Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Psychiatric adverse events associated with the COVID-19 vaccines approved in the Republic of Korea: a systematic review
- Seungeun Ryoo, Miyoung Choi, Nam-Kyong Choi, Hyoung-Shik Shin, Jun Hee Woo, Byung-Joo Park, Sanghoon Oh
- Received October 31, 2023 Accepted January 16, 2024 Published online March 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0325 [Epub ahead of print]
- 476 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This systematic review evaluated psychiatric adverse events (AEs) following vaccination against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We included studies that reported or investigated psychiatric AEs in individuals who had received an approved COVID-19 vaccine in the Republic of Korea. Systematic electronic searches of Ovid-Medline, Embase, CENTRAL, and KoreaMed databases were conducted on March 22, 2023. Risk of bias was assessed using the Risk of Bias Assessment Tool for Non-randomized Studies 2.0. The study protocol was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (CRD42023449422). Of the 301 articles initially selected, 7 were included in the final analysis. All studies reported on sleep disturbances, and 2 highlighted anxiety-related AEs. Sleep disorders like insomnia and narcolepsy were the most prevalent AEs, while depression was not reported. Our review suggests that these AEs may have been influenced by biological mechanisms as well as the broader psychosocial context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Although this study had limitations, such as a primary focus on the BNT162b2 vaccine and an observational study design, it offered a systematic, multi-vaccine analysis that fills a critical gap in the existing literature. This review underscores the need for continued surveillance of psychiatric AEs and guides future research to investigate underlying mechanisms, identify risk factors, and inform clinical management.
Original Articles
- COVID-19 infection among people with disabilities in 2021 prior to the Omicron-dominant period in the Republic of Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Seul-Ki Kang, Bryan Inho Kim
- Received July 11, 2023 Accepted January 16, 2024 Published online March 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0194 [Epub ahead of print]
- 388 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) among individuals with disabilities on a nationwide scale in the Republic of Korea, as limited research has examined this population.
Methods
Between January 1 and November 30, 2021, a total of 5,687 confirmed COVID-19 cases among individuals with disabilities were reported through the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency’s COVID-19 web reporting system. Follow-up continued until December 24, and demographic, epidemiological, and clinical characteristics were analyzed.
Results
Individuals with disabilities represented approximately 1.5% of confirmed cases, with a mean age of 58.1 years. Most resided in or near metropolitan areas (86.6%) and were male (60.6%). Frequent sources of infection included home (33.4%) and contact with confirmed cases (40.7%). Many individuals (75.9%) had underlying conditions, and 7.7% of cases were severe. People with disabilities showed significantly elevated risk of severe infection (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.63; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.47–1.81) and mortality (aOR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.43–1.91). Vaccination against COVID-19 was associated with significantly lower risk of severe infection (aORs for the first, second, and third doses: 0.6 [95% CI, 0.42–0.85], 0.28 [95% CI, 0.22–0.35], and 0.16 [95% CI, 0.05–0.51], respectively) and death (adjusted hazard ratios for the first and second doses: 0.57 [95% CI, 0.35–0.93] and 0.3 [95% CI, 0.23–0.40], respectively).
Conclusion
Individuals with disabilities showed higher risk of severe infection and mortality from COVID-19. Consequently, it is critical to strenghthenCOVID-19 vaccination initiatives and provide socioeconomic assistance for this vulnerable population.
- Evaluation of COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness in different high-risk facility types during a period of Delta variant dominance in the Republic of Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Min Jei Lee, Myung-Jae Hwang, Dong Seob Kim, Seon Kyeong Park, Jihyun Choi, Ji Joo Lee, Jong Mu Kim, Young-Man Kim, Young-Joon Park, Jin Gwack, Sang-Eun Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):418-426. Published online October 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0188
- 1,268 View
- 44 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 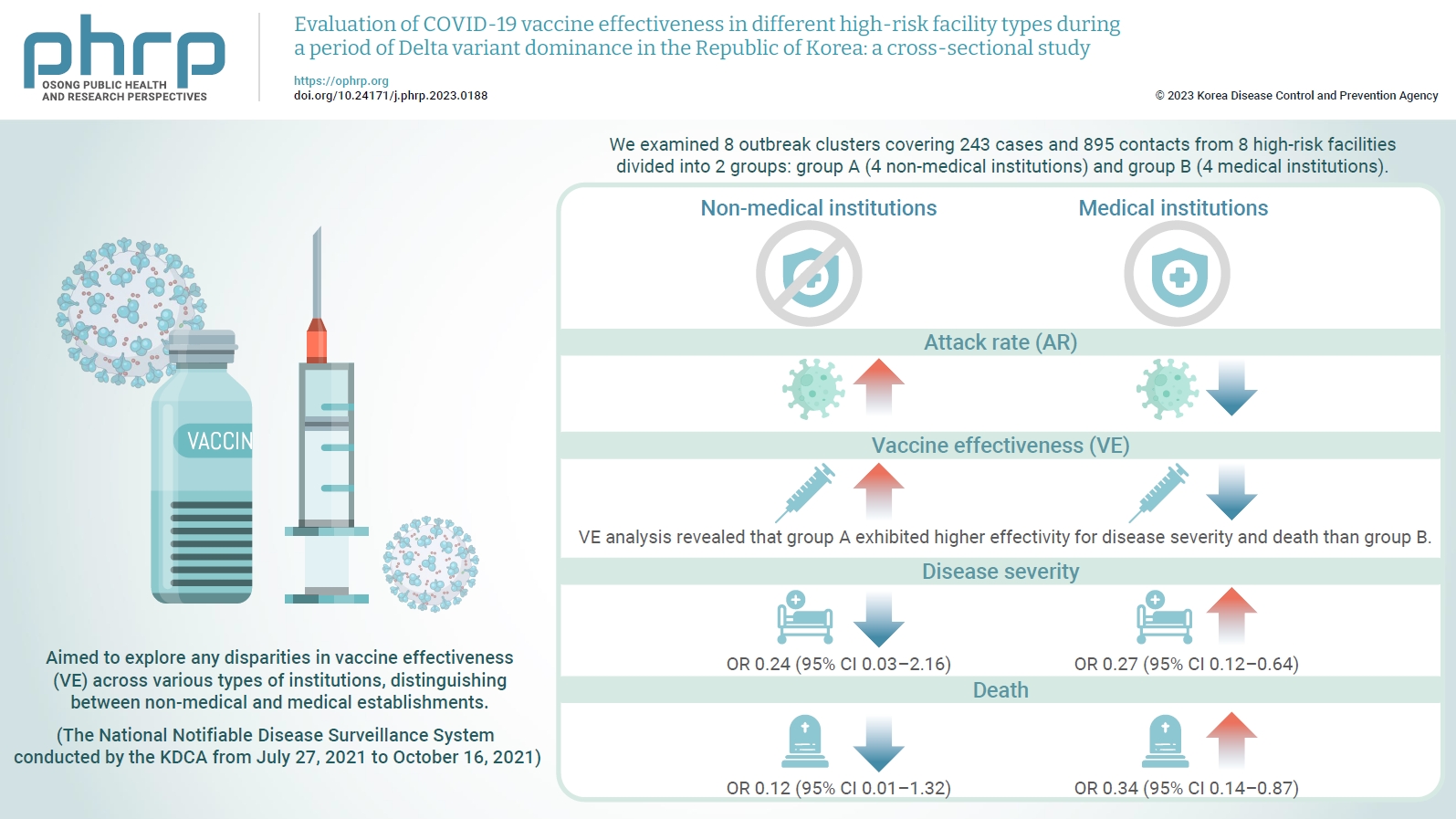
- Objectives
We evaluated the effectiveness of coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination in high-risk facilities in the Republic of Korea during the period when the highly transmissible Delta variant was prevalent. Additionally, we aimed to explore any disparities in vaccine effectiveness (VE) across various types of institutions, specifically distinguishing between non-medical and medical establishments. Methods: We examined 8 outbreak clusters covering 243 cases and 895 contacts from 8 high-risk facilities divided into 2 groups: group A (4 non-medical institutions) and group B (4 medical institutions). These clusters were observed from July 27, 2021 to October 16, 2021 for the attack rate (AR) and VE with respect to disease severity. A generalized linear model with a binomial distribution was used to determine the odds ratio (OR) for disease severity and death. Results: AR was notably lower in group B (medical institutions). Furthermore, VE analysis revealed that group A exhibited higher effectivity for disease severity and death than group B. The OR for disease severity was 0.24 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.03–2.16) for group A and 0.27 (95% CI, 0.12–0.64) for group B, with the OR for death at 0.12 (95% CI, 0.01–1.32) in group A and 0.34 (95% CI, 0.14–0.87) in group B. Conclusion: Although VE may vary across institutions, our findings underscore the importance of implementing vaccinations in high-risk facilities. Customized vaccination programs, tailored response plans, and competent management personnel are essential for effectively addressing and mitigating public health challenges.
