Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Analysis of pregnant women with critically severe COVID-19 in Republic of Korea from February 2020 and December 2021
- Ji Joo Lee, Sang-Eun Lee, Yeonjung Kim, Young-Joon Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(2):129-137. Published online April 5, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0025
- 1,297 View
- 58 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 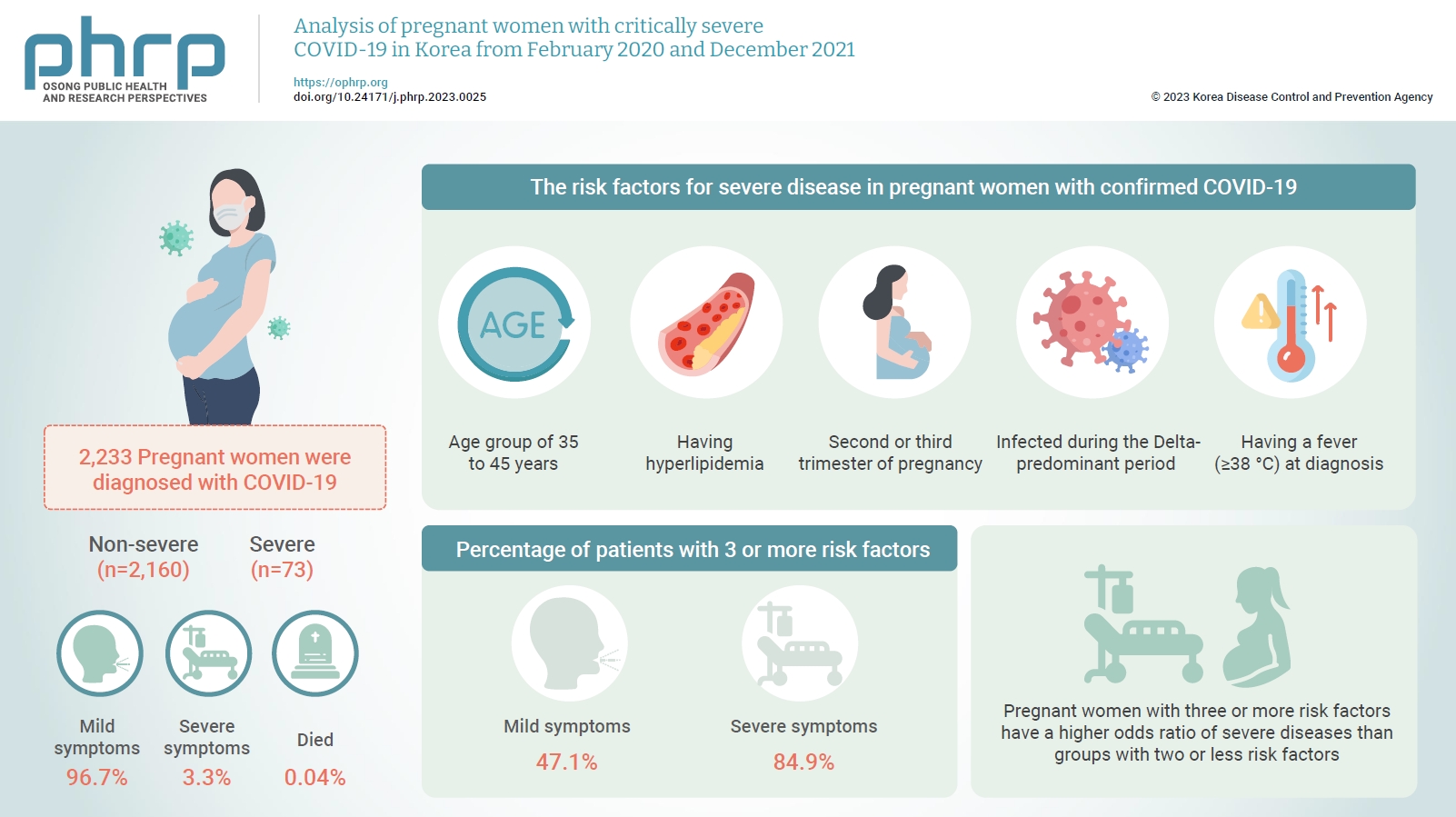
- Objectives
This study aimed to describe the characteristics and risk factors for severe disease in pregnant women infected with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from the early days of the COVID-19 epidemic in Korea to the predominant period of the Delta variant.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study was conducted among pregnant women diagnosed with COVID-19 between February 2020 and December 2021. Logistic regression analysis was performed to compare severe and mild cases after adjusting for pregnant women’s age, nationality, infection route, outbreak area, infection period, symptoms, underlying disease, smoking status, trimester, and COVID-19 vaccination status.
Results
In total, 2,233 pregnant women were diagnosed with COVID-19 by December 2021. Among these, 96.7% had mild symptoms, 3.3% had severe symptoms, and 0.04% died. The risk factors for severe disease in pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 were being in the age group of 35 to 45 years, having hyperlipidemia, being in the second or third trimester of pregnancy at the time of COVID-19 diagnosis, being infected during the Delta-predominant period, and having a fever (≥38 °C) at diagnosis. Furthermore, 47.1% of patients in the mild group and 84.9% of patients in the severe group had 3 or more risk factors.
Conclusion
Pregnant women with COVID-19 mainly experienced mild symptoms, but those with risk factors were at a higher risk of developing severe symptoms. Therefore, treatment and follow-up management should be thoroughly implemented.


 First
First Prev
Prev


