Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Osong Public Health Res Perspect > Volume 13(2); 2022 > Article
-
Review Article
Immune-related therapeutics: an update on antiviral drugs and vaccines to tackle the COVID-19 pandemic -
Iqra Mir1
 , Sania Aamir1
, Sania Aamir1 , Syed Rizwan Hussain Shah1
, Syed Rizwan Hussain Shah1 , Muhammad Shahid1
, Muhammad Shahid1 , Iram Amin1
, Iram Amin1 , Samia Afzal1
, Samia Afzal1 , Amjad Nawaz1
, Amjad Nawaz1 , Muhammad Umer Khan2
, Muhammad Umer Khan2 , Muhammad Idrees1
, Muhammad Idrees1
-
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives 2022;13(2):84-100.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0024
Published online: April 27, 2022
1Division of Molecular Virology and Infectious Diseases, National Centre of Excellence in Molecular Biology (CEMB), University of the Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan
2University Institute of Medical lab Technology, Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
- Corresponding author: Muhammad Shahid Division of Molecular Virology and Infectious Diseases, National Centre of Excellence in Molecular Biology (CEMB), University of the Punjab, 87-wWest Canal Bank Road, Thokar Niaz Baig, Lahore, Pakistan E-mail: shahidimran@cemb.edu.pk
- Iqra Mir and Sania Aamir contributed equally to this study as co-first authors.
© 2022 Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency.
This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
- 5,096 Views
- 97 Download
Abstract
- The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic rapidly spread globally. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which causes COVID-19, is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus with a reported fatality rate ranging from 1% to 7%, and people with immune-compromised conditions, children, and older adults are particularly vulnerable. Respiratory failure and cytokine storm-induced multiple organ failure are the major causes of death. This article highlights the innate and adaptive immune mechanisms of host cells activated in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection and possible therapeutic approaches against COVID-19. Some potential drugs proven to be effective for other viral diseases are under clinical trials now for use against COVID-19. Examples include inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (remdesivir, favipiravir, ribavirin), viral protein synthesis (ivermectin, lopinavir/ritonavir), and fusion of the viral membrane with host cells (chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, nitazoxanide, and umifenovir). This article also presents the intellectual groundwork for the ongoing development of vaccines in preclinical and clinical trials, explaining potential candidates (live attenuated-whole virus vaccines, inactivated vaccines, subunit vaccines, DNA-based vaccines, protein-based vaccines, nanoparticle-based vaccines, virus-like particles and mRNA-based vaccines). Designing and developing an effective vaccine (both prophylactic and therapeutic) would be a long-term solution and the most effective way to eliminate the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), a beta-coronavirus, was found to be associated with a pneumonia-associated respiratory syndrome that first emerged in Wuhan, China, in December 2019, and now has affected almost every territory of the world. SARS-CoV-2 is a single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) positive-sense virus, the genome of which is 96% identical to that of bat coronavirus. It binds angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in human cells through the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of its spike (S) protein; ultimately, membrane fusion occurs, followed by virus entry into lung cells by endocytosis [1,2]. After entry, SARS-CoV-2 hijacks the protein synthesis machinery of the host and utilizes it to produce its own proteins, through which viral genome replication occurs [3].
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the fatality rate of COVID-19 is 1% to 7%, although these rates should be interpreted with caution. COVID-19 patients show severe lung damage and typical pneumonia symptoms [4]. About 20% of SARS-CoV-2 infections in immune-compromised elderly patients with pre-existing health disorders such as hypertension, obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular problems, pulmonary fibrosis, interstitial lung disease, and asthma would develop severe respiratory illness, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), potentially leading to death. Furthermore, neurological problems have also been reported in experimental animals and humans with SARS-CoV-2 infection [5]. Although the fatality rate is less than 1% according to a study conducted in Korea, the rate of mortality is considerable due to the unprecedented scale of the COVID-19 pandemic [6]. Respiratory failure associated with COVID-19, a major cause of death, also occurred with previous related diseases, such as Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), which emerged in 2012, and the Spanish Flu, which caused a global pandemic from 1918 to 1920 [7].
- Antiviral therapy may shorten the course of COVID-19 and improve its outcomes, in addition to conventional treatment. Hemodynamic and ventilator support are also being used to treat COVID-19 patients [8]. Ventilators are needed to support patients with severe cases of COVID-19, through various modalities. A large number of patients with severe COVID-19 may develop multiple organ failure and lung injury, especially in the elderly, due to a cytokine storm, and treatment may involve immune-modulators [9].
- The epidemiological aspects of COVID-19, including data collection, compilation, and dissemination, have been investigated by numerous studies, which have made steady progress, assisted by significant advances in computational analysis. Meanwhile, in parallel, virus genome databases and molecular technology have enabled us to identify viruses and mutations. Screening of chemical libraries is an important approach to drug discovery, including large transcriptional signature databases and available molecules in different cell lines. Studies are being conducted to use these molecules for therapies [10]. Several products claimed to be effective against SARS-CoV-2 are available on the market. One of these is chlorine dioxide (ClO2), which the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warned against using for COVID-19, as it causes health risks. The enzymes of SARS-CoV-2 are targeted by various strategies that interfere with the viral cycle inside the host cell, using antiviral drugs that were previously used against MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, and RNA viruses such as hepatitis C virus (HCV), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Other target drugs are used to prevent COVID-19 virus entry at the host cell surface. Another strategy is immunomodulation, which includes using non-specific interferon (IFN) and immunoglobulins (Igs), such monoclonal antibodies and tyrosine kinase inhibitors, for COVID-19 treatment. Immunomodulation is needed either in the early stage of the disease to boost antiviral immunity or in severe cases of the disease to suppress the immune response when uncontrolled immunity causes organ damage and lung injury. Neutralizing antibodies (NAbs) that bind to the RBD of the S protein of COVID-19, prevent RBD from binding to ACE2 in human cells; therefore, NAbs may also be useful for the treatment of COVID-19 [11].
- This review covers key drugs and vaccines, including antiviral/anti-infective agents, that are registered in clinical trials for the treatment of COVID-19. This comprehensive review will provide a better understanding of immune-related therapeutic approaches to combat the COVID-19 pandemic.
Introduction
- Relevant literature was retrieved from databases including Scopus, PubMed, Medline, Embase, and Web of Science with the following keywords: “severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2,” “vaccines,” “COVID drugs,” “COVID immune modulator therapies,” and “immune response.” Preference was given to sources published through the end of 2021. A total of 300 articles were retrieved, out of which a 85 were selected for the present study. The selection criteria were high-citation articles published in credible journals, and most importantly, articles related to drug and vaccine therapy; articles on non-relevant topics with few citations were excluded. Statistics and approval data about drugs and vaccines were also retrieved from the websites of the WHO and FDA.
Search Methodology
- The innate immune response refers to the primary host defensive mechanisms against viral infection. Upon activation, intracellular, germline-encoded pathogen recognition receptors recognize uncapped mRNA and double-stranded RNA as unique pathogen-associated molecular patterns [12]. Innate immunity against viral diseases depends on the type-1 IFN response and its downstream signaling, which modulate a strong adaptive host response and also control viral replication. MERS-CoV uses a specific receptor, named dipeptidyl peptidase, for entry into the host cell, whereas SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 share the same structural subdomain of the S protein that binds to the same receptor, ACE2 [1]. Several studies have shown that both macrophages and dendritic cells (DCs) play significant roles, such as the initiation of the immune response in mucosal lymphoid tissue and viral destruction. Moreover, the S protein of SARS-CoV activates macrophages and DCs, leading to pro-inflammatory cytokines overproduction [13].
- The term “cytokine storm” refers to a rapid increase in the level of cytokines released in the human body due to an overstimulated host immune response against a pathogenic invader. ARDS is considered as an important stage of viral pathogenesis as it shows a significant correlation with cytokine release syndrome. A potentially fatal unconfined or uncontrolled anti-inflammatory response occurs when the effector cells of the human immune system release a large number of pro-inflammatory cytokines during ARDS [14]. The excess production of cytokines and chemokines was reported during previous outbreaks of SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV. The levels of cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-6 and IFN-α, as well as pro-inflammatory cytokines including CXCL-8, CXCL-10, and CCL-5, were elevated during MERS-CoV infection. Similarly, high levels of ILs (IL-33, IL-6, IL-18, IL-12, IL-1), IFNs (IFN-γ, IFN-α) and tumor necrosis factors (TNFs; TNF-β and TNF-α) were observed during SARS-CoV infection. The overreaction of the immune system in the human body induced by the cytokine storm may cause sudden death in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection due to serious complications such as multiple organ failure and ARDS [15].
