Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Household secondary attack rates and risk factors during periods of SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variant predominance in the Republic of Korea
- Jin Lee, Mijeong Ko, Seontae Kim, Dosang Lim, Gemma Park, Sang-Eun Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):263-271. Published online August 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0133
- 1,900 View
- 133 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
The household secondary attack rate (SAR) of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is an important indicator for community transmission. This study aimed to characterize transmission by comparing household SARs and identifying risk factors during the periods of Delta and Omicron variant predominance in Republic of Korea.
Methods
We defined the period of Delta variant predominance (Delta period) as July 25, 2021 to January 15, 2022, and the period of Omicron variant predominance (Omicron period) as February 7 to September 3, 2022. The number of index cases included was 214,229 for the Delta period and 5,521,393 for the Omicron period. To identify the household SARs and risk factors for each period, logistic regression was performed to determine the adjusted odds ratio (aOR).
Results
The SAR was 35.2% for the Delta period and 43.1% for the Omicron period. The aOR of infection was higher in 2 groups, those aged 0 to 18 years and ≥75 years, compared to those aged 19 to 49 years. Unvaccinated individuals (vs. vaccinated individuals) and individuals experiencing initial infection (vs. individuals experiencing a second or third infection) had an increased risk of infection with SARS-CoV-2.
Conclusion
This study analyzed the household SARs and risk factors. We hope that the results can help develop age-specific immunization plans and responses to reduce the SAR in preparation for emerging infectious diseases or potential new variants of SARS-CoV-2.
- Risk factors for transmission in a COVID-19 cluster infection in a high school in the Republic of Korea
- Jin-Hwan Jeon, Su Jin Kang, Se-Jin Jeong, Hyeon-Cheol Jang, Young-Joon Park, Sang-Eun Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):252-262. Published online July 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0125
- 3,460 View
- 192 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
This study aimed to examine the scale, characteristics, risk factors, and modes of transmission in a coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak at a high school in Seoul, Republic of Korea.
Methods
An epidemiological survey was conducted of 1,118 confirmed cases and close contacts from a COVID-19 outbreak at an educational facility starting on May 31, 2021. In-depth interviews, online questionnaires, flow evaluations, and CCTV analyses were used to devise infection prevention measures. Behavioral and spatial risk factors were identified, and statistical significance was tested.
Results
Among 3rd-year students, there were 33 confirmed COVID-19 cases (9.6%). Students who used a study room in the annex building showed a statistically significant 4.3-fold elevation in their relative risk for infection compared to those who did not use the study room. Moreover, CCTV facial recognition analysis confirmed that 17.8% of 3rd-year students did not wear masks and had the lowest percentage of mask-wearers by grade. The air epidemiological survey conducted in the study room in the annex, which met the 3 criteria for a closed space, confirmed that there was only 10% natural ventilation due to the poor ventilation system.
Conclusion
To prevent and manage the spread of COVID-19 in educational facilities, advance measures that consider the size, operation, and resources of each school are crucial. In addition, various survey methodologies should be used in future studies to quickly analyze a wider range of data that can inform an evidence-based quarantine response. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Detection of a cluster of Omicron's BA.4 sublineage in Northern Senegal and identification of the first XAS recombinant variant in Senegal
Martin Faye, Modeste Name Faye, Babacar Ndiaye, Moussa Moïse Diagne, Safietou Sankhe, Ndeye Marième Top, Amadou Diallo, Cheikh Loucoubar, Ndongo Dia, Amadou Alpha Sall, Ousmane Faye
Virus Research.2024; 339: 199259. CrossRef
- Detection of a cluster of Omicron's BA.4 sublineage in Northern Senegal and identification of the first XAS recombinant variant in Senegal
- Risk factors associated with death due to severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in hospitalized Korean patients (2018–2022)
- Jia Kim, Hyo-jeong Hong, Ji-hye Hwang, Na-Ri Shin, Kyungwon Hwang
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):151-163. Published online June 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0048
- 1,677 View
- 176 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 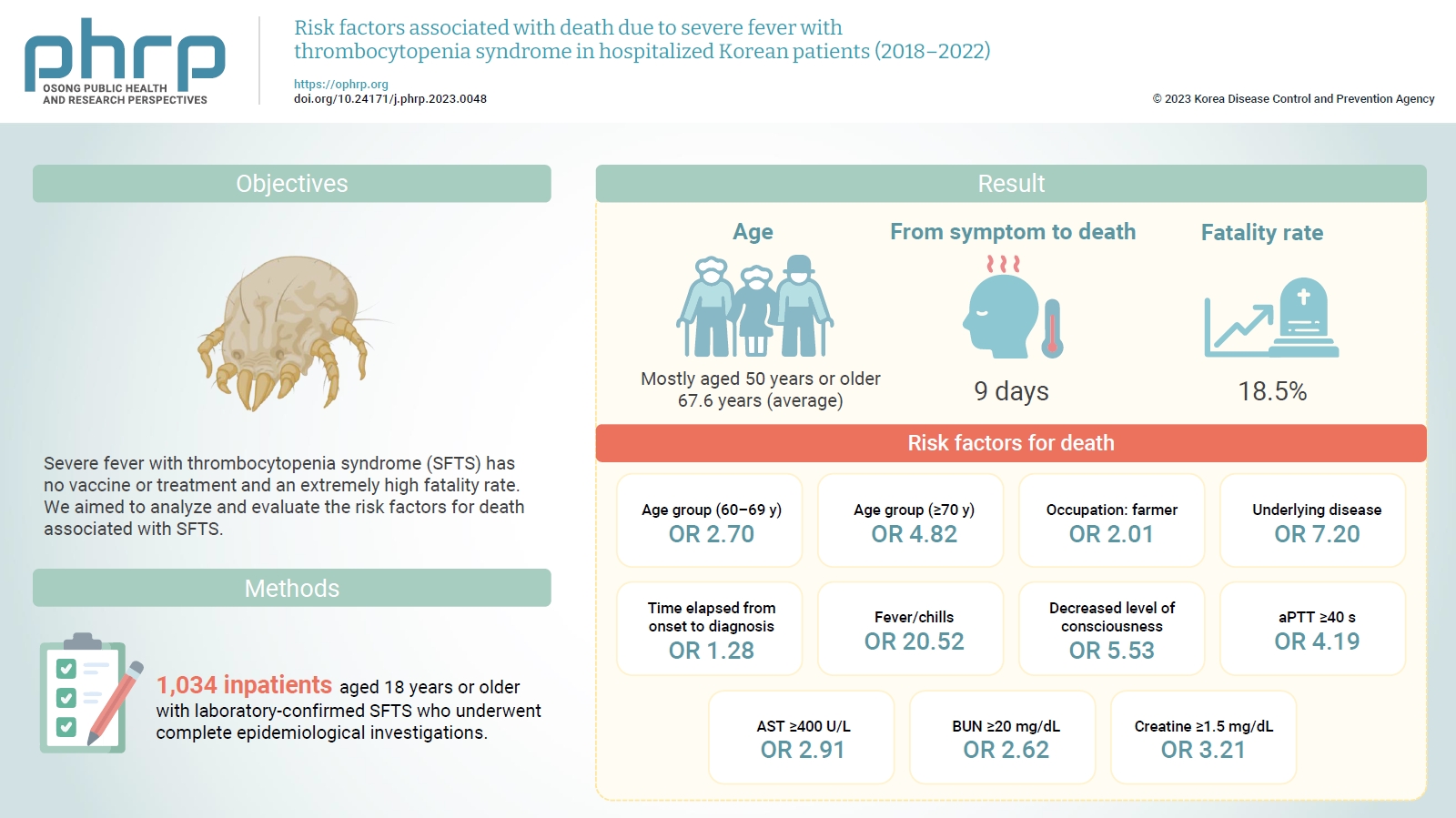
- Objectives
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) has no vaccine or treatment and an extremely high fatality rate. We aimed to analyze and evaluate the risk factors for death associated with SFTS.
