Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Prevalence, multidrug resistance, and biofilm formation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from fish mariculture environments in Cat Ba Island, Vietnam
- Kim Cuc Thi Nguyen, Phuc Hung Truong, Hoa Truong Thi, Xuan Tuy Ho, Phu Van Nguyen
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):56-67. Published online February 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0181
- 868 View
- 50 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 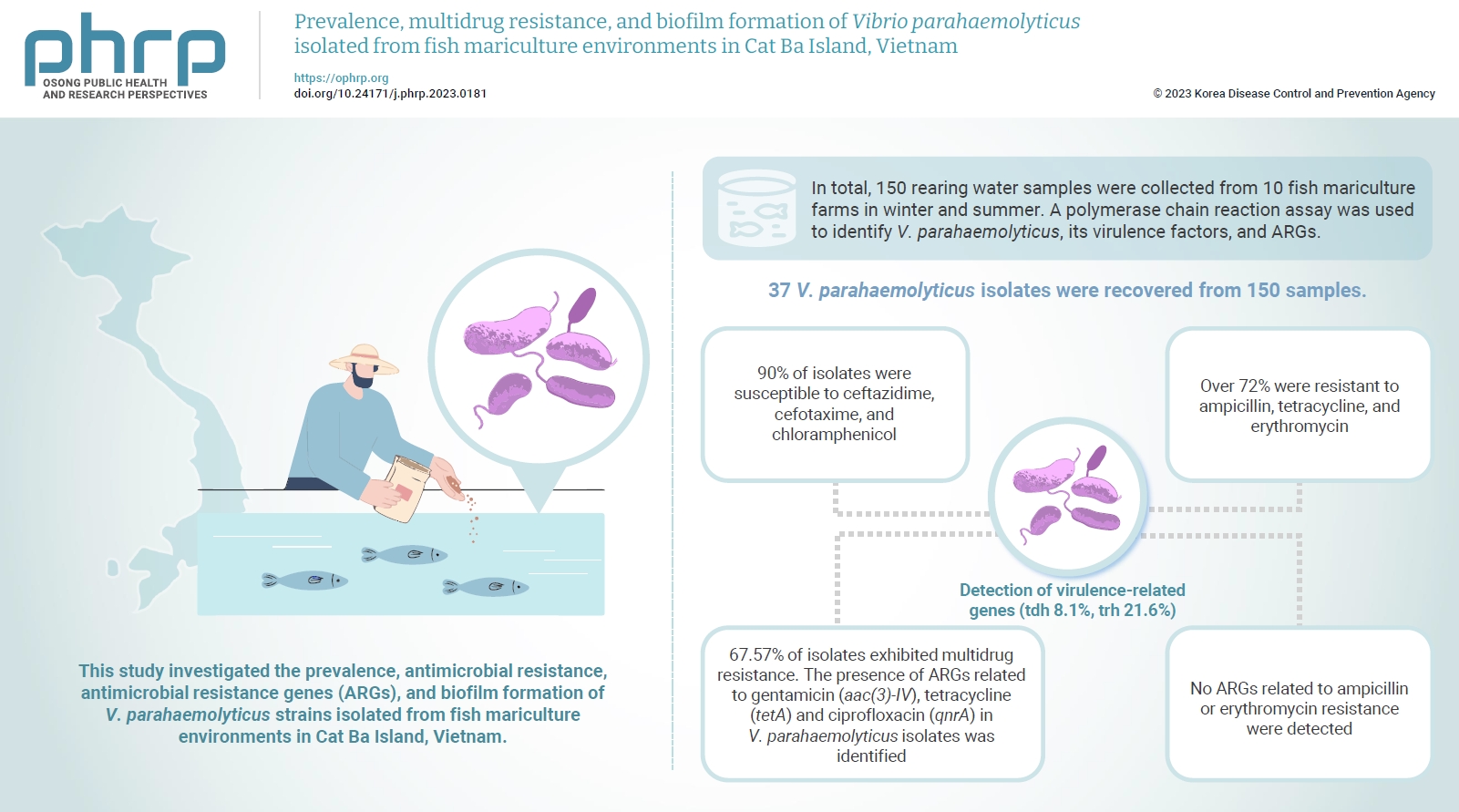
- Objectives
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is a major foodborne pathogen in aquatic animals and a threat to human health worldwide. This study investigated the prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs), and biofilm formation of V. parahaemolyticus strains isolated from fish mariculture environments in Cat Ba Island, Vietnam. Methods: In total, 150 rearing water samples were collected from 10 fish mariculture farms in winter and summer. A polymerase chain reaction assay was used to identify V. parahaemolyticus, its virulence factors, and ARGs. The antimicrobial resistance patterns and biofilm formation ability of V. parahaemolyticus strains were investigated using the disk diffusion test and a microtiter plate-based crystal violet method, respectively. Results: Thirty-seven V. parahaemolyticus isolates were recovered from 150 samples. The frequencies of the tdh and trh genes among V. parahaemolyticus isolates were 8.1% and 21.6%, respectively. More than 90% of isolates were susceptible to ceftazidime, cefotaxime, and chloramphenicol, but over 72% were resistant to ampicillin, tetracycline, and erythromycin. Furthermore, 67.57% of isolates exhibited multidrug resistance. The presence of ARGs related to gentamicin (aac(3)-IV), tetracycline (tetA) and ciprofloxacin (qnrA) in V. parahaemolyticus isolates was identified. Conversely, no ARGs related to ampicillin or erythromycin resistance were detected. Biofilm formation capacity was detected in significantly more multidrug-resistant isolates (64.9%) than non-multidrug-resistant isolates (18.9%). Conclusion: Mariculture environments are a potential source of antibiotic-resistant V. parahaemolyticus and a hotspot for virulence genes and ARGs diffusing to aquatic environments. Thus, the prevention of antibiotic-resistant foodborne vibriosis in aquatic animals and humans requires continuous monitoring.
- Profiling Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance Markers of Enterovirulent Escherichia Coli from Fecal Isolates of Adult Patients with Enteric Infections in West Cameroon
- Wiliane J. T. Marbou, Priyanka Jain, Sriparna Samajpati, Gourab Halder, Asish K. Mukhopadhyay, Shanta Dutta, Victor Kuete
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(4):216-230. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.4.11
- 7,789 View
- 130 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This study aimed to identify virulent and antimicrobial resistant genes in fecal
E. coli in Mbouda, Cameroon.Methods A total of 599 fecal samples were collected from patients with enteric infections who were ≥ 20 years old.