Brief Report
- Temporal association between the age-specific incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome and SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in Republic of Korea: a nationwide time-series correlation study
- Hyunju Lee, Donghyok Kwon, Seoncheol Park, Seung Ri Park, Darda Chung, Jongmok Ha
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):224-231. Published online June 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0050
- 2,066 View
- 89 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 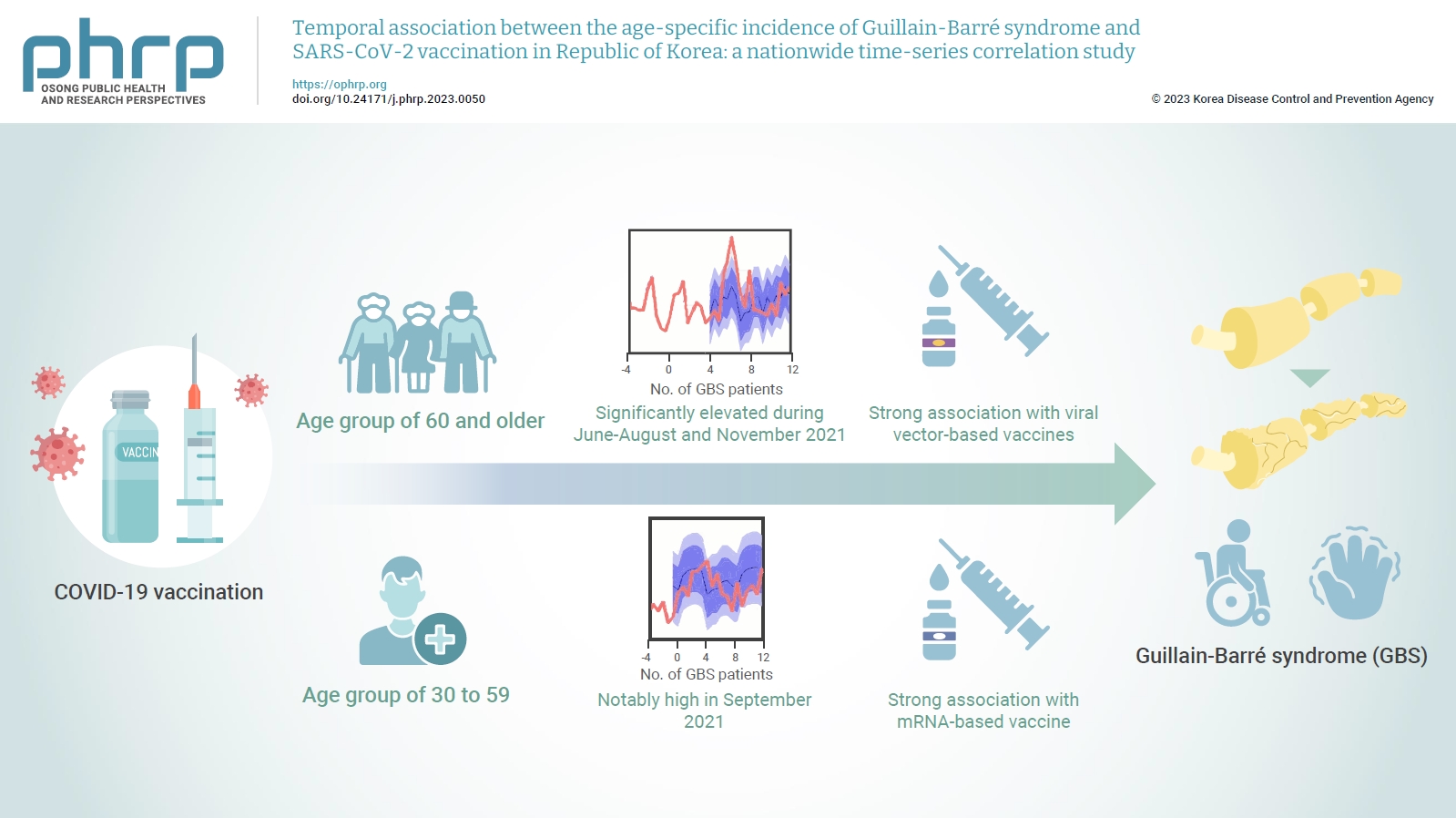
- Objectives
The incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) changed significantly during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Emerging reports suggest that viral vector-based vaccines may be associated with an elevated risk of GBS.
Methods
In this nationwide time-series correlation study, we examined the age-specific incidence of GBS from January 2011 to August 2022, as well as data on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccinations and infections from February 2021 to August 2022. We compared the forecasted estimates of age-specific GBS incidence, using the pre-SARS-CoV-2 period as a benchmark, with the actual incidence observed during the post-vaccination period of the pandemic. Furthermore, we assessed the temporal association between GBS, SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations, and COVID-19 for different age groups.
Results
In the age group of 60 and older, the rate ratio was significantly elevated during June-August and November 2021. A significant, strong positive association was observed between viral vector-based vaccines and GBS incidence trends in this age group (r=0.52, p=0.022). For the 30 to 59 years age group, the rate ratio was notably high in September 2021. A statistically significant, strong positive association was found between mRNA-based vaccines and GBS incidence in this age group (r=0.61, p=0.006).