Methods
Among reports from 2018 to 2022, we compared and analyzed 1,034 inpatients aged 18 years or older with laboratory-confirmed SFTS who underwent complete epidemiological investigations.
Results
Most of the inpatients with SFTS were aged 50 years or older (average age, 67.6 years). The median time from symptom onset to death was 9 days, and the average case fatality rate was 18.5%. Risk factors for death included age of 70 years or older (odds ratio [OR], 4.82); agriculture-related occupation (OR, 2.01); underlying disease (OR, 7.20); delayed diagnosis (OR, 1.28 per day); decreased level of consciousness (OR, 5.53); fever/chills (OR, 20.52); prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time (OR, 4.19); and elevated levels of aspartate aminotransferase (OR, 2.91), blood urea nitrogen (OR, 2.62), and creatine (OR, 3.21).
Conclusion
The risk factors for death in patients with SFTS were old age; agriculture-related occupation; underlying disease; delayed clinical suspicion; fever/chills; decreased level of consciousness; and elevated activated partial thromboplastin time, aspartate aminotransferase, blood urea nitrogen, and creatine levels.
- Risk factors for deaths associated with COVID-19 according to the cause of death classification in Republic of Korea
- Na-Young Kim, Seong-Sun Kim, Hyun Ju Lee, Dong Hwi Kim, Boyeong Ryu, Eunjeong Shin, Donghyok Kwon
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(2):89-99. Published online April 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0312
- 1,452 View
- 93 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
This study aimed to classify coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-related deaths according to whether COVID-19 was listed as the cause of death, and to investigate the differences in demographic characteristics and risk factors for COVID-19 death classifications.
Methods
A total of 5,625 deaths in South Korea among patients with confirmed COVID-19 from January 20, 2020 to December 31, 2021 were selected. Excluding false reports and unnatural deaths, 5,597 deaths were analyzed. Based on death report data, deaths were classified according to whether the cause of death was listed as COVID-19 (CD) or not (NCD). The epidemiological characteristics and causes of deaths were investigated using descriptive, univariate, and multivariate statistical analyses. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated to analyze the risk factors.
Results
The case fatality ratio was 0.89% and increased with age. Additionally, 96.4% of the subjects had an underlying disease, and 53.4% died in winter. The proportion of NCDs was 9.3%, of whom 19.1% died at home and 39.0% were confirmed to have COVID-19 after death. Malignant neoplasms (102/416 vs. 637/4,442; OR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.36−2.16; p<0.001) were significantly associated with NCD.
Conclusion
This is the first study to analyze risk factors by cause of death using COVID-19 death report data in South Korea. These results are expected to be used as evidence for establishing a death monitoring system that can collect timely information in a new infectious disease pandemic.
- Analysis of risk factors affecting suicidal ideation in South Korea by life cycle stage
- Ji-Young Hwang, Il-Su Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(5):314-323. Published online October 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0208
- 4,743 View
- 124 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study analyzed risk factors for suicidal ideation in South Koreans from a life cycle perspective.
Methods
A secondary analysis was conducted of data collected in 2015 as part of the 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). The participants comprised 5,935 individuals aged 12 years or older. The statistical analysis reflected the complex sampling design of the KNHANES, and the Rao-Scott chi-square test and multiple logistic regression analysis were performed.
Results
The prevalence of suicidal ideation was 5.7% in adolescents, 3.7% in young adults, 5.4% in middle-aged adults, and 7.0% in older adults. Depression and stress were risk factors in every stage of the life cycle. In those aged 12 to 19 years, activity restrictions were significantly associated with suicidal ideation. Education and subjective health status were risk factors in adults aged 20 to 39 years, and education, activity restrictions, and quality of life were the major risk factors in those aged 40 to 64 years. For adults 65 years of age or older, the risk of suicidal ideation was higher among those with inappropriate sleep time.
Conclusion
The risk factors for suicidal ideation were found to be different across stages of the life cycle. This suggests a need for individualized suicide prevention plans and specific government policies that reflect the characteristics of each life cycle stage. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between long working hours and the development of suicidal ideation among female workers: An 8-year population-based study using the Korean Longitudinal Survey of Women & Family (2012–2020)
Seong-Uk Baek, Yu-Min Lee, Jin-Ha Yoon
Psychiatry Research.2024; 333: 115731. CrossRef - Alcohol Consumption and Quality of Life in Middle-aged Men
Jeong-Sook Lee
International Journal of High Risk Behaviors and A.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Related to Suicidal Ideation by Gender and Age Group in Korean Adults
Eun Young Kim, Yong Whi Jeong, Jihye Lim, Dae Ryong Kang
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Sleep Duration and Symptoms of Depression Aged between 18 and 49: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES Ⅶ) from 2016 to 2018
Sung-Yong Choi, Ji-Eun Han, Jiae Choi, Minjung Park, Soo-Hyun Sung, Angela Dong-Min Sung
Healthcare.2022; 10(11): 2324. CrossRef
- Association between long working hours and the development of suicidal ideation among female workers: An 8-year population-based study using the Korean Longitudinal Survey of Women & Family (2012–2020)
- COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Laboratory Findings, Comorbidities, and Clinical Outcomes Comparing Medical Staff versus the General Population
- Mina Ebrahimi, Amal Saki Malehi, Fakher Rahim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(5):269-279. Published online October 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.5.02
- 8,442 View
- 125 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material This review compared coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) laboratory findings, comorbidities, and clinical outcomes in patients from the general population versus medical staff to aid diagnosis of COVID-19 in a more timely, efficient, and accurate way. Electronic databases were searched up to 23rd March, 2020. The initial search yielded 6,527 studies. Following screening, 24 studies were included [18 studies (11,564 cases) of confirmed COVID-19 cases in the general public, and 6 studies (394 cases) in medical staff] in this review. Significant differences were observed in white blood cell counts (