E. coli was isolated on the MacConkey agar and virulent genes were detected by multiplex/simplex PCR. Isolates in which ≥ 1 virulent gene was detected were subjected to antibiotic susceptibility testing. The resulting resistant isolates were subjected to PCR, followed by sequencing for resistant genes detection.Results There were 119 enterovirulent
E. coli identified, amongst which 47.05% were atypical enteropathogenicE. coli (EPEC), 36.97% enterotoxigenicE. coli , 10.08% Shiga toxin producingE. coli (STEC) and 5.88% were enteroinvasiveE. coli (EIEC). The occurrence of theeae gene (47.06%) was higher compared withCVD432 (33.61%),aaic (13.45%),stx2 (10.08%) andstx1 (0.84%). High resistance rates were noted for ampicillin (94.64% EPEC, 91.67% STEC, 59.09% EAEC, and 57.14% EIEC) and sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (100% EPEC and 83.33% STEC, 81.82% EAEC and 71.43% EIEC).sul2 (71.43%),tetB (64.71%),tetA (59.94%) andblaTEM (52.10%) were detected. A double mutation (S83L; D87N) was seen ingyrA and a single mutation (S80I) was observed inparC .Conclusion These findings suggested that measures should be taken to reduce the harm of
E. coli to public health.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Molecular epidemiology of antimicrobial resistance in central africa: A systematic review
Annicet-Clotaire Dikoumba, Richard Onanga, Laurette G. Mangouka, Larson Boundenga, Edgard-Brice Ngoungou, Sylvain Godreuil
Access Microbiology .2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Methanol extract from the seeds of Persea americana displays antibacterial and wound healing activities in rat model
Steve E. Ekom, Jean-De-Dieu Tamokou, Victor Kuete
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2022; 282: 114573. CrossRef - Characterization of diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli with special reference to antimicrobial resistance isolated from hospitalized diarrhoeal patients in Kolkata (2012–2019), India
Debjani Ghosh, Goutam Chowdhury, Prosenjit Samanta, Sreeja Shaw, Alok K. Deb, Mainak Bardhan, Asis Manna, Shin-ichi Miyoshi, Thandavarayan Ramamurthy, Shanta Dutta, Asish K. Mukhopadhyay
Journal of Applied Microbiology.2022; 132(6): 4544. CrossRef - Antibiotic resistomes and their chemical residues in aquatic environments in Africa
Aemere Ogunlaja, Olumuyiwa O. Ogunlaja, Olumide D. Olukanni, Gloria O. Taylor, Chidinma G. Olorunnisola, Victorien T. Dougnon, Wassiyath Mousse, Despo Fatta-Kassinos, Titus A.M. Msagati, Emmanuel I. Unuabonah
Environmental Pollution.2022; 312: 119783. CrossRef - Antibacterial and Therapeutic Potentials of the Capsicum annuum Extract against Infected Wound in a Rat Model with Its Mechanisms of Antibacterial Action
Steve Endeguele Ekom, Jean-De-Dieu Tamokou, Victor Kuete, Dorota Formanowicz
BioMed Research International.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Molecular epidemiology of antimicrobial resistance in central africa: A systematic review
- Association between Beta-lactam Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Factors in AmpC Producing Clinical Strains of
P. aeruginosa - Sanaz Dehbashi, Hamed Tahmasebi, Mohammad Reza Arabestani
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(6):325-333. Published online December 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.6.06
- 22,895 View
- 134 Download
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The purpose of this study was to determine the presence of
IMP andOXA genes in clinical strains ofPseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa ) that are carriers of theampC gene.Methods In this study, 105 clinical isolates of
P. aeruginosa were collected. Antibiotic resistance patterns were determined using the disk diffusion method. The strains carrying AmpC enzymes were characterized by a combination disk method. Multiplex-PCR was used to identify resistance and virulence genes, chi-square test was used to determine the relationship between variables.Results Among 105 isolates of
P. aeruginosa , the highest antibiotic resistance was to cefotaxime and aztreonam, and the least resistance was to colictin and ceftazidime. There were 49 isolates (46.66%) that showed an AmpC phenotype. In addition, the frequencies of the resistance genes were;OXA48 gene 85.2%,OXA199, 139 3.8%,OXA23 3.8%,OXA2 66.6%,OXA10 3.8%,OXA51 85.2% andOXA58 3.8%. TheIMP27 gene was detected in 9 isolates (8.57%) and theIMP3.34 was detected in 11 isolates (10.47%). Other genes detected included;lasR (17.1%),lasB (18%) andlasA (26.6%). There was a significant relationship between virulence factors and theOX andIMP genes (p ≤ 0.05).Conclusion The relationship between antibiotic resistance and virulence factors observed in this study could play an important role in outbreaks associated with
P. aeruginosa infections.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative bacteriome and antibiotic resistome analysis of water and sediment of the Ganga River of India
Ankita Srivastava, Digvijay Verma
World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of different virulence factors and their association with antimicrobial resistance among Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates from Egypt
Eva A. Edward, Marwa R. El Shehawy, Alaa Abouelfetouh, Elsayed Aboulmagd
BMC Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular epidemiology and collaboration of siderophore-based iron acquisition with surface adhesion in hypervirulent Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from wound infections
Hamed Tahmasebi, Sanaz Dehbashi, Mona Nasaj, Mohammad Reza Arabestani
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Decoding Genetic Features and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains Isolated from Bloodstream Infections
Tomasz Bogiel, Dagmara Depka, Mateusz Rzepka, Agnieszka Mikucka
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(16): 9208. CrossRef - Prevalence of the Genes Associated with Biofilm and Toxins Synthesis amongst the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Strains
Tomasz Bogiel, Dagmara Depka, Mateusz Rzepka, Joanna Kwiecińska-Piróg, Eugenia Gospodarek-Komkowska
Antibiotics.2021; 10(3): 241. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Study of the Relationship between the Production of β-Lactamase Enzymes and Iron/Siderophore Uptake Regulatory Genes in Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii
Mahyar Porbaran, Hamed Tahmasebi, MohammadReza Arabestani, Joseph Falkinham
International Journal of Microbiology.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Regulation of virulence and β-lactamase gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus isolates: cooperation of two-component systems in bloodstream superbugs
Sanaz Dehbashi, Hamed Tahmasebi, Behrouz Zeyni, Mohammad Reza Arabestani
BMC Microbiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef -
New approach to identify colistin‐resistant
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
by high‐resolution melting curve analysis assay
H. Tahmasebi, S. Dehbashi, M.R. Arabestani
Letters in Applied Microbiology.2020; 70(4): 290. CrossRef - Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa carrying virulence genes in hospitalized patients with urinary tract infection from Sanandaj, west of Iran
Safoura Derakhshan, Aslan Hosseinzadeh
Gene Reports.2020; 20: 100675. CrossRef - Prevalence and molecular typing of Metallo-β-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa with adhesion factors: A descriptive analysis of burn wounds isolates from Iran
