Article category
- Page Path
- HOME > Article category > Article category
Original Article
- Factors associated with the timely diagnosis of malaria and the utilization of types of healthcare facilities: a retrospective study in the Republic of Korea
- HyunJung Kim, Sangwoo Tak, So-dam Lee, Seongwoo Park, Kyungwon Hwang
- Received November 20, 2023 Accepted January 18, 2024 Published online April 16, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0349 [Epub ahead of print]
- 251 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to analyze trends in the timely diagnosis of malaria cases over the past 10 years in relation to the utilization of different types of healthcare facilities.
Methods
The study included 3,697 confirmed and suspected cases of malaria reported between January 1, 2013, and December 31, 2022, in the national integrative disease and healthcare management system. Some cases lacking a case report or with information missing from the case report were excluded from the analysis. A generalized linear model with a Poisson distribution was constructed to estimate rate ratios and 95% confidence intervals adjusted for other variables, such as distance.
Results
When cases involving diagnosis >5 days after symptom onset in confirmed patients (5DD) were examined according to the type of healthcare facility, the rate ratio of 5DD cases was found to be higher for public health facilities than for tertiary hospitals. Specifically, the rate ratio was higher when the diagnosis was established at a tertiary hospital, even after a participant had visited primary or secondary hospitals. In an analysis adjusted for the distance to each participant’s healthcare facility, the results did not differ substantially from the results of the crude analysis.
Conclusion
It is imperative to improve the diagnostic capabilities of public facilities and raise awareness of malaria at primary healthcare facilities for effective prevention and control.
Brief Report
- Gender differences in hepatitis A seropositivity rates according to the Republic of Korea’s vaccination policy
- Hyunjin Son, Sunhyun Ahn, Wonseo Park, Gayoung Chun, Unyeong Go, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
- Received September 18, 2023 Accepted January 22, 2024 Published online April 16, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0263 [Epub ahead of print]
- 353 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to investigate differences in the anti-hepatitis A (HAV) antibody seropositivity rate by age and gender.
Methods
We collected information on anti-HAV immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M status from samples submitted for HAV antibody testing in 2012–2022. A total of 1,333,615 cases were included in the analysis.
Results
By age, the seropositivity rate was represented by a U-shaped curve, such that the rate was low for the group aged 20 to 39 years and higher in those who were younger or older. Over time, the curve shifted rightward, and the seropositivity rate declined gradually in the group aged 35 to 39 years and older. A gender-based difference in antibody seropositivity rate was especially noticeable in the group aged 20 to 29 years. This difference between genders widened in the participants’ early 20s—when men in the Republic of Korea enlist in the military—and the divergence continued subsequently for older individuals.
Conclusion
These results indicate a higher risk of severe infection among older individuals and a gender-based difference in seroprevalence. Therefore, it is necessary to implement policies to promote vaccination in adults.
Special Article
- The COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Research Center: a cornerstone for strengthening safety evidence for COVID-19 vaccination in the Republic of Korea
- Na-Young Jeong, Hyesook Park, Sanghoon Oh, Seung Eun Jung, Dong-Hyun Kim, Hyoung-Shik Shin, Hee Chul Han, Jong-Koo Lee, Jun Hee Woo, Jaehun Jung, Joongyub Lee, Ju-Young Shin, Sun-Young Jung, Byung-Joo Park, Nam-Kyong Choi
- Received November 16, 2023 Accepted February 22, 2024 Published online April 4, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0343 [Epub ahead of print]
- 440 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Research Committee (CoVaSC) was established in November 2021 to address the growing need for independent, in-depth scientific evidence on adverse events (AEs) following coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination. This initiative was requested by the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency and led by the National Academy of Medicine of Korea. In September 2022, the COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Research Center was established, strengthening CoVaSC’s initiatives. The center has conducted various studies on the safety of COVID-19 vaccines. During CoVaSC’s second research year, from September 29, 2022 to July 19, 2023, the center was restructured into 4 departments: Epidemiological Research, Clinical Research, Communication & Education, and International Cooperation & Policy Research. Its main activities include (1) managing CoVaSC and the COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Research Center, (2) surveying domestic and international trends in AE causality investigation, (3) assessing AEs following COVID-19 vaccination, (4) fostering international collaboration and policy research, and (5) organizing regular fora and training sessions for the public and clinicians. Causality assessments have been conducted for 27 diseases, and independent research has been conducted after organizing ad hoc committees comprising both epidemiologists and clinical experts on each AE of interest. The research process included protocol development, data analysis, interpretation of results, and causality assessment. These research outcomes have been shared transparently with the public and healthcare experts through various fora. The COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Research Center plans to continue strengthening and expanding its research activities to provide reliable, high-quality safety information to the public.
Review Article
- Psychiatric adverse events associated with the COVID-19 vaccines approved in the Republic of Korea: a systematic review
- Seungeun Ryoo, Miyoung Choi, Nam-Kyong Choi, Hyoung-Shik Shin, Jun Hee Woo, Byung-Joo Park, Sanghoon Oh
- Received October 31, 2023 Accepted January 16, 2024 Published online March 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0325 [Epub ahead of print]
- 483 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This systematic review evaluated psychiatric adverse events (AEs) following vaccination against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We included studies that reported or investigated psychiatric AEs in individuals who had received an approved COVID-19 vaccine in the Republic of Korea. Systematic electronic searches of Ovid-Medline, Embase, CENTRAL, and KoreaMed databases were conducted on March 22, 2023. Risk of bias was assessed using the Risk of Bias Assessment Tool for Non-randomized Studies 2.0. The study protocol was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (CRD42023449422). Of the 301 articles initially selected, 7 were included in the final analysis. All studies reported on sleep disturbances, and 2 highlighted anxiety-related AEs. Sleep disorders like insomnia and narcolepsy were the most prevalent AEs, while depression was not reported. Our review suggests that these AEs may have been influenced by biological mechanisms as well as the broader psychosocial context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Although this study had limitations, such as a primary focus on the BNT162b2 vaccine and an observational study design, it offered a systematic, multi-vaccine analysis that fills a critical gap in the existing literature. This review underscores the need for continued surveillance of psychiatric AEs and guides future research to investigate underlying mechanisms, identify risk factors, and inform clinical management.