p < 0.001), lymphocyte counts (p < 0.001), platelet counts (p = 0.04), procalcitonin levels (p < 0.001), lactate dehydrogenase levels (p < 0.001), and creatinine levels (p = 0.03) when comparing infected medical staff with the general public. The mortality rate was higher in the general population than in medical staff (8% versus 2%). This review showed that during the early stages of COVID-19, laboratory findings alone may not be significant predictors of infection and may just accompany increasing C-reactive protein levels, erythrocyte sedimentation rates, and lactate dehydrogenase levels. In the symptomatic stage, the lymphocyte and platelet counts tended to decrease. Elevated D-dimer fibrin degradation product was associated with poor prognosis.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- microRNA-185 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection through the Modulation of the Host’s Lipid Microenvironment
Nadine Ahmed, Magen E. Francis, Noreen Ahmed, Alyson A. Kelvin, John Paul Pezacki
Viruses.2023; 15(9): 1921. CrossRef - Protective action of natural and induced immunization against the occurrence of delta or alpha variants of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a test-negative case-control study
Giovanni Corrao, Matteo Franchi, Federico Rea, Danilo Cereda, Antonio Barone, Catia Rosanna Borriello, Petra Giulia Della Valle, Michele Ercolanoni, Ida Fortino, Jose Jara, Olivia Leoni, Francesco Mazziotta, Elisabetta Pierini, Giuseppe Preziosi, Marcello
BMC Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Balancing Benefits and Harms of COVID-19 Vaccines: Lessons from the Ongoing Mass Vaccination Campaign in Lombardy, Italy
Giovanni Corrao, Federico Rea, Matteo Franchi, Danilo Cereda, Antonio Barone, Catia Rosanna Borriello, Giulia Petra Della Valle, Michele Ercolanoni, Jose Jara, Giuseppe Preziosi, Manuel Maffeo, Francesco Mazziotta, Elisabetta Pierini, Francesco Lecis, Pie
Vaccines.2022; 10(4): 623. CrossRef - Vulnerability Predictors of Post-Vaccine SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Disease—Empirical Evidence from a Large Population-Based Italian Platform
Giovanni Corrao, Matteo Franchi, Danilo Cereda, Francesco Bortolan, Olivia Leoni, Catia Rosanna Borriello, Petra Giulia Della Valle, Marcello Tirani, Giovanni Pavesi, Antonio Barone, Michele Ercolanoni, Jose Jara, Massimo Galli, Guido Bertolaso
Vaccines.2022; 10(6): 845. CrossRef - Factors associated with severe or fatal clinical manifestations of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection after receiving the third dose of vaccine
Giovanni Corrao, Matteo Franchi, Danilo Cereda, Francesco Bortolan, Olivia Leoni, Jose Jara, Giuseppina Valenti, Giovanni Pavesi
Journal of Internal Medicine.2022; 292(5): 829. CrossRef - Role of multiresolution vulnerability indices in COVID-19 spread in India: a Bayesian model-based analysis
Rupam Bhattacharyya, Anik Burman, Kalpana Singh, Sayantan Banerjee, Subha Maity, Arnab Auddy, Sarit Kumar Rout, Supriya Lahoti, Rajmohan Panda, Veerabhadran Baladandayuthapani
BMJ Open.2022; 12(11): e056292. CrossRef - A novel multi-omics-based highly accurate prediction of symptoms, comorbid conditions, and possible long-term complications of COVID-19
Debmalya Barh, Sandeep Tiwari, Bruno Silva Andrade, Marianna E. Weener, Aristóteles Góes-Neto, Vasco Azevedo, Preetam Ghosh, Kenneth Blum, Nirmal Kumar Ganguly
Molecular Omics.2021; 17(2): 317. CrossRef - Clinical and laboratory factors associated with coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid‐19): A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Le Huu Nhat Minh, Ali Ahmed‐Fouad Abozaid, Nam Xuan Ha, Loc Le Quang, Abdelrahman Gamil Gad, Ranjit Tiwari, Tran Nhat‐Le, Dinh Kim Quyen, Balqees AL‐Manaseer, Nguyen Dang Kien, Nguyen Lam Vuong, Ahmad Helmy Zayan, Le Huu Hanh Nhi, Kadek Agus Surya Dila, J
Reviews in Medical Virology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiologic and Clinic Characteristics of the First Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Hospitalized Patients from Galați County
Mihaela-Camelia Vasile, Anca-Adriana Arbune, Gabriela Lupasteanu, Constantin-Marinel Vlase, George-Cosmin Popovici, Manuela Arbune
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(18): 4210. CrossRef - Human Amniotic Fluid for the Treatment of Hospitalized, Symptomatic, and Laboratory-verified SARS-CoV-2 Patients
Mojgan Barati, Fakher Rahim
The Open Biology Journal.2021; 9(1): 36. CrossRef - Stratification of the risk of developing severe or lethal Covid-19 using a new score from a large Italian population: a population-based cohort study
Giovanni Corrao, Federico Rea, Flavia Carle, Salvatore Scondotto, Alessandra Allotta, Vito Lepore, Antonio D'Ettorre, Cinzia Tanzarella, Patrizia Vittori, Sabrina Abena, Marica Iommi, Liana Spazzafumo, Michele Ercolanoni, Roberto Blaco, Simona Carbone, Cr
BMJ Open.2021; 11(11): e053281. CrossRef
- microRNA-185 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection through the Modulation of the Host’s Lipid Microenvironment
- Risk Factors in Early Life for Preschool Children in Korea that are Associated with Being Overweight or Obese
- Jin Suk Ra, Hyun Jung Yun
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(1):15-26. Published online February 28, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.1.04
- 6,528 View
- 136 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The present study addressed the risk factors in early life for Korean preschool children that are associated with being overweight or obese.
Methods A descriptive cross-sectional design was used to conduct this study, which included 507 mothers with preschool children aged 3–5 years, who attended daycare centers. Data were acquired via a self-administered questionnaire completed by the mothers. Of the 650 questionnaires that were distributed, 507 (78%) were completed and sent back. Multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to identify risk factors in early life, which may contribute to being overweight or obese in preschool children.
Results Fifty-eight (11.4%) preschool children were overweight and 41 (8.1%) were obese. Multivariate logistic regression analysis with adjustment for covariates, revealed a significant association with the introduction of solid foods before 4 months of age [adjusted odds ratio (aOR) = 9.49,
p = 0.029] and a nonresponsive feeding style (aOR = 2.80,p = 0.043) with being overweight or obese in preschool children.Conclusion The findings of this study highlighted the need for parenting education programs on feeding practices to increase their understanding of hunger and satiety cues in infants, and appropriate timing for the introduction of solid foods.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Systematic review and meta‐analysis of breastfeeding and later overweight or obesity expands on previous study for World Health Organization
Bernardo Lessa Horta, Nigel Rollins, Mariane S. Dias, Valquiria Garcez, Rafael Pérez‐Escamilla
Acta Paediatrica.2023; 112(1): 34. CrossRef
- Systematic review and meta‐analysis of breastfeeding and later overweight or obesity expands on previous study for World Health Organization
- Enteroparasitism and Risk Factors Associated with Clinical Manifestations in Children and Adults of Jalisco State in Western Mexico
- María de la Luz Galván-Ramírez, Ana Luisa Madriz-Elisondo, Cynthia Guadalupe Temores Ramírez, Jorge de Jesús Romero Rameño, Dania Araceli de la O Carrasco, Marco Antonio Cardona López
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(1):39-48. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.1.08
- 8,314 View
- 123 Download
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives To determine the prevalence and risk factors associated with intestinal parasites in the population of San Juan Cosala, Jalisco, Mexico.