Hamed Tahmasebi, Sanaz Dehbashi, Mohammad Yousef Alikhani, Mahyar Porbaran, Mohammad Reza Arabestani
Gene Reports.2020; 21: 100853. CrossRef - Co-harboring of mcr-1 and β-lactamase genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by high-resolution melting curve analysis (HRMA): Molecular typing of superbug strains in bloodstream infections (BSI)
Hamed Tahmasebi, Sanaz Dehbashi, Mohammad Reza Arabestani
Infection, Genetics and Evolution.2020; 85: 104518. CrossRef - Relationship between Biofilm Regulating Operons and Various Β-Lactamase Enzymes: Analysis of the Clinical Features of Infections caused by Non-Fermentative Gram-Negative Bacilli (Nfgnb) from Iran
Mahyar Porbaran, Reza Habibipour
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2020; 14(3): 1723. CrossRef - Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains-Distribution of the Essential Enzymatic Virulence Factors Genes
Tomasz Bogiel, Małgorzata Prażyńska, Joanna Kwiecińska-Piróg, Agnieszka Mikucka, Eugenia Gospodarek-Komkowska
Antibiotics.2020; 10(1): 8. CrossRef - Biofilm Formation and β-lactamase Enzymes: A Synergism Activity in Acinetobacter baumannii Isolated from Wound Infection
Mahyar Porbaran, Reza Habibipour
Journal of Advances in Medical and Biomedical Rese.2019; 27(125): 34. CrossRef
- Comparative bacteriome and antibiotic resistome analysis of water and sediment of the Ganga River of India
- Relationships between Virulence Factors and Antimicrobial Resistance among
Escherichia coli Isolated from Urinary Tract Infections and Commensal Isolates in Tehran, Iran - Mohammad Reza Asadi Karam, Mehri Habibi, Saeid Bouzari
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(5):217-224. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.5.02
- 6,790 View
- 132 Download
- 30 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Uropathogenic
Escherichia coli (UPEC) are the major cause of urinary tract infections (UTIs). Here, we determined whether sensitivity to antibiotics was related to the prevalence of iron scavenging genes, or to biofilm and hemolysis formation.Methods A total of 110 UPEC and 30
E coli isolates were collected from the urine of UTI patients and feces of healthy individuals without UTI, respectively. The presence of iron receptor genes and phenotypic properties were evaluated by polymerase chain reaction and phenotypic methods, respectively. Susceptibility to routine antibiotics was evaluated using the disc diffusion method.Results The prevalence of iron scavenging genes ranged from 21.8% (
ireA ) to 84.5% (chuA ) in the UPEC. Resistance to ceftazidime and cefotaxime was significantly correlated with the presence offyuA andiutA iron genes. Biofilm production was significantly associated with the prevalence offyuA andhma iron genes. A higher degree of antibiotic resistance was exhibited by isolates that produced biofilms than by their non-biofilm producing counterparts.Conclusion Our study clearly indicates that biofilm production is associated with antibiotic resistance, and that iron receptors and hemolysin production also contribute to reduced antibiotic sensitivity. These results further our understanding of the role that these virulence factors play during UPEC pathogenesis, which in turn may be valuable for the development of novel treatment strategies against UTIs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Correlation between antimicrobial resistance, biofilm formation, and virulence determinants in uropathogenic Escherichia coli from Egyptian hospital
Sara A. Alshaikh, Tarek El-banna, Fatma Sonbol, Mahmoud H. Farghali
Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Multidrug resistance in pathogenic Escherichia coli isolates from urinary tract infections in dogs, Spain
Ana Abad-Fau, Eloisa Sevilla, Ainara Oro, Inmaculada Martín-Burriel, Bernardino Moreno, Mariano Morales, Rosa Bolea
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistant Escherichia coli isolated from wild mammals from two rescue and rehabilitation centers in Costa Rica: characterization and public health relevance
Rita Fernandes, Raquel Abreu, Isa Serrano, Roger Such, Encarnación Garcia-Vila, Sandy Quirós, Eva Cunha, Luís Tavares, Manuela Oliveira
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef -
Progress toward a vaccine for extraintestinal pathogenic
E. coli
(ExPEC) II: efficacy of a toxin-autotransporter dual antigen approach
Yikun Xing, Justin R. Clark, James D. Chang, Jacob J. Zulk, Dylan M. Chirman, Felipe-Andres Piedra, Ellen E. Vaughan, Haroldo J. Hernandez Santos, Kathryn A. Patras, Anthony W. Maresso, Kimberly A. Kline
Infection and Immunity.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC)-Associated Urinary Tract Infections: The Molecular Basis for Challenges to Effective Treatment
Shane Whelan, Brigid Lucey, Karen Finn
Microorganisms.2023; 11(9): 2169. CrossRef - Susceptibility and Virulence of Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Urinary Tract Infections in Benin
Funkè F. Assouma, Haziz Sina, Tomabu Adjobimey, Agossou Damien Pacôme Noumavo, Akim Socohou, Bawa Boya, Ange D. Dossou, Lauriane Akpovo, Basile Boni Saka Konmy, Jacques F. Mavoungou, Adolphe Adjanohoun, Lamine Baba-Moussa
Microorganisms.2023; 11(1): 213. CrossRef - Association Between Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Virulence Genes and Severity of Infection and Resistance to Antibiotics
Sofía Alejandra Fonseca-Martínez, Ruth Aralí Martínez-Vega, Ana Elvira Farfán-García, Clara Isabel González Rugeles, Libeth Yajaira Criado-Guerrero
Infection and Drug Resistance.2023; Volume 16: 3707. CrossRef - Incidence of biofilms among the multidrug resistant E. coli, isolated from urinary tract infections in the Nilgiris district, South India
A. P. Cardiliya, M. J. N. Chandrasekar, M. J. Nanjan
Brazilian Journal of Microbiology.2023; 54(3): 1809. CrossRef - Correlation of biofilm formation, virulence factors, and phylogenetic groups among Escherichia coli strains causing urinary tract infection: A global systematic review and meta-analysis
HosseinKarballaei Mirzahosseini, Farhad Najmeddin, Atabak Najafi, Arezoo Ahmadi, Hamidreza Sharifnia, Azad Khaledi, Mojtaba Mojtahedzadeh
Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.2023; 28(1): 66. CrossRef - Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis Caused by Co-Infection with Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Multidrug-Resistant Extended-Spectrum ß-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli: A Case Report
Shiori Kitaya, Chieko Miura, Ayano Suzuki, Yoshimichi Imai, Koichi Tokuda, Hajime Kanamori
Applied Microbiology.2023; 3(3): 1046. CrossRef - Fluoroquinolone resistance determinants in carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from urine clinical samples in Thailand
Parichart Boueroy, Peechanika Chopjitt, Rujirat Hatrongjit, Masatomo Morita, Yo Sugawara, Yukihiro Akeda, Tetsuya Iida, Shigeyuki Hamada, Anusak Kerdsin
PeerJ.2023; 11: e16401. CrossRef - Characterization of virulence determinants and phylogenetic background of multiple and extensively drug resistant Escherichia coli isolated from different clinical sources in Egypt
Rana El-baz, Heba Shehta Said, Eman Salama Abdelmegeed, Rasha Barwa
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology.2022; 106(3): 1279. CrossRef - A global systematic review and meta-analysis on correlation between biofilm producers and non-biofilm producers with antibiotic resistance in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Mitra Garousi, Sina Monazami Tabar, Hosein Mirazi, Parnia Asgari, Paniz Sabeghi, Astireh Salehi, Azad Khaledi, Mohammad Ghenaat Pisheh Sanani, Hossein Karballaei Mirzahosseini