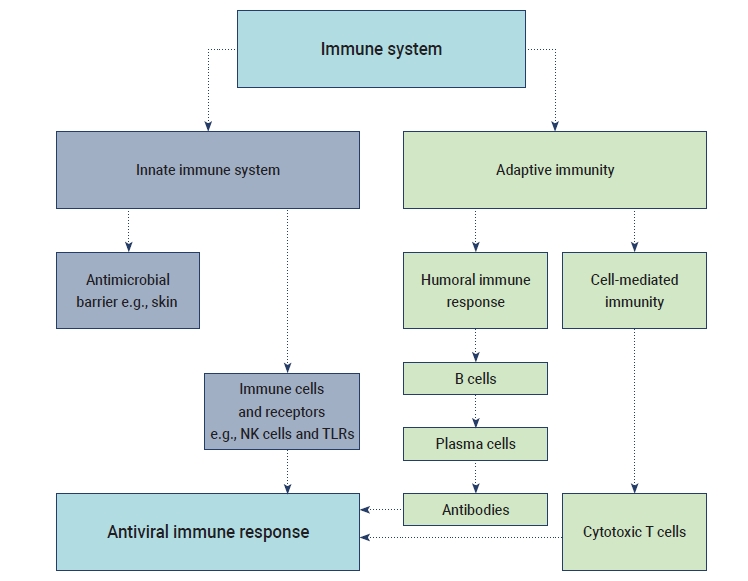
- The humoral B cell and cellular T cell responses are the main components of adaptive immunity. Helper T cells (Th1) cells are particularly important for adaptive immune responses to worm parasites and viruses. T cell responses are activated by the cytokine environment produced by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). Tc cells, also known as cytotoxic T lymphocytes, mainly kill cells infected with viruses, while Th cells play an essential role in the dictation of the overall mechanisms deployed during the adaptive response [16]. A high level of IgG is present in the plasma during the convalescent period, and then IgG titers disappear after recovery from COVID-19. The accumulation of inflammatory macrophages and the production of IL-8/MCP-1 triggered by anti-S-NAbs may cause severe lung injury despite inhibiting viral replication [17]. SARS-CoV-2 may induce lymphocytopenia through the induction of T lymphocyte-mediated apoptosis or programmed cell death. Recent studies have suggested that SARS-CoV-2 can infect T lymphocytes by either S protein-dependent or ACE2-mediated membrane fusion [18]. The immunological events (innate, adaptive immunity, cytokine antiviral response) that occur during SARS-CoV-2 infection are described in Figure 1.
Mechanism of Innate and Adaptive Responses
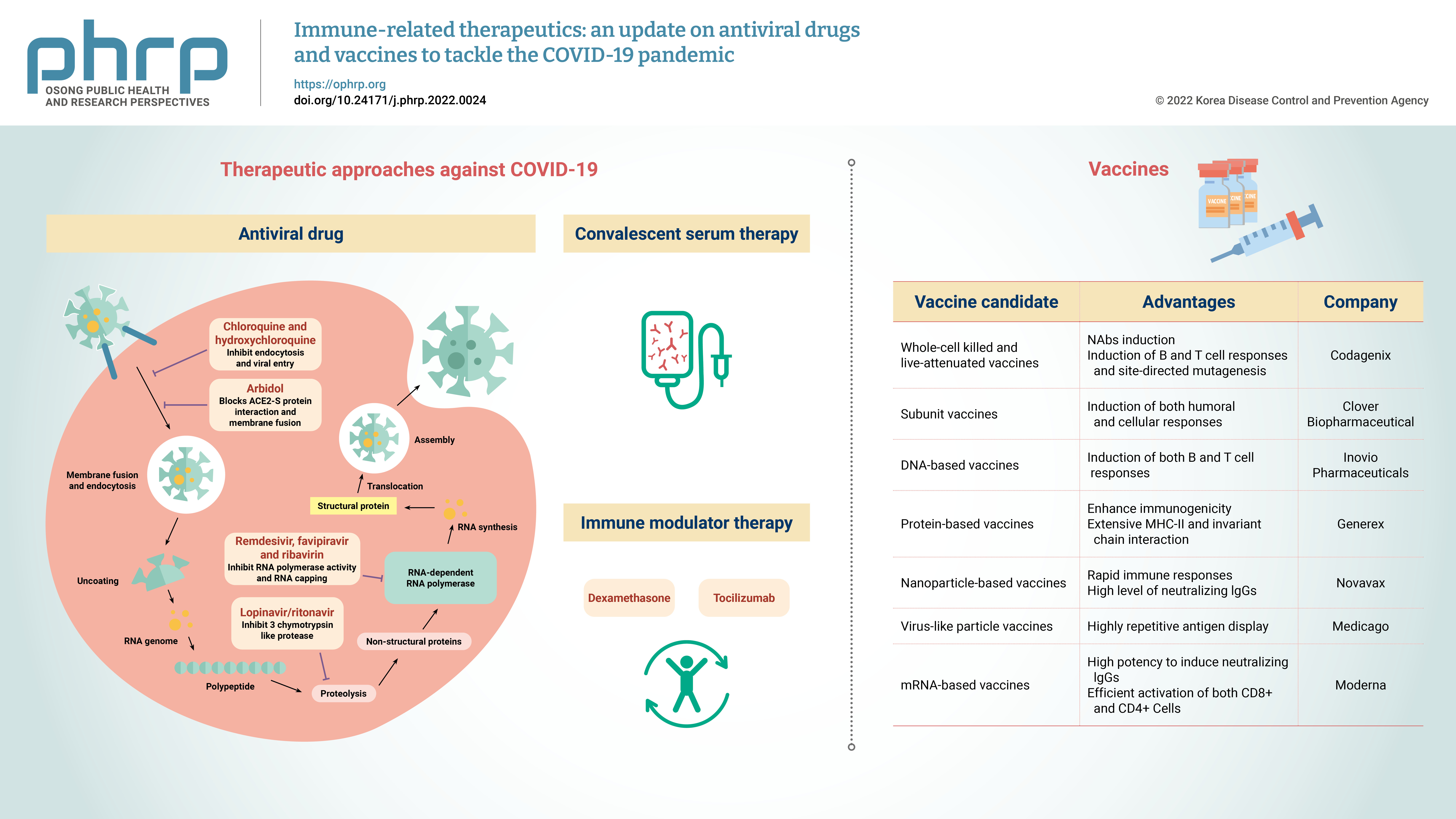
- Currently, the treatment of COVID-19 patients is mainly based on addressing their symptoms and repurposing therapeutic drugs. Therapies are categorized into 2 types according to their respective target: directly inhibiting viral replication directly by blocking binding to the entry receptor on the host cell membrane, or boosting the immune system by inhibiting the inflammatory response [19]. The steps involved in the SARS-CoV-2 replication cycle (attachment/endocytosis, membrane fusion, uncoating, translation, proteolysis, RNA synthesis, and assembly/exocytosis) provide possible targets for effective drug therapy (Figure 2). Table 1 summarizes the potential targets and mechanisms of repurposing therapeutic drugs for COVID-19 treatment.
- Inhibitors of RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase
- Remdesivir, previously named GS-5734, is a monophosphate prodrug of an adenosine analogue. The compound undergoes chemical conversion by a metabolic process and it is converted into an active nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) derivative, specifically, a C-adenosine analogue. It was discovered during the screening of antimicrobial agents with broad-spectrum activity against ssRNA viruses (Flaviviridae and Coronaviridae). Remdesivir showed promising results during the Ebola virus epidemic due to the selectivity of host RNA polymerase against Ebola virus infection and its lower 50% effective concentration (EC50) [20]. The promising therapeutic potential of remdesivir for COVID-19 is due to its strong in vitro, broad-spectrum activities against several novel coronaviruses, such as SARS-CoV-2, with a low EC90 (1.76 μM) and EC50 (0.77 μM) [21].
- The possible mechanism of remdesivir against various coronaviruses remains unknown, and several explanations of its potential effects have been prepared. First, remdesivir with intact 3'-5' exoribonuclease proofreading activity interacts with the RNA polymerase activity of non-structural protein-12 [22]. NTPs, which are pharmacologically active compounds and alternative substrates produced by remdesivir, are especially involved in RNA chain termination. Remdesivir incorporates active NTPs into viral RNA sequences, thereby inhibiting SARS-CoV replication [23]. Additionally, genetic barriers made it difficult for coronaviruses to develop resistance against remdesivir, suggesting that remdesivir is a highly effective therapy for coronaviruses [24].
- Chest radiography is considered a key component of the recovery criteria and disease diagnosis in the Chinese government’s Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). It should not be included in outcome measurements and exclusion/inclusion criteria [25]. Several studies on SARS-CoV have shown that remdesivir administration was only effective in the earliest stage (prior to the initial phase of the immunopathological process during pneumonia) [26]. In India, a clinical trial was conducted on 2,329 patients (of whom 29.69% had diabetes and 20.33% had hypertension) receiving oxygen therapy to evaluate the safety and efficacy of remdesivir. Of these patients, 65.38% were treated with remdesivir for 5 days, and it was overall well tolerated with some (n=119) adverse events like nausea, vomiting, and elevated liver enzymes. Death occurred in 6.77% of patients (mostly among those over 60 years of age), and 9.16% of patients showed no improvements. The factors associated with mortality included diabetes, age >60 years, and receiving high-intensity oxygen therapy. The remaining 84% of patients recovered [27].
