Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Psychiatric adverse events associated with the COVID-19 vaccines approved in the Republic of Korea: a systematic review
- Seungeun Ryoo, Miyoung Choi, Nam-Kyong Choi, Hyoung-Shik Shin, Jun Hee Woo, Byung-Joo Park, Sanghoon Oh
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(2):107-114. Published online March 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0325
- 652 View
- 31 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 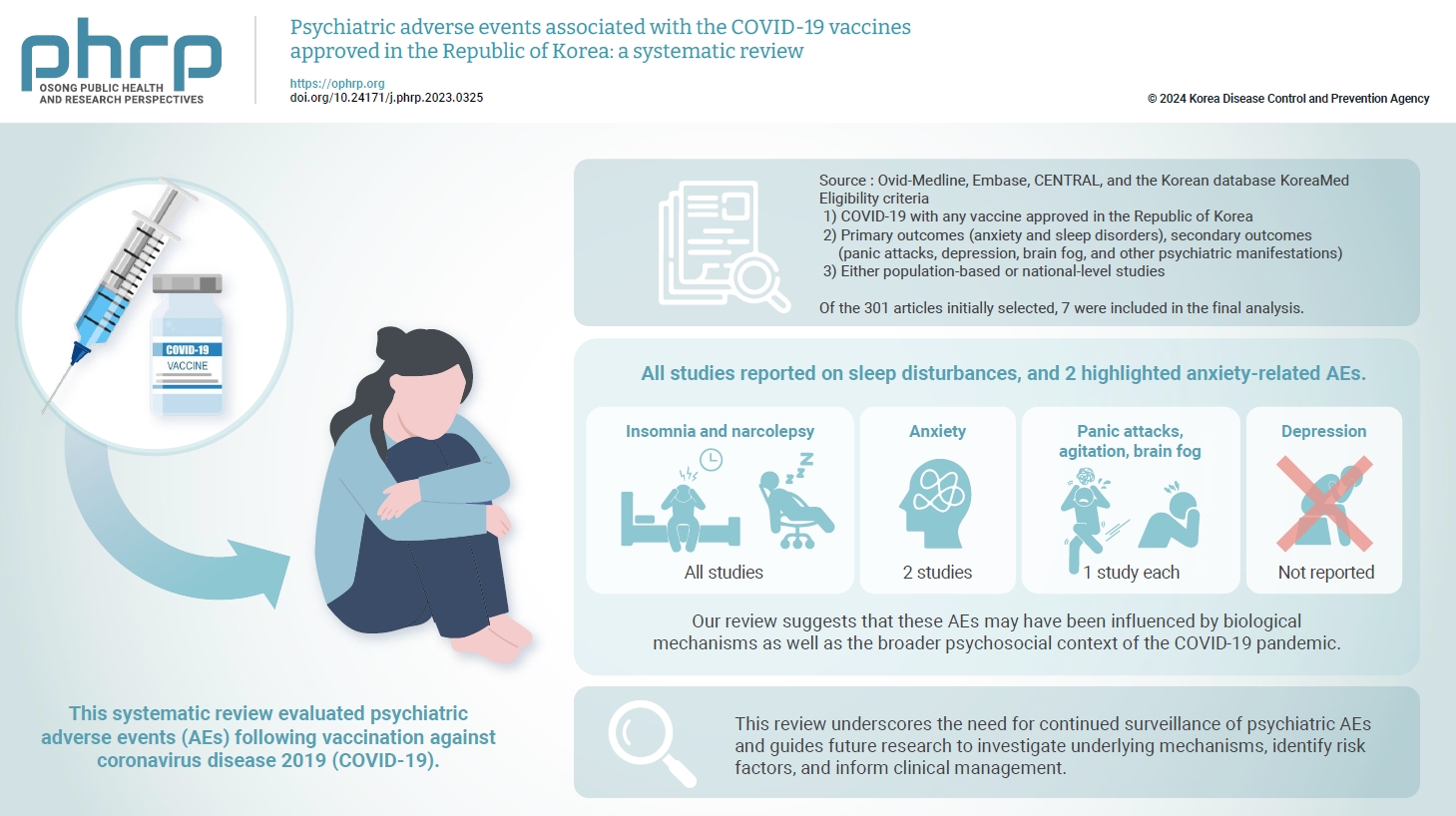
- This systematic review evaluated psychiatric adverse events (AEs) following vaccination against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We included studies that reported or investigated psychiatric AEs in individuals who had received an approved COVID-19 vaccine in the Republic of Korea. Systematic electronic searches of Ovid-Medline, Embase, CENTRAL, and KoreaMed databases were conducted on March 22, 2023. Risk of bias was assessed using the Risk of Bias Assessment Tool for Non-randomized Studies 2.0. The study protocol was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (CRD42023449422). Of the 301 articles initially selected, 7 were included in the final analysis. All studies reported on sleep disturbances, and 2 highlighted anxiety-related AEs. Sleep disorders like insomnia and narcolepsy were the most prevalent AEs, while depression was not reported. Our review suggests that these AEs may have been influenced by biological mechanisms as well as the broader psychosocial context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Although this study had limitations, such as a primary focus on the BNT162b2 vaccine and an observational study design, it offered a systematic, multi-vaccine analysis that fills a critical gap in the existing literature. This review underscores the need for continued surveillance of psychiatric AEs and guides future research to investigate underlying mechanisms, identify risk factors, and inform clinical management.