Microbial Pathogenesis.2022; 164: 105412. CrossRef - Virulence factors, antimicrobial resistance and the relationship between these characteristics in uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Farzaneh Firoozeh, Mohammad Zibaei, Farzad Badmasti, Azad Khaledi
Gene Reports.2022; 27: 101622. CrossRef - Association between Virulence Factors and Antimicrobial Resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates from North Kerala
Ramya Kumaran, R.V. Geetha, Sabitha Baby
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2022; 16(2): 867. CrossRef - Characterization of virulence factors and antibiotic resistance pattern of uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains in a tertiary care center
Naveen Kumar M, Sevitha Bhat, Archana Bhat K, Vishwas Saralaya, Shalini Shenoy Mulki
F1000Research.2022; 11: 1163. CrossRef - Antibiotic Resistance, Biofilm Formation and Sub-Inhibitory Hydrogen Peroxide Stimulation in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Prabin Dawadi, Santosh Khanal, Tista Prasai Joshi, Sudeep KC, Reshma Tuladhar, Bijaya Laxmi Maharjan, Anjani Darai, Dev Raj Joshi
Microbiology Insights.2022; 15: 117863612211352. CrossRef - Characterization of virulence factors and antibiotic resistance pattern of uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains in a tertiary care center
Naveen Kumar M, Sevitha Bhat, Archana Bhat K, Vishwas Saralaya, Shalini Shenoy Mulki
F1000Research.2022; 11: 1163. CrossRef - Insects, Rodents, and Pets as Reservoirs, Vectors, and Sentinels of Antimicrobial Resistance
Willis Gwenzi, Nhamo Chaukura, Norah Muisa-Zikali, Charles Teta, Tendai Musvuugwa, Piotr Rzymski, Akebe Luther King Abia
Antibiotics.2021; 10(1): 68. CrossRef - Virulence genes and phylogenetic groups of uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates from patients with urinary tract infection and uninfected control subjects: a case-control study
Seyedeh Elham Rezatofighi, Mahsa Mirzarazi, Mansour Salehi
BMC Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Virulence characterization and clonal analysis of uropathogenic Escherichia coli metallo-beta-lactamase-producing isolates
Fatemeh Zangane Matin, Seyedeh Elham Rezatofighi, Mohammad Roayaei Ardakani, Mohammad Reza Akhoond, Fahimeh Mahmoodi
Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Detection of Virulence-Associated Genes in Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Commercial Broilers
Tímea Kocúreková, Lívia Karahutová, Dobroslava Bujňáková
Antibiotics.2021; 10(11): 1303. CrossRef - Evaluation of Biofilm Formation and Virulence Genes and Association with Antibiotic Resistance Patterns of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Strains in Southwestern Iran
Mostafa Boroumand, Asghar Sharifi, Mohammad Amin Ghatei, Mohsen Sadrinasab
Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Differences of virulence factors, and antimicrobial susceptibility according to phylogenetic group in uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from Korean patients
Miri Hyun, Ji Yeon Lee, Hyun ah Kim
Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Bacterial Spectrum and Resistance Patterns Over Time in the Urine of Patients with Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Due to Spinal Cord Injury
Jürgen Pannek, Carmen Kurmann, Jörg Krebs, Valentin Habermacher, Jens Wöllner
Urologia Internationalis.2021; 105(5-6): 483. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta-analysis of antibiotic resistance patterns, and the correlation between biofilm formation with virulence factors in uropathogenic E. coli isolated from urinary tract infections
Fei Zhao, Huanxin Yang, Dezhong Bi, Azad Khaledi, Mingqi Qiao
Microbial Pathogenesis.2020; 144: 104196. CrossRef - A survey for phylogenetic relationship; presence of virulence genes and antibiotic resistance patterns of avian pathogenic and uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from poultry and humans in Yazd, Iran
Mansoureh Bakhshi, Hengameh Zandi, Mehdi Fatahi Bafghi, Akram Astani, Vahid Reza Ranjbar, Mahmood Vakili
Gene Reports.2020; 20: 100725. CrossRef - Biofilm formation, antimicrobial susceptibility and virulence genes of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from clinical isolates in Uganda
Paul Katongole, Fatuma Nalubega, Najjuka Christine Florence, Benon Asiimwe, Irene Andia
BMC Infectious Diseases.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between Virulence and Resistance among Gram-Negative Bacteria
Virginio Cepas, Sara M. Soto
Antibiotics.2020; 9(10): 719. CrossRef - Virulence factors of uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) and correlation with antimicrobial resistance
Chhaya Shah, Ratna Baral, Bijay Bartaula, Lok Bahadur Shrestha
BMC Microbiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Correlation between antimicrobial resistance, biofilm formation, and virulence determinants in uropathogenic Escherichia coli from Egyptian hospital
- Profiling of Virulence-associated Factors in
Shigella Species Isolated from Acute Pediatric Diarrheal Samples in Tehran, Iran - Sajad Yaghoubi, Reza Ranjbar, Mohammad Mehdi Soltan Dallal, Somayeh Yasliani Fard, Mohammad Hasan Shirazi, Mahmood Mahmoudi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(3):220-226. Published online June 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.3.09
- 4,536 View
- 61 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The genus
Shigella comprises the most infectious and diarrheagenic bacteria causing severe diseases, mostly in children under five years of age. This study aimed to detect nine virulence genes (ipaBCD ,VirA ,sen ,set1A ,set1B ,ial ,ipaH ,stx , andsat ) inShigella species (spp.) using multiplex polymerase chain reaction (MPCR) and to determine the relation ofShigella spp. from pediatric diarrheal samples with hospitalization and bloody diarrhea in Tehran, Iran.Methods Shigella spp. were isolated and identified using standard microbiological and serological methods. The virulence genes were detected using MPCR.Results Seventy-five
Shigella spp. (40S. sonnei , 33S. flexneri , 1S. dysenteriae , and 1S. boydii ) were isolated in this study. The prevalence ofial ,sen ,sat ,set1A , andset1B was 74.7%, 45.4%, 28%, 24%, and 24%, respectively. AllS. flexneri isolates, while noS. sonnei ,S. dysenteriae , orS. boydii isolates, containedsat ,set1A , andset1B . All isolates were positive foripaH ,ipaBCD , andvirA , while one (1.4%) of the isolates containedstx . The highest prevalence of virulence determinants was found inS. flexneri serotype IIa. Nineteen (57.6%) of 33S. flexneri isolates were positive foripaBCD ,ipaH ,virA ,ial , andsat . Thesen determinants were found to be statistically significantly associated with hospitalization and bloody diarrhea (p = 0.001).Conclusion This study revealed a high prevalence of enterotoxin genes in
S. flexneri , especially in serotype 2a, and has presented relations between a few clinical features of shigellosis and numerous virulence determinants of clinical isolates ofShigella spp.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Epidemiological analysis and prevention strategies in response to a shigellosis cluster outbreak: a retrospective case series in an alternative school in the Republic of Korea, 2023
Yeongseo Ahn, Sunmi Jin, Gemma Park, Hye Young Lee, Hyungyong Lee, Eunkyung Shin, Junyoung Kim, Jaeil Yoo, Yuna Kim
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2024; 15(1): 68. CrossRef - Invasion of HeLa Cells by Shigella Species Clinical Isolates Recovered from Pediatric Diarrhea
Zohreh Ghalavand, Marzieh Taheri, Gita Eslami, Mohammadmahdi Karimi-Yazdi, Mehrzad Sadredinamin
Foodborne Pathogens and Disease.2023; 20(11): 509. CrossRef - Plant-derived nanoparticles as alternative therapy against Diarrheal pathogens in the era of antimicrobial resistance: A review
Tesleem Olatunde Abolarinwa, Daniel Jesuwenu Ajose, Bukola Opeyemi Oluwarinde, Justine Fri, Kotsoana Peter Montso, Omolola Esther Fayemi, Adeyemi Oladapo Aremu, Collins Njie Ateba
Frontiers in Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Distribution of genes encoding virulence factors of Shigella strains isolated from children with diarrhea in southwest Iran
Nabi Jomehzadeh, Khadijah Ahmadi, Hazhir Javaherizadeh, Maryam Afzali
Molecular Biology Reports.2021; 48(2): 1645. CrossRef - Evaluate the distribution of virulence genes and to investigate antibiotic resistance pattern among Shigella species isolated from children with shigellosis in Iran
Samane Mohebi, Hossein Hosseini Nave, Kasra Javadi, Ali Amanati, Soudeh Kholdi, Mahtab Hadadi, Zahra Hashemizadeh, Mohammad Motamedifar
Gene Reports.2021; 23: 101189. CrossRef - Burden, Antibiotic Resistance, and Clonality of Shigella spp. Implicated in Community-Acquired Acute Diarrhoea in Lilongwe, Malawi
Abel F.N.D. Phiri, Akebe Luther King Abia, Daniel Gyamfi Amoako, Rajab Mkakosya, Arnfinn Sundsfjord, Sabiha Y. Essack, Gunnar Skov Simonsen
Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease.2021; 6(2): 63. CrossRef - Frequency and Antimicrobial Resistance of Shigella Species in Iran During 2000-2020
Farhad Moradi, Nahal Hadi, Maryam Akbari, Zahra Hashemizadeh, Reyhaneh Rouhi Jahromi
Jundishapur Journal of Health Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Virulence factors and molecular characteristics of Shigella flexneri isolated from calves with diarrhea
Zhen Zhu, Weiwei Wang, Mingze Cao, Qiqi Zhu, Tenghe Ma, Yongying Zhang, Guanhui Liu, Xuzheng Zhou, Bing Li, Yuxiang Shi, Jiyu Zhang
BMC Microbiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef -
Development of quinolone resistance and prevalence of different virulence genes among
Shigella flexneri
and
Shigella dysenteriae
in environmental water samples
B. Roy, S.K. Tousif Ahamed, B. Bandyopadhyay, N. Giri
Letters in Applied Microbiology.2020; 71(1): 86. CrossRef High Rates of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Gene Distribution Among Shigella spp. Isolated from Pediatric Patients in Tehran, Iran
Mohammadmahdi Karimi-Yazdi, Zohreh Ghalavand, Mahdi Shabani, Hamidreza Houri, Mehrzad Sadredinamin, Marzieh Taheri, Gita Eslami
Infection and Drug Resistance.2020; Volume 13: 485. CrossRef- Molecular characterization of Shigella species isolated from diarrheal patients in Tehran, Iran: phylogenetic typing and its association with virulence gene profiles and a novel description of Shigella invasion associated locus
Sina Arabshahi, Aytak Novinrooz, Reza Ranjbar, Abbas Ali Imani Fooladi
European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infect.2020; 39(9): 1727. CrossRef - Case report on a swift shift in uropathogens from Shigella flexneri to Escherichia coli: a thin line between bacterial persistence and reinfection
Kukwah Anthony Tufon, Djike Puepi Yolande Fokam, Youmbi Sylvain Kouanou, Henry Dilonga Meriki
Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Virulence-related genes are associated with clinical and nutritional outcomes of Shigella/Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli pathotype infection in children from Brazilian semiarid region: A community case-control study
Mariana Bona, Pedro Henrique Medeiros, Ana Karolina Santos, Thiago Freitas, Mara Prata, Herlice Veras, Marília Amaral, Daniel Oliveira, Alexandre Havt, Aldo Ângelo Lima
International Journal of Medical Microbiology.2019; 309(2): 151. CrossRef - Genotyping and diversity of virulence genes among Shigella sonnei isolated from children with diarrhoea
Hamed Memariani, Mojtaba Memariani
Reviews in Medical Microbiology.2019; 30(4): 217. CrossRef - Virulence gene profiles of Shigella species isolated from stool specimens in India: its association with clinical manifestation and antimicrobial resistance
Dhiviya Prabaa Muthuirulandi Sethuvel, Shalini Anandan, Joy Sarojini Michael, Dhivya Murugan, Ayyanraj Neeravi, Valsan Philip Verghese, Kamini Walia, Balaji Veeraraghavan
Pathogens and Global Health.2019; 113(4): 173. CrossRef - Prevalence of enterotoxin-encoding genes among diverse Shigella strains isolated from patients with diarrhea, southwest Iran
Mojtaba Moosavian, Sakineh Seyed-Mohammadi, Ahmad Farajzadeh Sheikh, Saeed Khoshnood, Aram Asarehzadegan Dezfuli, Morteza Saki, Gholamreza Ghaderian, Fatemeh Shahi, Mahtab Abdi, Fariba Abbasi
Acta Microbiologica et Immunologica Hungarica.2018; 66(1): 91. CrossRef - Frequency of Mutations in Quinolone Resistance-Determining Regions and Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance in Shigella Isolates Recovered from Pediatric Patients in Tehran, Iran: An Overlooked Problem
Sajad Yaghoubi, Reza Ranjbar, Mohammad Mehdi Soltan Dallal, Mohammad Hasan Shirazi, Mohammad Kazem Sharifi-Yazdi
Microbial Drug Resistance.2018; 24(6): 699. CrossRef
- Epidemiological analysis and prevention strategies in response to a shigellosis cluster outbreak: a retrospective case series in an alternative school in the Republic of Korea, 2023
- Phenotypic Assays to Determine Virulence Factors of Uropathogenic
Escherichia coli (UPEC) Isolates and their Correlation with Antibiotic Resistance Pattern - Mohsen Tabasi, Mohammad Reza Asadi Karam, Mehri Habibi, Mir Saeed Yekaninejad, Saeid Bouzari
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2015;6(4):261-268. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.08.002
- 3,507 View
- 21 Download
- 50 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Urinary tract infection caused by uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) strains is one of the most important infections in the world. UPEC encode widespread virulence factors closely related with pathogenesis of the bacteria. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the presence of different phenotypic virulence markers in UPEC isolates and determine their correlation with antibiotic resistance pattern.
Methods
UPEC isolates from patients with different clinical symptoms of UTI were collected and screened for biofilm and hemolysin production, mannose resistant, and mannose sensitive hemagglutination (MRHA and MSHA, respectively). In addition, antimicrobial resistance pattern and ESBL-producing isolates were recorded.
Results
Of the 156 UPEC isolates, biofilm and hemolysin formation was seen in 133 (85.3%) and 53 (34%) isolates, respectively. Moreover, 98 (62.8%) and 58 (37.2%) isolates showed the presence of Types 1 fimbriae (MSHA) and P fimbriae (MRHA), respectively. Our results also showed a relationship between biofilm formation in UPEC isolated from acute cystitis patients and recurrent UTI cases. Occurrence of UTI was dramatically correlated with the patients' profiles. We observed that the difference in antimicrobial susceptibilities of the biofilm and nonbiofilm former isolates was statistically significant. The UPEC isolates showed the highest resistance to ampicillin, tetracycline, amoxicillin, and cotrimoxazole. Moreover, 26.9% of isolates were ESBL producers.