Conclusion
Viral vector-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines were found to be temporally associated with an increased risk of GBS, particularly in older adults. To minimize age-specific and biological mechanism-specific adverse events, future vaccination campaigns should adopt a more personalized approach, such as recommending homologous mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines for older adults to reduce the heightened risk of GBS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- mRNA-LNP COVID-19 Vaccine Lipids Induce Complement Activation and Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines: Mechanisms, Effects of Complement Inhibitors, and Relevance to Adverse Reactions
Tamás Bakos, Tamás Mészáros, Gergely Tibor Kozma, Petra Berényi, Réka Facskó, Henriette Farkas, László Dézsi, Carlo Heirman, Stefaan de Koker, Raymond Schiffelers, Kathryn Anne Glatter, Tamás Radovits, Gábor Szénási, János Szebeni
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3595. CrossRef - Guillain–Barre syndrome following COVID-19 vaccination: a study of 70 case reports
Biki Kumar Sah, Zahra Fatima, Rajan Kumar Sah, Bushra Syed, Tulika Garg, Selia Chowdhury, Bikona Ghosh, Binita Kunwar, Anagha Shree, Vivek Kumar Sah, Anisha Raut
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2024; 86(4): 2067. CrossRef
- mRNA-LNP COVID-19 Vaccine Lipids Induce Complement Activation and Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines: Mechanisms, Effects of Complement Inhibitors, and Relevance to Adverse Reactions
Original Article
- The incidence and clinical characteristics of myocarditis and pericarditis following mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination in Republic of Korea adolescents from July 2021 to September 2022
- Ju-Young Sim, Seung-Yun Kim, Eun-Kyoung Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(2):76-88. Published online April 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0032
- 3,974 View
- 231 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 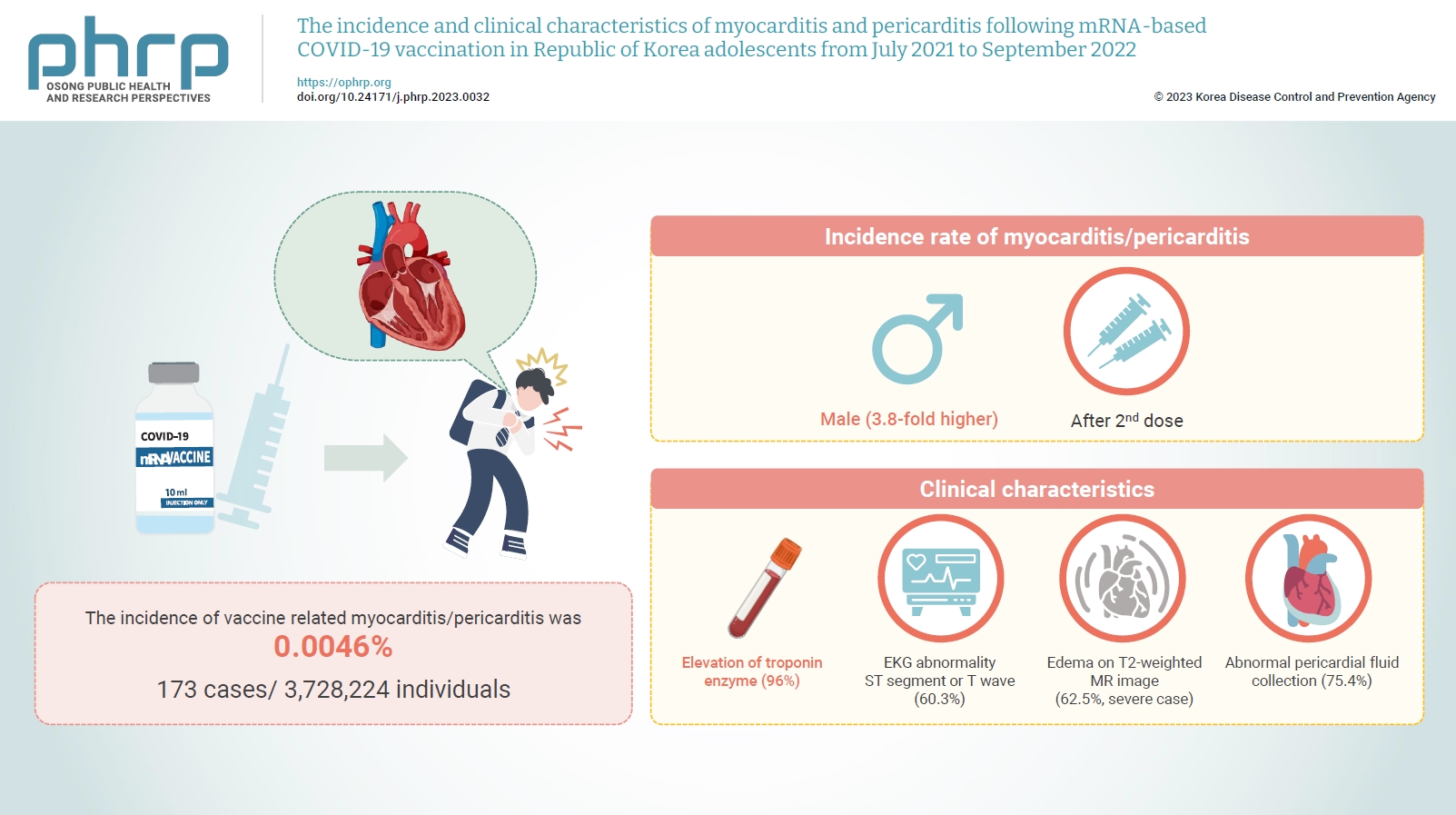
- Objectives
Age-specific information regarding myocarditis/pericarditis in adolescents following mRNA-based coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination in Asia remains insufficient. This study investigated the incidence and clinical characteristics of myocarditis/pericarditis in Republic of Korea adolescents after mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination.
Methods
This retrospective descriptive study utilized patient data from the Korea Immunization Management System. Incidence rates were calculated according to age and sex. Clinical characteristics (symptoms/signs, laboratory values, and imaging results) were compared between mild and severe cases.
Results
Between July 19, 2021 and September 30, 2022, 3,728,224 individuals aged 12 to 19 years received 6,484,165 mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, and 173 cases met the case definition for myocarditis/pericarditis: 151 mild (87.3%) and 22 severe (12.7%). The incidence was 3.8-fold higher in males than in females. Troponin I/ troponin T was elevated in 96% of myocarditis cases, demonstrating higher sensitivity than creatine kinase-myocardial band (67.6%) or C-reactive protein (75.2%). ST-segment or Twave on electrography abnormalities were found in 60.3% (85/141). Paroxysmal/sustained atrial/ventricular arrhythmias were more common in severe than in mild cases (45.5% vs. 16.8%, p=0.008). Edema on T2-weighted magnetic imaging occurred in 21.6% (8/37) and 62.5% (5/8) of mild and severe cases, respectively (p=0.03). Abnormal pericardial fluid collection or pericardial inflammation was found in 75.4% of pericarditis cases (49/65).