- The antiviral prodrug favipiravir (T-705), is a purine nucleotide analogue that is converted into its active form, T-705-4-ribofuranosyl-5'-triphosphate (T-705RTP). The agent halts viral replication by inhibiting viral RNA polymerase activity. Most preclinical data on favipiravir have been obtained from its activities against Ebola and influenza viruses. The drug also exerts broad-spectrum activity against RNA viruses [28]. Favipiravir, with an EC50 of 61.88 μM, was found to be highly effective in Vero E6 cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 in vitro [29].
- The entry of the favipiravir prodrug into virus-infected cells takes place by endocytosis. The agent then undergoes phosphorylation and phosphoribosylation and is converted into an active form of favipiravir, T-705 RTP [30]. The drug interferes with the process of nucleotide incorporation during replication and exerts antiviral effects by selectively targeting conserved residues in the catalytic domain of viral enzymes, such as RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). The increased frequency and number of point mutations, such as the replacement of cytosine (C) replacement with uracil (U) or thymine (T) and the replacement of guanine (G) with adenine (A), results from dysregulation in SARS-CoV replication. Favipiravir is a potential therapy for the treatment of human infections with RNA viruses including Ebola, influenza, and norovirus [31].
- Several clinical studies on the effectiveness of favipiravir against SARS-CoV-2 infection have been conducted in countries such as Japan and China. A randomized clinical trial (ChiCTR200030254) revealed that the treatment of COVID-19 patients with favipiravir led to a significantly higher clinical recovery rate (71.43%) than treatment with umifenovir (55.86%). The fever reduction and cough relief times in the favipiravir-treated group were shorter than in the umifenovir-treated group.
- However, in a clinical trial conducted in Saudi Arabia, in which 231 COVID-19 patients (treatment group) were treated with favipiravir and a placebo group of 119 patients were kept in a similar environment, the median time for viral clearance was 10 days in the treatment group versus 8 days in the placebo group, and the median time for clinical recovery was 7 days in both groups. This trial suggests that favipiravir does not shorten the time required for viral clearance [32]. The available clinical trials indicate that favipiravir relieves cough and fever but fails to accelerate viral clearance [33].
- Phase 3, open label, parallel arm and multicentre randomized controlled trial (RCT) by AlQahtani et al. [34] and a trial by Udwadia et al. [35] for improvement of clinical parameters and reduction of SARS-CoV-2 viral-load was performed. The results showed some clinical improvements but no reduction of viral load. According to these two trials the fivipiravir did not show significant efficacy for treatment of SARS-CoV-2 disease contradicting previous results reported by Rahman et al. [36]. The safety and efficacy of favipiravir alone or in combination with tocilizumab (TCZ) (NCT04310228, ChiCTR2000030894), IFN-alpha (ChiCTR2000029600) marboxil, baloxavir (ChiCTR2000029548, ChiCTR2000029544), and chloroquine phosphate (NCT04319900, ChiCTR2000030987) [37].
- Ribavirin is a synthetic guanosine nucleoside analogue that interrupts DNA and RNA viral replication. The main antiviral action of ribavirin is to inhibit RdRp activity. The chemical structure of ribavirin restricts viral RNA cap synthesis, a process that involves the methylation of natural guanosine, thereby protecting RNA from degradation [38]. It inhibits the function of inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase, an enzyme involved in the synthesis of the common precursor, guanine monophosphate. Ribavirin further enhances RNA destabilization by interfering with the mechanism of guanosine triphosphate production [39]. Ribavirin seems to be a promising candidate for the treatment of COVID-19 due to its potent antiviral activity against novel coronaviruses. However, ribavirin has limited in vitro activity against novel coronaviruses, and large concentrations are required to halt SARS-CoV-2 replication. Combined therapy and oral administration of high-dose ribavirin (1.2−2.4 g) every 8 hours are highly recommended [40].
- Adverse dose-dependent hepatotoxicity associated with ribavirin therapy is a major concern. High concentrations of ribavirin caused dose-dependent anemia due to hemolysis in >60% of patients in SARS-CoV-2 clinical trials. Similar clinical safety concerns were observed in large-scale studies on MERS. Blood transfusions were required in approximately 40% of infected individuals taking ribavirin in combination with IFN [41]. An elevated level of transaminase was reported in 75% of patients with SARS who received ribavirin. The application of ribavirin is prohibited in pregnancy due to its severe teratogenic effects. The substantial toxic effects and insufficient data on ribavirin efficacy for several novel coronaviruses suggest that its use for COVID-19 treatment may be limited. However, combined drug therapy gives the best option for clinical efficacy [42].
- Inhibitors of Viral Protein Synthesis
- Ivermectin has emerged as a pharmaceutical intervention in searching for the appropriate treatment for COVID-19. Ivermectin has in vitro, broad-spectrum antiviral activities against a wide range of RNA viruses. This FDA-approved drug also acts as an antiparasitic agent [43]. Several studies have confirmed that ivermectin is a specific importin (Imp) nuclear import inhibitor. The drug halts HIV-1 replication by inhibiting the interaction between the Imp α/β1 heterodimer, which is crucial for nuclear transport, and the HIV-1 integrase protein. Several actions of ivermectin have been reported, such as inhibition of viral and host protein nuclear import. It was found that ivermectin limits infection caused by RNA viruses such as the dengue, West Nile, and influenza viruses [44].
- A meta-analysis confirmed that ivermectin has a well-defined safety profile in humans. High-dose treatment has the same outcomes in terms of human safety as standard low doses of ivermectin. There is not yet sufficient evidence to make specific conclusions regarding the safety profile of ivermectin in pregnancy [45,46]. The most important step in the further assessment of potential benefits in COVID-19 patients is monitoring the multiple dosing regimen that provides the current approved doses of ivermectin that are safe for human use. Several in vitro studies suggested that ivermectin is a specific inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2. The antiviral action of ivermectin in hSLAM/Vero cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 for 2 hours was examined, and it was found that the level of viral RNA decreased by ~5,000 fold after 48 hours. This decrease was possibly due to the inhibition of nuclear import in SARS-CoV-2 infection mediated by the Impα/β1 heterodimer that interrupts the mechanisms of immune evasion, as in other ssRNA viruses. Further clinical trials, as well as in vitro and in vivo studies, are required to clarify the contribution of ivermectin to COVID-19 management [47].
- Lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/r) is a combination of 2 competitive inhibitors: an HIV-1 protease inhibitor and cytochrome P-450 (CYP3A4) inhibitor. The orally co-administrated LPV/r drug comprises fixed doses of lopinavir and ritonavir to boost concentrations of protease inhibitors [48]. Lopinavir is known to inhibit SARS-CoV replication by blocking 3C-like proteases. Lopinavir has no effect on cells where viral DNA has already integrated. The main antiviral activity of lopinavir involves preventing the rapid spread of SARS-CoV-2 infection in cells. The administered dose of lopinavir is higher than that of ritonavir. The co-administered drug is a pharmacokinetic enhancer that inhibits the inactivation and metabolism of lopinavir [49,50]. Lopinavir blocks the CYP system and is responsible for extensive drug interactions between ritonavir and lopinavir. LPV/r therapy seems highly effective in post-exposure prophylaxis against several coronaviruses, such as MERS-CoV [43].
- An open-label RCT was conducted individually on COVID-19 patients, in which they received 400 mg/100 mg of oral LPV/r twice daily with standard care. Adverse effects, such as asthenia, diarrhea, and nausea, were frequently reported in patients receiving LPV/r treatment [44]. Interestingly, several ongoing studies on confirmed COVID-19 cases in South Korea have shown that administration of LPV/r significantly reduced titers of SARS-CoV-2 and, in most cases, no SARS-CoV-2 titers were detected. However, a case report described a single patient during the initial COVID-19 outbreak in South Korea [51]. The major concern is LPV/r induced hepatoxicity, which may exacerbate liver injury in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection during the dosing regimen. Importantly, elevated alanine transaminase levels are considered as an exclusion criterion in some COVID-19 clinical trials, which means that LPV/r induced transaminitis may reduce the ability of patients to receive other drugs [49].
- Inhibitors of Virus-Host Cell Membrane Fusion
- Chloroquine is a potent, low-cost, and safe drug that is used to treat malarial diseases as well as autoimmune disorders and also possesses broad-spectrum antiviral activity [18]. Research implies that chloroquine can be effectively used against COVID-19, as it has been shown to suppress COVID-19 in vitro [15], thereby potentially reducing the time period of the disease course and providing good cure rates [52]. This drug is found to be effective in clinical trials in China and was added to the Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of COVID-19 by the National Commission of the People’s Republic of China.