Conclusion
This study indicated that there is a relationship between the phenotypic virulence traits of the UPEC isolates, patients' profiles, and antibiotic resistance. Detection of the phenotypic virulence factors could help to improve understanding of pathogenesis of UPEC isolates and better medical intervention. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multi-drug-resistant Escherichia coli in adult male patients with enlarged prostate attending general hospitals in Benue state
Cornelius Iwodi, Grace M. Gberikon, Innocent Okonkwo Ogbonna, Emmanuel O. Agada
Brazilian Journal of Microbiology.2024; 55(1): 447. CrossRef - Phylogenetic analysis, biofilm formation, antimicrobial resistance and relationship between these characteristics in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Talieh Mostaghimi, Abazar Pournajaf, Ali Bijani, Mohsen Mohammadi, Mehdi Rajabnia, Mehrdad Halaji
Molecular Biology Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Type 1 fimbrial phase variation in multidrug-resistant asymptomatic uropathogenic Escherichia coli clinical isolates upon adherence to HTB-4 cells
Arunita Ghosh, Mandira Mukherjee
Folia Microbiologica.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Characteristics of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases (ESBLs)-Producing Escherichia coli in Bloodstream Infection
Rongrong Li, Huaming Xu, Hao Tang, Jilu Shen, Yuanhong Xu
Infection and Drug Resistance.2023; Volume 16: 2043. CrossRef - Phenotypic Detection of Virulence Factors of Uropathogenic Enterobacteriaceae
Betu Rama Soujanya, G.S. Banashankari
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2023; 17(2): 931. CrossRef - Uropathogenic bacteria and deductive genomics towards antimicrobial resistance, virulence, and potential drug targets
Aaima Amin, Ramisha Noureen, Ayesha Iftikhar, Annam Hussain, Wadi B. Alonazi, Hafiz Muhammad Zeeshan Raza, Ifra Ferheen, Muhammad Ibrahim
International Microbiology.2023; 27(1): 325. CrossRef - Regarding the prospects of using Lactobacillus-based probiotics, D-mannose and cranberry extracts in therapy of urinary tract infections
O. A. Gromova, I. Yu. Torshin
Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproduction.2023; 17(4): 485. CrossRef - The Impact of Gold Nanoparticle Susceptibility on Drug Resistance Phenotypes in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Iman Hosseinpour, Leila Fozouni, Morteza Khademi, Mehdi Movaghari, Mohammad Mehdi Akhoondi
Journal of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Dis.2023; 11(3): 155. CrossRef - Biofilm Formation by Escherichia coli Isolated from Urinary Tract Infections from Aguascalientes, Mexico
Flor Yazmín Ramírez Castillo, Alma Lilian Guerrero Barrera, Josée Harel, Francisco Javier Avelar González, Philippe Vogeleer, José Manuel Arreola Guerra, Mario González Gámez
Microorganisms.2023; 11(12): 2858. CrossRef - Detection of Adhesion Encoding Genes, Antibacterial Susceptibility Test and Biofilm Formation of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Urinary Tract Infections in Children
Rezvan Goodarzi, Rasoul Yousefimashouf, Iraj Sedighi, Abbas Moradi, Fatemeh Nouri, Mohammad Taheri
Journal of Advances in Medical and Biomedical Rese.2022; 30(1): 1. CrossRef - A global systematic review and meta-analysis on correlation between biofilm producers and non-biofilm producers with antibiotic resistance in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Mitra Garousi, Sina Monazami Tabar, Hosein Mirazi, Parnia Asgari, Paniz Sabeghi, Astireh Salehi, Azad Khaledi, Mohammad Ghenaat Pisheh Sanani, Hossein Karballaei Mirzahosseini
Microbial Pathogenesis.2022; 164: 105412. CrossRef - Antibiotic resistance, phylogenetic typing, and virulence genes profile analysis of uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from patients in southern Iraq
Mohammed Allami, Masoumeh Bahreini, Mohammad Reza Sharifmoghadam
Journal of Applied Genetics.2022; 63(2): 401. CrossRef - Phylogenetic Group Distribution of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli and Related Antimicrobial Resistance Pattern: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review
Mehrdad Halaji, Amirhossein Fayyazi, Mehdi Rajabnia, Donya Zare, Abazar Pournajaf, Reza Ranjbar
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Genotypic assay to determine some virulence factors of Uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) isolates
Tsahel H. Al-Dulaimi, Ilham A Bunyan, Thikra A. Banimuslem
International journal of health sciences.2022; : 1593. CrossRef - Demonstrating the utility of Escherichia coli asymptomatic bacteriuria isolates’ virulence profile towards diagnosis and management—A preliminary analysis
Lalitha Maniam, Kumutha Malar Vellasamy, Hassan Mahmood Jindal, Vallikannu Narayanan, Mahmoud Danaee, Jamuna Vadivelu, Vinod Pallath, Abdelazeem Mohamed Algammal
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(5): e0267296. CrossRef - Urine Microscopy Score and Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio at Presentation are Good Biomarkers of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Upper Urinary Tract Infection when Assessed in Correlation with Virulence Factors of Escherichia coli and Blood Group Secret
Shanmugapriya Thiagarajan, Selvaraj Stephen, Santosh Kumar, Priscilla Charles, Sarangapani Kanagamuthu, Stanley Ambroise, Pragasam Viswanathan, Palanivel Chinnakali, Rajesh Nachiappa Ganesh
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2022; 16(2): 1074. CrossRef - Association between Virulence Factors and Antimicrobial Resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates from North Kerala
Ramya Kumaran, R.V. Geetha, Sabitha Baby
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2022; 16(2): 867. CrossRef - Molecular Characterization and Mutational Analysis of Fluoroquinolones and Tetracycline Resistant Genes of Escherichia coli Isolated from UTI Patients
Sadiq Azam, Nauman Khan, Noor Rehman, Ibrar khan, Amjad Ali, Muhammad Asghar, Azam Hayat, Gulesehra Mujib, Anila Farid
Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns of Escherichia coli from Urine Isolates
Taher I. Mahmod Shailabi, Osama H. Aldeeb, Abdullah F. Almaedani, Elham O. Borwis, Samar A. Amer
Al-Mukhtar Journal of Sciences.2022; 37(4): 372. CrossRef - Possible Relationship of Novel Phylogenetic Structure With Antimicrobial Resistance, Biofilm Formation, and Hemolytic Activity in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC)
Batoul Rahimifard, Vahid Soheili, Gholamreza Hashemitabar, Mahdi Askari Badouei
International Journal of Enteric Pathogens.2022; 10(3): 98. CrossRef - Virulence genes and phylogenetic groups of uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates from patients with urinary tract infection and uninfected control subjects: a case-control study
Seyedeh Elham Rezatofighi, Mahsa Mirzarazi, Mansour Salehi
BMC Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance of uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) isolated from urinary tract infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Gabriel Kambale Bunduki, Eva Heinz, Vincent Samuel Phiri, Patrick Noah, Nicholas Feasey, Janelisa Musaya
BMC Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Biofilm Formation and Virulence Genes and Association with Antibiotic Resistance Patterns of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Strains in Southwestern Iran
Mostafa Boroumand, Asghar Sharifi, Mohammad Amin Ghatei, Mohsen Sadrinasab
Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The urobiome, urinary tract infections, and the need for alternative therapeutics
Jennifer Jones, Craig P. Murphy, Roy D. Sleator, Eamonn P. Culligan
Microbial Pathogenesis.2021; 161: 105295. CrossRef - Clinical cases, drug resistance, and virulence genes profiling in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Ali Hozzari, Payam Behzadi, Parisa Kerishchi Khiabani, Mohammad Sholeh, Niloofar Sabokroo
Journal of Applied Genetics.2020; 61(2): 265. CrossRef Prevalence of Virulence Genes and Their Association with Antimicrobial Resistance Among Pathogenic E. coli Isolated from Egyptian Patients with Different Clinical Infections
Rehab Mahmoud Abd El-Baky, Reham Ali Ibrahim, Doaa Safwat Mohamed, Eman Farouk Ahmed, Zeinab Shawky Hashem
Infection and Drug Resistance.2020; Volume 13: 1221. CrossRefIn-vitro Investigation of Antibiotics Efficacy Against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Biofilms and Antibiotic Induced Biofilm Formation at Sub-Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Ciprofloxacin
Zara Rafaque, Nasira Abid, Nida Liaquat, Pashmina Afridi, Saima Siddique, Safia Masood, Sehrish Kanwal, Javid Iqbal Dasti
Infection and Drug Resistance.2020; Volume 13: 2801. CrossRef- Relationship between Virulence and Resistance among Gram-Negative Bacteria
Virginio Cepas, Sara M. Soto
Antibiotics.2020; 9(10): 719. CrossRef - In Vitro and In Vivo Biological Activity of Berberine Chloride against Uropathogenic E. coli Strains Using Galleria mellonella as a Host Model
Giulio Petronio Petronio, Marco Alfio Cutuli, Irene Magnifico, Noemi Venditti, Laura Pietrangelo, Franca Vergalito, Antonella Pane, Giovanni Scapagnini, Roberto Di Marco
Molecules.2020; 25(21): 5010. CrossRef - Study of virulence factors and antibiotic susceptibility pattern of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli
Mahendraswamy B Hiremath, R Lava
Indian Journal of Microbiology Research.2020; 7(4): 330. CrossRef - Virulence factors of uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) and correlation with antimicrobial resistance
Chhaya Shah, Ratna Baral, Bijay Bartaula, Lok Bahadur Shrestha
BMC Microbiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcome of acute urinary tract infections caused by uropathogenic Escherichia coli with phenotypically demonstrable virulence factors
Unnimaya Pullanhi, Sadia Khan, Vivek Vinod, Karthika Mohan, Anil Kumar
Annals of African Medicine.2019; 18(3): 138. CrossRef - Urinary tract infection: Pathogenicity, antibiotic resistance and development of effective vaccines against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Mohammad Reza Asadi Karam, Mehri Habibi, Saeid Bouzari
Molecular Immunology.2019; 108: 56. CrossRef - Systematic analysis of research on D-mannose and the prospects for its use in recurrent infections of the urinary tract in women of reproductive age
O. A. Gromova, I. Yu. Torshin, N. K. Tetruashvili
Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproduction.2019; 13(2): 119. CrossRef - Evaluation of pap and sfa Genes Relative Frequency P and S Fimbriae Encoding of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Hospitals and Medical Laboratories; Yasuj City, Southwest Iran
Mostafa Boroumand, Asghar Sharifi, Leila Manzouri, Seyed Sajjad Khoramrooz, Seyed Abdolmajid Khosravani
Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Extended spectrum β-lactamase producing uropathogenic Escherichia coli and the correlation of biofilm with antibiotics resistance in Nepal
Raju Shrestha, Santosh Khanal, Pramod Poudel, Karan Khadayat, Sajani Ghaju, Anita Bhandari, Sunil Lekhak, Narayan Dutt Pant, Manisha Sharma, Bishnu P. Marasini
Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Genotyping and Molecular Characterization of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases-Producing Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli in and Around Coimbatore District, Tamil Nadu, India
Mylsamy Muraleetharan, Thirumoorthy Viswanathan
Urological Science.2019; 30(6): 244. CrossRef - Investigation of P Fimbriae Presence in Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Urine Samples in Human, and Their Antibacterial Resistance
Emel Inegol Paykoc, Suheyla Turkyilmaz
Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - An evaluation of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli isolates in urinary tract infections from Aguascalientes, Mexico: cross-sectional study
Flor Y. Ramírez-Castillo, Adriana C. Moreno-Flores, Francisco J. Avelar-González, Francisco Márquez-Díaz, Josée Harel, Alma L. Guerrero-Barrera
Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential Mechanisms Underlying the Increased Excitability of the Bladder Afferent Pathways in Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
Doo Sang Kim
Urogenital Tract Infection.2018; 13(2): 26. CrossRef - Distribution of virulence genes and their association with antimicrobial resistance among uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates from Iranian patients
Yalda Malekzadegan, Reza Khashei, Hadi Sedigh Ebrahim-Saraie, Zahra Jahanabadi
BMC Infectious Diseases.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Important Virulence Factors and Related Genes in Uropathogenic E. coli and their Relation to Fluoroquinolone Resistance
Noha Mohammad Gohar, Hanaa Fathy Aly, Magda Ibrahim Ayoub
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2018; 12(3): 1393. CrossRef - Clonal and Virulence Distribution of UropathogenicEscherichia coliIsolated from Children in Korea
Dong Ho Kim, Chul Hee Choi
Journal of Bacteriology and Virology.2017; 47(1): 54. CrossRef - An Epidemiological Study on the Prevalence and Antibiotic Resistance Patterns of Bacteria Isolated from Urinary Tract Infections in Central Iran
Fahimeh Ghanbari, Farzad Khademi, Shirin Saberianpour, Mojtaba Shahin, Nafiseh Ghanbari, Kourosh Naderi, Tahereh Motalebi-Rad
Avicenna Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infe.2017; 4(3): 42214. CrossRef - Correlation Between hlyA and cnf1 Virulent Genes with Antibiotic Resistance and non-ESBLs Escherichia coli Isolates Collected from Patient with Urinary Tract Infections in Kerman, Iran
Zahra Hashemizadeh, Davood Kalantar-Neyestanaki, Shahla Mansouri
Archives of Pediatric Infectious Diseases.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Antibiotic Resistance Profile of Enterobacteria Involved in Urinary Infections in Bamako, Mali
Amadou Hamadoun Babana
MOJ Biology and Medicine.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Phenotypic and Molecular Characterization of some Virulence Factors in Multidrug Resistance Escherichia coli Isolated from Different Clinical Infections in Iraq
Ahmed Abduljabbar Ja Aljanaby, Qassim Mmuhsin Hashi Alfaham
American Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Bio.2017; 7(2): 65. CrossRef - Emerging nanotechnology based strategies for diagnosis and therapeutics of urinary tract infections: A review
M.S. Kumar, A.P. Das
Advances in Colloid and Interface Science.2017; 249: 53. CrossRef - Effects of single and combined use of bacteriophages and antibiotics to inactivate Escherichia coli
Nádia Valério, Cristiana Oliveira, Vânia Jesus, Tatiana Branco, Carla Pereira, Catarina Moreirinha, Adelaide Almeida
Virus Research.2017; 240: 8. CrossRef - Crystal Structures of Acyclic Nucleoside Phosphonates in Complex with Escherichia coli Hypoxanthine Phosphoribosyltransferase
Wai Soon Eng, Dana Hocková, Petr Špaček, Ondřej Baszczyňski, Zlatko Janeba, Lieve Naesens, Dianne T. Keough, Luke W. Guddat
ChemistrySelect.2016; 1(19): 6267. CrossRef
- Multi-drug-resistant Escherichia coli in adult male patients with enlarged prostate attending general hospitals in Benue state
- Multilocus Sequence Analysis of Housekeeping Genes and Antigenic Determinant Genes in
Bordetella pertussis Strains Isolated in Korea - Sang-Oun Jung, Yu Mi Moon, So-Hyeon Kim, Hwa Young Sung, Seung-Jik Kwon, Yeon Ho Kang, Jae Yon Yu
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2011;2(2):115-126. Published online June 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2011.08.003
- 3,200 View
- 14 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To confirm genotype diversities of clinical isolates of Bordetella pertussis and to evaluate the risk of pertussis outbreak in Korea.