Conclusion
Myocarditis/pericarditis occurred in rare cases following mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination. Most cases were mild, but the incidence was higher in adolescent males and after the second dose. As bivalent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 mRNA vaccination started in Republic of Korea in October 2022, the post-vaccination incidence of myocarditis/pericarditis should be closely monitored, considering clinical characteristics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Responses to Common Misconceptions Relating to COVID-19 Variant-Adapted mRNA Vaccines
George Kassianos, Pauline MacDonald, Ivan Aloysius, Shanti Pather
Vaccines.2024; 12(1): 57. CrossRef - To become a more stronger and safer country
Jong-Koo Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(2): 67. CrossRef
- Responses to Common Misconceptions Relating to COVID-19 Variant-Adapted mRNA Vaccines
Review Articles
- India’s efforts to achieve 1.5 billion COVID-19 vaccinations: a narrative review
- Kapil Singh, Ashwani Verma, Monisha Lakshminarayan
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(5):316-327. Published online October 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0104
- 3,664 View
- 91 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 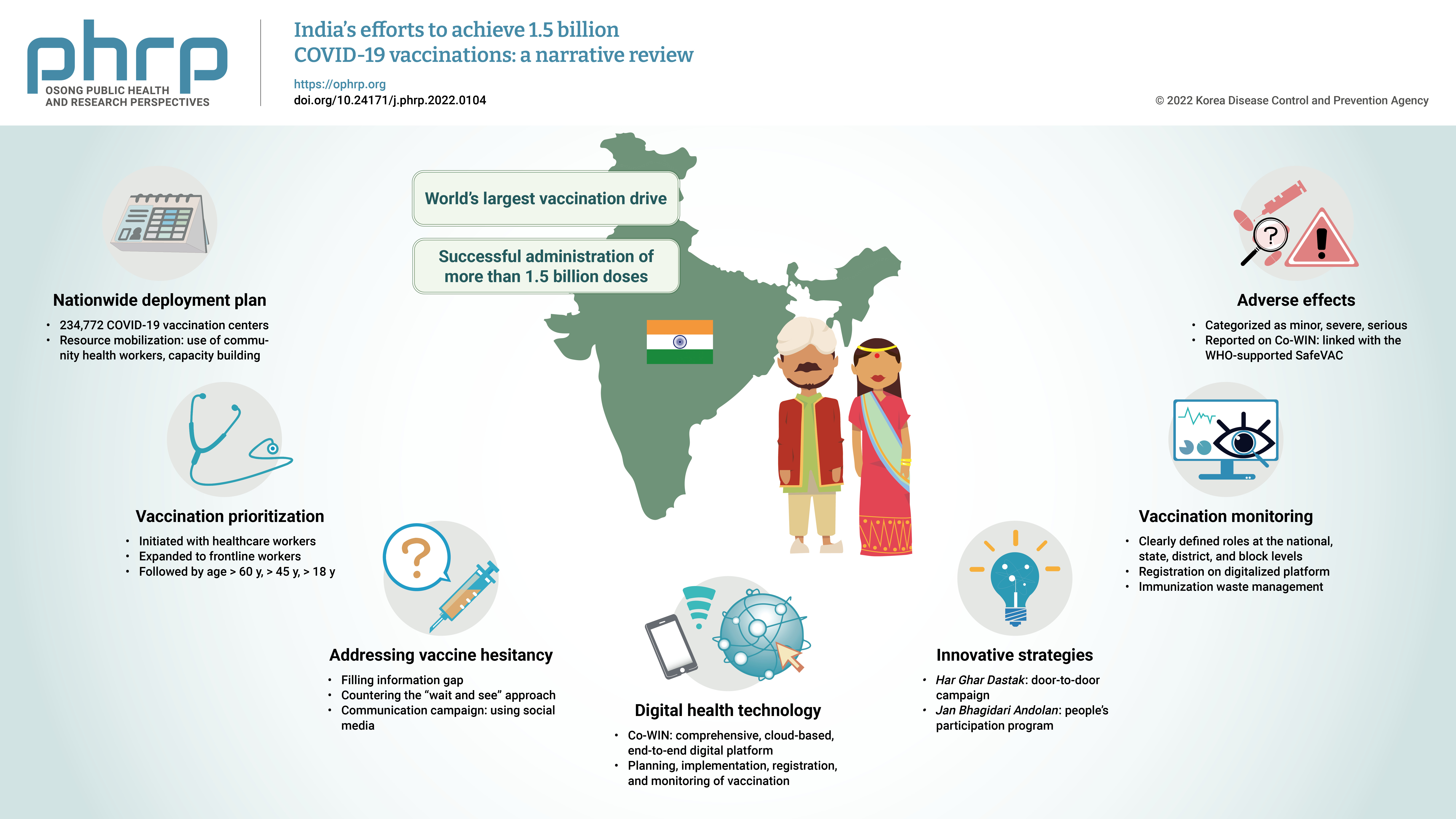
- The initial case of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in India was reported on January 30, 2020, and subsequently, the number of COVID-19-infected patients surged during the first wave of April 2020 and the second wave in the same month of 2021. The government of India imposed a strict nationwide lockdown in April 2020 and extended it until May 2020. The second wave of COVID-19 in India overwhelmed the country’s health facilities and exhausted its medical and paramedical workforce. This narrative review was conducted with the aim of summarizing the evidence drawn from policy documents of governmental and non-governmental organizations, as well as capturing India's COVID-19 vaccination efforts. The findings from this review cover the Indian government's vaccination initiatives, which ranged from steps taken to combat vaccine hesitancy to vaccination roadmaps, deployment plans, the use of digital health technology, vaccination monitoring, adverse effects, and innovative strategies such as Har Ghar Dastak and Jan Bhagidari Andolan (people’s participation). These efforts collectively culminated in the successful administration of more than 1.8 billion doses of COVID-19 vaccines in India. This review also provides insights into other countries’ responses to COVID-19 and guidance for future pandemics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Digital health technology used in emergency large-scale vaccination campaigns in low- and middle-income countries: a narrative review for improved pandemic preparedness
Paula Mc Kenna, Lindsay A. Broadfield, Annik Willems, Serge Masyn, Theresa Pattery, Ruxandra Draghia-Akli
Expert Review of Vaccines.2023; 22(1): 243. CrossRef - Media Reporting Relating to COVID-19 Vaccination as a Driver of Vaccine Hesitancy Prior to the Second Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic in India: A Content Analysis of Newspaper and Digital Media Reports
Saurav Basu, Himanshi Sharma
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An assessment of the strategy and status of COVID-19 vaccination in India
Sneh Lata Gupta, Surbhi Goswami, Ananya Anand, Namrata Naman, Priya Kumari, Priyanka Sharma, Rishi K. Jaiswal
Immunologic Research.2023; 71(4): 565. CrossRef - Development of a Choice-framework for Covid vaccines in India using a multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Tarun K. George, Nayana P. Nair, Awnish Kumar Singh, A. Dilesh Kumar, Arup Deb Roy, Varshini Neethi Mohan, Gagandeep Kang
Vaccine.2023; 41(25): 3755. CrossRef - COVID-19 Booster Dose Coverage and Hesitancy among Older Adults in an Urban Slum and Resettlement Colony in Delhi, India
Nandini Sharma, Saurav Basu, Heena Lalwani, Shivani Rao, Mansi Malik, Sandeep Garg, Rahul Shrivastava, Mongjam Meghachandra Singh