Methods A total of 277 samples from 104 participants were analysed using direct smear, flotation, formaldehyde/ethyl acetate, and modified Kinyoun’s acid-fast stain methods. The Graham method was applied only for samples from children under 12 years of age for the diagnosis of
Enterobius vermicularis. Results The prevalence of parasite infections in the study population was 77.9% including:
Entamoeba histolytica/E. dispar/E. moshkovskii/E. bangladeshi (37.5%),Giardia intestinalis (11.5%);commensals: Endolimax nana (44.2%),Entamoeba coli (27.9%),Chilomastix mesnili (6.7%) andIodamoeba bütschlii , (2.9%); emerging intestinal protozoans:Blastocystis spp. (49%),Cryptosporidium spp. (7.7%) andCyclospora cayetanensis (2.9%); and helminths:Enterobius vermicularis (18.3%) andAscaris lumbricoides (5.8%). The results also showed that 58.64% of the studied population presented polyparasitism. A significant association was found between protozoan infections and housewives, and houses that were not built with concrete ceilings, brick walls and cement floors (p < 0.05).Conclusion Polyparasitism was observed in over half the study population. The most prevalent parasite was
Blastocystis spp, whilst the prevalence of helminths was less than that of protozoans. The risk factors for infection to intestinal parasites were being a housewife and not having solid brick, cement and concrete materials for house construction.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intestinal parasite infections associated with sociodemographic and seasonal factors in the Western Amazon
Gustavo Henrique Sinhorin, Ana Carolina Gomes Carneiro, Beatrice Emeli Silva Farias, Patrícia de Almeida, Antônio Ralph Medeiros-Sousa, Leonardo Augusto Kohara Melchior, Andreia Fernandes Brilhante
Parasitology Research.2023; 122(2): 419. CrossRef - Prevalence of Enterobius vermicularis among children in Iran: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis
Elnaz Moussavi, Mohammad Houssaini, Nader Salari, Mahvan Hemmati, Ahmad Abdullahi, Ali Asghar Khaleghi, Shamarina Shohaimi, Masoud Mohammadi
Parasite Epidemiology and Control.2023; 22: e00315. CrossRef - Improved household flooring is associated with lower odds of enteric and parasitic infections in low- and middle-income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Hugo Legge, Rachel L. Pullan, Benn Sartorius, Srinivasa Rao Mutheneni
PLOS Global Public Health.2023; 3(12): e0002631. CrossRef - Enterobiasis among Yemeni children: a cross-sectional study
Abdulelah H. Al-Adhroey, Yahya A. Al-Ansi, Mohammed A. Al-Kholani, Abdulrahman H. Amer, Marwan M. Al-Khyat, Fadia H. Al Hubaishi, Radhwan H. Aziz, Ebrahim S. Al-Khateeb, Souad A. Al-Gabri, Tawfik M. Al-Gabri
Journal of Parasitic Diseases.2022; 46(3): 722. CrossRef - Prevalence of human cryptosporidiosis in the Americas: systematic review and meta-analysis
Higor Wilson Jann, Mauro Jorge Cabral-Castro, João Victor Barreto Costa, Alba Cristina Miranda de Barros Alencar, José Mauro Peralta, Regina Helena Saramago Peralta
Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de São P.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Frecuencia de parasitosis intestinal en escuelas primarias en Veracruz, México
Vanessa Oceguera-Segovia, Gabriel Obed Martínez-Rodríguez, Janet Michelle Villafuerte-Ordaz, Xóchitl Magnolia Alanís-Reyes, Angel Alberto Puig-Lagunes
Revista Mexicana de Pediatría.2022; 89(4): 146. CrossRef - Intestinal protozoa and helminths in ulcerative colitis and the influence of anti-parasitic therapy on the course of the disease
Abdurakhim Toychiev, Behzod Navruzov, Dinora Pazylova, Nikolay Davis, Najiya Badalova, Svetlana Osipova
Acta Tropica.2021; 213: 105755. CrossRef - Contamination of fresh produce sold on the Italian market with Cyclospora cayetanensis and Echinococcus multilocularis
Alessandra Barlaam, Tamirat T. Temesgen, Kristoffer R. Tysnes, Laura Rinaldi, Nicola Ferrari, Anna R. Sannella, Giovanni Normanno, Simone M. Cacciò, Lucy J. Robertson, Annunziata Giangaspero
Food Microbiology.2021; 98: 103792. CrossRef - The role of environmental factors in the realization of the epidemic process on ascariasis
Anton A. Martsev
Hygiene and sanitation.2021; 100(3): 218. CrossRef - Epidemiology of Intestinal Parasites in Pediatric Patients: Example of Ordu Province
Emine YURDAKUL ERTÜRK, Ülkü KARAMAN, Yeliz KAŞKO ARICI, Cemil ÇOLAK, Gamze YOLALAN, Şermin TOP
Online Türk Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2021; 6(3): 391. CrossRef - Molecular genotyping of Blastocystis spp. in wild mammals from Mexico
Fernando Martinez-Hernandez, Jose Alejandro Martinez-Ibarra, Eduardo Lopez-Escamilla, Claudia Villanueva-Garcia, Claudia Irais Muñoz-Garcia, Emilio Rendon-Franco, Pablo Maravilla, Guiehdani Villalobos
Parasitology Research.2020; 119(1): 97. CrossRef - The association between the lack of safe drinking water and sanitation facilities with intestinal Entamoeba spp infection risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Hamid Atabati, Hamid Kassiri, Ehsan Shamloo, Mitra Akbari, Ali Atamaleki, Fatemeh Sahlabadi, Nguyen Thi Thuy Linh, Ali Rostami, Yadolah Fakhri, Amin Mousavi Khaneghah, Chia Kwung Fan
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(11): e0237102. CrossRef - Cyclospora cayetanensis and Cyclosporiasis: An Update
Sonia Almeria, Hediye N. Cinar, Jitender P. Dubey
Microorganisms.2019; 7(9): 317. CrossRef
- Intestinal parasite infections associated with sociodemographic and seasonal factors in the Western Amazon
- Intra-Oral Factors Influencing Halitosis in Young Women
- Ho Sun Shon, Kyoung Ok Kim, Jae Kwan Jung, Eun Jong Cha, Su Ok Lee, Kyung Ah Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(6):340-347. Published online December 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.6.08
- 5,248 View
- 40 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The aim of this research was to determine intra-oral factors that affect halitosis in young women.
Methods This study was performed between March 2014 to May 2014, and included 35 women in their 20s with good oral health. Correlation and logistic regression analyses were performed to investigate the change in halitosis immediately, and 1 hour after scaling.
Results In both oral gas (OG) and extraoral gas (EG) groups, halitosis was reduced after scaling compared to before scaling. The logistic regression analysis of oral state factors in OG showed that as oral fluid [odds ratio (OR) = 0.792,
p = 0.045] and dental plaque (OR = 0.940,p = 0.016) decreased by 1 unit, the OR in the OG group decreased (> 50). In addition, as glucose levels in the oral cavity (OR = 1.245,p = 0.075) and tongue coating index (OR = 2.912,p = 0.064) increased by 1 unit, the OR in the OG group increased (> 50). Furthermore, in the EG group, as oral fluid (OR = 0.66,p = 0.01) and dental plaque (OR = 0.95,p = 0.04) decreased, the OR in the EG group decreased (> 50) significantly.Conclusion To control halitosis, it is necessary to increase oral fluid and decrease the amount of tongue plaque. Furthermore, maintaining a healthy oral environment, aided by regular scaling and removal of dental plaque, may significantly control halitosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and associated factors of self‐reported halitosis among institutionalized adolescents: Cross‐sectional study
Francisco Wilker Mustafa Gomes Muniz, Laura Barreto Moreno, Taciane Menezes da Silviera, Cassiano Kuchenbecker Rösing, Paulo Roberto Grafitti Colussi
International Journal of Dental Hygiene.2023; 21(2): 409. CrossRef - Validation of the Romanian Version of the Halitosis Associated Life-Quality Test (HALT) in a Cross-Sectional Study among Young Adults
Raluca Briceag, Aureliana Caraiane, Gheorghe Raftu, Melania Lavinia Bratu, Roxana Buzatu, Liana Dehelean, Mariana Bondrescu, Felix Bratosin, Bogdan Andrei Bumbu
Healthcare.2023; 11(19): 2660. CrossRef - Role of Probiotics in Halitosis of Oral Origin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Studies
Nansi López-Valverde, Antonio López-Valverde, Bruno Macedo de Sousa, Cinthia Rodríguez, Ana Suárez, Juan Manuel Aragoneses
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Microbiota in intra-oral halitosis – characteristics, effects of antibacterial mouth rinse treatment
D. S. Vikina, I. N. Antonova, V. V. Tec, T. E. Lazareva
Parodontologiya.2020; 25(1): 4. CrossRef
- Prevalence and associated factors of self‐reported halitosis among institutionalized adolescents: Cross‐sectional study
- Association between Beta-lactam Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Factors in AmpC Producing Clinical Strains of
P. aeruginosa - Sanaz Dehbashi, Hamed Tahmasebi, Mohammad Reza Arabestani
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(6):325-333. Published online December 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.6.06
- 22,890 View
- 134 Download
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The purpose of this study was to determine the presence of