- Chloroquine is captured in the membrane-bound acidic medium and low-pH organelles such as lysosomes, endosomes, and digestive vacuoles, and due to its weakly basic nature, it interacts with these organelles and increases their pH [53]. This action prevents viral entry, replication, and fusion by disturbing pH-dependent mechanisms and also inhibits glycosylation of viral glycoprotein and host receptor proteins [54]. Chloroquine is also effective in preventing the assembly of virion particles in Golgi-endoplasmic reticulum intermediate compartments [55]. Chloroquine does not alter the biosynthesis of viral glycoproteins of the spikes; instead, it affects the terminal glycosylation of the ACE2 protein receptor, which prevents viral binding to human cells [56]. In cell cultures, chloroquine was effective even when viral particles had already entered cells by trapping the endosomes via pH increase, disturbing fusion of the viral envelope with the endosomal membrane [54]. Based on the findings of 1 study, a 500-mg oral dose of chloroquine given once or twice a day was recommended for COVID-19 treatment [57].
- Hydroxychloroquine is safe to use, easily available, cost-effective, and less toxic than chloroquine; furthermore, it has been found to show antiviral properties against COVID-19 [58]. It has direct-acting antiviral properties, as well as immunomodulatory activities [59] that decrease the production of TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6 to downregulate the overreaction of the immune system (cytokines), which can cause inflammatory effects [60]. Host cell autophagy and the activities of lysosome-induced mechanisms are also blocked by this drug . According to a study, patients with severe COVID-19 had high cytokine concentrations in their blood, indicating that excessive cytokine production or overreaction of the immune system aggravates this condition. Hydroxychloroquine also inhibits the entry of virus particles into the cell by blocking the glycosylation of host receptors, thereby preventing the fusion of viral S proteins with the host receptor ACE2 [61].
- A study conducted in France observed that when COVID-19 patients were treated with hydroxychloroquine, they showed a reduction of viral load followed by complete removal of the virus. Combined hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin therapy showed high efficiency in lowering the viral titer [62]; however, their regular use increases the risk of heart problems, such as heart attack [63]. An oral dose of hydroxychloroquine of 400 mg once a day [49] or 400 mg twice a day for 2 days followed by a 200-mg dose twice regularly is recommended [58].
- Nitazoxanide is an FDA-approved drug used for the treatment of several protozoal infections such as giardia. In Brazil, this drug is used to treat norovirus and rotavirus infections due to its broad antiviral activity and safe history [64]. Nitazoxanide has also been used for the treatment of hepatitis B and C [65]. Nitazoxanide interferes with viral infections through enhancing the activity of the immune system and host cellular defense mechanisms [66,67] by increasing foreign nucleic acid-sensing mechanisms and type I IFN pathways [66].
- Many studies have demonstrated that nitazoxanide can be utilized for the treatment of coronaviruses if viral content is in the low micromolar range [68]. Viral-induced blockage of IFN mechanisms (of the host) is inhibited by nitazoxanide, and a low 50% inhibitory concentration was obtained for all coronavirus infections [60].
- Umifenovir, also referred to using its brand name, Arbidol, is also used for treating influenza infections [69] in countries such as Russia and China. It prevents the entry of virus particles into the cells and acts as an entry inhibitor, since it inhibits the fusion of the viral membrane with host cell endosomes during the endocytosis process by targeting the viral glycoprotein hemagglutinin [70]. Umifenovir was found to contain a potential inhibitory factor that helps to reduce the synthesis of viral progeny in vitro [71]. Umifenovir has antiviral properties that reduced the growth of viruses in cultured cells [72]. It can be used by itself for the treatment of COVID-19 infection, as well as in combination with other drugs [60]. Furthermore, a study showed that a umifenovir dose of 10 to 30 µM reduced the concentration of coronavirus up to 60 times as compared to the control group. It was used in China for the treatment of COVID-19 infections [73].
Current Antiviral Drugs for COVID-19 Treatment
Remdesivir
Favipiravir
Ribavirin
Ivermectin
Lopinavir/ritonavir
Chloroquine
Hydroxychloroquine
Nitazoxanide
Umifenovir
- Convalescent serum therapy is a type of passive antibody therapy in which blood serum containing NAbs from a patient who has recovered from an infection is taken and administered to treat another infected patient [74]. The final goal is the same as a vaccine (i.e., to generate antibodies against the infectious agent), but in this therapy the antibodies are already available. However, to enhance the efficiency of convalescent serum therapy, it is suggested to utilize hyperimmune-IgG from people who recovered recently from COVID-19 for the large-scale production of antibodies [75]. Potential serum donors should be from the same area as the recipient patient because specific viral strains are present in certain geographic areas. This therapeutic approach can regulate phagocytosis and cytotoxicity, as well as producing an additional viral neutralizing effect in combination with antiviral drugs [76].
- The viral load and severity of the symptoms of COVID-19 define the required amount of antibodies for convalescent serum therapy; however, NAbs in a very small amount can be efficient in treating the early symptoms of COVID-19. This passive immunity usually lasts for weeks or months [76]. The optimal timing of antibody use depends on the rate of mutation of the viral agent, although antibodies can be collected and stored for a long time. Hence, serum should be used within a few days of collection, and the antibodies cannot be effective if used beyond the context of a specific outbreak [77]. The major limitation of this therapy is the non-availability of matched control subjects who were not on antibody therapy.
Convalescent Serum Therapy
- Immune modulator therapies are medications used to reduce the overreaction of the immune response to prevent permanent damage. The types of immune modulator therapies include non-specific therapies and targeted cell therapies. Non-specific therapies suppress the entire immune system, which is very effective but involves more side effects, whereas targeted cell therapies suppress specific proteins/cells of the immune system to stop its overreaction. The 3 distinct phases of COVID-19 are the early phase (immune response is suppressed by viral replication via kappa light chain), the pulmonary phase (activation of the immune system after hypoxia development), and the hyperinflammatory phase (when ARDS, cytokine storm, and septic shock occur). At this stage, the IL levels are very high, and the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommended using certain immune modulators—even steroids—to treat this condition [78]. Dexamethasone (DEX) is highly recommended [79] and a United Kingdom RECOVERY trial showed the benefits of low-dose DEX in patients who required high-intensity oxygen therapy and were on mechanical ventilation [80]. Another immune modulator used to treat high IL-6 levels, which drive the cytokine storm, is TCZ [78], and retrospective data from China have shown the effectiveness of TCZ in COVID-19 patients [81]. Cumulative data showed that TCZ is not highly effective in COVID-19 patients; however, some RCTs have reported contradictory findings [82]. The manufacturer of TCZ conducted 2 RCTs: the COVACTA and EMPACTA trials [83]. The COVACTA trial showed no mortality differences, whereas the EMPACTA trial showed a reduction in the need for mechanical ventilation with no impact on the survival rate in COVID-19 patients who received TCZ and standard of care. The largest RCTs on the clinical efficacy of TCZ are the RECOVERY and REMAP-CAP trials, both of which demonstrated mortality benefits and a decrease in mechanical ventilation therapy. The RECOVERY trial clearly reported the efficacy of combined TCZ and DEX in comparison with DEX monotherapy, with mortality rates of 29% and 35%, respectively [84].
Immune Modulator Therapies
- Vaccines are biological preparations that stimulate the immune response against pathogenic microorganisms. Effective and safe vaccine production is critical to control the rapid spread of SARS-CoV-2, and vaccines help prevent SARS-CoV-2 re-infection. Antiviral vaccines are categorized into the following 7 types: live attenuated-whole virus inactivated, subunit, DNA-based, protein-based, nanoparticle, virus-like particles (VLPs), and mRNA-based vaccines. As of February 2022, global research and development efforts focusing on vaccines include 114 candidate vaccines in clinical trials, 75 preclinical trials in animals, and 14 approved for emergency use. Table 2 summarizes the immunogenic composition, advantages, and leading companies developing vaccines for COVID-19.
- Whole-Cell Killed and Live-Attenuated Vaccines
- Live attenuated and inactivated vaccines are based on the antigenic properties of weakened and killed forms of viruses. Inactivated vaccines are composed of inactivated entire virus particles, mainly derived from toxoids or viruses. These specific virus-derived components lose their pathogenicity by chemical modification [85]. Inactivated vaccines provide major advantages due to their inherent immunogenicity and their capability to trigger toll-like receptors (TLRs), such as TLR7/8, TLR3, and TLR9. However, additional testing is required to ensure the safety of live attenuated vaccines. An increase in infectivity has been observed in immunization with inactivated whole SARS-CoV-2 and live coronavirus vaccines in several studies, and this is considered a major problem regarding the safety of coronavirus vaccines [86]. Another problem is the excretion of attenuated SARS-CoV-2 viral particles and their transmission to non-vaccinated people [87], and there may be chances of recombination between circulating and vaccine viral strains, which may induce the generation of new strains [88].