Vaccines.2023; 11(7): 1177. CrossRef - Review of the unmet medical need for vaccination in adults with immunocompromising conditions: An Indian perspective
Ashok Vaid, Neha Rastogi, T. Mark Doherty, Peter San Martin, Yashpal Chugh
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Translating the COVID-19 experience in widening the HPV vaccination campaign for cervical cancer in India
Aruni Ghose, Anisha Agarwal, Bhawna Sirohi, Shona Nag, Linus Chuang, Swarupa Mitra
Gynecologic Oncology Reports.2023; 48: 101247. CrossRef - Symptomatic prevalence of covid-19 in vaccinated and non-vaccinated population
Jay Bhupesh Pandya, Nirali Milind Shethia, Divya Bangera, Shailaja Gada Saxena
IP International Journal of Medical Microbiology a.2023; 9(2): 110. CrossRef - Active surveillance of adverse events following COVID-19 vaccines in a tertiary care hospital
Naveena Mary Cherian, Dravya Anna Durai, Muhammed Jaisel, Divyansh Sharma, Juny Sebastian, Chetak Kadabasal Basavaraja, Merrin Mathew
Therapeutic Advances in Vaccines and Immunotherapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of ayurvedic formulation, NAOQ19 along with standard care in the treatment of mild-moderate COVID-19 patients: A double blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multicentric trial
Pankaj Bhardwaj, Kalaiselvan Ganapathy, Monika Pathania, K.H. Naveen, Jaykaran Charan, Siddhartha Dutta, Ravisekhar Gadepalli, Srikanth Srinivasan, Manoj Kumar Gupta, Akhil D. Goel, Naresh Midha, Bharat Kumar, Meenakshi Sharma, Praveen Sharma, Mithu Baner
Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine.2023; 14(6): 100778. CrossRef - Balancing Routine and Pandemic: The Synergy of India’s Universal Immunization Program and COVID-19 Vaccination Program
Pawan Kumar, Ashish Birendra Chakraborty, Suhas Dhandore, Pritu Dhalaria, Ajeet Kumar Singh, Disha Agarwal, Kapil Singh, Pretty Priyadarshini, Paras Jain, Vidushi Bahl, Gunjan Taneja
Vaccines.2023; 11(12): 1776. CrossRef - Unveiling vaccine safety: a narrative review of pharmacovigilance in India's COVID-19 vaccination
Megha Hegde, Saurav Raj, Dhananjay Tikadar, Sanatkumar B Nyamagoud
Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Digital health technology used in emergency large-scale vaccination campaigns in low- and middle-income countries: a narrative review for improved pandemic preparedness
- Points to consider for COVID-19 vaccine quality control and national lot release in Republic of Korea: focus on a viral vector platform
- Jung Hun Ju, Naery Lee, Sun-hee Kim, Seokkee Chang, Misook Yang, Jihyun Shin, Eunjo Lee, Sunhwa Sung, Jung-Hwan Kim, Jin Tae Hong, Ho Jung Oh
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(1):4-14. Published online February 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0311
- 5,790 View
- 169 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 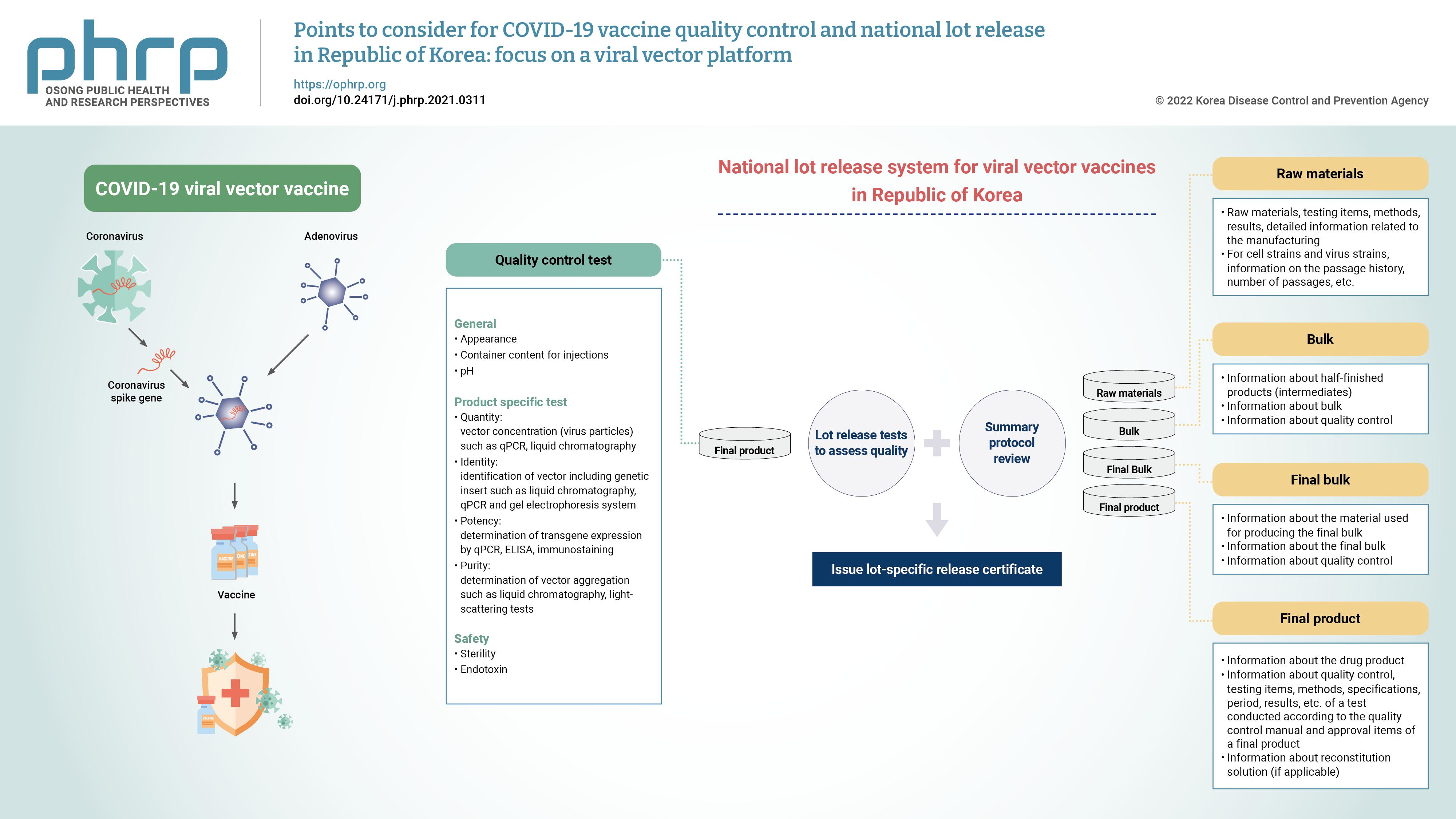
- Due to the global public health crisis caused by the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, the importance of vaccine development has increased. In particular, a rapid supply of vaccines and prompt deployment of vaccination programs are essential to prevent and overcome the spread of COVID-19. As a part of the vaccine regulations, national lot release is regulated by the responsible authorities, and this process involves the assessment of the lot before a vaccine is marketed. A lot can be released for use when both summary protocol (SP) review and quality control testing are complete. Accelerated lot release is required to distribute COVID-19 vaccines in a timely manner. In order to expedite the process by simultaneously undertaking the verification of quality assessment and application for approval, it is necessary to prepare the test methods before marketing authorization. With the prolonged pandemic and controversies regarding the effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccine against new variants, public interest for the development of a new vaccine are increasing. Domestic developers have raised the need to establish standard guidance on the requirements for developing COVID-19 vaccine. This paper presents considerations for quality control in the manufacturing process, test items, and SP content of viral vector vaccines.
Original Articles
- Factors influencing acceptance of the COVID-19 vaccine in Malaysia: a web-based survey
- June Fei Wen Lau, Yuan Liang Woon, Chin Tho Leong, Hoon Shien Teh
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(6):361-373. Published online November 25, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0085
- 13,416 View
- 513 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has set a precedent for the fastest-produced vaccine as a result of global collaboration and outreach. This study explored Malaysians’ acceptance of the COVID-19 vaccine and its associated factors.
Methods
A cross-sectional anonymous web-based survey was disseminated to Malaysian adults aged ≥18 years old via social media platforms between July 10, 2020 and August 31, 2020.
Results
In the analysis of 4,164 complete responses, 93.2% of participants indicated that they would accept the COVID-19 vaccine if it was offered for free by the Malaysian government. The median out-of-pocket cost that participants were willing to pay for a COVID-19 vaccine was Malaysian ringgit (MYR) 100 (interquartile range [IQR], 100) if it was readily available and MYR 150 (IQR, 200) if the supply was limited. Respondents with a low likelihood of vaccine hesitancy had 13 times higher odds of accepting the COVID-19 vaccine (95% confidence interval [CI], 8.69 to 19.13). High perceived risk and severity were also associated with willingness to be vaccinated, with adjusted odds ratios of 2.22 (95% CI, 1.44 to 3.41) and 2.76 (95% CI, 1.87 to 4.09), respectively. Age and ethnicity were the only independent demographic characteristics that predicted vaccine uptake.
Conclusion
Public health strategies targeting perceived risk, perceived susceptibility and vaccine hesitancy could be effective in enhancing vaccine uptake. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Awareness, knowledge, disease prevention practices, and immunization attitude of hepatitis E virus among food handlers in Klang Valley, Malaysia
Sakshaleni Rajendiran, Wong Li Ping, Yuvaneswary Veloo, Syahidiah Syed Abu Thahir
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID-19 vaccine uptake and its determinants among teenagers and their parents in Zhejiang, China: An online cross-sectional study
Yu Huang, Qingqing Wu, Shuiyang Xu, Xiang Zhao, Lei Wang, Qiaohong Lv, Suxian Wu, Xuehai Zhang
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine.2023; 16(4): 176. CrossRef - Factors influencing parents’ hesitancy to vaccinate their children aged 5–11 years old against COVID-19: results from a cross-sectional study in Malaysia
Roy Rillera Marzo, Ritankar Chakraborty, Shean Yih Soh, Hui Zhu Thew, Collins Chong, Ching Sin Siau, Khairuddin Bin Abdul Wahab, Indang Ariati Binti Ariffin, Shekhar Chauhan, Ken Brackstone, Bijaya Kumar Padhi, Petra Heidler
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A survey on Malaysian’s acceptance and perceptions towards COVID-19 booster dose
Suresh Rajakumar, Noorasyikin Shamsuddin, Mohammed Abdullah Alshawsh, Sutha Rajakumar, Hasniza Zaman Huri
Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal.2023; 31(11): 101797. CrossRef - Cross-sectional assessment of predictors for COVID-19 vaccine uptake: an online survey in Greece
Petros Galanis, Irene Vraka, Olga Siskou, Olympia Konstantakopoulou, Aglaia Katsiroumpa, Ioannis Moisoglou, Daphne Kaitelidou
Vacunas.2022; 23: S60. CrossRef - Key predictors of COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in Malaysia: An integrated framework
Jason Wei Jian Ng, Santha Vaithilingam, Mahendhiran Nair, Li-Ann Hwang, Kamarul Imran Musa, Anat Gesser-Edelsburg
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(5): e0268926. CrossRef - Intention to receive a COVID-19 vaccine booster dose and associated factors in Malaysia
Li Ping Wong, Haridah Alias, Yan-Li Siaw, Mustakiza Muslimin, Lee Lee Lai, Yulan Lin, Zhijian Hu
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Determinants of COVID-19 vaccine acceptance in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Ayenew Mose, Abebaw Wasie, Solomon Shitu, Kassahun Haile, Abebe Timerga, Tamirat Melis, Tadesse Sahle, Amare Zewdie, Dong Keon Yon
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(6): e0269273. CrossRef - When do persuasive messages on vaccine safety steer COVID-19 vaccine acceptance and recommendations? Behavioural insights from a randomised controlled experiment in Malaysia
Nicholas Yee Liang Hing, Yuan Liang Woon, Yew Kong Lee, Hyung Joon Kim, Nurhyikmah M Lothfi, Elizabeth Wong, Komathi Perialathan, Nor Haryati Ahmad Sanusi, Affendi Isa, Chin Tho Leong, Joan Costa-Font
BMJ Global Health.2022; 7(7): e009250. CrossRef - COVID-19 vaccine acceptance rate and its predictors in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Getaneh Mulualem Belay, Tewodros Getaneh Alemu, Masresha Asmare Techane, Chalachew Adugna Wubneh, Nega Tezera Assimamaw, Tadesse Tarik Tamir, Addis Bilal Muhye, Destaye Guadie Kassie, Amare Wondim, Bewuketu Terefe, Bethlehem Tigabu Tarekegn, Mohammed Seid
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross-sectional assessment of predictors for COVID-19 vaccine uptake: an online survey in Greece
Petros Galanis, Irene Vraka, Olga Siskou, Olympia Konstantakopoulou, Aglaia Katsiroumpa, Ioannis Moisoglou, Daphne Kaitelidou
Vacunas (English Edition).2022; 23: S60. CrossRef
- Awareness, knowledge, disease prevention practices, and immunization attitude of hepatitis E virus among food handlers in Klang Valley, Malaysia
- Perceptions of the COVID-19 vaccine and willingness to receive vaccination among health workers in Nigeria
- Oluseyi Ademola Adejumo, Olorunfemi Akinbode Ogundele, Cynthia Roli Madubuko, Rosena Olubanke Oluwafemi, Ogochukwu Chinedum Okoye, Kenechukwu Chukwuemeka Okonkwo, Sunday Samson Owolade, Oladimeji Adedeji Junaid, Olutoyin Morenike Lawal, Adenike Christianah Enikuomehin, Maureen Iru Ntaji, Aisha Sokunbi, Aina Omodele Timothy, Olatunji Sunday Abolarin, Emmanuel Olalekan Ali, John Oghenevwirhe Ohaju-Obodo
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(4):236-243. Published online July 19, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0023
- 11,532 View
- 455 Download
- 39 Web of Science
- 36 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
The study aimed to examine health workers’ perceptions of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine in Nigeria and their willingness to receive the vaccine when it becomes available.