Original Articles
- AI-powered COVID-19 forecasting: a comprehensive comparison of advanced deep learning methods
- Muhammad Usman Tariq, Shuhaida Binti Ismail
- Received October 13, 2023 Accepted January 26, 2024 Published online March 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0287 [Epub ahead of print]
- 335 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic continues to pose significant challenges to the public health sector, including that of the United Arab Emirates (UAE). The objective of this study was to assess the efficiency and accuracy of various deep-learning models in forecasting COVID-19 cases within the UAE, thereby aiding the nation’s public health authorities in informed decision-making.
Methods
This study utilized a comprehensive dataset encompassing confirmed COVID-19 cases, demographic statistics, and socioeconomic indicators. Several advanced deep learning models, including long short-term memory (LSTM), bidirectional LSTM, convolutional neural network (CNN), CNN-LSTM, multilayer perceptron, and recurrent neural network (RNN) models, were trained and evaluated. Bayesian optimization was also implemented to fine-tune these models.
Results
The evaluation framework revealed that each model exhibited different levels of predictive accuracy and precision. Specifically, the RNN model outperformed the other architectures even without optimization. Comprehensive predictive and perspective analytics were conducted to scrutinize the COVID-19 dataset.
Conclusion
This study transcends academic boundaries by offering critical insights that enable public health authorities in the UAE to deploy targeted data-driven interventions. The RNN model, which was identified as the most reliable and accurate for this specific context, can significantly influence public health decisions. Moreover, the broader implications of this research validate the capability of deep learning techniques in handling complex datasets, thus offering the transformative potential for predictive accuracy in the public health and healthcare sectors.
- Effect of Paxlovid in COVID-19 treatment during the periods of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.5 and BN.1 subvariant dominance in the Republic of Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Dong-Hwi Kim, Min-Gyu Yoo, Na-Young Kim, So Young Choi, Minjeong Jang, Misuk An, Se-Jin Jeong, Jungyeon Kim
- Received August 16, 2023 Accepted January 18, 2024 Published online March 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0230 [Epub ahead of print]
- 266 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study was conducted to assess the efficacy of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), particularly those aged 60 years and older. Using real-world data, the period during which the BN.1 Omicron variant was dominant was compared to the period dominated by the BA.5 variant.
Methods
In this retrospective cohort study, data were collected regarding 2,665,281 patients infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 between July 24, 2022, and March 31, 2023. Propensity score matching was utilized to match patients who received nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in a 1:4 ratio between BN.1 and BA.5 variant groups. Multivariable logistic regression analysis was employed to assess the effects of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir within these groups.
Results
Compared to the prior period, the efficacy of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir did not significantly differ during the interval of Omicron BN.1 variant dominance in the Republic of Korea. Among patients treated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, a significantly lower risk of mortality was observed in the BN.1 group (odds ratio [OR], 0.698; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.557–0.875) compared to the BA.5 group. However, this treatment did not significantly reduce the risk of severe or critical illness, including death, for those in the BN.1 group (OR, 0.856; 95% CI, 0.728–1.007).
Conclusion
Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir has maintained its effectiveness against COVID-19, even with the emergence of the BN.1 Omicron subvariant. Consequently, we strongly recommend the administration of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir to patients exhibiting COVID-19-related symptoms, irrespective of the dominant Omicron variant or their vaccination status, to mitigate disease severity and decrease the risk of mortality.
- COVID-19 infection among people with disabilities in 2021 prior to the Omicron-dominant period in the Republic of Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Seul-Ki Kang, Bryan Inho Kim
- Received July 11, 2023 Accepted January 16, 2024 Published online March 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0194 [Epub ahead of print]
- 394 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) among individuals with disabilities on a nationwide scale in the Republic of Korea, as limited research has examined this population.
Methods
Between January 1 and November 30, 2021, a total of 5,687 confirmed COVID-19 cases among individuals with disabilities were reported through the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency’s COVID-19 web reporting system. Follow-up continued until December 24, and demographic, epidemiological, and clinical characteristics were analyzed.
Results
Individuals with disabilities represented approximately 1.5% of confirmed cases, with a mean age of 58.1 years. Most resided in or near metropolitan areas (86.6%) and were male (60.6%). Frequent sources of infection included home (33.4%) and contact with confirmed cases (40.7%). Many individuals (75.9%) had underlying conditions, and 7.7% of cases were severe. People with disabilities showed significantly elevated risk of severe infection (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.63; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.47–1.81) and mortality (aOR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.43–1.91). Vaccination against COVID-19 was associated with significantly lower risk of severe infection (aORs for the first, second, and third doses: 0.6 [95% CI, 0.42–0.85], 0.28 [95% CI, 0.22–0.35], and 0.16 [95% CI, 0.05–0.51], respectively) and death (adjusted hazard ratios for the first and second doses: 0.57 [95% CI, 0.35–0.93] and 0.3 [95% CI, 0.23–0.40], respectively).
Conclusion
Individuals with disabilities showed higher risk of severe infection and mortality from COVID-19. Consequently, it is critical to strenghthenCOVID-19 vaccination initiatives and provide socioeconomic assistance for this vulnerable population.
Commentary
- Challenges in capacity building of national immunization programs and emergency or pandemic vaccination responses in the Global Health Security Agenda member countries
- Sookhyun Lee, Jung Ju Oh, Sang Hyun Park, Dasol Ro, Ye Jin Jeong, So Yoon Kim
- Received June 14, 2023 Accepted January 16, 2024 Published online March 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0159 [Epub ahead of print]
- 225 View
- 9 Download
Editorial
- What are the strategies for national health security in preparation for the next pandemic?
- Jong-Koo Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):1-2. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2024.0056
- 578 View
- 156 Download
Original Articles
- Impact of long COVID-19 on posttraumatic stress disorder as modified by health literacy: an observational study in Vietnam
- Han Thi Vo, Tien Duc Dao, Tuyen Van Duong, Tan Thanh Nguyen, Binh Nhu Do, Tinh Xuan Do, Khue Minh Pham, Vinh Hai Vu, Linh Van Pham, Lien Thi Hong Nguyen, Lan Thi Huong Le, Hoang Cong Nguyen, Nga Hoang Dang, Trung Huu Nguyen, Anh The Nguyen, Hoan Van Nguyen, Phuoc Ba Nguyen, Hoai Thi Thanh Nguyen, Thu Thi Minh Pham, Thuy Thi Le, Thao Thi Phuong Nguyen, Cuong Quoc Tran, Kien Trung Nguyen
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):33-44. Published online February 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0261
- 763 View
- 54 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 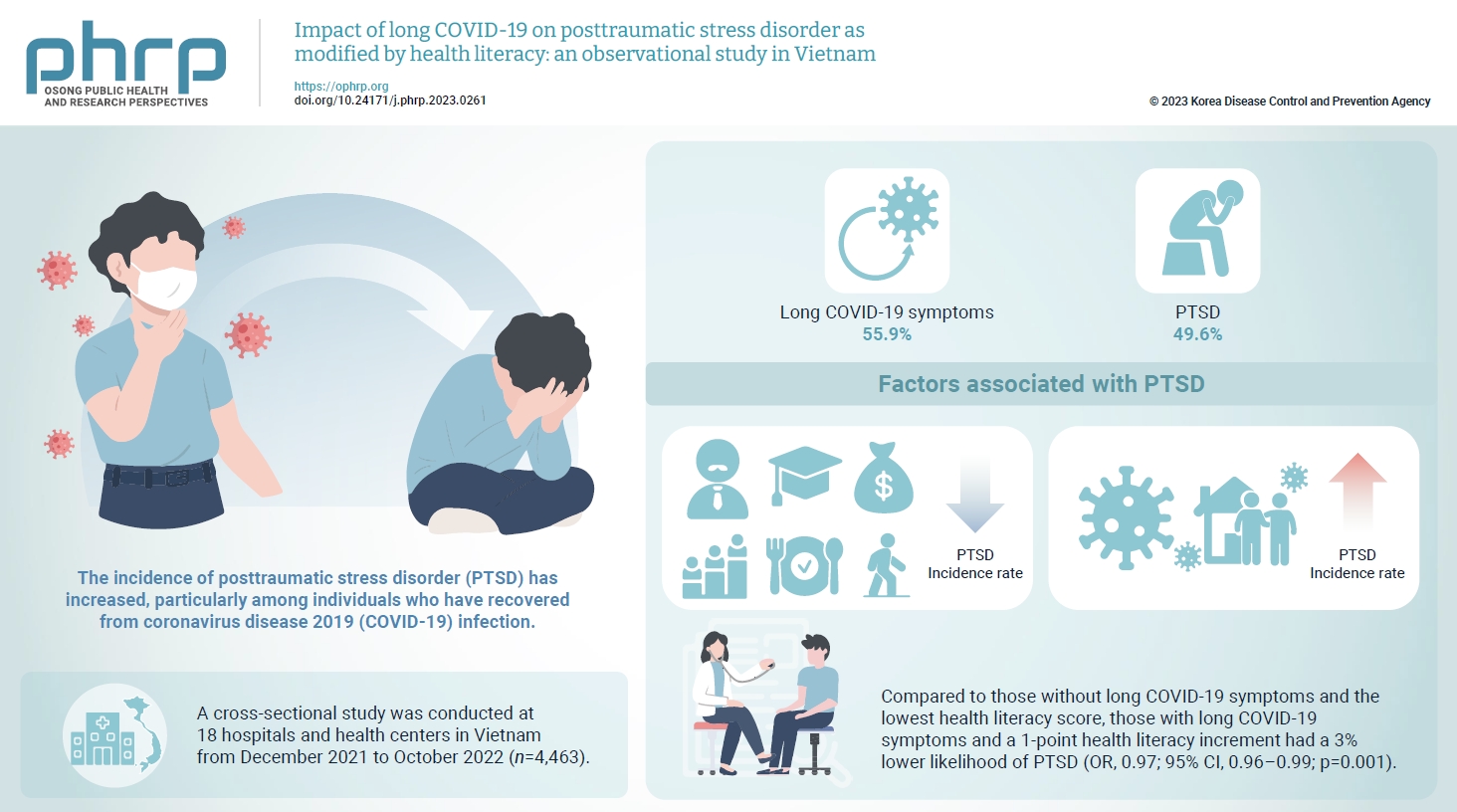
- Objectives
The prevalence of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) has increased, particularly among individuals who have recovered from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection. Health literacy is considered a “social vaccine” that helps people respond effectively to the pandemic. We aimed to investigate the association between long COVID-19 and PTSD, and to examine the modifying role of health literacy in this association. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted at 18 hospitals and health centers in Vietnam from December 2021 to October 2022. We recruited 4,463 individuals who had recovered from COVID-19 infection for at least 4 weeks. Participants provided information about their sociodemographics, clinical parameters, health-related behaviors, health literacy (using the 12-item short-form health literacy scale), long COVID-19 symptoms and PTSD (Impact Event Scale-Revised score of 33 or higher). Logistic regression models were used to examine associations and interactions. Results: Out of the study sample, 55.9% had long COVID-19 symptoms, and 49.6% had PTSD. Individuals with long COVID-19 symptoms had a higher likelihood of PTSD (odds ratio [OR], 1.86; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.63–2.12; p<0.001). Higher health literacy was associated with a lower likelihood of PTSD (OR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.97–0.99; p=0.001). Compared to those without long COVID-19 symptoms and the lowest health literacy score, those with long COVID-19 symptoms and a 1-point health literacy increment had a 3% lower likelihood of PTSD (OR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.96–0.99; p=0.001). Conclusion: Health literacy was found to be a protective factor against PTSD and modified the negative impact of long COVID-19 symptoms on PTSD.