- Effect of Paxlovid in COVID-19 treatment during the periods of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.5 and BN.1 subvariant dominance in the Republic of Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Dong-Hwi Kim, Min-Gyu Yoo, Na-Young Kim, So Young Choi, Minjeong Jang, Misuk An, Se-Jin Jeong, Jungyeon Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(2):137-149. Published online March 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0230
- 402 View
- 19 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 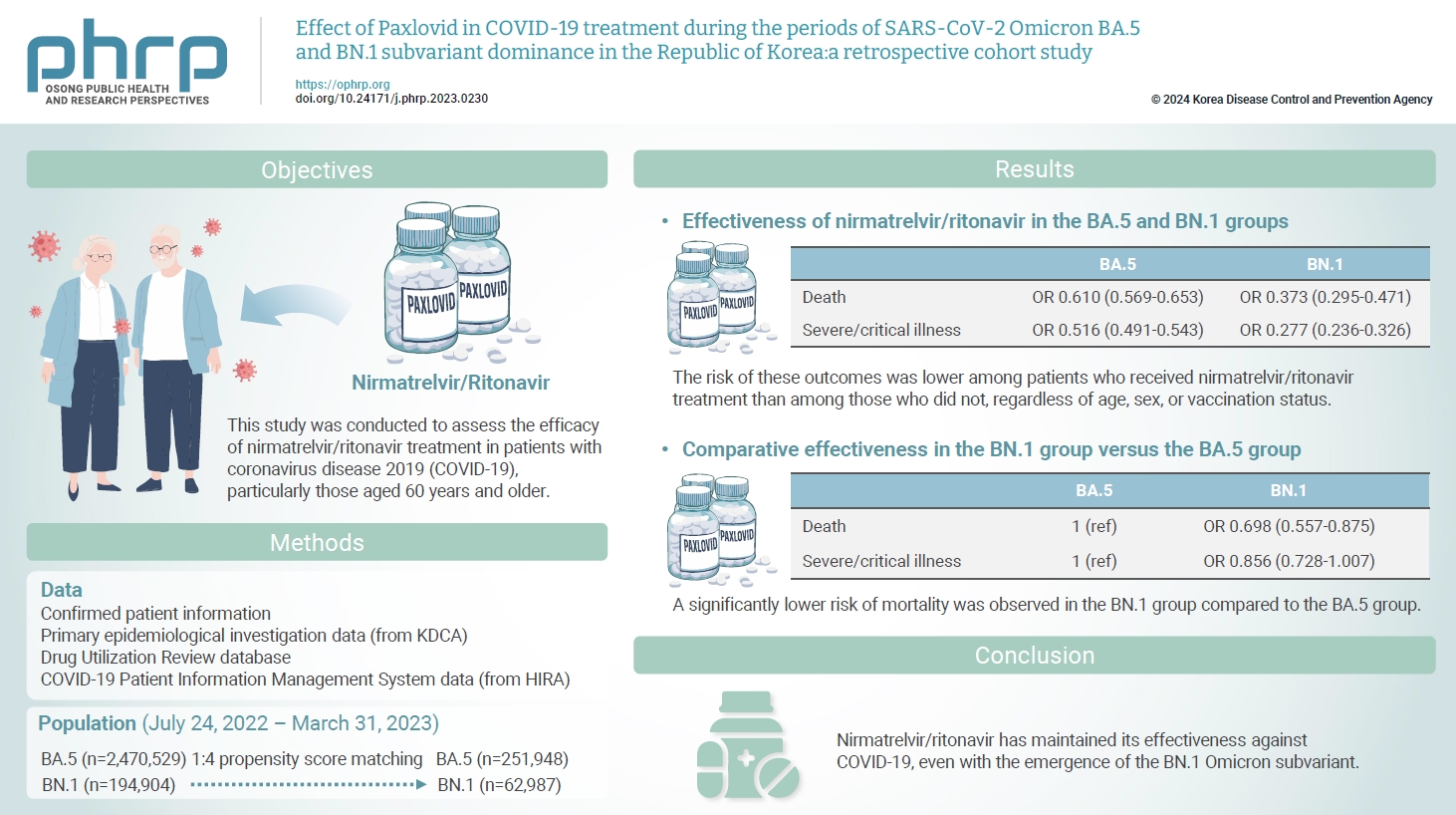
- Objectives
This study was conducted to assess the efficacy of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), particularly those aged 60 years and older. Using real-world data, the period during which the BN.1 Omicron variant was dominant was compared to the period dominated by the BA.5 variant.
Methods
In this retrospective cohort study, data were collected regarding 2,665,281 patients infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 between July 24, 2022, and March 31, 2023. Propensity score matching was utilized to match patients who received nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in a 1:4 ratio between BN.1 and BA.5 variant groups. Multivariable logistic regression analysis was employed to assess the effects of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir within these groups.
Results
Compared to the prior period, the efficacy of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir did not significantly differ during the interval of Omicron BN.1 variant dominance in the Republic of Korea. Among patients treated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, a significantly lower risk of mortality was observed in the BN.1 group (odds ratio [OR], 0.698; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.557–0.875) compared to the BA.5 group. However, this treatment did not significantly reduce the risk of severe or critical illness, including death, for those in the BN.1 group (OR, 0.856; 95% CI, 0.728–1.007).
Conclusion
Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir has maintained its effectiveness against COVID-19, even with the emergence of the BN.1 Omicron subvariant. Consequently, we strongly recommend the administration of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir to patients exhibiting COVID-19-related symptoms, irrespective of the dominant Omicron variant or their vaccination status, to mitigate disease severity and decrease the risk of mortality.
- JYNNEOS vaccine safety monitoring in the Republic of Korea, 2022: a cross-sectional study
- Jaeeun Lee, Seunghyun Lewis Kwon, Jinhee Park, Hyuna Bae, Hyerim Lee, Geun-Yong Kwon
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):433-438. Published online October 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0182
- 908 View
- 38 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 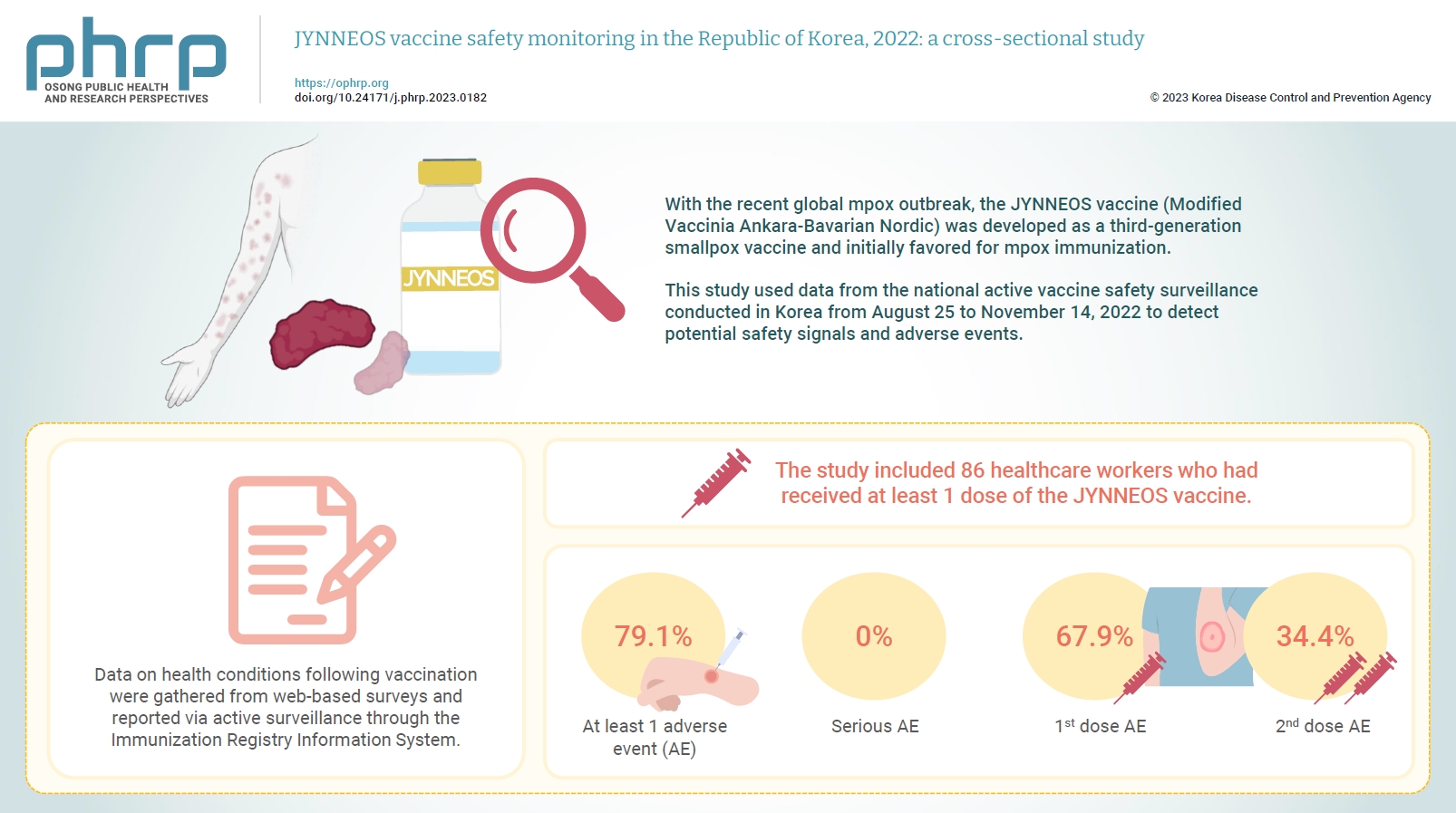
- Objectives
With the recent global mpox outbreak, the JYNNEOS vaccine (Modified Vaccinia Ankara-Bavarian Nordic) was developed as a third-generation smallpox vaccine and initially favored for mpox immunization. Vaccine-associated side effects contribute to vaccine hesitancy. Consequently, tracking adverse events post-immunization is crucial for safety management. This study used data from the national active vaccine safety surveillance conducted in Korea from August 25 to November 24, 2022 to detect potential safety signals and adverse events. Methods: Data on health conditions following vaccination were gathered from web-based surveys and reported via active surveillance through the Immunization Registry Information System. This follow-up system functioned via a text message link, surveying adverse