 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 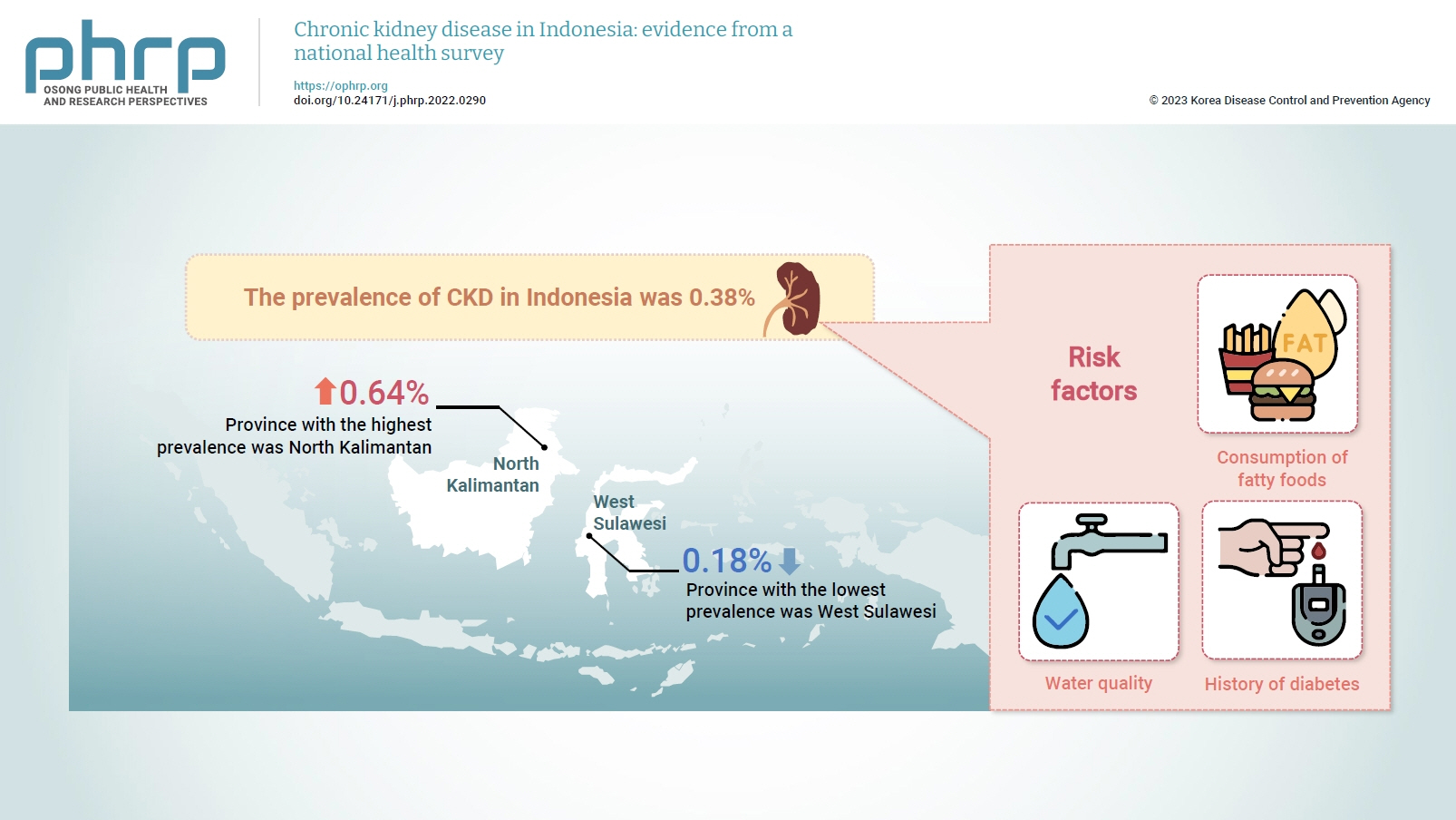
- Objectives
Several previous studies have stated that consuming certain foods and beverages might increase the risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD). This study aimed to examine the relationships of food and beverage consumption with other risk factors for CKD. Methods: Data sources included the 2018 Basic Health Research (Riskesdas) and the National Socio-Economic Survey (Susenas), which were analyzed using a cross-sectional design. The study samples were households from 34 provinces in Indonesia, and the analysis was performed with provincial aggregates. Data were analyzed using risk factor analysis followed by linear regression to identify relationships with CKD. Results: The prevalence of CKD in Indonesia was 0.38%. The province with the highest prevalence was North Kalimantan (0.64%), while the lowest was found in West Sulawesi (0.18%). Five major groups were formed from 15 identified risk factors using factor analysis. A linear regression model presented 1 significant selected factor (p=0.006, R2 =31%). The final model of risk factors included water quality, consumption of fatty foods, and a history of diabetes. Conclusion: Drinking water quality, fatty food consumption, and diabetes are associated with CKD. There is a need to monitor drinking water, as well as to promote health education and provide comprehensive services for people with diabetes, to prevent CKD.