Methods
This multi-center cross-sectional study used non-probability convenience sampling to enroll 1,470 hospital workers aged 18 and above from 4 specialized hospitals. A structured and validated self-administered questionnaire was used for data collection. Data entry and analysis were conducted using IBM SPSS ver. 22.0.
Results
The mean age of respondents was 40±6 years. Only 53.5% of the health workers had positive perceptions of the COVID-19 vaccine, and only slightly more than half (55.5%) were willing to receive vaccination. Predictors of willingness to receive the COVID-19 vaccine included having a positive perception of the vaccine (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 4.55; 95% confidence interval [CI], 3.50−5.69), perceiving a risk of contracting COVID-19 (AOR, 1.50; 95% CI, 1.25–3.98), having received tertiary education (AOR, 3.50; 95% CI, 1.40−6.86), and being a clinical health worker (AOR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.01−1.68).
Conclusion
Perceptions of the COVID-19 vaccine and willingness to receive the vaccine were sub-optimal among this group. Educational interventions to improve health workers' perceptions and attitudes toward the COVID-19 vaccine are needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nigerians’ attitudes and perceptions towards vaccine acceptance during and after the COVID-19 pandemic
Jonas Lotanna Ibekwe, Victor Oluwafemi Femi-Lawal, Jolly Akor Thomas, Faith Uzoamaka Okei, Moses Ojomakpenen Ojile, Oluwatobiloba Oladipupo Akingbulugbe
Journal of Medicine, Surgery, and Public Health.2024; 2: 100066. CrossRef - Knowledge, attitudes, and factors determining the willingness for COVID-19 vaccination among students in Bangladesh: An online-based cross-sectional study
Ashis Talukder, Soheli Sharmin, Chuton Deb Nath, Iqramul Haq, Md. Ismail Hossain, Md. Jakaria Habib, Sabiha Shirin Sara
Journal of Public Health.2024; 32(4): 663. CrossRef - Healthcare professionals’ perception and COVID-19 vaccination attitudes in North-Western Ghana: A multi-center analysis
Augustine Ngmenemandel Balegha, Suburu Abdul-Aziz, Louis Mornah, Pracheth Raghuveer
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0298810. CrossRef - Behavioral Insights from Vaccine Adoption in Nigeria: Cross-Sectional Survey Findings
Sohail Agha, Ifeanyi Nsofor, Drew Bernard, Sarah Francis, Nandan Rao
Interactive Journal of Medical Research.2024; 13: e47817. CrossRef - COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in Latin America and Africa: a scoping review
Bruna Aparecida Gonçalves, Camila Carvalho de Souza Amorim Matos, Jonathan Vicente dos Santos Ferreira, Renata Fortes Itagyba, Vinicius Rocha Moço, Marcia Thereza Couto
Cadernos de Saúde Pública.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Suspecting the Figures: What Church Leaders Think About Government’s Commitment to Combating COVID-19 in Nigeria
Uchechukwu M. Agbo, George C. Nche
Journal of Asian and African Studies.2023; 58(5): 725. CrossRef - Access to COVID-19 vaccines and testing in Africa: the importance of COVAX - Nigeria as a case study
Rafaella Fortini Queiroz Grenfell, Oyetunde Timothy Oyeyemi
Pathogens and Global Health.2023; 117(2): 152. CrossRef - COVID-19 vaccine acceptance prediction: The roles of students’ attitude towards science and mathematics and knowledge of COVID-19 pandemic
Sunday Ogbu, Ogochukwu Ebere Emenike, Amaka Loretta Nwankwo
Electronic Journal of Medical and Educational Tech.2023; 16(2): em2304. CrossRef - Factors associated with COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among healthcare workers in Cameroon and Nigeria: a web-based cross-sectional study
Jerry Brown Aseneh, Valirie Ndip Agbor, Benjamin Momo Kadia, Elvis Anyaehiechukwu Okolie, Chinelo Janefrances Ofomata, Christie Linonge Etombi, Domin Sone M Ekaney, Yvonne Walburga Joko Fru
International Health.2023; 15(6): 702. CrossRef - Willingness to COVID-19 vaccination: Empirical evidence from EU
Imran Ur Rahman, Arslan Austin, Naveed Nelson
Heliyon.2023; 9(5): e15776. CrossRef - Radiographers’ knowledge, attitude and adherence to standard COVID-19 precautions and the policy implications: a national cross-sectional study in Nigeria
Charles Ikechukwu Ezema, Okechukwu Felix Erondu, Ogochukwu Kelechi Onyeso, Chiedozie James Alumona, Andrew Wueseter Ijever, Charity Ndidiamaka Amarachukwu, Amaeze Augustine Amaeze
Annals of Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Declining trends in vaccine confidence across sub-Saharan Africa: A large-scale cross-sectional modeling study
A. de Figueiredo, E. Temfack, R. Tajudeen, H. J. Larson
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge and acceptance of COVID-19 vaccine among healthcare workers in Enugu metropolis, Enugu state, Nigeria
Kelechi U. Imediegwu, Jude C. Abor, Chiamaka Q. Onyebuchukwu, Hilary I. Ugwu, Ogechi I. Ugwu, Udo Ego Anyaehie, Oluchi A. Onyia
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID-19 vaccination acceptance (uptake, hesitancy, intention to receive and timeliness of the intention to receive) and the determinants among health workers in Ebonyi state, Nigeria: an analytical cross-sectional study
Ugwu I Omale, Onyinyechukwu U Oka, Chidinma I Amuzie, Victor U Uduma, Azuka S Adeke, Cordis O Ikegwuonu, Glory E Nkwo, Ugochi I A Nwali, Osarhiemen Iyare, Richard L Ewah, Olaedo O Nnachi, Okechukwu O Ukpabi, Ifeyinwa M Okeke
BMJ Open.2023; 13(7): e068668. CrossRef - Hesitação vacinal contra a COVID-19 na América Latina e África: uma revisão de escopo
Bruna Aparecida Gonçalves, Camila Carvalho de Souza Amorim Matos, Jonathan Vicente dos Santos Ferreira, Renata Fortes Itagyba, Vinicius Rocha Moço, Marcia Thereza Couto
Cadernos de Saúde Pública.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Social Ecological Model: A Framework for Understanding COVID-19 Vaccine Uptake among Healthcare Workers—A Scoping Review
Damian Naidoo, Anna Meyer-Weitz, Kaymarlin Govender
Vaccines.2023; 11(9): 1491. CrossRef - Health service factors affecting the COVID-19 vaccination campaign in a Ghanaian metropolis: A qualitative exploratory study
Susanna Aba Aba Abraham, John Oti Amoah, Dorcas Frempomaa Agyare, Deogratias Kaheeru Sekimpi, Diana Bosomtwe-Duker, Andrews Adjei Druye, Gifty Osei Berchie, Dorcas Obiri-Yeboah
BMJ Open.2023; 13(12): e076184. CrossRef - ‘Why Should I Take the COVID-19 Vaccine after Recovering from the Disease?’ A Mixed-methods Study of Correlates of COVID-19 Vaccine Acceptability among Health Workers in Northern Nigeria
Zubairu Iliyasu, Muhammad R. Garba, Auwalu U. Gajida, Taiwo G. Amole, Amina A. Umar, Hadiza M. Abdullahi, Aminatu A. Kwaku, Hamisu M. Salihu, Muktar H. Aliyu
Pathogens and Global Health.2022; 116(4): 254. CrossRef - A Global Map of COVID-19 Vaccine Acceptance Rates per Country: An Updated Concise Narrative Review
Malik Sallam, Mariam Al-Sanafi, Mohammed Sallam
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2022; Volume 15: 21. CrossRef - Knowledge, Attitudes, and Perception towards COVID-19 Vaccination among the Adult Population: A Cross-Sectional Study in Turkey
Meliha Cagla Sonmezer, Taha Koray Sahin, Enes Erul, Furkan Sacit Ceylan, Muhammed Yusuf Hamurcu, Nihal Morova, Ipek Rudvan Al, Serhat Unal
Vaccines.2022; 10(2): 278. CrossRef - Factors influencing COVID-19 vaccine uptake among adults in Nigeria
Halimat Adedeji-Adenola, Olubusola A. Olugbake, Shakirat A. Adeosun, Ismaeel Yunusa
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(2): e0264371. CrossRef - Perception and Prevention Practices Relating to Covid 19 Infection Among Elderly in Ogun State, Nigeria
Adenitire G., Agbede C.O.