IMP andOXA genes in clinical strains ofPseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa ) that are carriers of theampC gene.Methods In this study, 105 clinical isolates of
P. aeruginosa were collected. Antibiotic resistance patterns were determined using the disk diffusion method. The strains carrying AmpC enzymes were characterized by a combination disk method. Multiplex-PCR was used to identify resistance and virulence genes, chi-square test was used to determine the relationship between variables.Results Among 105 isolates of
P. aeruginosa , the highest antibiotic resistance was to cefotaxime and aztreonam, and the least resistance was to colictin and ceftazidime. There were 49 isolates (46.66%) that showed an AmpC phenotype. In addition, the frequencies of the resistance genes were;OXA48 gene 85.2%,OXA199, 139 3.8%,OXA23 3.8%,OXA2 66.6%,OXA10 3.8%,OXA51 85.2% andOXA58 3.8%. TheIMP27 gene was detected in 9 isolates (8.57%) and theIMP3.34 was detected in 11 isolates (10.47%). Other genes detected included;lasR (17.1%),lasB (18%) andlasA (26.6%). There was a significant relationship between virulence factors and theOX andIMP genes (p ≤ 0.05).Conclusion The relationship between antibiotic resistance and virulence factors observed in this study could play an important role in outbreaks associated with
P. aeruginosa infections.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative bacteriome and antibiotic resistome analysis of water and sediment of the Ganga River of India
Ankita Srivastava, Digvijay Verma
World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of different virulence factors and their association with antimicrobial resistance among Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates from Egypt
Eva A. Edward, Marwa R. El Shehawy, Alaa Abouelfetouh, Elsayed Aboulmagd
BMC Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular epidemiology and collaboration of siderophore-based iron acquisition with surface adhesion in hypervirulent Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from wound infections
Hamed Tahmasebi, Sanaz Dehbashi, Mona Nasaj, Mohammad Reza Arabestani
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Decoding Genetic Features and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains Isolated from Bloodstream Infections
Tomasz Bogiel, Dagmara Depka, Mateusz Rzepka, Agnieszka Mikucka
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(16): 9208. CrossRef - Prevalence of the Genes Associated with Biofilm and Toxins Synthesis amongst the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Strains
Tomasz Bogiel, Dagmara Depka, Mateusz Rzepka, Joanna Kwiecińska-Piróg, Eugenia Gospodarek-Komkowska
Antibiotics.2021; 10(3): 241. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Study of the Relationship between the Production of β-Lactamase Enzymes and Iron/Siderophore Uptake Regulatory Genes in Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii
Mahyar Porbaran, Hamed Tahmasebi, MohammadReza Arabestani, Joseph Falkinham
International Journal of Microbiology.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Regulation of virulence and β-lactamase gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus isolates: cooperation of two-component systems in bloodstream superbugs
Sanaz Dehbashi, Hamed Tahmasebi, Behrouz Zeyni, Mohammad Reza Arabestani
BMC Microbiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef -
New approach to identify colistin‐resistant
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
by high‐resolution melting curve analysis assay
H. Tahmasebi, S. Dehbashi, M.R. Arabestani
Letters in Applied Microbiology.2020; 70(4): 290. CrossRef - Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa carrying virulence genes in hospitalized patients with urinary tract infection from Sanandaj, west of Iran
Safoura Derakhshan, Aslan Hosseinzadeh
Gene Reports.2020; 20: 100675. CrossRef - Prevalence and molecular typing of Metallo-β-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa with adhesion factors: A descriptive analysis of burn wounds isolates from Iran
Hamed Tahmasebi, Sanaz Dehbashi, Mohammad Yousef Alikhani, Mahyar Porbaran, Mohammad Reza Arabestani
Gene Reports.2020; 21: 100853. CrossRef - Co-harboring of mcr-1 and β-lactamase genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by high-resolution melting curve analysis (HRMA): Molecular typing of superbug strains in bloodstream infections (BSI)
Hamed Tahmasebi, Sanaz Dehbashi, Mohammad Reza Arabestani
Infection, Genetics and Evolution.2020; 85: 104518. CrossRef - Relationship between Biofilm Regulating Operons and Various Β-Lactamase Enzymes: Analysis of the Clinical Features of Infections caused by Non-Fermentative Gram-Negative Bacilli (Nfgnb) from Iran
Mahyar Porbaran, Reza Habibipour
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2020; 14(3): 1723. CrossRef - Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains-Distribution of the Essential Enzymatic Virulence Factors Genes
Tomasz Bogiel, Małgorzata Prażyńska, Joanna Kwiecińska-Piróg, Agnieszka Mikucka, Eugenia Gospodarek-Komkowska
Antibiotics.2020; 10(1): 8. CrossRef - Biofilm Formation and β-lactamase Enzymes: A Synergism Activity in Acinetobacter baumannii Isolated from Wound Infection
Mahyar Porbaran, Reza Habibipour
Journal of Advances in Medical and Biomedical Rese.2019; 27(125): 34. CrossRef
- Comparative bacteriome and antibiotic resistome analysis of water and sediment of the Ganga River of India
- Relationships between Virulence Factors and Antimicrobial Resistance among
Escherichia coli Isolated from Urinary Tract Infections and Commensal Isolates in Tehran, Iran - Mohammad Reza Asadi Karam, Mehri Habibi, Saeid Bouzari
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(5):217-224. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.5.02
- 6,769 View
- 132 Download
- 30 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Uropathogenic
Escherichia coli (UPEC) are the major cause of urinary tract infections (UTIs). Here, we determined whether sensitivity to antibiotics was related to the prevalence of iron scavenging genes, or to biofilm and hemolysis formation.Methods A total of 110 UPEC and 30
E coli isolates were collected from the urine of UTI patients and feces of healthy individuals without UTI, respectively. The presence of iron receptor genes and phenotypic properties were evaluated by polymerase chain reaction and phenotypic methods, respectively. Susceptibility to routine antibiotics was evaluated using the disc diffusion method.Results The prevalence of iron scavenging genes ranged from 21.8% (
ireA ) to 84.5% (chuA ) in the UPEC. Resistance to ceftazidime and cefotaxime was significantly correlated with the presence offyuA andiutA iron genes. Biofilm production was significantly associated with the prevalence offyuA andhma iron genes. A higher degree of antibiotic resistance was exhibited by isolates that produced biofilms than by their non-biofilm producing counterparts.Conclusion Our study clearly indicates that biofilm production is associated with antibiotic resistance, and that iron receptors and hemolysin production also contribute to reduced antibiotic sensitivity. These results further our understanding of the role that these virulence factors play during UPEC pathogenesis, which in turn may be valuable for the development of novel treatment strategies against UTIs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Correlation between antimicrobial resistance, biofilm formation, and virulence determinants in uropathogenic Escherichia coli from Egyptian hospital
Sara A. Alshaikh, Tarek El-banna, Fatma Sonbol, Mahmoud H. Farghali
Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Multidrug resistance in pathogenic Escherichia coli isolates from urinary tract infections in dogs, Spain
Ana Abad-Fau, Eloisa Sevilla, Ainara Oro, Inmaculada Martín-Burriel, Bernardino Moreno, Mariano Morales, Rosa Bolea
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistant Escherichia coli isolated from wild mammals from two rescue and rehabilitation centers in Costa Rica: characterization and public health relevance
Rita Fernandes, Raquel Abreu, Isa Serrano, Roger Such, Encarnación Garcia-Vila, Sandy Quirós, Eva Cunha, Luís Tavares, Manuela Oliveira
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef -
Progress toward a vaccine for extraintestinal pathogenic
E. coli
(ExPEC) II: efficacy of a toxin-autotransporter dual antigen approach
Yikun Xing, Justin R. Clark, James D. Chang, Jacob J. Zulk, Dylan M. Chirman, Felipe-Andres Piedra, Ellen E. Vaughan, Haroldo J. Hernandez Santos, Kathryn A. Patras, Anthony W. Maresso, Kimberly A. Kline
Infection and Immunity.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC)-Associated Urinary Tract Infections: The Molecular Basis for Challenges to Effective Treatment
Shane Whelan, Brigid Lucey, Karen Finn
Microorganisms.2023; 11(9): 2169. CrossRef - Susceptibility and Virulence of Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Urinary Tract Infections in Benin