events and health conditions beginning on the second day post-vaccination. Information about specific adverse events, including both local and systemic reactions, was collected. Results: The study included 86 healthcare workers who had received at least 1 dose of the JYNNEOS vaccine. Among the respondents, 79.1% reported experiencing at least 1 adverse event, with the majority being local reactions at the injection site. The incidence of adverse events was higher following the first dose (67.9%) than after the second dose (34.4%). The most frequently reported adverse event for both doses was mild pain at the injection site. Conclusion: The study provides crucial information on the safety of the JYNNEOS vaccine, demonstrating that most adverse events were manageable and predominantly localized to the injection site. Nonetheless, additional research is needed on the safety of various vaccine administration techniques and the vaccine’s effects on broader demographics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adverse Reactions After Intradermal Vaccination With JYNNEOS for Mpox in Korea
So Yun Lim, Yu Mi Jung, Yeonjae Kim, Gayeon Kim, Jaehyun Jeon, BumSik Chin, Min-Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Adverse Reactions After Intradermal Vaccination With JYNNEOS for Mpox in Korea
- Effects of an arteriovenous fistula stenosis prevention program in patients receiving hemodialysis
- Haegyeong Lee, Gyuli Baek, Eunju Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):279-290. Published online August 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0101
- 1,277 View
- 143 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
To increase the efficiency of hemodialysis, an appropriate vascular pathway must be created, and its function must be maintained. This study aimed to identify the effects of an arteriovenous fistula (AVF) stenosis prevention program on upper muscular strength, blood flow, physiological indexes, and self-efficacy among patients receiving hemodialysis.
Methods
The participants were patients receiving hemodialysis at Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center in Daegu, Republic of Korea. They were divided into experimental and control groups based on the day of the week they received hemodialysis at the outpatient department and included 25 participants each. The study was conducted for 8 weeks.
Results
The AVF stenosis prevention program was effective in improving upper extremity muscle strength (F=15.23, p<0.001) and blood flow rate (F=36.00, p<0.001). As a result of the program, the phosphorus index level, which is a physiological indicator in hemodialysis patients, decreased (F=8.64, p<0.001). Encouragement and support through text messages and practice lists also resulted in an increase in self-efficacy (F=18.62, p<0.001).
Conclusion
The AVF stenosis prevention program in this study resulted in an increase in upper extremity muscle strength through grip strength exercises and was effective in preventing AVF stenosis by increasing the blood flow rate.
- Prevalence and patterns of adverse events following childhood immunization and the responses of mothers in Ile-Ife, South West Nigeria: a facility-based cross-sectional survey
- Olorunfemi Akinbode Ogundele, Funmito Omolola Fehintola, Mubarak Salami, Rahmat Usidebhofoh, Mary Aderemi Abaekere
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):291-299. Published online July 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0071
- 2,235 View
- 133 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 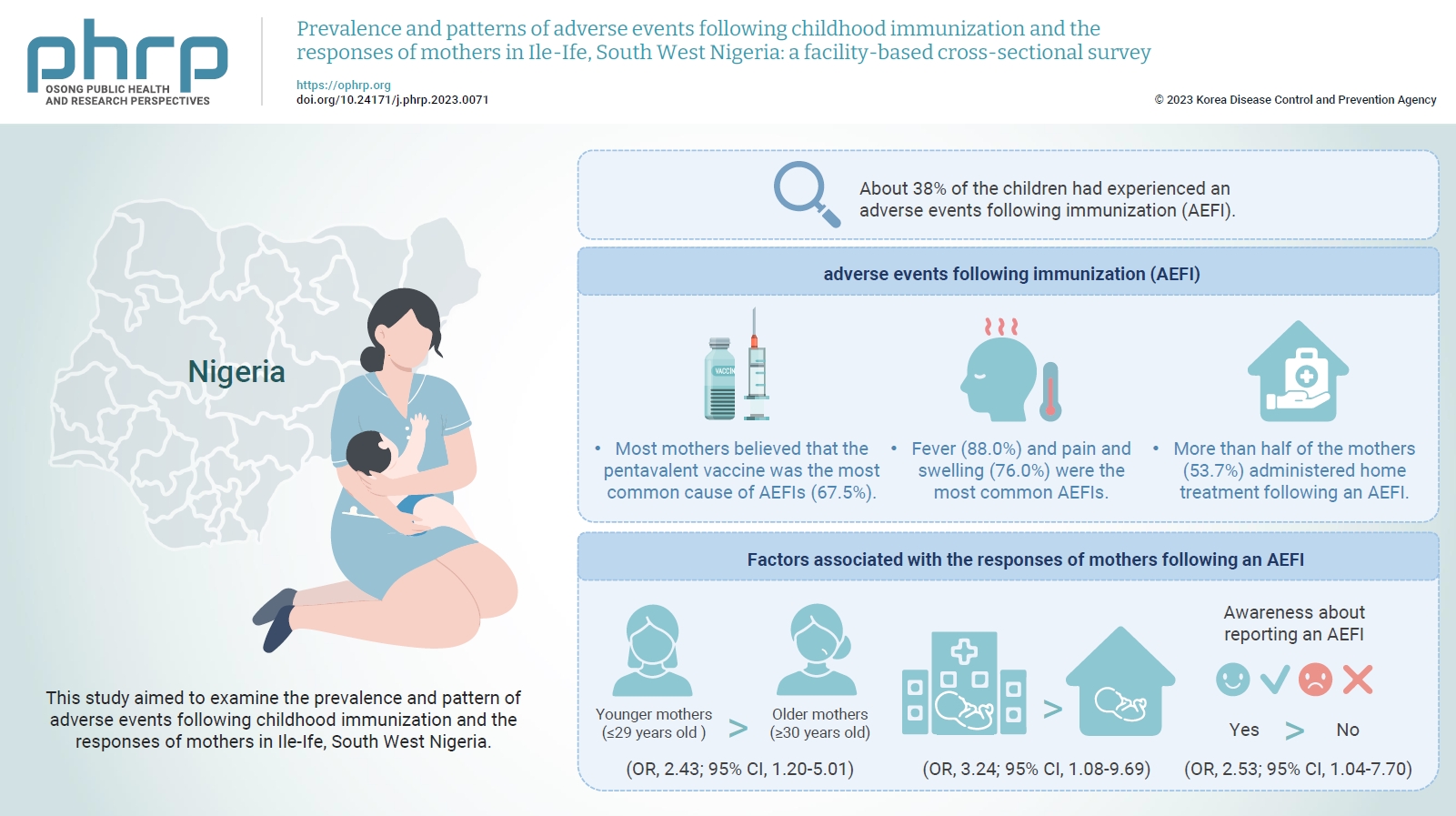
- Objectives
This study aimed to examine the prevalence and pattern of adverse events following childhood immunization and the responses of mothers in Ile-Ife, South West Nigeria.
Methods
This descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted among 422 mothers of children aged 0 to 24 months attending any of the 3 leading immunization clinics in Ile-Ife, Nigeria. The respondents were selected using the multi-stage sampling technique. Data were collected using a pretested structured interviewer-administered questionnaire and analyzed using IBM SPSS ver. 26.0. The chi-square test was used to test associations, while binary logistic regression was used to determine the predictors of mothers’ responses to adverse events following immunization (AEFIs). A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
The mean age of the respondents was 29.99±5.74 years. About 38% of the children had experienced an AEFI. Most mothers believed that the pentavalent vaccine was the most common cause of AEFIs (67.5%). Fever (88.0%) and pain and swelling (76.0%) were the most common AEFIs. More than half of the mothers (53.7%) administered home treatment following an AEFI. Younger mothers (odds ratio [OR], 2.43; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.20–5.01), mothers who delivered their children at a healthcare facility (OR, 3.24; 95% CI, 1.08–9.69), and mothers who were knowledgeable about reporting AEFIs (OR, 2.53; 95% CI, 1.04–7.70) were most likely to respond appropriately to AEFIs.
Conclusion
The proportion of mothers who responded poorly to AEFIs experienced by their children was significant. Therefore, strategies should be implemented to improve mothers’ knowledge about AEFIs to improve their responses.
- Results of contact tracing for SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sub-lineages (BA.4, BA.5, BA.2.75) and the household secondary attack risk
- Mi Yu, Sang-Eun Lee, Hye Young Lee, Hye-jin Kim, Yeong-Jun Song, Jian Jeong, Ae Kyung Park, Il-Hwan Kim, Eun-jin Kim, Young-Joon Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):173-179. Published online June 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0285
- 1,394 View
- 58 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
This study aimed to assess the contact tracing outcomes of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron sub-lineages BA.4, BA.5, and BA.2.75 within Republic of Korea, and to generate foundational data for responding to future novel variants.
Methods
We conducted investigations and contact tracing for 79 confirmed BA.4 cases, 396 confirmed BA.5 cases, and 152 confirmed BA.2.75 cases. These cases were identified through random sampling of both domestically confirmed and imported cases, with the goal of evaluating the pattern of occurrence and transmissibility.
Results
We detected 79 instances of Omicron sub-lineage BA.4 across a span of 46 days, 396 instances of Omicron sub-lineage BA.5 in 46 days, and 152 instances of Omicron sub-lineage BA.2.75 over 62 days. One patient with severe illness was confirmed among the BA.5 cases; however, there were no reports of severe illness in the confirmed BA.4 and BA.2.75 cases. The secondary attack risk among household contacts were 19.6% for BA.4, 27.8% for BA.5, and 24.3% for BA.2.75. No statistically significant difference was found between the Omicron sub-lineages.
Conclusion
BA.2.75 did not demonstrate a higher tendency for transmissibility, disease severity, or secondary attack risk within households when compared to BA.4 and BA.5. We will continue to monitor major SARS-CoV-2 variants, and we plan to enhance the disease control and response systems.
- Carbapenem resistance in critically important human pathogens isolated from companion animals: a systematic literature review
- Angie Alexandra Rincón-Real, Martha Cecilia Suárez-Alfonso
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(6):407-423. Published online December 16, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0033
- 3,075 View
- 150 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study aimed to describe the presence and geographical distribution of Gram-negativebacteria considered critical on the priority list of antibiotic-resistant pathogens publishedby the World Health Organization, including carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae,carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter spp., and carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.A systematic review of original studies published in 5 databases between 2010 and 2021 wasconducted, including genotypically confirmed carbapenem-resistant isolates obtained fromcanines, felines, and their settings. Fifty-one articles met the search criteria. Carbapenemresistant isolates were found in domestic canines and felines, pet food, and on veterinarymedical and household surfaces. The review found that the so-called “big five”—that is, the5 major carbapenemases identified worldwide in Enterobacterales (New Delhi metallo-βlactamase, active-on-imipenem, Verona integron-encoded metallo-β-lactamase, Klebsiellapneumoniae carbapenemase, and oxacillin [OXA]-48-like)—and the 3 most importantcarbapenemases from Acinetobacter spp. (OXA-23-like, OXA-40-like, and OXA-58-like) hadbeen detected in 8 species in the Enterobacteriaceae family and 5 species of glucose nonfermenting bacilli on 5 continents. Two publications used molecular analysis to confirmcarbapenem-resistant bacteria transmission between owners and dogs. Isolating criticallyimportant human carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria from domestic canines andfelines highlights the importance of including these animal species in surveillance programsand antimicrobial resistance containment plans as part of the One Health approach.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- First report of a blaNDM-5-carrying Escherichia coli sequence type 12 isolated from a dog with pyometra in Japan
Kazuki Harada, Tadashi Miyamoto, Michiyo Sugiyama, Tetsuo Asai
Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The European Union summary report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2021–2022
EFSA Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiological analysis and prevention strategies in response to a shigellosis cluster outbreak: a retrospective case series in an alternative school in the Republic of Korea, 2023
Yeongseo Ahn, Sunmi Jin, Gemma Park, Hye Young Lee, Hyungyong Lee, Eunkyung Shin, Junyoung Kim, Jaeil Yoo, Yuna Kim
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2024; 15(1): 68. CrossRef - The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2020/2021
EFSA Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistome-based surveillance identifies ESKAPE pathogens as the predominant gram-negative organisms circulating in veterinary hospitals
Flavia Zendri, Cajsa M. Isgren, Jane Devaney, Vanessa Schmidt, Rachel Rankin, Dorina Timofte
Frontiers in Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Unveiling the emergence of multidrug-resistant pathogens in exotic pets from France: a comprehensive study (2017-2019)
Sandro Cardoso, Aurélie Le Loc’h, Inês Marques, Anabela Almeida, Sérgio Sousa, Maria José Saavedra, Sofia Anastácio, Eduarda Silveira
One Health & Implementation Research.2023; 3(4): 161. CrossRef
- First report of a blaNDM-5-carrying Escherichia coli sequence type 12 isolated from a dog with pyometra in Japan
- Menstrual hygiene management and its determinants among adolescent girls in low-income urban areas of Delhi, India: a community-based study
- Suneela Garg, Nidhi Bhatnagar, Mongjam Meghachandra Singh, Saurav Basu, Amod Borle, Yamini Marimuthu, Falak Azmi, Yomri Dabi, Indu Bala
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(4):273-281. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0127
- 3,538 View
- 255 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Menstrual hygiene management (MHM) in developing countries is linked to human rights, social justice, and the education and empowerment of young girls. The objective of this study was to assess menstrual hygiene practices and their determinants among adolescent girls, including school dropouts, and the effects of pad distribution programs in urban resettlement areas of Delhi, India.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted from March 2019 to February 2020 in urban resettlement colonies and 2 villages of Delhi among 1,130 adolescent girls aged 10 to 19 years, who were interviewed face to face.
Results
In total, 954 participants (84.4%) used only disposable sanitary pads, 150 (13.3%) used both sanitary pads and cloths, and 26 (2.3%) used only cloths (n=1,130). Most school-going girls utilized the scheme for pad distribution, but only two-thirds of the girls who were out of school utilized the scheme. In the adjusted analysis, girls with lower educational status, those who had dropped out of school, and those from the Muslim religious community were more likely to use cloths for MHM.
Conclusion
More than 4 out of 5 adolescent girls in Delhi in low-income neighborhoods preferred sanitary pads for MHM. The government free pad scheme reached near-universal utilization among school-going girls (97%), but the subsidized pad scheme for girls who did not attend school was insufficiently utilized (75%). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Associated with Exclusive Use of Hygienic Methods during Menstruation among Adolescent Girls (15–19 Years) in Urban India: Evidence from NFHS-5
Doli Roy, Nuruzzaman Kasemi, Manik Halder, Malasree Majumder
Heliyon.2024; 10(8): e29731. CrossRef - Enhancement of Health-related Quality of Life among School-going Adolescent Girls with Improvement in Menstrual Hygiene Knowledge and Practices
Akanksha Goyal, Sunita Agarwal
Archives of Medicine and Health Sciences.2024; 12(1): 73. CrossRef - Menstrual Hygiene Problems and Challenges Faced by Adolescent Females in Rural Areas: A Narrative Review
Vijiya Kashyap, Sonali G Choudhari
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Perceived difficulties in maintaining menstrual hygiene practices among indigenous adolescents during seasonal water scarcity periods in Bandarban hill district of Bangladesh: A cross-sectional study
Imdadul Haque Talukdar, M.A. Rifat, Plabon Sarkar, Nobonita Saha, Mesfin Kassaye Tessma, Md. Ibrahim Miah
International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental.2023; 254: 114268. CrossRef - Menstrual hygiene practices among adolescent women in rural India: a cross-sectional study
Aditya Singh, Mahashweta Chakrabarty, Shivani Singh, Rakesh Chandra, Sourav Chowdhury, Anshika Singh
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Factors Associated with Exclusive Use of Hygienic Methods during Menstruation among Adolescent Girls (15–19 Years) in Urban India: Evidence from NFHS-5
- Social determinants of adherence to COVID-19 preventive guidelines: a comprehensive review
- Zahra Jorjoran Shushtari, Yahya Salimi, Sina Ahmadi, Nader Rajabi-Gilan, Marzieh Shirazikhah, Akbar Biglarian, Ali Almasi, Mohammad Ali Mohammadi Gharehghani
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(6):346-360. Published online December 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0180
- 7,508 View
- 162 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Adherence to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) preventive guidelines (ACPG) is an important strategy to control the COVID-19 pandemic effectively. The present study aimed to identify and summarize the social determinants of ACPG among the general population. A comprehensive review was performed from December 2019 to February 2021 through searching electronic databases. Two independent reviewers assessed and selected relevant studies. Next, the characteristics and main findings of the included studies were summarized. Finally, the World Health Organization’s conceptual framework of social determinants of health was used to synthesize the identified social determinants of ACPG. Forty-one of 453 retrieved articles met the inclusion criteria. The study results showed different patterns of ACPG among various communities. Furthermore, 84 social determinants were identified and categorized into structural and intermediary determinants. ACPG is a set of complex behaviors associated with different individual sociodemographic and behavioral characteristics; living and working conditions; COVID-19 knowledge, attitudes, and risk perceptions; exposure to sources and information level; leisure activities; social support; trust; social norms; psychosocial well-being; socio-economic position; and the socio-economic and political context. Interventions to promote ACPG among the general population should consider the identified social determinants of ACPG.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- ISO 50001 based energy management system: a bibliometric perspective
Marlina Pandin, Sik Sumaedi, Aris Yaman, Meilinda Ayundyahrini, Nina Konitat Supriatna, Nurry Widya Hesty
International Journal of Energy Sector Management.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of long COVID-19 on posttraumatic stress disorder as modified by health literacy: an observational study in Vietnam
Han Thi Vo, Tien Duc Dao, Tuyen Van Duong, Tan Thanh Nguyen, Binh Nhu Do, Tinh Xuan Do, Khue Minh Pham, Vinh Hai Vu, Linh Van Pham, Lien Thi Hong Nguyen, Lan Thi Huong Le, Hoang Cong Nguyen, Nga Hoang Dang, Trung Huu Nguyen, Anh The Nguyen, Hoan Van Nguye
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2024; 15(1): 33. CrossRef - Cognitive predictors of COVID-19 mitigation behaviors in vaccinated and unvaccinated general population members
Anna Hudson, Peter A. Hall, Sara C. Hitchman, Gang Meng, Geoffrey T. Fong
Vaccine.2023; 41(27): 4019. CrossRef - Utilisation of rehabilitation due to mental disorders during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: a difference-in-differences analysis
Matthias Bethge, David Fauser, Pia Zollmann, Marco Streibelt
BMC Psychiatry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Perceptions about COVID-19 preventive measures among Ghanaian women
Frank Kyei-Arthur, Martin Wiredu Agyekum, Grace Frempong Afrifa-Anane, Reuben Tete Larbi, Peter Kisaakye, Dario Ummarino
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(4): e0284362. CrossRef - Cognitive and Emotional Motivation to Explain Infection-Prevention Behaviors with Social Support as a Mediator During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study in Korea
Myonghwa Park, Keunyeob Oh, Hyungjun Kim, Xing Fan, Thi-Thanh-Thnh Giap, Rhayun Song
Patient Preference and Adherence.2023; Volume 17: 1063. CrossRef - Factors Influencing COVID-19 Prevention Behavior: A Community-based Cross-sectional Study
Ernawaty Ernawaty, Nabilla Belqys Dherindri
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2023; 11(E): 191. CrossRef - The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Outcomes in Acute Pancreatitis: A Propensity Score Matched Study Comparing before and during the Pandemic
Patricia Mihaela Rădulescu, Elena Irina Căluianu, Emil Tiberius Traşcă, Dorin Mercuţ, Ion Georgescu, Eugen Florin Georgescu, Eleonora Daniela Ciupeanu-Călugăru, Maria Filoftea Mercuţ, Răzvan Mercuţ, Vlad Padureanu, Costin Teodor Streba, Cristina Călăraşu,
Diagnostics.2023; 13(14): 2446. CrossRef - COVID-19 in social networks: unravelling its impact on youth risk perception, motivations and protective behaviours during the initial stages of the pandemic
Marta Anson, Ksenia Eritsyan
International Journal of Adolescence and Youth.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bi-directional associations between mask usage and beliefs about reasons for masking before and after the downgrading of the legal status of COVID-19 in Japan: A longitudinal study
Michio Murakami
International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction.2023; 97: 104072. CrossRef - Geoepidemiological perspective on COVID-19 pandemic review, an insight into the global impact
Alexandre Vallée
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of COVID-19 Pandemic on Using CTS and MRI in Iran: Evidence from an Interrupted Time Series Analysis
Monireh Mahmood Pour-Azari, Nasim Badiee, Ali Kazemi Karyani, Shahin Soltani, Satar Rezaei
Journal of Health Reports and Technology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between social isolation and loneliness with COVID-19 vaccine uptake in Japan: a nationwide cross-sectional internet survey
Tomohiko Ukai, Takahiro Tabuchi
BMJ Open.2023; 13(11): e073008. CrossRef - Exploration of factors associated with mask-wearing and hand disinfection in Japan after the coronavirus disease outbreak: A longitudinal study
Michio Murakami, Mei Yamagata, Asako Miura
International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction.2023; 98: 104107. CrossRef - Social Determinants of Adherence to COVID-19 Preventive Guidelines in Iran: A Qualitative Study
Sina Ahmadi, Zahra Jorjoran Shushtari, Marzieh Shirazikhah, Akbar Biglarian, Seyed Fahim Irandoost, Toktam Paykani, Ali Almasi, Nader Rajabi-Gilan, Nafiul Mehedi, Yahya Salimi
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, .2022; 59: 004695802210841. CrossRef - Determinants of observing health protocols related to preventing COVID-19 in adult women: A qualitative study in Iran
Javad Yoosefi Lebni, Saeede Pavee, Mandana Saki, Arash Ziapour, Ahmad Ahmadi, Mehdi Khezeli
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Adherence to Coronavirus Disease 2019 Preventive Measures in a Representative Sample of the Population of the Canton of Vaud, Switzerland
Audrey Butty, Nolwenn Bühler, Jérôme Pasquier, Julien Dupraz, Vincent Faivre, Sandrine Estoppey, Cloé Rawlinson, Semira Gonseth Nusslé, Murielle Bochud, Valérie D’Acremont
International Journal of Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Quarantine preparedness – the missing factor in COVID-19 behaviour change? Qualitative insights from Australia
Angela Davis, Stephanie Munari, Joseph Doyle, Brett Sutton, Allen Cheng, Margaret Hellard, Lisa Gibbs
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on hospital admissions for nine diseases in Iran: insight from an interrupted time series analysis
Sina Ahmadi, Ali Kazemi-Karyani, Nasim Badiee, Sarah Byford, Ali Mohammadi, Bakhtiar Piroozi, Satar Rezaei
Cost Effectiveness and Resource Allocation.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychosocial Determinants of Hand Hygiene, Facemask Wearing, and Physical Distancing During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Wei Liang, Yanping Duan, Feifei Li, Ryan E Rhodes, Xiang Wang, Dehiwala Liyanage Ishanka Harshani Kusum Peiris, Lin Zhou, Borui Shang, Yide Yang, Julien S Baker, Jiao Jiao, Wei Han
Annals of Behavioral Medicine.2022; 56(11): 1174. CrossRef
- ISO 50001 based energy management system: a bibliometric perspective
- Validity and reliability of the Health-Related Quality of Life Instrument with 8 Items (HINT-8) in Korean breast cancer patients
- Juyoung Kim, Min-Woo Jo, Hyeon-Jeong Lee, Sei-Hyun Ahn, Byung Ho Son, Jong Won Lee, Sae Byul Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(4):254-263. Published online August 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0005
- 6,617 View
- 127 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
This study evaluated the validity and reliability of the Health-Related Quality of Life Instrument with 8 Items (HINT-8) in postoperative breast cancer patients in South Korea.
Methods
The study included 300 breast cancer patients visiting a tertiary hospital. We measured health-related quality of life (HRQoL) using the HINT-8, the 5-level EQ-5D version (EQ-5D-5L), and the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast (FACT-B). Discriminatory ability, known-group validity, and convergent validity were assessed. Reliability was evaluated with the Cohen kappa, weighted kappa, and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC).
Results
The EQ-5D-5L indexes (p<0.001) and EQ visual analogue scale (VAS) scores (p<0.001) were significantly higher in subjects with no problems in each item of the HINT-8 than in those with problems. The FACT-B total scores were also higher in subjects without problems on the HINT-8. Older age, lower education level, and comorbidities were associated with a lower HINT-8 index. The HINT-8 index was correlated with the EQ-5D-5L index and the EQ VAS, with correlation coefficients of 0.671 (p<0.001) and 0.577 (p<0.001), respectively. The correlation coefficients between the HINT-8 and the FACT-B ranged from 0.390 to 0.714. The ICC was 0.690 (95% confidence interval, 0.580–0.780).
Conclusion
The HINT-8 showed appropriate validity for capturing HRQoL in postoperative breast cancer patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health-related quality of life of premenopausal young breast cancer survivors undergoing endocrine therapy
Kyungmi Lee, Hye Suk Jun
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2024; 68: 102496. CrossRef - Smartphone application-based rehabilitation in patients with chronic respiratory and cardiovascular diseases
Chiwook Chung, Ah-Ram Kim, Dongbum Kim, Hee Kwon, Seong Ho Lee, Il-Young Jang, Min-Woo Jo, Do-Yoon Kang, Sei Won Lee
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Willingness to pay for integrative healthcare services to treat sleep disturbances: Evidence from a nationwide survey
Min Kyung Hyun
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2023; 58: 102223. CrossRef - Internal Structure of the Health-Related Quality of Life Instrument with 8-Items in a Nationally Representative Population
Eun-Hyun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(3): 359. CrossRef - Factors influencing health-related quality of life for young single-person households: the mediating effect of resilience
Soo Jin Lee, Sujin Lee, Xianglan Jin
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(3): 160. CrossRef - Smartphone application-based rehabilitation in patients with chronic respiratory and cardiovascular diseases: a randomised controlled trial study protocol
Chiwook Chung, Ah-Ram Kim, Il-Young Jang, Min-Woo Jo, Seongho Lee, Dongbum Kim, Hee Kwon, Do-Yoon Kang, Sei Won Lee
BMJ Open.2023; 13(9): e072698. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life among cancer patients and survivors and its relationship with current employment status
Woorim Kim, Kyu-Tae Han, Seungju Kim
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(5): 4547. CrossRef - Associations between Food Groups and Health-Related Quality of Life in Korean Adults
Shamirah Nabbosa, Sunghee Lee
Nutrients.2022; 14(17): 3643. CrossRef - Validity of the Health-Related Quality of Life Instrument with 8 Items (HINT-8) in the Korean Elderly: A Cross-Sectional Study
Seon-Ha Kim, Miok Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(3): 248. CrossRef
- Health-related quality of life of premenopausal young breast cancer survivors undergoing endocrine therapy
- Sex differences in weight perception and weight gain among Black college students in the USA
- Jounghee Lee, Jaesin Sa, Jean-Philippe Chaput, James Heimdal, Beatrice Nelson, Beom-Young Cho, Elizabeth Kwon
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(2):96-104. Published online April 29, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.12.2.07
- 5,994 View
- 122 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aims of this study were to examine the prevalence of overweight/obesity and to explore sex differences in body weight perceptions and correlates of weight gain among Black students at 2 historically Black colleges and universities (HBCUs) in the USA.
Methods
Participants completed a paper-based survey, and their height and weight were measured (67% completion rate).
Results
The overweight and obesity rates were 33.8% and 26.9%, respectively. More females than males accurately assessed their weight (p <0.05). Body weight underestimation was associated with male sex, excellent/very good perceived overall health, and not being informed by a doctor of having overweight or obesity (p <0.01). Higher odds of ≥5% weight gain were related to female sex, living on campus, and not being informed by a doctor of having overweight or obesity (p <0.05).