International Journal of Public Health and Pharmac.2022; 2(1): 29. CrossRef - Predicting nursing students' intention to attend face‐to‐face classes on school reopening: A theory of planned behavior application
Ryan Michael F. Oducado, Jerome V. Cleofas, Gil P. Soriano
Nursing Forum.2022; 57(5): 733. CrossRef - COVID-19 vaccination in Nigeria: A rapid review of vaccine acceptance rate and the associated factors
Oluwatosin Olu-Abiodun, Olumide Abiodun, Ngozi Okafor, Nusirat Elelu
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(5): e0267691. CrossRef - COVID-19 vaccine acceptance among health care workers in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Martin Ackah, Louise Ameyaw, Mohammed Gazali Salifu, Delali Pearl Afi Asubonteng, Cynthia Osei Yeboah, Eugene Narkotey Annor, Eunice Abena Kwartemaa Ankapong, Hosea Boakye, Muhammad Shahzad Aslam
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(5): e0268711. CrossRef - A national survey of COVID-19 vaccine acceptance in Nigeria
Ahmad Ibrahim Al-Mustapha, Ochulor Okechukwu, Ademola Olayinka, Oyeniyi Rasheed Muhammed, Muftau Oyewo, Samuel A. Owoicho, Ahmed Tijani Abubakar, Abdulsalam Olabisi, Aliyu Jibril, Simon Ereh, Oluwatosin Enoch Fakayode, Oluwaseun Adeolu Ogundijo, Nusirat E
Vaccine.2022; 40(33): 4726. CrossRef - COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in Africa: a scoping review
Betty B. B. Ackah, Michael Woo, Lisa Stallwood, Zahra A. Fazal, Arnold Okpani, Ugochinyere Vivian Ukah, Prince A. Adu
Global Health Research and Policy.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID-19 Vaccine Acceptance and Associated Factors Among College Students in Dessie City, Northeastern Ethiopia
Gete Berihun, Zebader Walle, Daniel Teshome, Leykun Berhanu, Mohammed Derso
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2022; Volume 15: 1735. CrossRef - Career Aspiration Fulfillment and COVID-19 Vaccination Intention among Nigerian Youth: An Instrumental Variable Approach
Abayomi Samuel Oyekale
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(16): 9813. CrossRef - COVID-19 Vaccine Attitude and Its Predictors Among People Living With Chronic Health Conditions in Ibadan, Nigeria
Lucia Yetunde Ojewale, Rotimi Felix Afolabi, Adesola Ogunniyi
International Journal of Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy and the experience of violence among women and girls living with and at risk of HIV in Nigeria
Morenike Oluwatoyin Folayan, Olujide Arije, Amaka Enemo, Aaron Sunday, Amira Muhammad, Hasiya Yunusa Nyako, Rilwan Mohammed Abdullah, Henry Okiwu, Erik Lamontagne
African Journal of AIDS Research.2022; 21(4): 306. CrossRef - Willingness to receive COVID-19 vaccine: A survey among medical radiation workers in Nigeria
Grace Ben Inah, Samuel Archibong Efanga, Ekaete Vincent Ukpong, Christiana Ifeyinwa Obiora
Calabar Journal of Health Sciences.2022; 6: 80. CrossRef - Acceptance of COVID-19 vaccine among healthcare workers in Africa, systematic review and meta-analysis
Zerihun Figa, Tesfaye Temesgen, Addisu Getnet Zemeskel, Moges Ganta, Asrat Alemu, Mesfin Abebe, Zemachu Ashuro
Public Health in Practice.2022; 4: 100343. CrossRef - Perception and willingness to accept COVID-19 Vaccines: A cross-sectional survey of the general population of Sokoto State, Nigeria
Oche Mansur Oche, Habibullah Adamu, Musa Yahaya, Hudu Garba Illo, Abdulaziz Mohammad Danmadami, Adamu Ijapa, Asmau Mohammad Wali, Hamza Yusuf, Hafsat Muhammad, Abba Aji, Harapan Harapan
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(12): e0278332. CrossRef - COVID-19 vaccination acceptance among community members and health workers in Ebonyi state, Nigeria: study protocol for a concurrent-independent mixed method analyses of intention to receive, timeliness of the intention to receive, uptake and hesitancy to
Ugwu I Omale, Osarhiemen Iyare, Richard L Ewah, Chidinma I Amuzie, Onyinyechukwu U Oka, Victor U Uduma, Azuka S Adeke, Cordis O Ikegwuonu, Olaedo O Nnachi, Okechukwu O Ukpabi, Ifeyinwa M Okeke, Glory E Nkwo, Ugochi IA Nwali
BMJ Open.2022; 12(12): e061732. CrossRef - Drivers of COVID-19 Vaccine Uptake amongst Healthcare Workers (HCWs) in Nigeria
Sohail Agha, Adaobi Chine, Mathias Lalika, Samikshya Pandey, Aparna Seth, Alison Wiyeh, Alyssa Seng, Nandan Rao, Akhtar Badshah
Vaccines.2021; 9(10): 1162. CrossRef
- Nigerians’ attitudes and perceptions towards vaccine acceptance during and after the COVID-19 pandemic



 First
First Prev
Prev