- Currently, 4 live attenuated vaccines have entered clinical trials in humans [89]. Sinopharm and Sinovac have entered phase 3 clinical trials and are 79.3% effective [90]. Johnson & Johnson is producing a similar vaccine to that for Ebola by expressing an important part of SARS-CoV-2 in an adenovirus vector [91].
- A live attenuated influenza vaccine expressing the S protein of SARS-CoV-2 was prepared by researchers at Hong Kong University. The Codagenix company is introducing various SARS-CoV-2 vaccine strategies, including “codon deoptimization,” a technology that reduces virus virulence. Moreover, Codagenix, in collaboration with India’s Serum Institute, Ltd., is developing a promising SARS-CoV-2 live virus vaccine that is currently in preclinical trials. This technology has allowed the rapid production of COVID-19 vaccine candidates by using viral deoptimization to recode viral genome sequences, thereby providing synthetic “rationally designed” SARS-CoV-2 attenuated vaccines [92].
- Subunit Vaccines
- Subunit vaccines contain 1 or multiple antigens that stimulate host immune responses due to their strong immunogenicity. Generally, subunit vaccines can be easily produced and are very safe, but adjuvants are also added to initiate strong protective cell-mediated responses [93]. Vaccines targeting the S protein neutralize viral infections due to their ability to produce antibodies that may block membrane fusion and virus binding. In the case of SARS-CoV-2, the S protein is largely involved in membrane fusion and receptor binding [94]; hence, the main targets for subunit vaccines are coronavirus structural proteins such as the S protein, which is the major antigenic determinant, as it elicits NAbs and host defense mechanisms [95].
- Clover Biopharmaceuticals used the “Trimer-Tag” technology to produce trimeric fusion proteins of SARS-CoV-2 for subunit vaccine development. The RBD located in the SARS-CoV-2 S protein was recognized. The Vector Institute in Russia designed a subunit vaccine named EpiVacCorona, which has entered a phase 3 clinical trial [96]. Forty-six subunit vaccines from different research institutes have entered preclinical trials to date [97]. Several studies suggested the interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 RBD and ACE2 is slightly different from the SARS-CoV-ACE2 interaction, since the SARS-CoV-2 RBD binds more tightly to the ACE2 receptor. Therefore, coronavirus subunit vaccines have great potential for preventing COVID-19 [98]. Subunit vaccines have the advantage of reducing host immunoprecipitation, thereby preventing the docking of RBD to the ACE2 receptor. The high similarity (greater than 80%) in the amino acid sequences of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV RBDs and their ability of binding to the same ACE2 receptor make them a promising target for either subunit or protein vaccines [86].
- DNA-Based Vaccines
- DNA-based vaccines induce immune responses after translation into proteins [70]. It is easy to produce these genetic vaccines, with a low production cost, and their purification is very convenient, unlike recombinant protein-based vaccines. As nucleic acid structures are simple, they obviate the risk of protein misfolding, which is a concern for recombinant protein-based vaccines [99]. However, the ability to induce immunogenicity may be influenced by factors such as the quantity of plasmid delivered, the most suitable time interval, and the route of genetic vaccine administration [70].
- Immunogens that can be utilized for the production of DNA vaccines were listed in patent application WO2015081155, which focused on protein or amino acid sequences derived from the S proteins of MERS-CoV. Humoral and cell-mediated immune responses are stimulated by the viral S protein consensus sequences, and the level of NAbs and IgG titers is also enhanced. Increased amounts of immune cells, such as CD3+CD4+ and CD3+CD8+, are produced, leading to the production of IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2 [3].
- The patent application WO2005081716 mentioned some procedures for stimulating the immune response, such as T cell mediated responses (CD8+) induced in response to antigens of SARS-CoV-2. The gene gun delivery method was used to deliver chimeric nucleic acids in vivo using DNA-coated gold particles into an animal model (mice). These nucleic acids were transcribed and then translated into calreticulin, which was associated with an antigenic peptide of SARS-CoV. The immune system of the mice was stimulated, involving both humoral and cell-mediated immune responses, which were induced due to the fusion of calreticulin and nucleocapsid. Decreased titers were observed in vaccinated mice against the vaccinia vector, which was inserted to express the N protein of SARS-CoV [3].
- Inovio Pharmaceuticals produced a genetic vaccine named INO-4800, a potential DNA vaccine [70]. It entered a phase 2 clinical trial, and it was found that grade 1 and 2 adverse effects were present that did not increase with the second dose [100]. Karolinska Institute / Cobra Biologics produced a DNA vaccine that has entered a phase 1 clinical trial [101], and a plasmid DNA vaccine by Osaka University has entered phase 2/3 clinical trials [102].
- Protein-Based Vaccines
- A protein vaccine was produced against SARS-CoV by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), which was able to stimulate the immune response in animal models. Engineering of a structural protein immunogen and an adjuvant with an oil-protein emulsion was done, and its insertion in animal models was able to stimulate a strong immune response, such as NAbs and antiviral IgG antibodies [3].
- A collaboration was done between Chinese company Clover Biopharmaceuticals and GSK at the end of February 2020 to analyze and select a potential candidate for COVID-19 vaccine development. The COVID-19 S-Trimer was produced by Clover Biopharmaceuticals, and GSK presented the adjuvant system. S-Trimer is a COVID-19 trimeric S protein subunit that can serve as a potential vaccine candidate. This spike protein plays a role in viral entry into host cells by binding to the ACE2 host cell surface receptor. Thus, this trimeric S protein can serve as a primary target antigen for vaccine production. The S protein was synthesized using the expression system of mammalian cell cultures. The trimer-tag technology was used for Trimer-S protein production, which is a novel drug development platform for synthesizing new fusion proteins that are covalently trimerized [3].
- The University of Oxford has produced a protein-based vaccine composed of the COVID-19 S protein nucleotide sequence and non-replicating adenovirus vector. The significance of using this non-replicating virus is its comparative safety for young people, especially children, and people with pre-existing diseases. As COVID-19 uses the ACE2 receptors of the host cell membrane, adenoviral vectors mainly target the respiratory and gastrointestinal epithelium, which are crucial sites of expression of ACE2 receptors. This vaccine is under clinical trials [22,70].
- Generex, along with some Chinese companies, is developing a COVID-19 vaccine. Hybrid viral peptides were produced utilizing the process of immune system activation. The composition of these hybrid peptides includes an invariant chain peptide for APC, an invariant chain and antigen epitope linking structure, and an antigen epitope that binds to the major histocompatibility complex II molecule [3].
- Nanoparticle-Based Vaccines
- Nanoparticle-based strategies for vaccine production are considered as an alternative to conventional strategies for the incorporation of antigens. Nanoparticles have dimensions similar to those of viruses and proteins, with examples including polymeric nanoparticles, liposomes, self-assembled nanoparticles, VLPs, and inorganic nanoparticles [103]. Antigenic epitopes are conjugated with nanoparticles (natural or synthetic) either through encapsulation or by covalent linkage, so these particles can act as viruses to elicit an immune response [104]. These nanoparticles can be delivered through mucosal sites (e.g., oral or intranasal routes), subcutaneously, or intramuscularly [105].
- Novavax is a clinical-stage biotechnology company that is developing a COVID-19 vaccine using the S protein antigen of the coronavirus and conjugating it with matrix adjuvant in order to enhance the immune response and to stimulate high amounts of NAbs using recombinant nanoparticle-based technology. The expression system for this vaccine is a baculovirus system, in which this protein was expressed in a stable form. In preclinical trials, NVX CoV2373 elicited antibodies that play a role in blocking the virus spike protein from binding to targeted receptors. A saponin-based matrix (patented by Novavax) was found to have a potential effect in stimulating the entry of APCs towards the site of injection. A phase 1 clinical trial was started in May 2020 and the results showed 90% efficacy in US and 86.3% efficacy in UK with none of safety concerns reported.
- VLPs Vaccines
- The multi-protein structures of viral antigens are self-assembled to form non-infectious VLPs that closely resemble the morphological organization of native virions [106]. VLPs are highly immunogenic as compared to subunit vaccines for 2 specific reasons: their particulate nature and display of highly repetitive virus-specific epitopes arrayed on the membrane surface. The interaction between VLPs and APCs, such as DCs, is due to the particular nature of VLPs, which induce a potent humoral and cell-mediated immune response [106,107].
- VLPs are produced by expressing MERS- and SARS-CoV-specific antigens in recombinant vector systems that provide important guidelines for vaccine development against COVID-19. The production of coronavirus VLPs is based either simultaneously or individually on structural proteins, such as E, S, N, and M of SARS-CoV, expressed in Sf9 insect cells and baculovirus [108]. The patterns of protein glycosylation have a major impact on the protective capacity and immunogenicity of VLPs. Glycoengineered Nicotiana benthamiana has been developed, in which the α-1,3-fucosyltransferase (FucT) and β-1,2-xylosyltransferase (XylT) genes are knocked out, which significantly reduced the production of core α-1,3-fucosylated and xylosylated proteins with no phenotypic variation [109]. The Medicago company used heterologous expression systems to develop VLP vaccines within 3 weeks after the SARS-CoV-2 S protein sequence was identified. The company has a high production capacity (10 million doses of VLPs within a month). Until the end of 2021, 5 VLPs vaccine against COVID-19 are in clinical trials and 17 more are in preclinical stages [110].