Funkè F. Assouma, Haziz Sina, Tomabu Adjobimey, Agossou Damien Pacôme Noumavo, Akim Socohou, Bawa Boya, Ange D. Dossou, Lauriane Akpovo, Basile Boni Saka Konmy, Jacques F. Mavoungou, Adolphe Adjanohoun, Lamine Baba-Moussa
Microorganisms.2023; 11(1): 213. CrossRef - Association Between Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Virulence Genes and Severity of Infection and Resistance to Antibiotics
Sofía Alejandra Fonseca-Martínez, Ruth Aralí Martínez-Vega, Ana Elvira Farfán-García, Clara Isabel González Rugeles, Libeth Yajaira Criado-Guerrero
Infection and Drug Resistance.2023; Volume 16: 3707. CrossRef - Incidence of biofilms among the multidrug resistant E. coli, isolated from urinary tract infections in the Nilgiris district, South India
A. P. Cardiliya, M. J. N. Chandrasekar, M. J. Nanjan
Brazilian Journal of Microbiology.2023; 54(3): 1809. CrossRef - Correlation of biofilm formation, virulence factors, and phylogenetic groups among Escherichia coli strains causing urinary tract infection: A global systematic review and meta-analysis
HosseinKarballaei Mirzahosseini, Farhad Najmeddin, Atabak Najafi, Arezoo Ahmadi, Hamidreza Sharifnia, Azad Khaledi, Mojtaba Mojtahedzadeh
Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.2023; 28(1): 66. CrossRef - Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis Caused by Co-Infection with Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Multidrug-Resistant Extended-Spectrum ß-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli: A Case Report
Shiori Kitaya, Chieko Miura, Ayano Suzuki, Yoshimichi Imai, Koichi Tokuda, Hajime Kanamori
Applied Microbiology.2023; 3(3): 1046. CrossRef - Fluoroquinolone resistance determinants in carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from urine clinical samples in Thailand
Parichart Boueroy, Peechanika Chopjitt, Rujirat Hatrongjit, Masatomo Morita, Yo Sugawara, Yukihiro Akeda, Tetsuya Iida, Shigeyuki Hamada, Anusak Kerdsin
PeerJ.2023; 11: e16401. CrossRef - Characterization of virulence determinants and phylogenetic background of multiple and extensively drug resistant Escherichia coli isolated from different clinical sources in Egypt
Rana El-baz, Heba Shehta Said, Eman Salama Abdelmegeed, Rasha Barwa
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology.2022; 106(3): 1279. CrossRef - A global systematic review and meta-analysis on correlation between biofilm producers and non-biofilm producers with antibiotic resistance in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Mitra Garousi, Sina Monazami Tabar, Hosein Mirazi, Parnia Asgari, Paniz Sabeghi, Astireh Salehi, Azad Khaledi, Mohammad Ghenaat Pisheh Sanani, Hossein Karballaei Mirzahosseini
Microbial Pathogenesis.2022; 164: 105412. CrossRef - Virulence factors, antimicrobial resistance and the relationship between these characteristics in uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Farzaneh Firoozeh, Mohammad Zibaei, Farzad Badmasti, Azad Khaledi
Gene Reports.2022; 27: 101622. CrossRef - Association between Virulence Factors and Antimicrobial Resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates from North Kerala
Ramya Kumaran, R.V. Geetha, Sabitha Baby
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2022; 16(2): 867. CrossRef - Characterization of virulence factors and antibiotic resistance pattern of uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains in a tertiary care center
Naveen Kumar M, Sevitha Bhat, Archana Bhat K, Vishwas Saralaya, Shalini Shenoy Mulki
F1000Research.2022; 11: 1163. CrossRef - Antibiotic Resistance, Biofilm Formation and Sub-Inhibitory Hydrogen Peroxide Stimulation in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Prabin Dawadi, Santosh Khanal, Tista Prasai Joshi, Sudeep KC, Reshma Tuladhar, Bijaya Laxmi Maharjan, Anjani Darai, Dev Raj Joshi
Microbiology Insights.2022; 15: 117863612211352. CrossRef - Characterization of virulence factors and antibiotic resistance pattern of uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains in a tertiary care center
Naveen Kumar M, Sevitha Bhat, Archana Bhat K, Vishwas Saralaya, Shalini Shenoy Mulki
F1000Research.2022; 11: 1163. CrossRef - Insects, Rodents, and Pets as Reservoirs, Vectors, and Sentinels of Antimicrobial Resistance
Willis Gwenzi, Nhamo Chaukura, Norah Muisa-Zikali, Charles Teta, Tendai Musvuugwa, Piotr Rzymski, Akebe Luther King Abia
Antibiotics.2021; 10(1): 68. CrossRef - Virulence genes and phylogenetic groups of uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates from patients with urinary tract infection and uninfected control subjects: a case-control study
Seyedeh Elham Rezatofighi, Mahsa Mirzarazi, Mansour Salehi
BMC Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Virulence characterization and clonal analysis of uropathogenic Escherichia coli metallo-beta-lactamase-producing isolates
Fatemeh Zangane Matin, Seyedeh Elham Rezatofighi, Mohammad Roayaei Ardakani, Mohammad Reza Akhoond, Fahimeh Mahmoodi
Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Detection of Virulence-Associated Genes in Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Commercial Broilers
Tímea Kocúreková, Lívia Karahutová, Dobroslava Bujňáková
Antibiotics.2021; 10(11): 1303. CrossRef - Evaluation of Biofilm Formation and Virulence Genes and Association with Antibiotic Resistance Patterns of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Strains in Southwestern Iran
Mostafa Boroumand, Asghar Sharifi, Mohammad Amin Ghatei, Mohsen Sadrinasab
Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Differences of virulence factors, and antimicrobial susceptibility according to phylogenetic group in uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from Korean patients
Miri Hyun, Ji Yeon Lee, Hyun ah Kim
Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Bacterial Spectrum and Resistance Patterns Over Time in the Urine of Patients with Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Due to Spinal Cord Injury
Jürgen Pannek, Carmen Kurmann, Jörg Krebs, Valentin Habermacher, Jens Wöllner
Urologia Internationalis.2021; 105(5-6): 483. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta-analysis of antibiotic resistance patterns, and the correlation between biofilm formation with virulence factors in uropathogenic E. coli isolated from urinary tract infections
Fei Zhao, Huanxin Yang, Dezhong Bi, Azad Khaledi, Mingqi Qiao
Microbial Pathogenesis.2020; 144: 104196. CrossRef - A survey for phylogenetic relationship; presence of virulence genes and antibiotic resistance patterns of avian pathogenic and uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from poultry and humans in Yazd, Iran
Mansoureh Bakhshi, Hengameh Zandi, Mehdi Fatahi Bafghi, Akram Astani, Vahid Reza Ranjbar, Mahmood Vakili
Gene Reports.2020; 20: 100725. CrossRef - Biofilm formation, antimicrobial susceptibility and virulence genes of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from clinical isolates in Uganda
Paul Katongole, Fatuma Nalubega, Najjuka Christine Florence, Benon Asiimwe, Irene Andia
BMC Infectious Diseases.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between Virulence and Resistance among Gram-Negative Bacteria
Virginio Cepas, Sara M. Soto
Antibiotics.2020; 9(10): 719. CrossRef - Virulence factors of uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) and correlation with antimicrobial resistance
Chhaya Shah, Ratna Baral, Bijay Bartaula, Lok Bahadur Shrestha
BMC Microbiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Correlation between antimicrobial resistance, biofilm formation, and virulence determinants in uropathogenic Escherichia coli from Egyptian hospital
- Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors and Obesity Levels in Korean Adults: Results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007–2015
- Kwanjun Park, Sunmi Lim, Yoonhyung Park, Woong Ju, Yoonhee Shin, Hansol Yeom
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(4):150-159. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.4.03
- 5,208 View
- 34 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The increase in the obesity rate in adult males in Korea is higher than countries in the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development and other Asian countries. We examined the trends and prevalence of major risk factors for cardiovascular disease by evaluating the weight status amongst adults from 2007 to 2015.
Methods The study included 37,402 adults, who participated in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The prevalence trends of cardiovascular disease risk factors were estimated for each body mass index group.
Results From 2007 to 2015, significant increases in the prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia were observed in normal weight adults (0.03 percentage point (%p), 0.06%p, and 0.13%p, respectively). Amongst the overweight and obese adults, a significant increase in the prevalence of hypercholesterolemia was observed, During this period, the prevalence of smoking decreased amongst obese adults and no significant changes in drinking habits and physical activity were noted across all body mass index groups.