Conclusion
Given the high overweight and obesity rates among Black students, HBCUs in the USA should develop intervention strategies for the prevention and management of overweight and obesity. College health educators at HBCUs need to provide regular check-ups or health screenings that help male students perceive their weight accurately and prevent weight underestimation. It is important for HBCUs to monitor and address weight gain among Black students as early as possible. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sociodemographic factors associated with weight perception of adolescents: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Kaihan Yang, Anqi Zhao, Yujie Xie, Zhanyi Xu, Yubinxin Peng, Haiyang Tang
Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Nursin.2023; 36(2): 95. CrossRef
- Sociodemographic factors associated with weight perception of adolescents: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
- Use of Menstrual Sanitary Products in Women of Reproductive Age: Korea Nurses’ Health Study
- Hansol Choi, Nam-Kyoo Lim, Heeja Jung, Oksoo Kim, Hyun-Young Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(1):20-28. Published online February 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.12.1.04
- 9,624 View
- 259 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material Objectives The use of menstrual hygiene products and its effect on women’s health remains under studied. Patterns of menstrual hygiene product use and the rationale behind choices among Korean women aged 18–45 years were examined.
Methods This cross-sectional study was a part of the Korea Nurses’ Health Study. A total of 20,613 nurses participated, and 8,658 nurses participated in Module 7 which included a menstrual hygiene products-related survey. The data were collected through the mobile survey using a self-reported questionnaire. Participants’ use of menstrual hygiene products and related characteristics were analyzed using frequency (percentage) or mean (SD).
Results The most common types of menstrual hygiene products across all age groups were disposable menstrual pads (89.0%), followed by cloth menstrual pads (4.5%), tampons (4.2%), and only 1.6% used a menstrual cup. Disposable menstrual pads were the most common across all age groups, but in those aged under 30 years this was followed by tampon use (6%). The most important criteria when choosing a menstrual hygiene product was comfort for disposable menstrual pads (31.3%) and tampons (41.5%), natural ingredients or organic products for cloth menstrual pads (51.4%), and custom fit for the menstrual cup (50.7%). However, for all menstrual hygiene products (except cloth menstrual pads), there was a higher proportion of anxiety than perception of safety, and low awareness of toxic shock syndrome.
Conclusion It is important for women to use menstrual hygiene products with confidence. More research is needed to better understand potential health effects of menstrual hygiene products.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- MIMA 2.0 - Compact and portable Multifunctional IoT integrated Menstrual Aid
Kumar J. Jyothish, Shreya Shivangi, Amish Bibhu, Subhankar Mishra, Sulagna Saha
Internet of Things.2024; 25: 101075. CrossRef - Knowledge, attitude, and practice of menstrual hygiene at a medical and health sciences university
Rajani Dube, Huma Zaidi, Shehla Shafi Khan
Journal of Advanced Pharmacy Education and Researc.2024; 14(1): 63. CrossRef - Gynecological and Obstetric Crisis in Gaza Conflict Area: A Call for Action
Ibraheem Alkhawaldeh, Hamza Alsalhi, Mostafa Moawad, Yasmeen Jamal Alabdallat
JAP Academy Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Reusable period products: use and perceptions among young people in Victoria, Australia
Caitlin Ramsay, Julie Hennegan, Caitlin H. Douglass, Sarah Eddy, Alexandra Head, Megan S. C. Lim
BMC Women's Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploratory systematic review and meta-analysis on period poverty
Gayathri Delanerolle, Xiao-Jie Yang, Heitor Cavalini, Om P Kurmi, Camilla Mørk Røstvik, Ashish Shetty, Lucky Saraswat, Julie Taylor, Sana Sajid, Shanaya Rathod, Jian-Qing Shi, Peter Phiri
World Journal of Meta-Analysis.2023; 11(5): 196. CrossRef - Key findings on women’s reproductive health: the Korea Nurses’ Health Study
Chiyoung Cha, Heeja Jung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(2): 81. CrossRef - Nonconventional Menstrual Hygiene Products and its Usage among Reproductive age Group Women in India – A Cross-Sectional Study
Dharmaraj Rock Britto, Neethu George, Abdul Malik Shagirunisha Rizvana, Josephin Shalini Ratchagar, Tamilarasan Muniyapillai, Karthikeyan Kulothungan
Journal of Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Scienc.2023; 18(3): 357. CrossRef - Assessment of knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding menstruation and menstrual hygiene among early-reproductive aged women in Bangladesh: a cross-sectional survey
Abu Bakkar Siddique, Sudipto Deb Nath, Mahfuza Mubarak, Amena Akter, Sanjida Mehrin, Mst Jemi Hkatun, Antara Parvine Liza, M. Ziaul Amin
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Use and perceptions on reusable and non-reusable menstrual products in Spain: A mixed-methods study
Laura Medina-Perucha, Tomàs López-Jiménez, Anna Sofie Holst, Constanza Jacques-Aviñó, Jordina Munrós-Feliu, Cristina Martínez-Bueno, Carme Valls-Llobet, Diana Pinzón Sanabria, Mª Mercedes Vicente-Hernández, Anna Berenguera, Muhammad Shahzad Aslam
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(3): e0265646. CrossRef - Women’s attitudes toward certification logos, labels, and advertisements for organic disposable sanitary pads: results from a multi-city cross-sectional survey
Hayeon Kim, Jinyoung Jung, Yun-Kyoung Song, Taegwon Chang, Sungmin Park, Jiwon Park, Kyungim Kim
BMC Women's Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Sanitation and hygiene practices of secondary school students from Mtwara town in Tanzania
Obadia Kyetuza Bishoge, Ademola Kabir Aremu, Dickson Dare Ajayi, Sayoki Godfrey Mfinanga
International Journal of Health Promotion and Educ.2022; : 1. CrossRef
- MIMA 2.0 - Compact and portable Multifunctional IoT integrated Menstrual Aid
- Primary Healthcare Under Transformation in 3 Eastern European Countries: Quality Satisfaction as Rated by Students
- Sviatlana Ahiyevets, Andrei Shpakou, Joanna Baj-Korpak, Ewa Kleszczewska, Katarzyna Rzatkiewicz, Krzysztof Mancewicz, Valentina Stetsenko, Semen Stetsenko
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(5):286-295. Published online October 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.5.04
- 5,654 View
- 152 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This study aimed to determine the reasons for student dissatisfaction with the quality of primary healthcare (PHC) in countries under healthcare system transformation (Belarus, Poland, and Ukraine) to identify reserves and make improvements.
Methods A comparative multipopulation survey was translated, verified, and completed during face-to-face interviews during March 2019 to May 2019. There were 700 Humanities students included in this study to determine satisfaction with the quality of PHC provided by the family doctor. Satisfaction was assessed according to the availability of the doctor, the level of organization of the institution, the service process, the quality of the interaction with the doctor, adherence to the rights of patients, and any additional financial expense incurred by the patient.
Results Politeness and attentiveness of doctors were rated highly. Dissatisfaction was associated with the negative attitude of medical personnel towards the patient. One in 10 respondents replied that medical confidentiality was not observed. More than 65% of students had paid for diagnostic tests/or treatments, and some respondents from Poland and Ukraine were asked by the doctor to pay for services without a receipt.