- mRNA-Based Vaccines
- mRNA is an intermediate molecule between the translation of a protein-encoding DNA sequence and the synthesis of proteins by cytosolic ribosomes. Two basic types of RNA-based vaccines have recently been studied: self-amplifying mRNA derived from viruses and non-replicating mRNA [111]. Antiviral mRNA-based vaccines hold 4 major efficacy and safety advantages over traditional vaccines. First, virally derived mRNA-based vaccines reduce potential risks, such as mutagenesis induced by retrotransposon insertion and infectious diseases, since mRNA is naturally degraded in the cell’s microenvironment [112]. Second, the high efficacy of immunogens due to structural modification of engineered mRNA improves its translation efficacy and stability. Third, mRNA vaccines possess a very high potency to elicit powerful antiviral NAbs with 1 or 2 combined low-dose passive immunizations [113]. The NAbs activate both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, inducing a strong host immune response [114]. Fourth, the production of appropriate mRNA vaccine doses on a large scale to treat massive populations is facilitated by engineered structurally modified mRNA production. These parameters are considered very crucial for making mRNA-1273, the most suitable vaccine that elicits a rapid immune response against COVID-19 [115,116].
- The important steps for the production of mRNA-based vaccines are the selection of specific antigens, optimization of codons, the modification and screening of nucleotides, optimization of delivery vehicles, the induction of immune responses against selected antigens, and testing for safety to assess risk associated with vaccines [117]. An mRNA vaccine has not yet been approved to be released on the market. The safety evaluation and establishment of quality standards may take a longer time. The Moderna company developed the mRNA-1273 vaccine, an mRNA molecule that encodes the SARS-CoV-2 S protein. The company has manufactured this vaccine in clinical batches for animal experiments and is also planning to conduct the first clinical trial in 20 to 25 healthy individuals in April, 2021. The Bluebird pharmaceutical company, in collaboration with Jiaotong University and Fudan University, used 2 different procedures to develop mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. The first uses an mRNA molecule that can express the RBD and S protein of SARS-CoV-2, and it is under clinical trials on mice to evaluate vaccine efficacy. The second uses mRNA for in vivo expression [92].
Vaccines
- The emergence of the third outbreak of viruses related to Coronaviridae within the first 2 decades of the 21st century has shown the world that there is a need to improve research on therapeutic issues and to develop a more systematic approach in order to identify potential targeted agents for therapeutic purposes. Viral genetic recombination, rapid mutations, and inter-species transmission pose a serious threat to global health [54]. The outbreak of COVID-19 has challenged our existing public health measures and current antiviral strategies [70].
- A determined effort is needed in order to synthesize potential drugs, vaccines, and antiviral strategies in order to tackle coronavirus infections to eliminate the devastating impacts of viruses on human health and healthcare systems. The COVID-19 pandemic has shown the importance of developing broad-spectrum antiviral drugs and the need to apply artificial intelligence to the field of drug development in order to produce efficient therapeutic candidates relatively rapidly and at much less cost as compared to the traditional expensive and labor-intensive methods. In order to fulfill long-term drug development goals, inhibitors targeting viral replication and infectious cycles should be identified, as well as determining the viral agents responsible for the development of symptoms and associated disease and death of the host. Animal models should be established that can demonstrate the stages of viral diseases in humans, as well as vaccine candidates fulfilling the criteria of safety and efficacy. Collaboration between pharmaceutical companies and research institutes is needed in order to produce drug candidates more rapidly, with increased therapeutic potential and improved access for patients [3,54].
- Vaccines for COVID-19 must fulfill the criteria of being effective for all people including persons over the age of 60, individuals having chronic infections, and frontline health care workers. All existing vaccine strategies have their own benefits as well as limitations. There is a need to modify current strategies rapidly, and then safety and efficacy must be evaluated for modified strategies [118].
- A tremendous amount of data and literature related to the study of COVID-19 structure, genome, genomic mutations, and potential therapeutic targets has already been gathered, and the field is continuing to make progress, implying that there is a need to continue advancing our research methodology and interpretations. All the published data have been extracted from small-scale clinical trials, which may result in an increased risk of bias or imprecise results. Large-scale clinical trials are needed in order to support the evidence of the efficacy and safety of antiviral strategies [49].
Future Perspectives
- COVID-19 has proven to be a global threat inflicting adverse effects on human health and healthcare systems, as well as global economic losses. This article presents a comprehensive intellectual framework related to the research and development of SARS-CoV-2-related immune mechanisms, auspicious drugs, and potential vaccine candidates. Due to the immediate need for COVID-19 treatment and the lack of specific drugs, vaccines, and therapeutic agents targeting this virus, the best current strategy used for rapid treatment is drug repurposing, as there is no officially approved drug to tackle COVID-19. Drugs that were previously effective against other RNA viruses, including SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, HCV, Ebola, and influenza, as well as anti-inflammatory drugs, are being considered for treatment against COVID-19. Some drugs target the viral replication cycle, while others act as agents to boost the activity of the immune system. Apart from developing new drugs and clinical and preclinical trials for old drugs, the design and development of therapeutic and prophylactic vaccines are indispensable for long-term applications; nonetheless, safety and efficacy trials of vaccines present a major challenge. The most effective way of controlling the ongoing spread of the COVID-19 pandemic is to follow appropriate standard operating procedures and preventive measures, use personal protection kits, implement social distancing, maintain good hygiene, and take steps to promote early diagnoses, which may contribute to a decrease in viral transmission, preservation of lives, and a reduced burden on the medical system and economy.
Conclusion
-
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
-
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
-
Funding
None.
-
Availability of Data
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
-
Authors’ Contributions
Conceptualization: IM, SA, MS; Data curation: IA, AN, SA; Data analysis: MUK, SRHS; Methodology: IM, SA; Supervision: MS, MI; Writing-original draft: AN, IA; Writing-review & editing: all authors.
Article information


COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; NAb, neutralizing antibody; RBD, receptor-binding domain; N, nucleocapsid; S, spike; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; VLP, virus-like particle; E, envelope protein; M, membrane protein; IgG, immunoglobulin G.