Methods
Seven housekeeping genes and 10 antigenic determinant genes from clinical B. pertussis isolates were analyzed by Multilocus sequence typing (MLST).
Results
More variant pattern was observed in antigenic determinant genes. Especially, PtxS1 gene was the most variant gene; five genotypes were observed from eight global genotypes. In the bacterial type, the number of observed sequence types in the isolates was seven and the most frequent form was type 1 (79.6%). This major sequence type also showed a time-dependent transition pattern. Older isolates (1968 and 1975) showed type 1 and 6 in housekeeping genes and antigenic determinant genes, respectively. However, these were changed to type 2 and 1 in isolates 1999–2008. This transition was mainly attributed to genotype change of PtxS1 and Fim3 gene; the tendency of genotype change was to avoid vaccine-derived genotype. In addition, there was second transition in 2009. In this period, only the sequence type of antigenic determinant genes was changed to type 2. Based Upon Related Sequence Types (BURST) analysis confirmed that there were two clonal complexes (ACCI and ACCII) in the Korean isolates. Moreover, the recently increased sequence type was revealed as AST2 derived from AST 3 in ACCI.
Conclusions
Genotype changes in Korean distributing strains are still progressing and there was a specific driving force in antigenic determinant genes. Therefore continuous surveillance of genotype change of the distributing strains should be performed to confirm interrelationship of genotype change with vaccine immunity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characterization of Bordetella pertussis Strains Isolated from India
Shweta Alai, Manish Gautam, Sonali Palkar, Jitendra Oswal, Sunil Gairola, Dhiraj P. Dhotre
Pathogens.2022; 11(7): 794. CrossRef - Variation in Bordetella pertussis Susceptibility to Erythromycin and Virulence-Related Genotype Changes in China (1970-2014)
Ying Yang, Kaihu Yao, Xiang Ma, Wei Shi, Lin Yuan, Yonghong Yang, Daniela Flavia Hozbor
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(9): e0138941. CrossRef - Recent Trends of Antigenic Variation inBordetella pertussisIsolates in Korea
So-Hyun Kim, Jin Lee, Hwa Young Sung, Jae Yon Yu, Seong Han Kim, Mi Sun Park, Sang-Oun Jung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2014; 29(3): 328. CrossRef
- Characterization of Bordetella pertussis Strains Isolated from India
- Distribution of Virulence Genes and Their Association of Serotypes in Pathogenic
Escherichia coli Isolates From Diarrheal Patients in Korea - Seung-Hak Cho, Kyung-Hwan Oh, Seong-Han Kim, Hee-Bok Oh, Mi-Sun Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2010;1(1):29-35. Published online December 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2010.12.008
- 3,522 View
- 18 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To characterise the genetic and serological diversity of pathogenic Escherichia coli, we tested 111 E coli strains isolated from diarrhoeal patients in Korea between 2003 and 2006.
Methods
The isolates were tested through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and slide agglutination method for the detection of virulence genes and serotypes, respectively. To compare the expression of Shiga toxin (stx)-1 and stx2 genes, real-time quantitative reverse-transcriptase PCR and rapid exprssion assay, reversed-passive latex agglutination, were performed.
Results
Forty-nine Shiga toxin-producing E coli (STEC) strains and 62 non-STEC strains, including 20 enteropathogenic E coli, 20 enterotoxigenic E coli, 20 enteroaggregative E coli, and 2 enteroinvasive E coli were randomly chosen from the strains isolated from diarrhoeal patients in Korea between 2003 and 2006. PCR analysis indicated that locus of enterocyte effacement pathogenicity island, that is, eaeA, espADB, and tir genes were present in STEC, enteropathogenic E coli, and enteroinvasive E coli. Quorum sensing-related gene luxS was detected in most of pathogenic E coli strains. Major serotypes of the STEC strains were O157 (26%) and O26 (20%), whereas the non-STEC strains possessed various serotypes. Especially, all the strains with serotype O157 carried stx2 and the tested virulence factors. Of the STEC strains, the data of real-time quantitative reverse-transcriptase PCR and reversed-passive latex agglutination tests showed that messenger RNA- and protein expression of stx2 gene were higher than those of stx1 gene.
Conclusion
Our results provide the epidemiological information regarding the trend of STEC and non-STEC infections in the general population and show the fundamental data in association of serotypes with virulence genes in diarrhoeagenic E coli strains from Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Analysis of Human and Animal E. coli: Serotyping, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Virulence Gene Profiling
Mahmoud M. Bendary, Marwa I. Abdel-Hamid, Walaa A. Alshareef, Hanan M. Alshareef, Rasha A. Mosbah, Nasreen N. Omar, Mohammad M. Al-Sanea, Majid Alhomrani, Abdulhakeem S. Alamri, Walaa H. Moustafa
Antibiotics.2022; 11(5): 552. CrossRef - Antimicrobial peptide human β-defensin-2 improves in vitro cellular viability and reduces pro-inflammatory effects induced by enteroinvasive Escherichia coli in Caco-2 cells by inhibiting invasion and virulence factors’ expression
Alessandra Fusco, Vittoria Savio, Brunella Perfetto, Roberto Mattina, Giovanna Donnarumma
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Distribution of Pathogenicity Island Markers and H-Antigen Types of Escherichia coli O25b/ST131 Isolates from Patients with Urinary Tract Infection in Iran
Masoumeh Rasoulinasab, Fereshteh Shahcheraghi, Mohammad Mehdi Feizabadi, Bahram Nikmanesh, Azade Hajihasani, Shahram Sabeti, Mohammad Mehdi Aslani
Microbial Drug Resistance.2021; 27(3): 369. CrossRef - Development and validation of a predictive model for pathogenic Escherichia coli in fresh‐cut produce
You Jin Kim, Ju Yeon Park, Soo Hwan Suh, Mi‐Gyeong Kim, Hyo‐Sun Kwak, Soon Han Kim, Eun Jeong Heo
Food Science & Nutrition.2021; 9(12): 6866. CrossRef - In vitro antibacterial activity of poly (amidoamine)-G7 dendrimer
Mitra Gholami, Rashin Mohammadi, Mohsen Arzanlou, Fakhraddin Akbari Dourbash, Ebrahim Kouhsari, Gharib Majidi, Seyed Mohsen Mohseni, Shahram Nazari
BMC Infectious Diseases.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Occurrence of pathogenic Escherichia coli in commercially available fresh vegetable products in Korea
Hyun Jung Kim, Minseon Koo, A-Ram Jeong, Seung-Youb Baek, Joon-Il Cho, Soon-Ho Lee, In-Gyun Hwang
Journal of the Korean Society for Applied Biologic.2014; 57(3): 367. CrossRef
- Comparative Analysis of Human and Animal E. coli: Serotyping, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Virulence Gene Profiling



 First
First Prev
Prev