- Prevalence, multidrug resistance, and biofilm formation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from fish mariculture environments in Cat Ba Island, Vietnam
- Kim Cuc Thi Nguyen, Phuc Hung Truong, Hoa Truong Thi, Xuan Tuy Ho, Phu Van Nguyen
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):56-67. Published online February 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0181
- 800 View
- 48 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 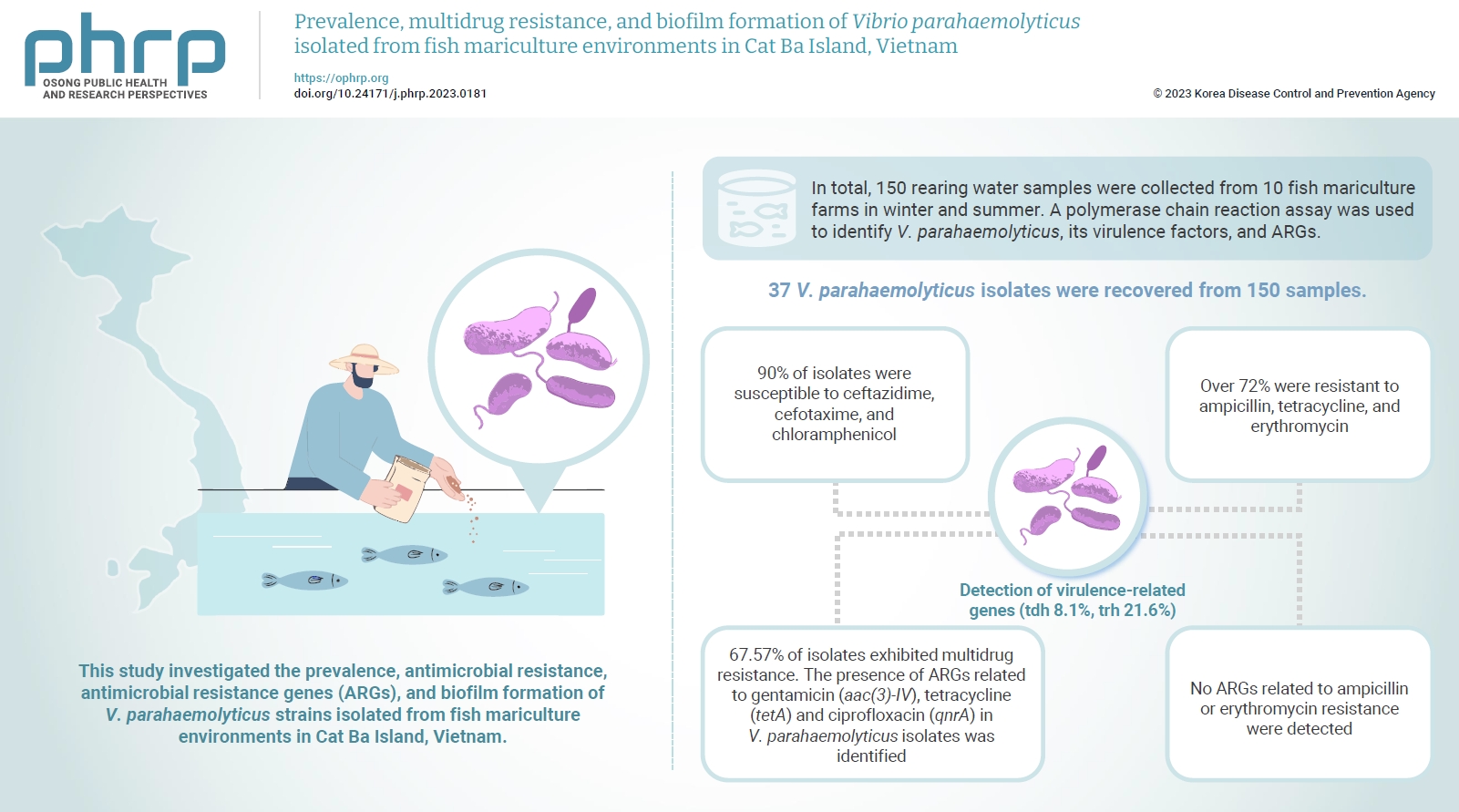
- Objectives
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is a major foodborne pathogen in aquatic animals and a threat to human health worldwide. This study investigated the prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs), and biofilm formation of V. parahaemolyticus strains isolated from fish mariculture environments in Cat Ba Island, Vietnam. Methods: In total, 150 rearing water samples were collected from 10 fish mariculture farms in winter and summer. A polymerase chain reaction assay was used to identify V. parahaemolyticus, its virulence factors, and ARGs. The antimicrobial resistance patterns and biofilm formation ability of V. parahaemolyticus strains were investigated using the disk diffusion test and a microtiter plate-based crystal violet method, respectively. Results: Thirty-seven V. parahaemolyticus isolates were recovered from 150 samples. The frequencies of the tdh and trh genes among V. parahaemolyticus isolates were 8.1% and 21.6%, respectively. More than 90% of isolates were susceptible to ceftazidime, cefotaxime, and chloramphenicol, but over 72% were resistant to ampicillin, tetracycline, and erythromycin. Furthermore, 67.57% of isolates exhibited multidrug resistance. The presence of ARGs related to gentamicin (aac(3)-IV), tetracycline (tetA) and ciprofloxacin (qnrA) in V. parahaemolyticus isolates was identified. Conversely, no ARGs related to ampicillin or erythromycin resistance were detected. Biofilm formation capacity was detected in significantly more multidrug-resistant isolates (64.9%) than non-multidrug-resistant isolates (18.9%). Conclusion: Mariculture environments are a potential source of antibiotic-resistant V. parahaemolyticus and a hotspot for virulence genes and ARGs diffusing to aquatic environments. Thus, the prevention of antibiotic-resistant foodborne vibriosis in aquatic animals and humans requires continuous monitoring.
Commentary
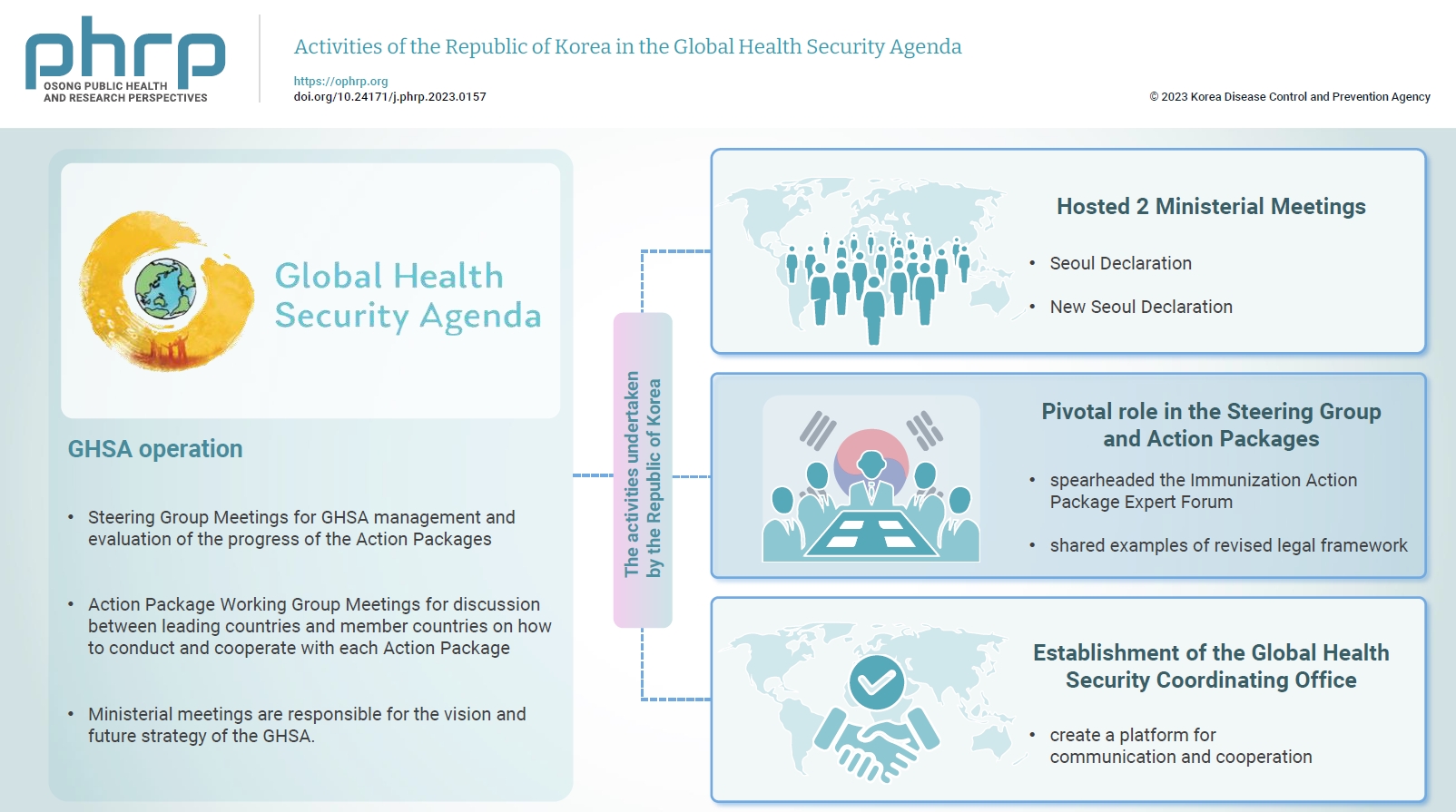
- Activities of the Republic of Korea in the Global Health Security Agenda
- Gang Lip Kim, Sookhyun Lee, So Yoon Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):90-93. Published online February 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0157
- 580 View
- 138 Download
Original Article
- Epidemiological analysis and prevention strategies in response to a shigellosis cluster outbreak: a retrospective case series in an alternative school in the Republic of Korea, 2023
- Yeongseo Ahn, Sunmi Jin, Gemma Park, Hye Young Lee, Hyungyong Lee, Eunkyung Shin, Junyoung Kim, Jaeil Yoo, Yuna Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):68-76. Published online February 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0298
- 972 View
- 51 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 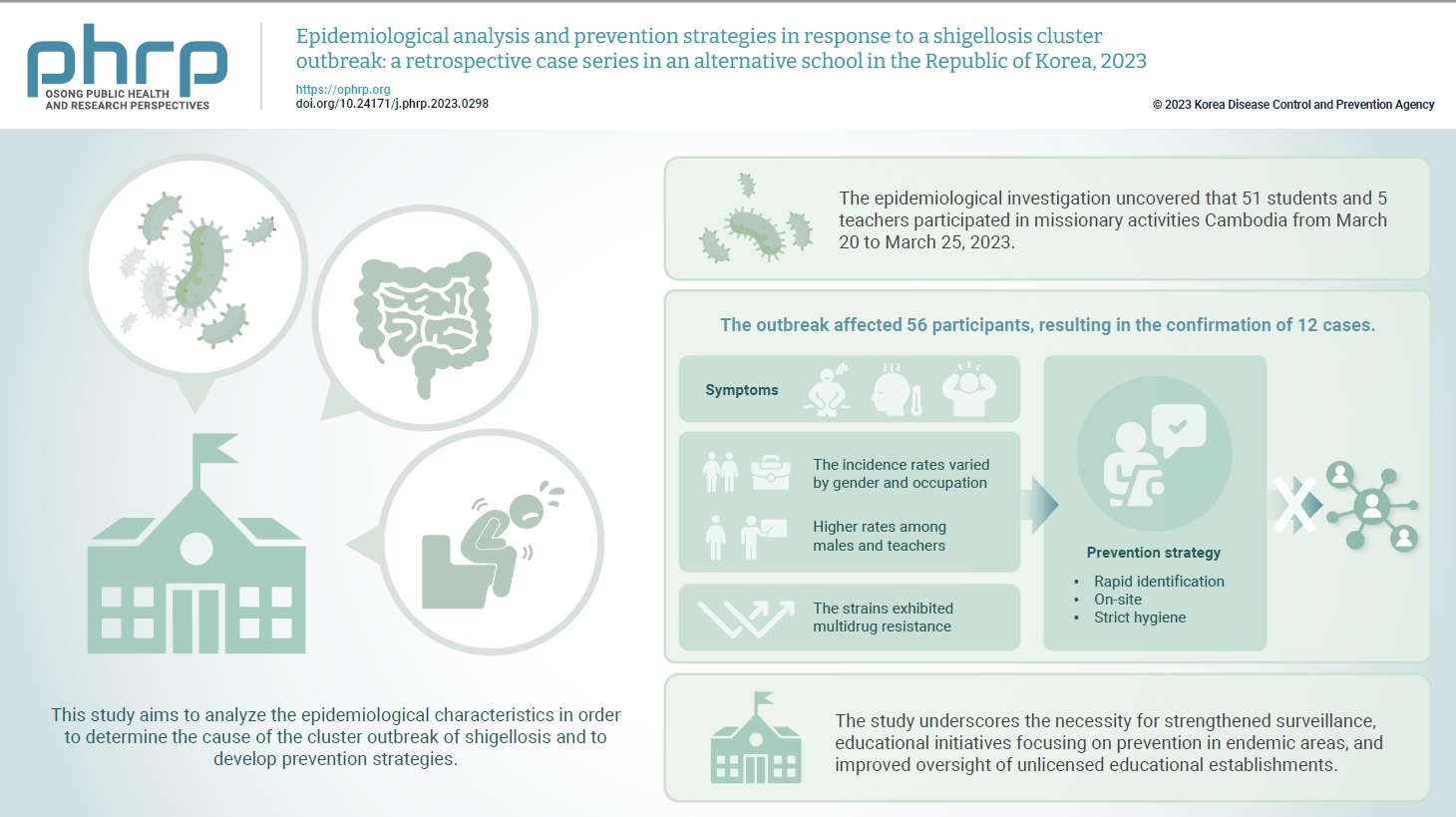
- Objectives