- Estimating the prevalence of oral manifestations in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review
- Ankita Gupta, Kriti Shrivastav, Amit Agrawal, Abhishek Purohit, Roshan Chanchlani
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):388-417. Published online September 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0033
- 2,812 View
- 94 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 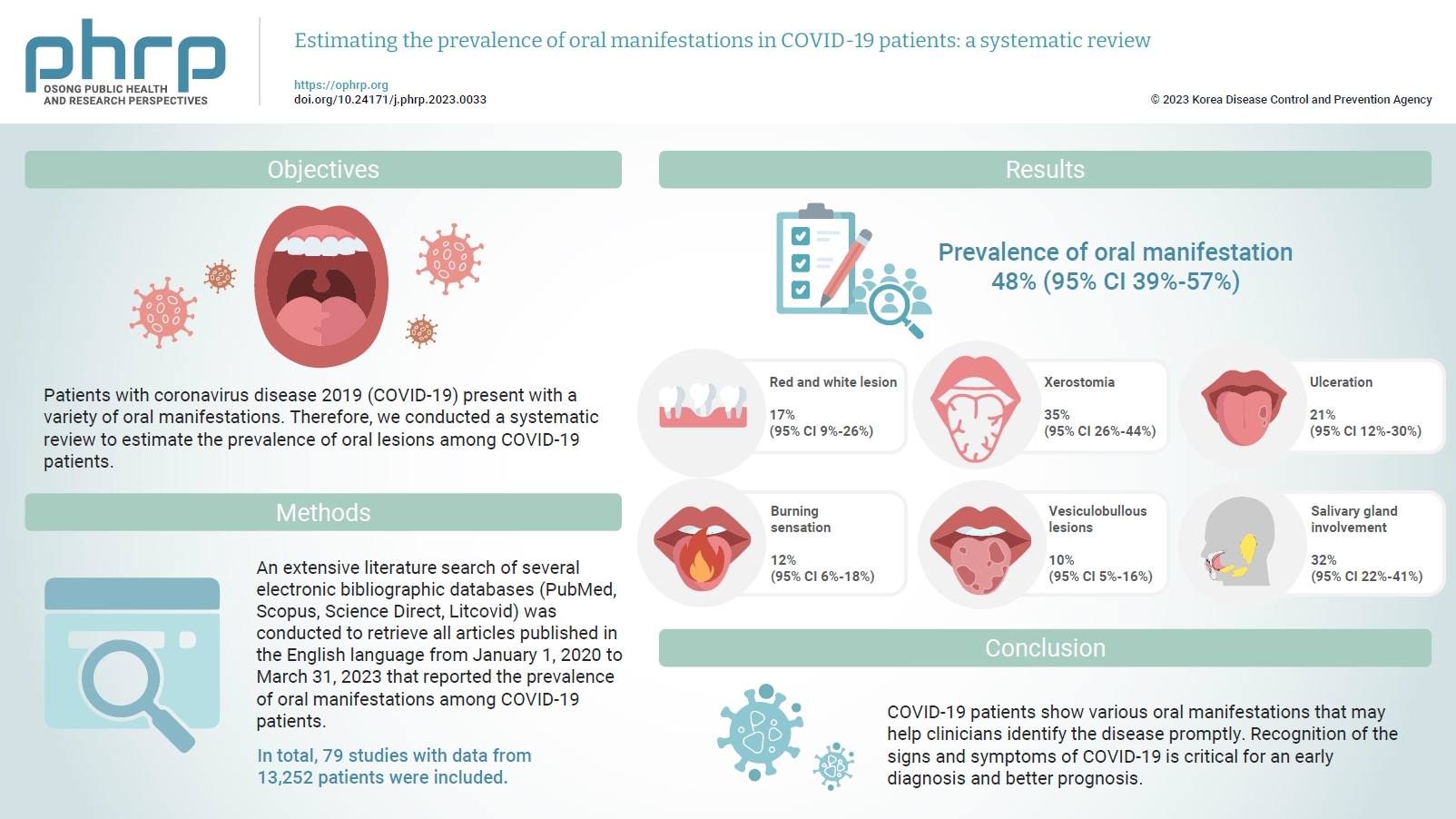
- Objectives
Patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) present with a variety of oral manifestations. Therefore, we conducted a systematic review to estimate the prevalence of oral lesions among COVID-19 patients. Methods: An extensive literature search of several electronic bibliographic databases (PubMed, Scopus, Science Direct, Litcovid) was conducted to retrieve all articles published in the English language from January 1, 2020 to March 31, 2023 that reported the prevalence of oral manifestations among COVID-19 patients. A meta-analysis of pooled prevalence was performed using Jamovi ver. 2.3 (2022). The I2 and Q statistics were used to assess heterogeneity between studies, and p-values <0.01 were considered statistically significant. Results: In total, 79 studies with data from 13,252 patients were included. The articles were predominantly published in 2020 (n=33), and Italy was the most common country (n=14). Most of the affected patients more than 50 years old and women (56.6%). The most common sites of involvement were the tongue (n=65), followed by the oral mucosa (n=37) and lips (n=19). High heterogeneity was found between studies. The most common oral manifestation was taste alteration, followed by xerostomia and ulceration, showing pooled prevalence rates of 48%, 35%, and 21%, respectively. Conclusion: COVID-19 patients show various oral manifestations that may help clinicians identify the disease promptly. Recognition of the signs and symptoms of COVID-19 is critical for an early diagnosis and better prognosis.
Review Article
- Effects of medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hae Ok Jeon, Myung-Ock Chae, Ahrin Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(5):328-340. Published online October 12, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0168
- 3,582 View
- 170 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to understand the characteristics of medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses, and to investigate the average effect size by combining the individual effects of these interventions. Data from studies meeting the inclusion criteria were systematically collected in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis guidelines. The results showed that the average effect size (Hedges’ g) of the finally selected medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses calculated using a random-effects model was 0.500 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.342−0.659). Of the medication adherence interventions, an implementation intention intervention (using face-to-face meetings and telephone monitoring with personalized behavioral strategies) and a health belief model–based educational program were found to be highly effective. Face-to-face counseling was a significantly effective method of implementing medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses (Hedges’ g=0.531, 95% CI, 0.186−0.877), while medication adherence interventions through education and telehealth counseling were not effective. This study verified the effectiveness of personalized behavioral change strategies and cognitive behavioral therapy based on the health belief model, as well as face-to-face meetings, as medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses.
Original Article
- Effects of an arteriovenous fistula stenosis prevention program in patients receiving hemodialysis
- Haegyeong Lee, Gyuli Baek, Eunju Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):279-290. Published online August 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0101
- 1,261 View
- 143 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
To increase the efficiency of hemodialysis, an appropriate vascular pathway must be created, and its function must be maintained. This study aimed to identify the effects of an arteriovenous fistula (AVF) stenosis prevention program on upper muscular strength, blood flow, physiological indexes, and self-efficacy among patients receiving hemodialysis.
Methods
The participants were patients receiving hemodialysis at Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center in Daegu, Republic of Korea. They were divided into experimental and control groups based on the day of the week they received hemodialysis at the outpatient department and included 25 participants each. The study was conducted for 8 weeks.
Results
The AVF stenosis prevention program was effective in improving upper extremity muscle strength (F=15.23, p<0.001) and blood flow rate (F=36.00, p<0.001). As a result of the program, the phosphorus index level, which is a physiological indicator in hemodialysis patients, decreased (F=8.64, p<0.001). Encouragement and support through text messages and practice lists also resulted in an increase in self-efficacy (F=18.62, p<0.001).
Conclusion
The AVF stenosis prevention program in this study resulted in an increase in upper extremity muscle strength through grip strength exercises and was effective in preventing AVF stenosis by increasing the blood flow rate.



 First
First Prev
Prev