Conclusion The prevalence of obesity in Korean adults is increasing, and it is necessary to implement interventions to prevent further weight gain and obesity-associated cardiovascular disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in middle-aged Lithuanian women in different body mass index and waist circumference groups
Egidija Rinkūnienė, Emilija Petrulionytė, Vilma Dženkevičiūtė, Žaneta Petrulionienė, Augustė Senulytė, Roma Puronaitė, Aleksandras Laucevičius
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(1): 27. CrossRef - The effect of a nutrition program based on the Health Behavior Interaction Model on primary school students’ nutritional attitudes and behaviors
Ayşe Burcu Başçı, Oya Nuran Emiroğlu, Bilge Kalanlar
Journal of Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Thirty-six Year Trends in Mortality from Diseases of Circulatory System in Korea
Jongmin Baek, Hokyou Lee, Hyeok-Hee Lee, Ji Eun Heo, So Mi Jemma Cho, Hyeon Chang Kim
Korean Circulation Journal.2021; 51(4): 320. CrossRef - The identification of established modifiable mid-life risk factors for cardiovascular disease which contribute to cognitive decline: Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (KLoSA)
Yebeen Ysabelle Boo, Otto-Emil Jutila, Meghan A. Cupp, Logan Manikam, Sung-Il Cho
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research.2021; 33(9): 2573. CrossRef - A Healthy Diet Rich in Calcium and Vitamin C Is Inversely Associated with Metabolic Syndrome Risk in Korean Adults from the KNHANES 2013–2017
Sunmin Park, Kyungjin Kim, Byung-Kook Lee, Jaeouk Ahn
Nutrients.2021; 13(4): 1312. CrossRef - Classification and Prediction on the Effects of Nutritional Intake on Overweight/Obesity, Dyslipidemia, Hypertension and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Deep Learning Model: 4–7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyerim Kim, Dong Hoon Lim, Yoona Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(11): 5597. CrossRef - Trends in cardiovascular disease risk factors by BMI category among adults in England, 2003‐2018
Shaun Scholes, Linda Ng Fat, Jennifer S. Mindell
Obesity.2021; 29(8): 1347. CrossRef - Precision Medicine and Cardiovascular Health: Insights from Mendelian Randomization Analyses
Wes Spiller, Keum Ji Jung, Ji-Young Lee, Sun Ha Jee
Korean Circulation Journal.2020; 50(2): 91. CrossRef - Association of the Healthy Eating Index with Estimated Cardiovascular Age in Adults from the KNHANES 2013–2017
Sunmin Park, Kyungjin Kim, Byung-Kook Lee, Jaeouk Ahn
Nutrients.2020; 12(10): 2912. CrossRef
- Prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in middle-aged Lithuanian women in different body mass index and waist circumference groups
- The 2nd Meeting of National Control Laboratories for Vaccines and Biologicals in the Western Pacific
- Hokyung Oh, Jinho Shin, Chung Keel Lee, Masaki Ochiai, Kiyoko Nojima, Chang Kweng Lim, Sanj Raut, Irene Lisovsky, Stella Williams, Ki Young Yoo, Dong-Yeop Shin, Manabu Ato, Qiang Ye, Kiwon Han, Chulhyun Lee, Naery Lee, Ji Young Hong, Kikyung Jung, Pham Van Hung, Jayoung Jeong
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(3):133-139. Published online June 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.3.10
- 4,252 View
- 107 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The Second Meeting of the National Control Laboratories for Vaccines and Biologicals in the Western Pacific, was jointly organized by the National Institute of Food and Drug Safety Evaluation of the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety in the Republic of Korea, and by the World Health Organization Regional Office for the Western Pacific.
In the National Lot Release Systems session countries including Canada, China, Japan, Malaysia, Vietnam, and the Republic of Korea, all shared information on their current Lot Release Systems, including current practices and developments in risk-based official lot release of vaccines.
In the session on Quality Control of Blood Products, experts from the National Institute for Biological Standards and Control shared quality control and research results for; blood coagulation factor VIII products, and the measurement of procoagulant activity in immunoglobulin products. Representatives from Japan proposed a regional collaborative study to test aggregated immunoglobulin free from complement activity. A cell-based Japanese encephalitis vaccine potency assay was proposed by representatives from Korea and they also called for voluntary participation of other National Control Laboratories in a collaborative study, on the first Korean
Gloydius anti-venom standard. Participants agreed in general to continue communicating, and coordinate presentation of the study results.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A collaborative study to establish the second national standard for hepatitis B immunoglobulin in Korea
Chan Woong Choi, Su Kyoung Seong, Ki Won Han, Hyun Jeong Kim, Kyung Hee Sohn, Sun Bo Shim, Yun Su Bang, JungHwan Cho, In Soo Shin
Biologicals.2023; 82: 101679. CrossRef - Report on the seventh meeting of national control laboratories for vaccines and biologicals of the WHO Western Pacific and South-East Asia member states
Sun Bo Shim, Chan Woong Choi, Jin Ho Shin, Jong Won Kim, Silke Schepelmann, Jae Ho Jung, Harish Chander, Ratih Pujilestari, Madoka Kuramitsu, Masaki Ochiai, Nee Yuan Qi, Geraldine N. Dimapilis, Luu Thi Dung, Hyung Sil Moon, In Soo Shin
Biologicals.2023; 84: 101712. CrossRef
- A collaborative study to establish the second national standard for hepatitis B immunoglobulin in Korea
- Age-differentiated Risk Factors of Suicidal Ideation among Young and Middle-aged Korean Adults
- Ahra Jo, Minho Jeon, Heeyoung Oh
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(3):201-210. Published online June 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.3.07
- 4,122 View
- 36 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This study aimed to determine the prevalence of suicidal ideation among young and middle-aged adults, and explore the risk factors that affect suicidal ideation.
Methods A descriptive study design was used for secondary data analysis. A total sample of 5,214 was drawn from two waves (2012–2013) of the 7th Korea Health Panel (KHP) survey. The KHP data were collected by a well-trained interviewer using the face-to-face method during home visits as well as self-report method. Descriptive statistics of frequency, percentage, chi-square test, and logistic regression analysis were performed using SPSS 22.0.
Results The prevalence of suicidal ideation in young and middle-aged adults was 4.4% and 5.6%, respectively. For young adults, suicidal ideation risk was higher among those with low income or heavy drinking habits. In middle-aged adults, low income, poor perceived health status, negative perception of peer-compared health status, and negative social perspective were the major risk factors.