In March 2023, an alternative school in the Republic of Korea reported 12 cases of shigellosis. This study aims to analyze the epidemiological characteristics in order to determine the cause of the cluster outbreak of shigellosis and to develop prevention strategies. Methods: This study focused on 12 patients with confirmed Shigella infection and investigated their demographics, clinical features, epidemiology, diagnostics, and antimicrobial susceptibility. Following the identification of Shigella, we conducted follow-up rectal smear cultures to manage patients, implementing isolation and control measures. Results: This study investigated the emergence of multidrug-resistant Shigella following missionary activities in Cambodia, documenting a cluster infection within an alternative school in Daejeon, the Republic of Korea. The outbreak affected 56 participants, resulting in the confirmation of 12 cases. The incidence rates varied by gender and occupation, with higher rates among males and teachers. All 12 cases demonstrated multidrug resistance. Challenges included delayed pathogen confirmation and suboptimal adherence to isolation criteria. The incident prompted revisions in the criteria for isolation release, focusing on symptom resolution. The study underscores the necessity for strengthened surveillance, educational initiatives focusing on prevention in endemic areas, and improved oversight of unlicensed educational establishments. Conclusion: Successful response strategies included swift situation assessment, collaborative efforts, effective infection control measures, and modified criteria for isolation release. Continued surveillance of multidrug-resistant strains is recommended, especially in regions with a high prevalence.