Conclusion Dissatisfaction with the quality of PHC in countries under transformation of the health system was largely due to ethical aspects of the doctor-patient relationship. Therefore, ethical standards need to be upheld and patients need to be aware of these standards using medical education materials covering the moral aspects of the relationship between medical personnel and patient.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The perception of outpatient care quality by healthcare users in Ukraine
Valentyna Anufriyeva, Milena Pavlova, Tetiana Stepurko, Wim Groot
International Journal of Healthcare Management.2024; 17(1): 25. CrossRef - Satisfaction with primary health care in Ukraine in 2016–2020: A difference-in-differences analysis on repeated cross-sectional data
Valentyna Anufriyeva, Milena Pavlova, Tetiana Chernysh (Stepurko), Wim Groot
Health Policy.2023; 137: 104916. CrossRef
- The perception of outpatient care quality by healthcare users in Ukraine
- Relationship Between Assertion and Aggression with Addiction Potential: A Cross-Sectional Study in 2019
- Mohammad Amiri, Zakieh Sadeghi, Elham Sadeghi, Ahmad Khosravi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(4):231-238. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.4.12
- 6,204 View
- 89 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This study aimed to determine the relationship between assertion and aggression with addiction potential among students in Shahroud University of Medical Sciences.
Methods In this cross-sectional study conducted in 2019, 500 students of Shahroud University of Medical Sciences, were selected by multistage random sampling, for a study using the Addiction Potential Scale, and Assertion and Aggression Questionnaires. Data were analyzed using ANOVA, Chi-square,
t test, Pearson’s correlation coefficient, and the linear regression model.Results The mean scores of addiction potential, aggression, and assertion were 32.7 ± 17.2, 41.5 ± 12.9 and 139.4 ± 22.3, respectively. In this study, 38.8% (
N = 194) of students had high aggression and 76.8% (N = 384) had high assertion. In the regression model, aggression, history of drug and addictive substances abuse, history of tobacco use, and history of alcohol abuse were significantly related to addiction potential (p ≤ 0.05). There was a negative relationship between assertion and addiction potential so that with one-unit increase in the assertion score, the addiction potential score decreased by −0.11.Conclusion Given the direct relationship between aggression and addiction potential, and since more than three-quarters of the students had moderate to high aggression, it is necessary to pay more attention to this issue. Interventions may play an important role in improving the current situation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perceived personality traits and parenting styles on addiction potentiality among nursing students
Sabah AliMohammed Elsisi, MonaHamdy Mostafa, Mohamed AbdEl-Fattah Khalil, Sayeda Mohamed
Egyptian Nursing Journal.2023; 20(1): 138. CrossRef - From emotional intelligence to suicidality: a mediation analysis in patients with borderline personality disorder
Mohsen Khosravi, Fahimeh Hassani
BMC Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Addiction Potential and its Correlates Among Medical Students
Mohammad Amiri, Ahmad Khosravi, Reza Chaman, Zakieh Sadeghi, Elham Sadeghi, Mehdi Raei
The Open Public Health Journal.2021; 14(1): 32. CrossRef - Exploring the Influence of Parenting Style on Adolescents’ Maladaptive Game Use through Aggression and Self-Control
Hyeon Gyu Jeon, Sung Je Lee, Jeong Ae Kim, Gyoung Mo Kim, Eui Jun Jeong
Sustainability.2021; 13(8): 4589. CrossRef
- Perceived personality traits and parenting styles on addiction potentiality among nursing students
- Epidemiological Characteristics of Field Tick-Borne Pathogens in Gwang-ju Metropolitan Area, South Korea, from 2014 to 2018
- Jung Wook Park, Seung Hun Lee, Gi Seong Lee, Jin Jong Seo, Jae Keun Chung
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(4):177-184. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.4.06
- 6,379 View
- 101 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The importance of tick-borne diseases is increasing because of climate change, with a lack of long-term studies on tick-borne pathogens in South Korea. To understand the epidemiological characteristics of tick-borne diseases, the monthly distribution of field ticks throughout the year was studied in South Korea between May 2014 and April 2018 in a cross sectional study.
Methods The presence of various tick-borne pathogens (
Rickettsia species,Borrelia species,Anaplasma phagocytophilum ) was confirmed by using polymerase chain reaction, to provide information for a prevention strategy against tick-borne pathogenic infections, through increased understanding of the relationship between seasonal variation and risk of infection withRickettsia species. This was performed using logistic regression analysis (SPSS 20, IBM, USA) of the data obtained from the study.Results During the study period there were 11,717 ticks collected and 4 species identified.
Haemapysalis longicornis was the most common species (n = 10,904, 93.1%), followed byHaemapysalis flava (n = 656, 5.6%),Ixodes nipponensis (n = 151, 1.3%), andAmblyomma testudinarium (n = 6, 0.05%) The results of this cross-sectional study showed thatHaemapysalis flava carried a higher risk of transmission ofRickettsia species than other tick species (p < 0.05).Conclusion In conclusion, due attention should be paid to preventing tick-borne infections in humans whilst engaged in outdoor activities in Spring and Autumn, particularly in places where there is a high prevalence of ticks.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effective Methods of Estimation of Pathogen Prevalence in Pooled Ticks
Gerardo Fracasso, Marika Grillini, Laura Grassi, Francesco Gradoni, Graziana da Rold, Michela Bertola
Pathogens.2023; 12(4): 557. CrossRef - Applying next generation sequencing to detect tick-pathogens in Dermacentor nuttalli, Ixodes persulcatus, and Hyalomma asiaticum collected from Mongolia
Graham A. Matulis, Jira Sakolvaree, Bazartseren Boldbaatar, Nora Cleary, Ratree Takhampunya, B. Katherine Poole-Smith, Abigail A. Lilak, Doniddemberel Altantogtokh, Nyamdorj Tsogbadrakh, Nitima Chanarat, Nittayaphon Youngdech, Erica J. Lindroth, Jodi M. F
Ticks and Tick-borne Diseases.2023; 14(5): 102203. CrossRef - Molecular Detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Ehrlichia Species in Ticks Removed from Humans in the Republic of Korea
Yu-Jung Kim, Ji Ye Seo, Seong Yoon Kim, Hee Il Lee
Microorganisms.2022; 10(6): 1224. CrossRef - Molecular Detection and Phylogeny of Tick-Borne Pathogens in Ticks Collected from Dogs in the Republic of Korea
A-Tai Truong, Jinhyeong Noh, Yeojin Park, Hyun-Ji Seo, Keun-Ho Kim, Subin Min, Jiyeon Lim, Mi-Sun Yoo, Heung-Chul Kim, Terry A. Klein, Hyunkyoung Lee, Soon-Seek Yoon, Yun Sang Cho
Pathogens.2021; 10(5): 613. CrossRef - iSeq 100 for metagenomic pathogen screening in ticks
Ju Yeong Kim, Myung-hee Yi, Alghurabi Areej Sabri Mahdi, Tai-Soon Yong
Parasites & Vectors.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular Identification of Borrelia spp. from Ticks in Pastures Nearby Livestock Farms in Korea
Haeseung Lee, Seung-Hun Lee, SungShik Shin, Dongmi Kwak
Insects.2021; 12(11): 1011. CrossRef
- Effective Methods of Estimation of Pathogen Prevalence in Pooled Ticks



 First
First Prev
Prev