Conclusion There is considerable risk of suicidal ideation in adulthood. Opportunities for increased income, avoidance of heavy drinking, and the construction of positive subjective health status and social perspective should be considered in suicide prevention interventions for Korean young and middle-aged adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Psychosocial risk factors of youth suicide in the Western Pacific: a scoping review
Mohammad Izzat Morshidi, Peter K. H. Chew, Lidia Suárez
Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology.2024; 59(2): 201. CrossRef - Spatial and temporal trends and risk factors for intentional carbon monoxide poisoning hospitalizations in England between 2002 and 2016
Aina Roca-Barceló, Helen Crabbe, Rebecca Close, Helena Fahie, Giovanni S. Leonardi, Frédéric B. Piel
Journal of Affective Disorders.2023; 329: 168. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on intensive care
admissions and mortality due to self-poisoning:
A retrospective comparative study from a tertiary care
hospital
Aneela Α. Kidwai, Komal Fareed, Jamal Ara, Mahnoor Khalil, Shaista Ahmed, Syeda Urooj Riaz, Yumna Ahmed
Public Health and Toxicology.2023; 3(3): 1. CrossRef - Spectrum and predictors of suicidal risk among incarcerated youth in a correctional facility in Kaduna, Northern Nigeria
Marufah Dupe Lasisi, Folorunsho Tajudeen Nuhu, Femi Adebayo, Edwin Ehi Eseigbe, Taiwo Lateef Sheikh
Vulnerable Children and Youth Studies.2022; 17(2): 147. CrossRef - Alcohol use and its association with suicide attempt, suicidal thoughts and non-suicidal self-harm in two successive, nationally representative English household samples
Sarah Ledden, Paul Moran, David Osborn, Alexandra Pitman
BJPsych Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between Suicidal Ideation and Relatives’ Physical and Mental Health among Community Residents: Differences between Family Members and Lineal Consanguinity
Caifeng Li, Zhen Wei, Yifan Wang, Long Sun
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(23): 15997. CrossRef - Factors affecting suicidal ideation among premenopausal and postmenopausal women
Go‐Un Kim, Hae Kyoung Son, Mi‐Young Kim
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2021; 28(3): 356. CrossRef - Depression and suicidal ideation among HIV seropositive patients attending the special treatment clinic of the University of Calabar Teaching Hospital, Calabar, Nigeria
Elvis Mbu Bisong, Chidi John Okafor, Agam Ebaji Ayuk, Udeme Essien Asibong, Henry Ohem Okpa
Calabar Journal of Health Sciences.2021; 4: 64. CrossRef - The role of ageing in the wish to be dead: disentangling age, period and cohort effects in suicide ideation in European population
M. Cabello, L. A. Rico-Uribe, J. C. Martinez-Ávila, A. Sánchez-Niubò, F. F. Caballero, G. Borges, B. Mellor-Marsá, J. M. Haro, M. Prina, S. Koskinen, J. L. Ayuso-Mateos
Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Suicide Risk and Comorbidity of Mood Disorder and Alcohol Use Disorder: Using Common Data Model in Psychiatry
Yong Hyuk Cho, Eunyoung Lee, Eun Sil Her, Gyubeom Hwang, Ki-Young Lim, Jai Sung Noh, Yunmi Shin, Chang Hyung Hong, Hyun Woong Roh, Dongyun Lee, Heirim Lee, Doyeop Kim, Rae Woong Park, Bumhee Park, Sang Joon Son
Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association.2021; 60(3): 232. CrossRef - Analysis of risk factors affecting suicidal ideation in South Korea by life cycle stage
Ji-Young Hwang, Il-Su Park
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2021; 12(5): 314. CrossRef - Association of chronic diseases and lifestyle factors with suicidal ideation among adults aged 18–69 years in Eswatini: evidence from a population-based survey
Mfundi President Sebenele Motsa, Hung-Yi Chiou, Yi-Hua Chen
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross-national prevalence and factors associated with suicide ideation and attempts in older and young-and-middle age people
Maria Cabello, Marta Miret, José Luis Ayuso-Mateos, Felix Feliz Caballero, Somnath Chatterji, Beata Tobiasz-Adamczyk, Josep Maria Haro, Seppo Koskinen, Matilde Leonardi, Guilherme Borges
Aging & Mental Health.2020; 24(9): 1533. CrossRef - Characteristics, causality, and suicidal behavior: a qualitative study of family members with suicide history in Wonogiri, Indonesia
Susana Nurtanti, Sri Handayani, Nita Yunianti Ratnasari, Putri Halimu Husna, Tantut Susanto
Frontiers of Nursing.2020; 7(2): 169. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Suicidal Ideation among Middle Class Korean: Focusing on Psychosocial Comparison - An Analysis of a Nationwide Survey of the 8th Korea Health Panel Data
Ahra Jo, Bora Kang, Youngju Seo, Eunha Gil, Heeyoung Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nurs.2018; 29(1): 1. CrossRef - The Function of Personality in Suicidal Ideation from the Perspective of the Interpersonal-Psychological Theory of Suicide
Marc Baertschi, Alessandra Costanza, Alessandra Canuto, Kerstin Weber
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2018; 15(4): 636. CrossRef - To Be or Not to Be
Hae-Wol Cho, Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2017; 8(3): 157. CrossRef
- Psychosocial risk factors of youth suicide in the Western Pacific: a scoping review
- Low Levels of Extensively Drug-resistant Tuberculosis among Multidrug Resistant Tuberculosis Isolates and Their Relationship to Risk Factors: Surveillance in Tehran, Iran; 2006 to 2014
- Alireza Hadizadeh Tasbiti, Shamsi Yari, Mostafa Ghanei, Mohammad Ali Shokrgozar, Abolfazl Fateh, Ahmadreza Bahrmand
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(2):116-123. Published online April 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.2.03
- 3,696 View
- 27 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) is more expensive and difficult to treat than multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), and outcomes for patients are much worse; therefore, it is important that clinicians understand the magnitude and distribution of XDR-TB. We conducted a retrospective study to compare the estimated incidence of and risk factors for M/XDR-TB with those of susceptible TB controls.
Methods Sputum culture and drug susceptibility testing (DST) were performed in patients with known or suspected TB. Strains that were identified as MDR were subjected to DST for second-line drugs using the proportion method.
Results Among 1,442 TB patients (mean age, 46.48 ± 21.24 years) who were culture-positive for
Mycobacterium tuberculosis , 1,126 (78.1%) yielded isolates that were resistant to at least one first-line drug; there were 33 isolates (2.3%) of MDR-TB, of which three (0.2%) were classified as XDR-TB. Ofloxacin resistance was found in 10 (0.7%) isolates. Women were 15% more likely than men to yield M/XDR-TB isolates, but this difference was not significant. In a multivariate analysis comparing susceptible TB with X/MDR-TB, only one variable—the number of previous treatment regimens—was associated with MDR (odds ratio, 1.06; 95% confidence interval, 1.14–21.2).Conclusion The burden of M/XDR-TB cases is not sizeable in Iran. Nonetheless, strategies must be implemented to identify and cure patients with pre-XDR-TB before they develop XDR-TB. Our results provide a greater understanding of the evolution and spread of M/XDR-TB in an environment where drug-resistant TB has a low incidence.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Global prevalence of drug-resistant tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Nader Salari, Amir Hossein Kanjoori, Amin Hosseinian-Far, Razie Hasheminezhad, Kamran Mansouri, Masoud Mohammadi
Infectious Diseases of Poverty.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pre-extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis among pulmonary multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients in Eastern Nigeria
Ndubuisi O. Nwachukwu, Amara E. Ulasi, Christopher U. Okoronkwo, Valentine N. Unegbu
Lung India.2023; 40(6): 492. CrossRef - Mycobacterium tuberculosis PPE7 Enhances Intracellular Survival of Mycobacterium smegmatis and Manipulates Host Cell Cytokine Secretion Through Nuclear Factor Kappa B and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling
Jing Suo, Xinyan Wang, Rongchuan Zhao, Pengjiao Ma, Liang Ge, Tao Luo
Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research.2022; 42(10): 525. CrossRef - The burden of pre-extensively and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis among MDR-TB patients in the Amhara region, Ethiopia
Agumas Shibabaw, Baye Gelaw, Wondwossen Gebreyes, Richard Robinson, Shu-Hua Wang, Belay Tessema, Shampa Anupurba
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(2): e0229040. CrossRef Spoligotype and Drug Susceptibility Profiles of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex Isolates in Golestan Province, North Iran
Noormohamad Mansoori, Farzam Vaziri, Sirus Amini, Sharareh Khanipour, Shahin Pourazar Dizaji, Masoumeh Douraghi
Infection and Drug Resistance.2020; Volume 13: 2073. CrossRef- A comparative study of phenotypic and genotypic first- and second-line drug resistance testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Fatemeh Sakhaee, Morteza Ghazanfari, Nayereh Ebrahimzadeh, Farzam Vaziri, Fatemeh Rahimi Jamnani, Mehdi Davari, Safoora Gharibzadeh, Fatemeh Hemati Mandjin, Abolfazl Fateh, Seyed Davar Siadat
Biologicals.2017; 49: 33. CrossRef
- Global prevalence of drug-resistant tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis



 First
First Prev
Prev