Review Article
- Predictors of outcomes 3 to 12 months after traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Younes Iderdar, Maryem Arraji, Nadia Al Wachami, Morad Guennouni, Karima Boumendil, Yassmine Mourajid, Noureddine Elkhoudri, Elmadani Saad, Mohamed Chahboune
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):3-17. Published online February 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0288
- 1,042 View
- 72 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 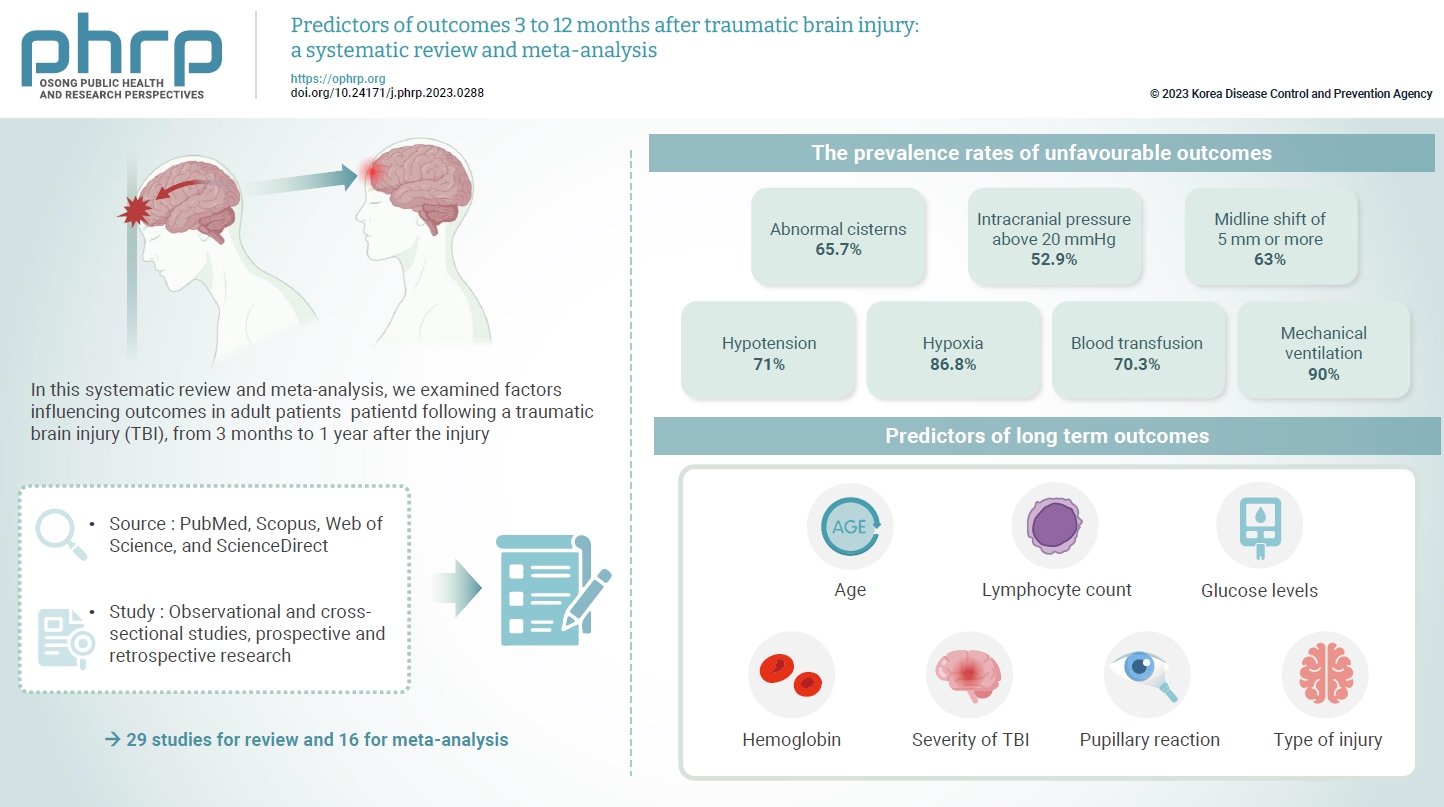
- The exact factors predicting outcomes following traumatic brain injury (TBI) remain elusive. In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we examined factors influencing outcomes in adult patients with TBI, from 3 months to 1 year after injury. A search of four electronic databases—PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and ScienceDirect—yielded 29 studies for review and 16 for meta-analysis, in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis guidelines. In patients with TBI of any severity, mean differences were observed in age (8.72 years; 95% confidence interval [CI], 4.77–12.66 years), lymphocyte count (−0.15 109/L; 95% CI, −0.18 to −0.11), glucose levels (1.20 mmol/L; 95% CI, 0.73–1.68), and haemoglobin levels (−0.91 g/dL; 95% CI, −1.49 to −0.33) between those with favourable and unfavourable outcomes. The prevalence rates of unfavourable outcomes were as follows: abnormal cisterns, 65.7%; intracranial pressure above 20 mmHg, 52.9%; midline shift of 5 mm or more, 63%; hypotension, 71%; hypoxia, 86.8%; blood transfusion, 70.3%; and mechanical ventilation, 90%. Several predictors were strongly associated with outcome. Specifically, age, lymphocyte count, glucose level, haemoglobin level, severity of TBI, pupillary reaction, and type of injury were identified as potential predictors of long-term outcomes.
Short Communication
- Characteristics of a large outbreak arising from a school field trip after COVID-19 restrictions were eased in 2022
- Sueng-Jin Kim, Eun-Young Kim, Jeonghee Yu
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):83-89. Published online February 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0264
- 873 View
- 22 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 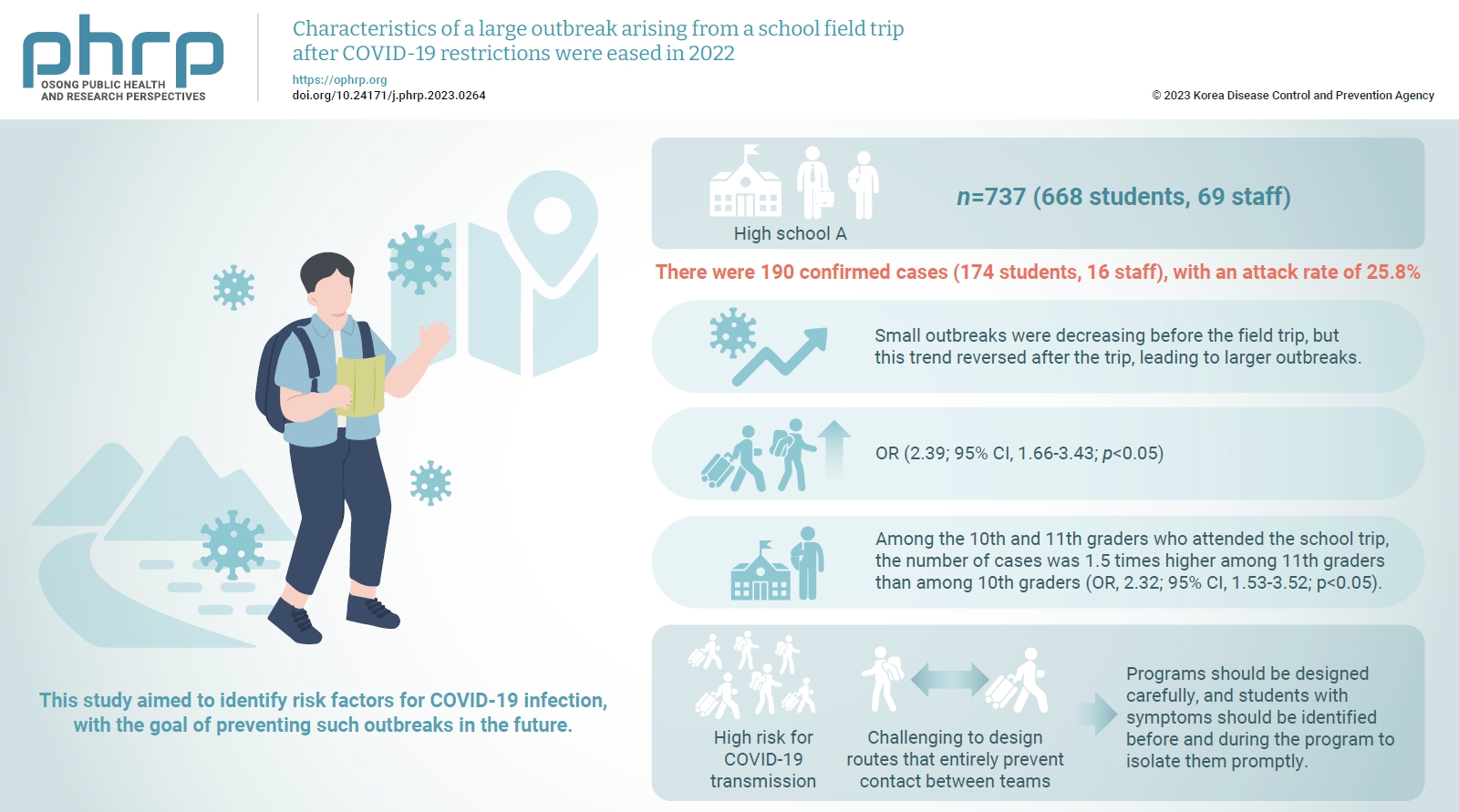
- Objectives
This study analyzed a large outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) that occurred during a high school field trip in the Jeonbuk region and aimed to identify risk factors for COVID-19 infection, with the goal of preventing such outbreaks in the future. Methods: A retrospective cohort study of 737 participants, including 668 students and 69 staff at High School A, was designed to describe the epidemiological characteristics of this large COVID-19 outbreak. Logistic regression analysis was performed to calculate relative risks (odds ratios [ORs]) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Results: There were 190 confirmed cases (174 students, 16 staff), with an attack rate of 25.8%. Small outbreaks were decreasing before the field trip, but this trend reversed after the trip, leading to larger outbreaks. Logistic regression showed an OR of 2.39 (95% CI, 1.66–3.43; p<0.05) for COVID-19 infection among field trip participants. Among them, 11th graders had an OR of 2.32 (95% CI, 1.53–3.52; p<0.05) compared to 10th graders, while no significant risk difference was found within same-grade teams. Conclusion: There was a high risk for COVID-19 transmission during extracurricular activities with a large number of participants, such as field trips, even after the nationwide Omicron variant epidemic subsided. Even when students are separated into teams and follow different routes, it is challenging to design routes that entirely prevent contact between teams. Thus, programs should be designed carefully, and students with symptoms should be identified before and during the program to isolate them promptly.


 First
First Prev
Prev


