Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Osong Public Health Res Perspect > Volume 10(4); 2019 > Article
-
Original Article
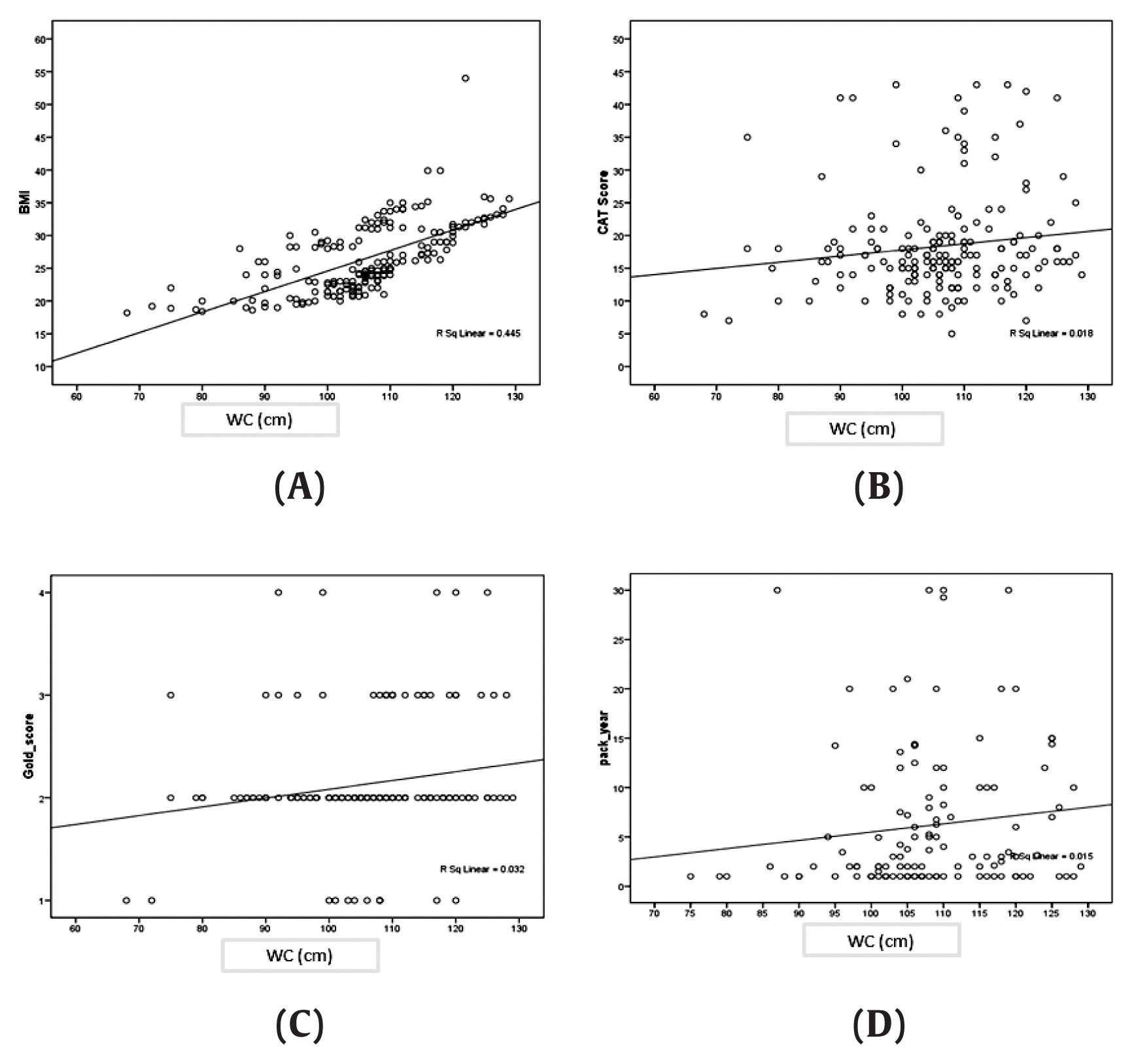
Waist Circumference and Spirometric Measurements in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease - Ali Alavi Foumania, Mohammad Masoud Neyaraghb, Zahra Abbasi Ranjbarc, Ehsan Kazemnezhad Leylic, Shima Ildaria, Alireza Jafaria
-
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives 2019;10(4):240-245.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.4.07
Published online: August 31, 2019
aInflammatory Lung Disease Research Center, Department of Internal Medicine, Razi Hospital, School of Medicine, Guilan University of Medical Sciences, Rasht, Iran
bDepartment of Internal Medicine, Student Research Committee, Faculty of Medicine, Guilan University of Medical Sciences, Rasht, Iran
cRazi Clinical Research Development Center, Guilan University of Medical Sciences, Rasht, Iran
- *Corresponding author: Alireza Jafari, Inflammatory Lung Disease Research Center, Department of Internal Medicine, Razi Hospital, School of Medicine, Guilan University of Medical Sciences, Rasht, Iran, Email: dr.alireza.jafariii@gmail.com
• Received: April 29, 2019 • Revised: July 15, 2019 • Accepted: July 24, 2019
Copyright ©2019, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- The role of abdominal obesity in the development of cardiopulmonary disorders in aluminum industry workers
Egor S. Filimonov, Olga Yu. Korotenko, Evgeniya V. Ulanova
Hygiene and sanitation.2023; 102(4): 328. CrossRef - Blood Levels of Indicators of Lower Respiratory Tract Damage in Chronic Bronchitis in Patients with Abdominal Obesity
Elena V. Kashtanova, Yana V. Polonskaya, Evgeniia V. Striukova, Liliia V. Shcherbakova, Evgenii A. Kurtukov, Viktoriya S. Shramko, Ekaterina M. Stakhneva, Yulia I. Ragino
Diagnostics.2022; 12(2): 299. CrossRef - Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and its Correlation with Body Mass Index, Airflow Obstruction, Dyspnea, and Exercise Index and C-Reactive Protein
D. Suresh Kumar, Richard Samuel, Viola Savy DSouza, Madhu Keshava Bangera
Indian Journal of Respiratory Care.2022; 11(4): 314. CrossRef - Prevalence of chronic bronchitis against a background of abdominal obesity in young people aged 25–44 in Novosibirsk
Yu. I. Ragino, E. A. Kurtukov, D. V. Denisova, Ya. V. Polonskaya, L. V. Shcherbakova
Bulletin of Siberian Medicine.2021; 20(1): 105. CrossRef - Abdominal obesity and the level of markers of lower respiratory tract damage in patients with chronic bronchitis
E.V. Kashtanova, Ya.V. Polonskaya, L.V. Scherbakova, I.I. Logvinenko, E.F. Kurtukov, D.V. Denisova, Yu.I. Ragino
Profilakticheskaya meditsina.2021; 24(5): 35. CrossRef


 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