- 1. Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020;579:270−3.PubMedPMC
- 2. Ou X, Liu Y, Lei X, et al. Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV. Nat Commun 2020;11:1620. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. Chen Y, Liu Q, Guo D. Emerging coronaviruses: genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis. J Med Virol 2020;92:418−23.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Jiang S, Xia S, Ying T, et al. A novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) causing pneumonia-associated respiratory syndrome. Cell Mol Immunol 2020;17:554. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Gattinoni L, Coppola S, Cressoni M, et al. COVID-19 does not lead to a "Typical" acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2020;201:1299−300.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Onder G, Rezza G, Brusaferro S. Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy. JAMA 2020;323:1775−6.PubMed
- 7. Ruan Q, Yang K, Wang W, et al. Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China. Intensive Care Med 2020;46:846−8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Alhazzani W, Moller MH, Arabi YM, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: guidelines on the management of critically ill adults with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Intensive Care Med 2020;46:854−87.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Phua J, Weng L, Ling L, et al. Intensive care management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): challenges and recommendations. Lancet Respir Med 2020;8:506−17.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Kandeel M, Al-Nazawi M. Virtual screening and repurposing of FDA approved drugs against COVID-19 main protease. Life Sci 2020;251:117627. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell 2020;181:271−80.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Zhong J, Tang J, Ye C, et al. The immunology of COVID-19: is immune modulation an option for treatment? Lancet Rheumatol 2020;2:e428−36.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Zimmer C. Bad news wrapped in protein: inside the coronavirus genome. The New York TImes [Internet]. 2020 Apr 3 [cited 2020 Apr 12]. Available from: https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/04/03/science/coronavirus-genome-bad-news-wrapped-in-protein.html.Article
- 14. Channappanavar R, Perlman S. Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology. Semin Immunopathol 2017;39:529−39.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. Zheng HY, Zhang M, Yang CX, et al. Elevated exhaustion levels and reduced functional diversity of T cells in peripheral blood may predict severe progression in COVID-19 patients. Cell Mol Immunol 2020;17:541−3.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Liu WJ, Zhao M, Liu K, et al. T-cell immunity of SARS-CoV: implications for vaccine development against MERS-CoV. Antiviral Res 2017;137:82−92.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Zhou G, Zhao Q. Perspectives on therapeutic neutralizing antibodies against the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Int J Biol Sci 2020;16:1718−23.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 18. Liang Y, Wang ML, Chien CS, et al. Highlight of immune pathogenic response and hematopathologic effect in SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-Cov-2 infection. Front Immunol 2020;11:1022. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 19. Lu H. Drug treatment options for the 2019-new coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Biosci Trends 2020;14:69−71.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Siegel D, Hui HC, Doerffler E, et al. Discovery and synthesis of a phosphoramidate prodrug of a pyrrolo[2,1-f][triazin-4-amino] adenine C-Nucleoside (GS-5734) for the treatment of ebola and emerging viruses. J Med Chem 2017;60:1648−61.PubMedPMC
- 21. Al-Tawfiq JA, Al-Homoud AH, Memish ZA. Remdesivir as a possible therapeutic option for the COVID-19. Travel Med Infect Dis 2020;34:101615. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. Agostini ML, Andres EL, Sims AC, et al. Coronavirus susceptibility to the antiviral remdesivir (GS-5734) is mediated by the viral polymerase and the proofreading exoribonuclease. mBio 2018;9:e00221−18.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 23. Warren TK, Jordan R, Lo MK, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys. Nature 2016;531:381−5.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Svarovskaia ES, Gane E, Dvory-Sobol H, et al. L159F and V321A sofosbuvir-associated hepatitis C virus NS5B substitutions. J Infect Dis 2015;213:1240−7.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Li Z, Wang X, Cao D, et al. Rapid review for the anti-coronavirus effect of remdesivir. Drug Discov Ther 2020;14:73−6.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Sheahan TP, Sims AC, Graham RL, et al. Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses. Sci Transl Med 2017;9:eaal3653.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 27. Gupte V, Hegde R, Sawant S, et al. Safety and clinical outcomes of remdesivir in hospitalised COVID-19 patients: a retrospective analysis of active surveillance database. BMC Infect Dis 2022;22:1. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 28. Furuta Y, Komeno T, Nakamura T. Favipiravir (T-705), a broad spectrum inhibitor of viral RNA polymerase. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci 2017;93:449−63.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Wang M, Cao R, Zhang L, et al. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res 2020;30:269−71.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Furuta Y, Gowen BB, Takahashi K, et al. Favipiravir (T-705), a novel viral RNA polymerase inhibitor. Antiviral Res 2013;100:446−54.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 31. De Clercq E. New nucleoside analogues for the treatment of hemorrhagic fever virus infections. Chem Asian J 2019;14:3962−8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 32. Bosaeed M, Alharbi A, Mahmoud E, et al. Efficacy of favipiravir in adults with mild COVID-19: a randomized, double-blind, multicentre, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Clin Microbiol Infect 2022;28:602−8.PubMedPMC
- 33. Negru PA, Radu AF, Vesa CM, et al. Therapeutic dilemmas in addressing SARS-CoV-2 infection: Favipiravir versus Remdesivir. Biomed Pharmacother 2022;147:112700. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 34. AlQahtani M, Kumar N, Aljawder D, et al. Randomized controlled trial of favipiravir, hydroxychloroquine, and standard care in patients with mild/moderate COVID-19 disease. Sci Rep 2022;12:4925. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Udwadia ZF, Singh P, Barkate H, et al. Efficacy and safety of favipiravir, an oral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor, in mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a randomized, comparative, open-label, multicenter, phase 3 clinical trial. Int J Infect Dis 2021;103:62−71.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 36. Rahman MM, Masum MH, Wajed S, et al. A comprehensive review on COVID-19 vaccines: development, effectiveness, adverse effects, distribution and challenges. Virusdisease 2022;1−22.Article
- 37. Wu R, Wang L, Kuo HD, et al. An update on current therapeutic drugs treating COVID-19. Curr Pharmacol Rep 2020;6:56−70.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 38. Graci JD, Cameron CE. Mechanisms of action of ribavirin against distinct viruses. Rev Med Virol 2006;16:37−48.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 39. Khalili JS, Zhu H, Mak NS, et al. Novel coronavirus treatment with ribavirin: groundwork for an evaluation concerning COVID-19. J Med Virol 2020;92:740−6.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 40. Foolad F, Aitken SL, Shigle TL, et al. Oral versus aerosolized ribavirin for the treatment of respiratory syncytial virus infections in hematopoietic cell transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 2019;68:1641−9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 41. Arabi YM, Shalhoub S, Mandourah Y, et al. Ribavirin and interferon therapy for critically Ill patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome: a multicenter observational study. Clin Infect Dis 2020;70:1837−44.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 42. Altınbas S, Holmes JA, Altınbas A. Hepatitis C virus infection in pregnancy: an update. Gastroenterol Nurs 2020;43:12−21.PubMed
- 43. Caly L, Druce JD, Catton MG, et al. The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Antiviral Res 2020;178:104787. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 44. Simsek Yavuz S, Unal S. Antiviral treatment of COVID-19. Turk J Med Sci 2020;50(SI-1). 611−9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 45. Nicolas P, Maia MF, Bassat Q, et al. Safety of oral ivermectin during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health 2020;8:e92−e100.ArticlePubMed
- 46. Navarro M, Camprubi D, Requena-Mendez A, et al. Safety of high-dose ivermectin: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Antimicrob Chemother 2020;75:827−34.ArticlePubMed
- 47. Ketkar H, Yang L, Wormser GP, et al. Lack of efficacy of ivermectin for prevention of a lethal Zika virus infection in a murine system. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2019;95:38−40.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 48. McCreary EK, Pogue JM. Coronavirus disease 2019 treatment: a review of early and emerging options. Open Forum Infect Dis 2020;7:ofaa105. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 49. Sanders JM, Monogue ML, Jodlowski TZ, et al. Pharmacologic treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. JAMA 2020;323:1824−36.PubMed
- 50. Cvetkovic RS, Goa KL. Lopinavir/ritonavir: a review of its use in the management of HIV infection. Drugs 2003;63:769−802.ArticlePubMed
- 51. Lim J, Jeon S, Shin HY, et al. Case of the index patient who caused tertiary transmission of COVID-19 infection in Korea: the application of lopinavir/ritonavir for the treatment of COVID-19 infected pneumonia monitored by quantitative RT-PCR. J Korean Med Sci 2020;35:e79.PubMedPMC
- 52. Gao J, Tian Z, Yang X. Breakthrough: chloroquine phosphate has shown apparent efficacy in treatment of COVID-19 associated pneumonia in clinical studies. Biosci Trends 2020;14:72−3.ArticlePubMed
- 53. Savarino A, Boelaert JR, Cassone A, et al. Effects of chloroquine on viral infections: an old drug against today's diseases? Lancet Infect Dis 2003;3:722−7.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 54. Hu TY, Frieman M, Wolfram J. Insights from nanomedicine into chloroquine efficacy against COVID-19. Nat Nanotechnol 2020;15:247−9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 55. Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med 2020;382:727−33.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 56. Vincent MJ, Bergeron E, Benjannet S, et al. Chloroquine is a potent inhibitor of SARS coronavirus infection and spread. Virol J 2005;2:69. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 57. Colson P, Rolain JM, Lagier JC, et al. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine as available weapons to fight COVID-19. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2020;105932. PubMedPMC
- 58. Yao X, Ye F, Zhang M, et al. In vitro antiviral activity and projection of optimized dosing design of hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Clin Infect Dis 2020;71:732−9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 59. Amawi H, Abu Deiab GI, A Aljabali AA, et al. COVID-19 pandemic: an overview of epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnostics and potential vaccines and therapeutics. Ther Deliv 2020;11:245−8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 60. Zhang J, Xie B, Hashimoto K. Current status of potential therapeutic candidates for the COVID-19 crisis. Brain Behav Immun 2020;87:59−73.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 61. Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020;395:497−506.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 62. Gautret P, Lagier JC, Parola P, et al. Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2020;56:105949. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 63. Lane JC, Weaver J, Kostka K, et al. Risk of hydroxychloroquine alone and in combination with azithromycin in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a multinational, retrospective study. Lancet Rheumatol 2020;2:E698−E711.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 64. Rossignol JF. Nitazoxanide: a first-in-class broad-spectrum antiviral agent. Antiviral Res 2014;110:94−103.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 65. Rossignol JF. Nitazoxanide, a new drug candidate for the treatment of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J Infect Public Health 2016;9:227−30.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 66. Jasenosky LD, Cadena C, Mire CE, et al. The FDA-approved oral drug nitazoxanide amplifies host antiviral responses and inhibits Ebola virus. iScience 2019;19:1279−90.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 67. Frieman M, Baric R. Mechanisms of severe acute respiratory syndrome pathogenesis and innate immunomodulation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2008;72:672−85.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 68. Cao J, Forrest JC, Zhang X. A screen of the NIH Clinical Collection small molecule library identifies potential anti-coronavirus drugs. Antiviral Res 2015;114:1−10.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 69. Kadam RU, Wilson IA. Structural basis of influenza virus fusion inhibition by the antiviral drug Arbidol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017;114:206−14.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 70. Tu YF, Chien CS, Yarmishyn AA, et al. A review of SARS-CoV-2 and the ongoing clinical trials. Int J Mol Sci 2020;21:2657. ArticlePMC
- 71. Wang Z, Chen X, Lu Y, et al. Clinical characteristics and therapeutic procedure for four cases with 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia receiving combined Chinese and Western medicine treatment. Biosci Trends 2020;14:64−8.ArticlePubMed
- 72. Khamitov RA, Loginova SIa, Shchukina VN, et al. Antiviral activity of arbidol and its derivatives against the pathogen of severe acute respiratory syndrome in the cell cultures. Vopr Virusol 2008;53:9−13. Russian.
- 73. Li Y, Xie Z, Lin W, et al. An exploratory randomized controlled study on the efficacy and safety of lopinavir/ritonavir or arbidol treating adult patients hospitalized with mild/moderate COVID-19 (ELACOI). [Preprint]. Posted 2020 Apr 15. medRxiv 2020.03.19.20038984. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.19.20038984.Article
- 74. Bloch EM, Shoham S, Casadevall A, et al. Deployment of convalescent plasma for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. J Clin Invest 2020;130:2757−65.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 75. Fauci AS, Lane HC, Redfield RR. Covid-19: navigating the uncharted. N Engl J Med 2020;382:1268−9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 76. Casadevall A, Pirofski LA. The convalescent sera option for containing COVID-19. J Clin Invest 2020;130:1545−8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 77. Roback JD, Guarner J. Convalescent plasma to treat COVID-19: possibilities and challenges. JAMA 2020;323:1561−2.ArticlePubMed
- 78. Khadke S, Ahmed N, Ahmed N, et al. Harnessing the immune system to overcome cytokine storm and reduce viral load in COVID-19: a review of the phases of illness and therapeutic agents. Virol J 2020;17:154. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 79. Bhimraj A, Morgan RL, Shumaker AH, et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with COVID-19. Clin Infect Dis 2020;Apr 27 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa478.Article
- 80. RECOVERY Collaborative Group, Horby P, Lim WS, et al. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2021;384:693−704.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 81. Xu X, Han M, Li T, et al. Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020;117:10970−5.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 82. Hermine O, Mariette X, Tharaux PL, et al. Effect of tocilizumab vs usual care in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 and moderate or severe pneumonia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med 2021;181:32−40.PubMed
- 83. Parr JB. Time to reassess tocilizumab's role in COVID-19 pneumonia. JAMA Intern Med 2021;181:12−5.ArticlePubMed
- 84. Al-Hajeri H, Baroun F, Abutiban F, et al. Therapeutic role of immunomodulators during the COVID-19 pandemic: a narrative review. Postgrad Med 2022;134:160−79.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 85. Sharma A, Krause A, Worgall S. Recent developments for Pseudomonas vaccines. Hum Vaccin 2011;7:999−1011.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 86. Jiang S, Bottazzi ME, Du L, et al. Roadmap to developing a recombinant coronavirus S protein receptor-binding domain vaccine for severe acute respiratory syndrome. Expert Rev Vaccines 2012;11:1405−13.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 87. Chen Y, Li L. SARS-CoV-2: virus dynamics and host response. Lancet Infect Dis 2020;20:515−6.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 88. Higdon MM, Wahl B, Jones CB, et al. A systematic review of COVID-19 vaccine efficacy and effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 infection and disease. [Preprint]. Posted 2021 Sep 25. medRxiv 2021.09.17.21263549. medRxiv 2021.09.17.21263549. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.09.17.21263549.Article
- 89. Peng XL, Cheng JS, Gong HL, et al. Advances in the design and development of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Mil Med Res 2021;8:67. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 90. Loo KY, Letchumanan V, Ser HL, et al. COVID-19: insights into potential vaccines. Microorganisms 2021;9:605. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 91. Livingston EH, Malani PN, Creech CB. The Johnson & Johnson vaccine for COVID-19. JAMA 2021;325:1575. ArticlePubMed
- 92. Zhang J, Zeng H, Gu J, et al. Progress and prospects on vaccine development against SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines (Basel) 2020;8:153. ArticlePMC
- 93. Takashima Y, Osaki M, Ishimaru Y, et al. Artificial molecular clamp: a novel device for synthetic polymerases. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2011;50:7524−8.ArticlePubMed
- 94. Ji W, Wang W, Zhao X, et al. Cross-species transmission of the newly identified coronavirus 2019-nCoV. J Med Virol 2020;92:433−40.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 95. He Y, Jiang S. Vaccine design for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Viral Immunol 2005;18:327−32.ArticlePubMed
- 96. Baran I. SARS-CoV-2 vaccine development studies. Edited by Karagoz C, Kaptanoglu A, Savas S: Medical sciences and biotechnology book. Konak/Izmir. Turkey: Izmir Kavram Vocational School; 2020. pp 65−78.
- 97. Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet 2020;395:507−13.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 98. Tai W, He L, Zhang X, et al. Characterization of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of 2019 novel coronavirus: implication for development of RBD protein as a viral attachment inhibitor and vaccine. Cell Mol Immunol 2020;17:613−20.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 99. Sheahan TP, Sims AC, Leist SR, et al. Comparative therapeutic efficacy of remdesivir and combination lopinavir, ritonavir, and interferon beta against MERS-CoV. Nat Commun 2020;11:222. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 100. Mammen MP, Tebas P, Agnes J, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of INO-4800 DNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: a preliminary report of a randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled, Phase 2 clinical trial in adults at high risk of viral exposure. [Preprint]. Posted 2021 May 7. medRxiv 2021.05.07.21256652. medRxiv 2021.05.07.21256652. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.05.07.21256652.Article
- 101. Sumirtanurdin R, Barliana MI. Coronavirus disease 2019 vaccine development: an overview. Viral Immunol 2021;34:134−44.ArticlePubMed
- 102. Ndwandwe D, Wiysonge CS. COVID-19 vaccines. Curr Opin Immunol 2021;71:111−6.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 103. Laval JM, Mazeran PE, Thomas D. Nanobiotechnology and its role in the development of new analytical devices. Analyst 2000;125:29−33.ArticlePubMed
- 104. Al-Halifa S, Gauthier L, Arpin D, et al. Nanoparticle-based vaccines against respiratory viruses. Front Immunol 2019;10:22. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 105. Schneider CS, Xu Q, Boylan NJ, et al. Nanoparticles that do not adhere to mucus provide uniform and long-lasting drug delivery to airways following inhalation. Sci Adv 2017;3:e1601556.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 106. Roldao A, Mellado MC, Castilho LR, et al. Virus-like particles in vaccine development. Expert Rev Vaccines 2010;9:1149−76.ArticlePubMed
- 107. Chackerian B. Virus-like particles: flexible platforms for vaccine development. Expert Rev Vaccines 2007;6:381−90.ArticlePubMed
- 108. Mortola E, Roy P. Efficient assembly and release of SARS coronavirus-like particles by a heterologous expression system. FEBS Lett 2004;576:174−8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 109. Lu X, Chen Y, Bai B, et al. Immune responses against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus induced by virus-like particles in mice. Immunology 2007;122:496−502.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 110. Rosales-Mendoza S. Will plant-made biopharmaceuticals play a role in the fight against COVID-19? Expert Opin Biol Ther 2020;20:545−8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 111. Pardi N, Hogan MJ, Porter FW, et al. mRNA vaccines: a new era in vaccinology. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2018;17:261−79.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 112. Lim B, Lee K. Stability of the osmoregulated promoter-derived proP mRNA is posttranscriptionally regulated by RNase III in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 2015;197:1297−305.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 113. Pardi N, Weissman D. Nucleoside modified mRNA vaccines for infectious diseases. Methods Mol Biol 2017;1499:109−21.PubMed
- 114. Knights AJ, Nuber N, Thomson CW, et al. Modified tumour antigen-encoding mRNA facilitates the analysis of naturally occurring and vaccine-induced CD4 and CD8 T cells in cancer patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2009;58:325−38.ArticlePubMed
- 115. Zarghampoor F, Azarpira N, Khatami SR, et al. Improved translation efficiency of therapeutic mRNA. Gene 2019;707:231−8.ArticlePubMed
- 116. Ohto T, Konishi M, Tanaka H, et al. Inhibition of the inflammatory pathway enhances both the in vitro and in vivo transfection activity of exogenous in vitro-transcribed mRNAs delivered by lipid nanoparticles. Biol Pharm Bull 2019;42:299−302.PubMed
- 117. Jahanafrooz Z, Baradaran B, Mosafer J, et al. Comparison of DNA and mRNA vaccines against cancer. Drug Discov Today 2020;25:552−60.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 118. Chen WH, Strych U, Hotez PJ, et al. The SARS-CoV-2 vaccine pipeline: an overview. Curr Trop Med Rep 2020;7:61−4.Article
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations




 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite